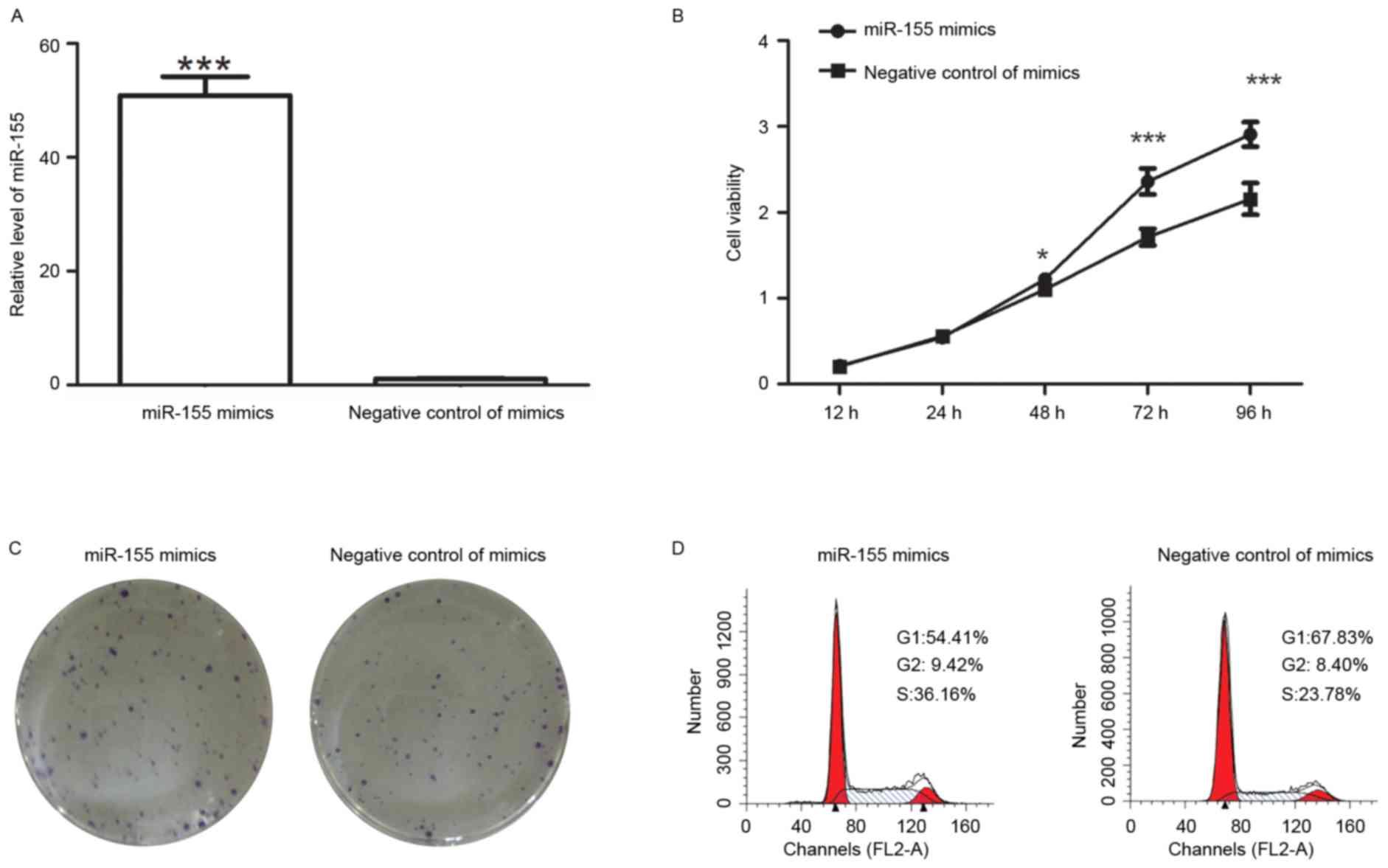
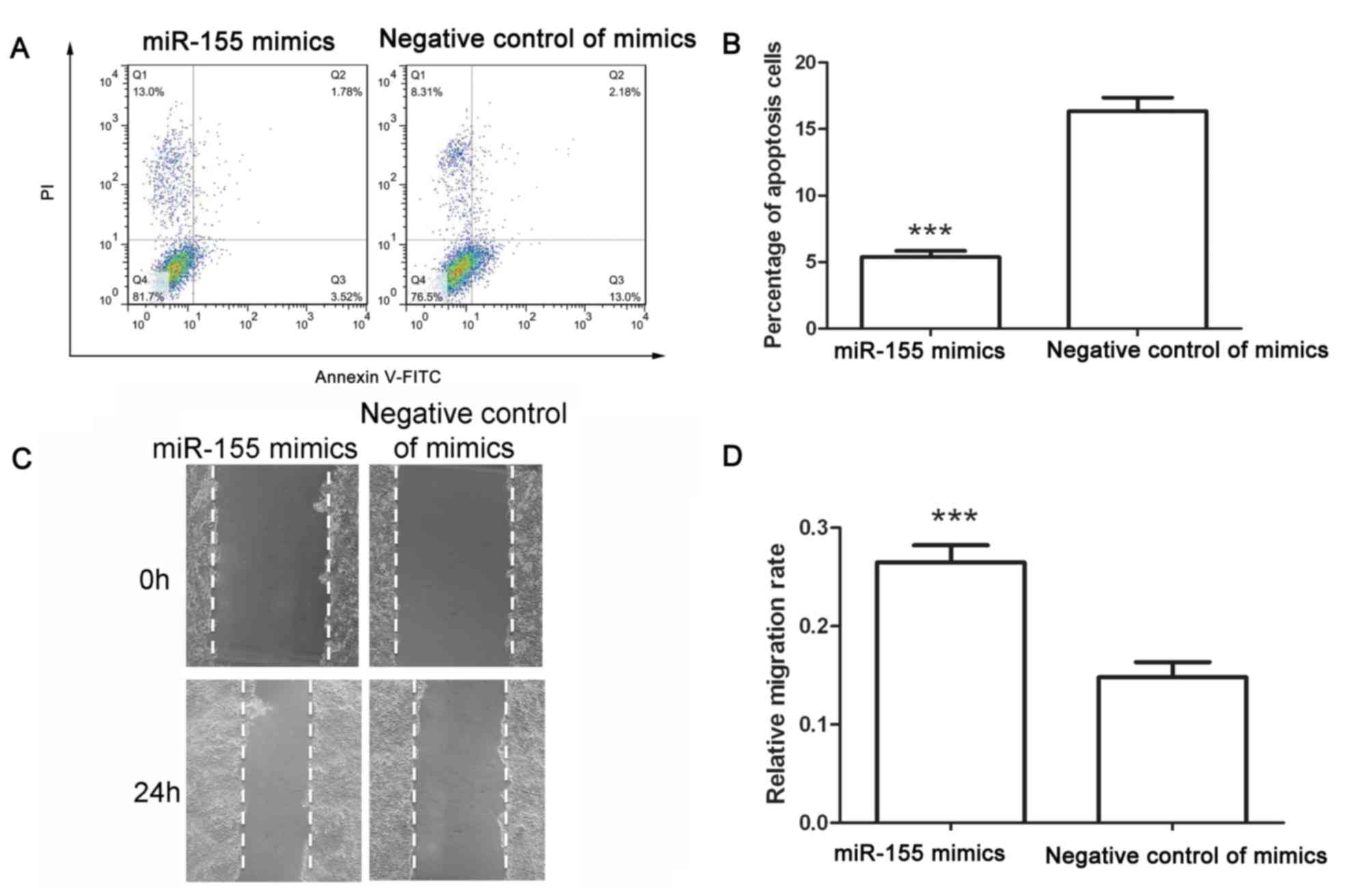
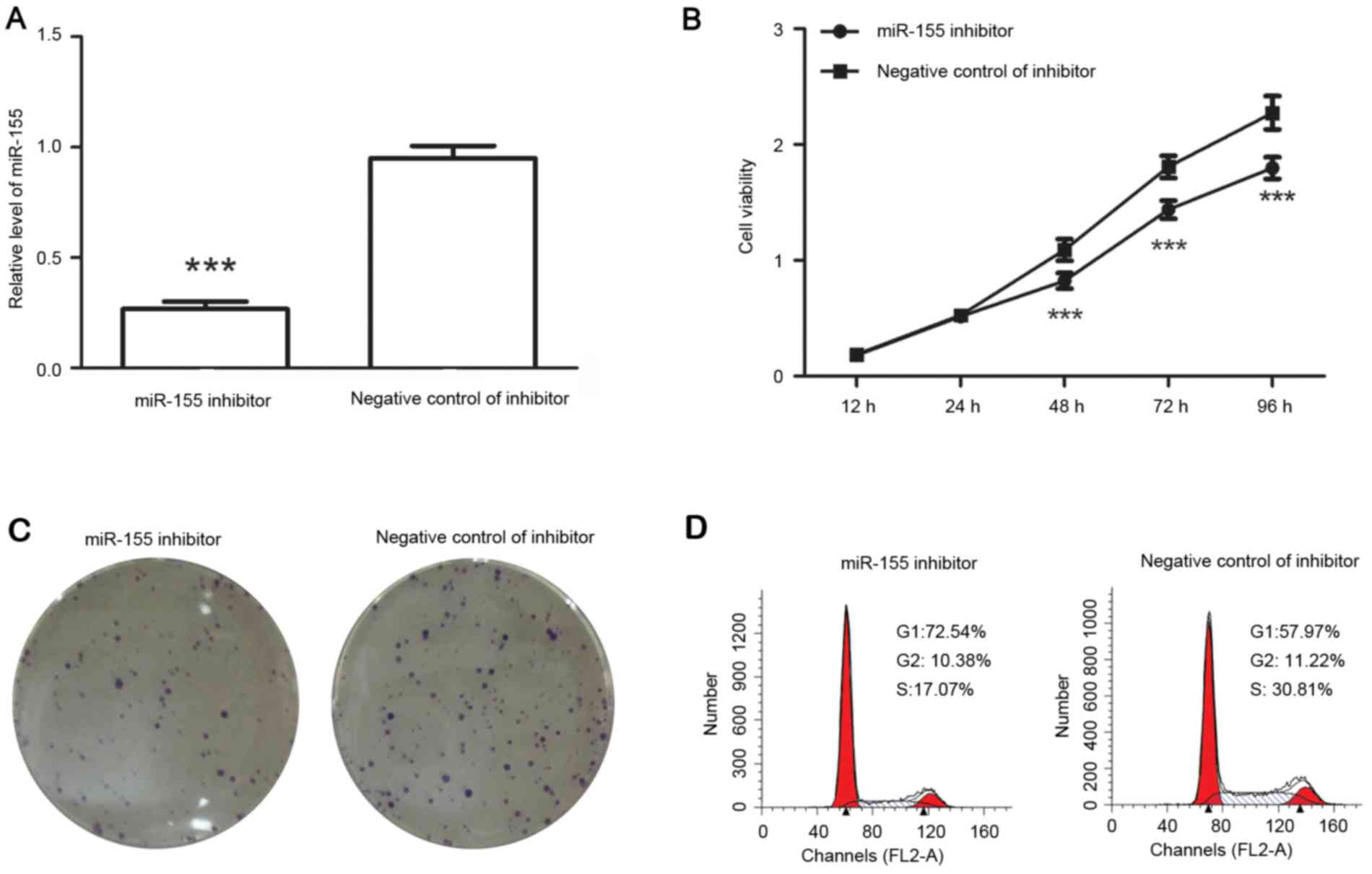
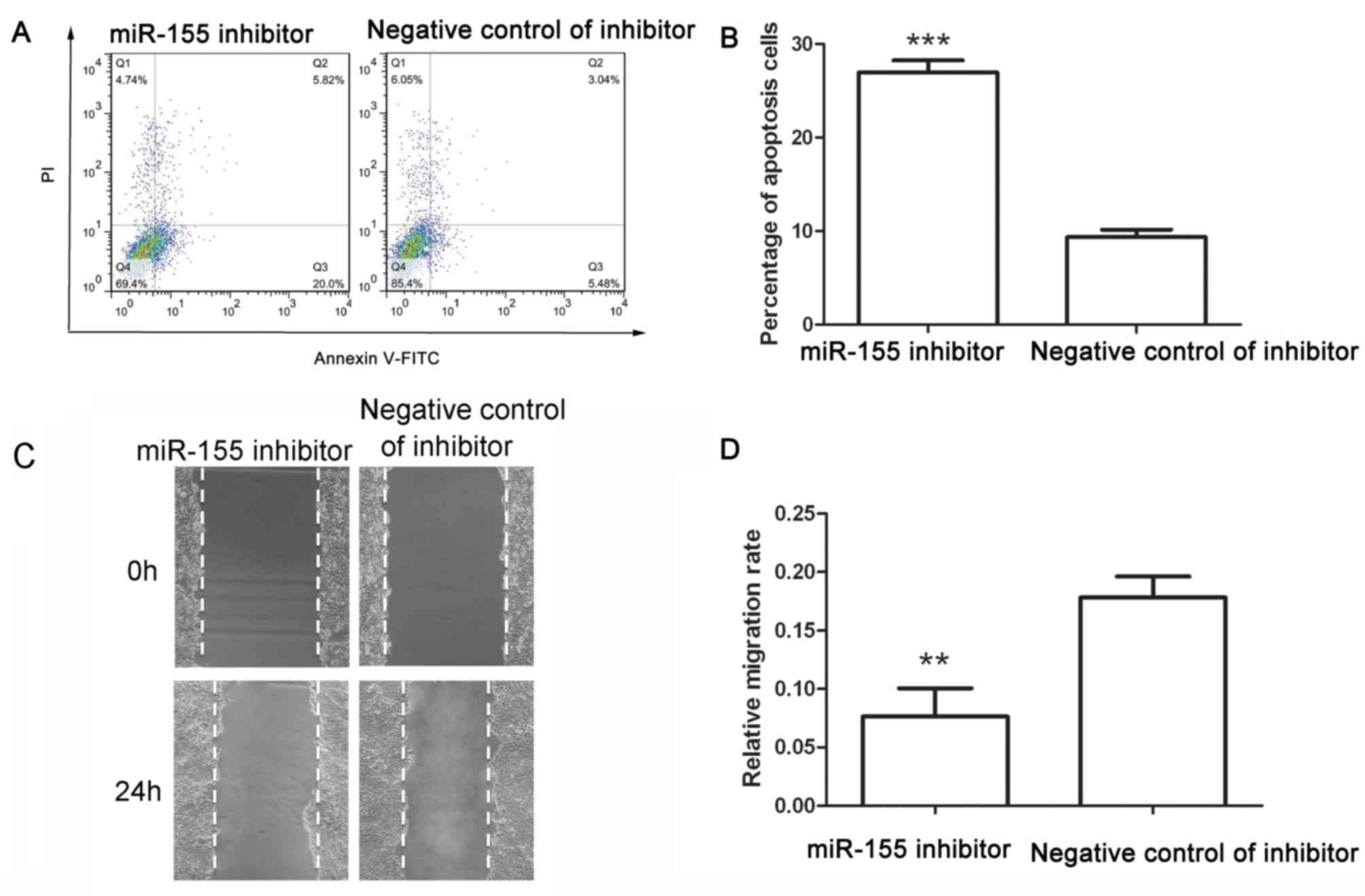
|
1
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meltzer PS: Cancer genomics: Small RNAs
with big impacts. Nature. 435:745–746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Foshay KM and Gallicano GI: Small RNAs,
big potential: The role of MicroRNAs in stem cell function. Curr
Stem Cell Res Ther. 2:264–271. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
O'Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WS, Round JL,
Scholz RL, Chaudhuri AA, Kahn ME, Rao DS and Baltimore D:
MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing
inflammatory T cell development. Immunity. 33:607–619. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calame K: MicroRNA-155 function in B
Cells. Immunity. 27:825–827. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vigorito E, Perks KL, Abreu-Goodger C,
Bunting S, Xiang Z, Kohlhaas S, Das PP, Miska EA, Rodriguez A,
Bradley A, et al: microRNA-155 regulates the generation of
immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity. 27:847–859.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan L, Hu F, Yan X, Wei Y, Ma W, Wang Y,
Lu S and Wang Z: Inhibition of microRNA-155 ameliorates
experimental autoimmune myocarditis by modulating Th17/Treg immune
response. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:1063–1079. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao Y, Ma X, Yao Y, Li H, Fan Y, Zhang Y,
Zhao C, Wang L, Ma M, Lei Z and Zhang X: miR-155 regulates the
proliferation and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells
by targeting E2F2. Oncotarget. 7:20324–20337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Wang W, Li X, He S, Yao J, Wang
X, Zhang D and Sun X: MicroRNA-155 promotes tumor growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting ARID2. Int J Oncol.
