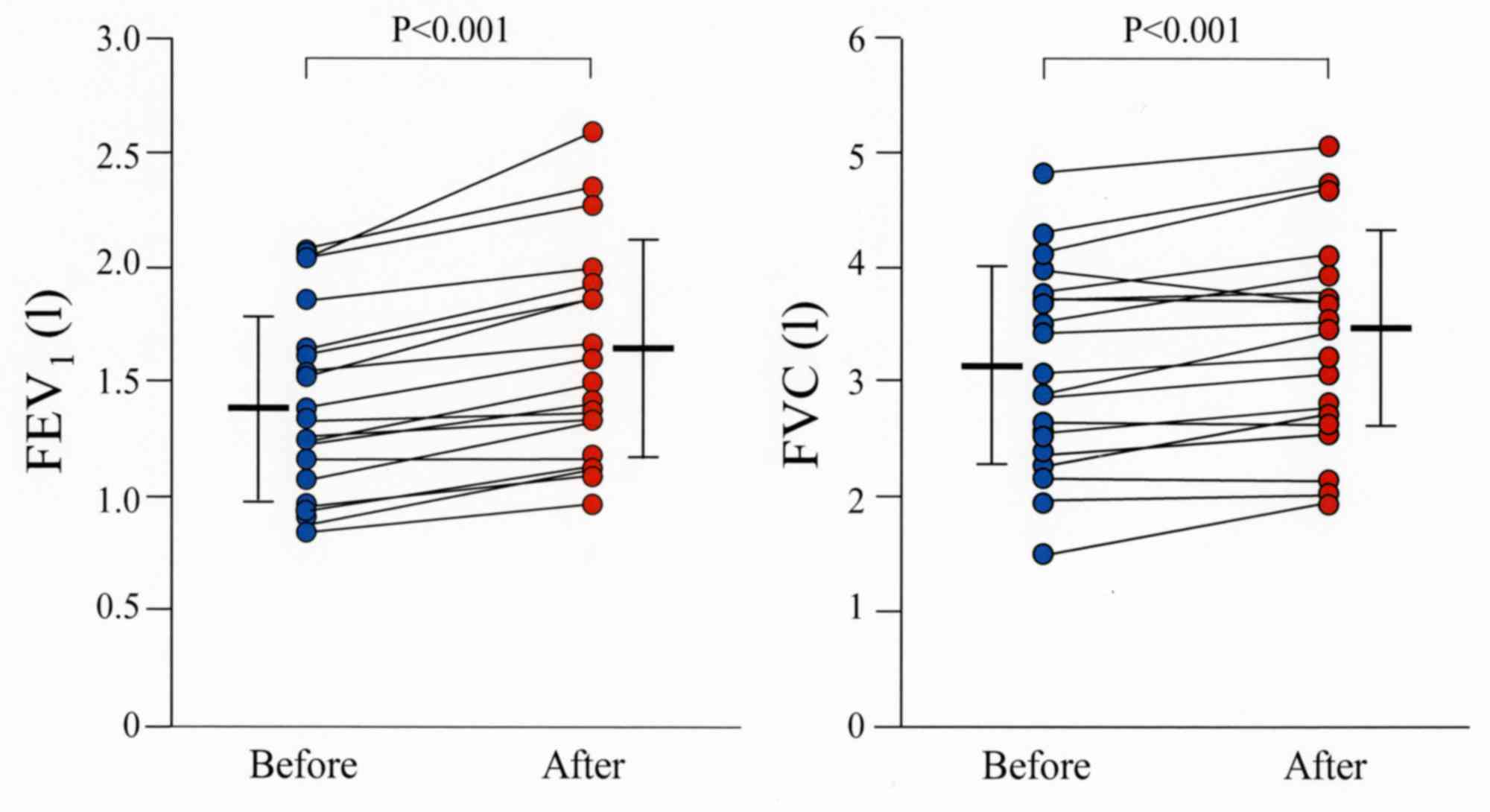