48:2425–2434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sumara I, Maerki S and Peter M: E3
ubiquitin ligases and mitosis: Embracing the complexity. Trends
Cell Biol. 18:84–94. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang HG, Wang J, Yang X, Hsu HC and
Mountz JD: Regulation of apoptosis proteins in cancer cells by
ubiquitin. Oncogene. 23:2009–2015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bernassola F, Karin M, Ciechanover A and
Melino G: The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: Multiple players
in cancer development. Cancer Cell. 14:10–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jing Z, Li L, Wang X, Wang M, Cai Y, Jin
ZI and Zhang YE: High c-Cbl expression in gliomas is associated
with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Oncol Lett.
11:2787–2791. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Severe N, Miraoui H and Marie PJ: The
casitas B lineage lymphoma (Cbl) mutant G306E enhances osteogenic
differentiation in human mesenchymal stromal cells in part by
decreased Cbl-mediated platelet-derived growth factor receptor
alpha and fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 ubiquitination. J
Biol Chem. 286:24443–24450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shashar M, Siwak J, Tapan U, Lee SY, Meyer
RD, Parrack P, Tan J, Khatami F, Francis J, Zhao Q, et al: c-Cbl
mediates the degradation of tumorigenic nuclear β-catenin
contributing to the heterogeneity in Wnt activity in colorectal
tumors. Oncotarget. 7:71136–71150. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Cao H, Lu N, Liu L, Wang B, Hu T,
Israel DA, Peek RM Jr, Polk DB and Yan F: Berberine inhibits
proliferation and down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor
through activation of Cbl in colon tumor cells. PLoS One.
8:e566662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qu YL, Wang HF, Sun ZQ, Tang Y, Han XN, Yu
XB and Liu K: Up-regulated miR-155-5p promotes cell proliferation,
invasion and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6988–6994. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Velazquez KT, Enos RT, McClellan JL,
Cranford TL, Chatzistamou I, Singh UP, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS,
Fan D and Murphy EA: MicroRNA-155 deletion promotes tumorigenesis
in the azoxymethane-dextran sulfate sodium model of colon cancer.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 310:G347–G358. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM and
Callen DF: The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 21:1236–1243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu
H, Liu MF and Wang ED: MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in
breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
gene. Cancer Res. 70:3119–3127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun Y, Wang M, Lin G, Sun S, Li X, Qi J
and Li J: Serum microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track
disease in breast cancer. PLoS One. 7:e470032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie Q, Chen X, Lu F, Zhang T, Hao M, Wang
Y, Zhao J, McCrae MA and Zhuang H: Aberrant expression of microRNA
155 may accelerate cell proliferation by targeting sex-determining
region Y box 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 118:2431–2442.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tiago DM, Conceição N, Caiado H, Laizé V
and Cancela ML: Matrix Gla protein repression by miR-155 promotes
oncogenic signals in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. FEBS Lett.
590:1234–1241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li S, Chen T, Zhong Z, Wang Y, Li Y and
Zhao X: microRNA-155 silencing inhibits proliferation and migration
and induces apoptosis by upregulating BACH1 in renal cancer cells.
Mol Med Rep. 5:949–954. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma Z, Ma Y, Xia Q, Li Y, Li R, Chang W,
Chen J, Leng Z and Tao K: MicroRNA-155 expression inversely
correlates with pathologic stage of gastric cancer and it inhibits
gastric cancer cell growth by targeting cyclin D1. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 142:1201–1212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dai Y, Qiu Z, Diao Z, Shen L, Xue P, Sun H
and Hu Y: MicroRNA-155 inhibits proliferation and migration of
human extravillous trophoblast derived HTR-8/SVneo cells via
down-regulating cyclin D1. Placenta. 33:824–829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li T, Yang J, Lv X, Liu K, Gao C, Xing Y
and Xi T: miR-155 regulates the proliferation and cell cycle of
colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2. Biotechnol Lett.
36:1743–1752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang GJ, Xiao HX, Tian HP, Liu ZL, Xia SS
and Zhou T: Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and
invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of
claudin-1 expression. Int J Mol Med. 31:1375–1380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Babar IA, Cheng CJ, Booth CJ, Liang X,
Weidhaas JB, Saltzman WM and Slack FJ: Nanoparticle-based therapy
in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155)-dependent mouse model of
lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E1695–E1704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jablonska E, Gorniak P, Prusisz W,
Kiliszek P, Szydlowski M, Sewastianik T, Bialopiotrowicz E, Polak
A, Prochorec-Sobieszek M, Szumera-Cieckiewicz A, et al:
Downregulation of deptor By miR-155 promotes cell survival through
activation of PI3K/AKT and NFkB signaling in ABC-type diffuse large
B-cell Lymphomas. Blood. 128:17612016.
|
|
34
|
Huang C: Roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in
cell adhesion and migration. Cell Adh Migr. 4:10–18. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Teckchandani AM, Panetti TS and Tsygankov
AY: c-Cbl regulates migration of v-Abl-transformed NIH 3T3
fibroblasts via Rac1. Exp Cell Res. 307:247–258. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Teckchandani AM, Birukova AA, Tar K, Verin
AD and Tsygankov AY: The multidomain protooncogenic protein c-Cbl
binds to tubulin and stabilizes microtubules. Exp Cell Res.
306:114–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mitchison TJ and Cramer LP: Actin-based
cell motility and cell locomotion. Cell. 84:371–379. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jekely G, Sung HH, Luque CM and Rørth P:
Regulators of endocytosis maintain localized receptor tyrosine
kinase signaling in guided migration. Dev Cell. 9:197–207. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shen M and Yen A: c-Cbl tyrosine
kinase-binding domain mutant G306E abolishes the interaction of
c-Cbl with CD38 and fails to promote retinoic acid-induced cell
differentiation and G0 arrest. J Biol Chem. 284:25664–25677. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lo FY, Tan YH, Cheng HC, Salgia R and Wang
YC: An E3 ubiquitin ligase: c-Cbl: A new therapeutic target of lung
cancer. Cancer. 117:5344–5350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
An W, Nadeau SA, Mohapatra BC, Feng D,
Zutshi N, Storck MD, Arya P, Talmadge JE, Meza JL, Band V and Band
H: Loss of Cbl and Cbl-b ubiquitin ligases abrogates hematopoietic
stem cell quiescence and sensitizes leukemic disease to
chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 6:10498–10509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim SY, Kim JH and Song JJ: c-Cbl
shRNA-expressing adenovirus sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
prostate cancer DU-145 through increases of DR4/5. Cancer Gene
Ther. 20:82–87. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brennan T, Adapala NS, Barbe MF, Yingling
V and Sanjay A: Abrogation of Cbl-PI3K interaction increases bone
formation and osteoblast proliferation. Calcif Tissue Int.
89:396–410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Severe N, Dieudonné FX, Marty C, Modrowski
D, Patiño-García A, Lecanda F, Fromigué O and Marie PJ: Targeting
the E3 ubiquitin casitas B-lineage lymphoma decreases osteosarcoma
cell growth and survival and reduces tumorigenesis. J Bone Miner
Res. 27:2108–2117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|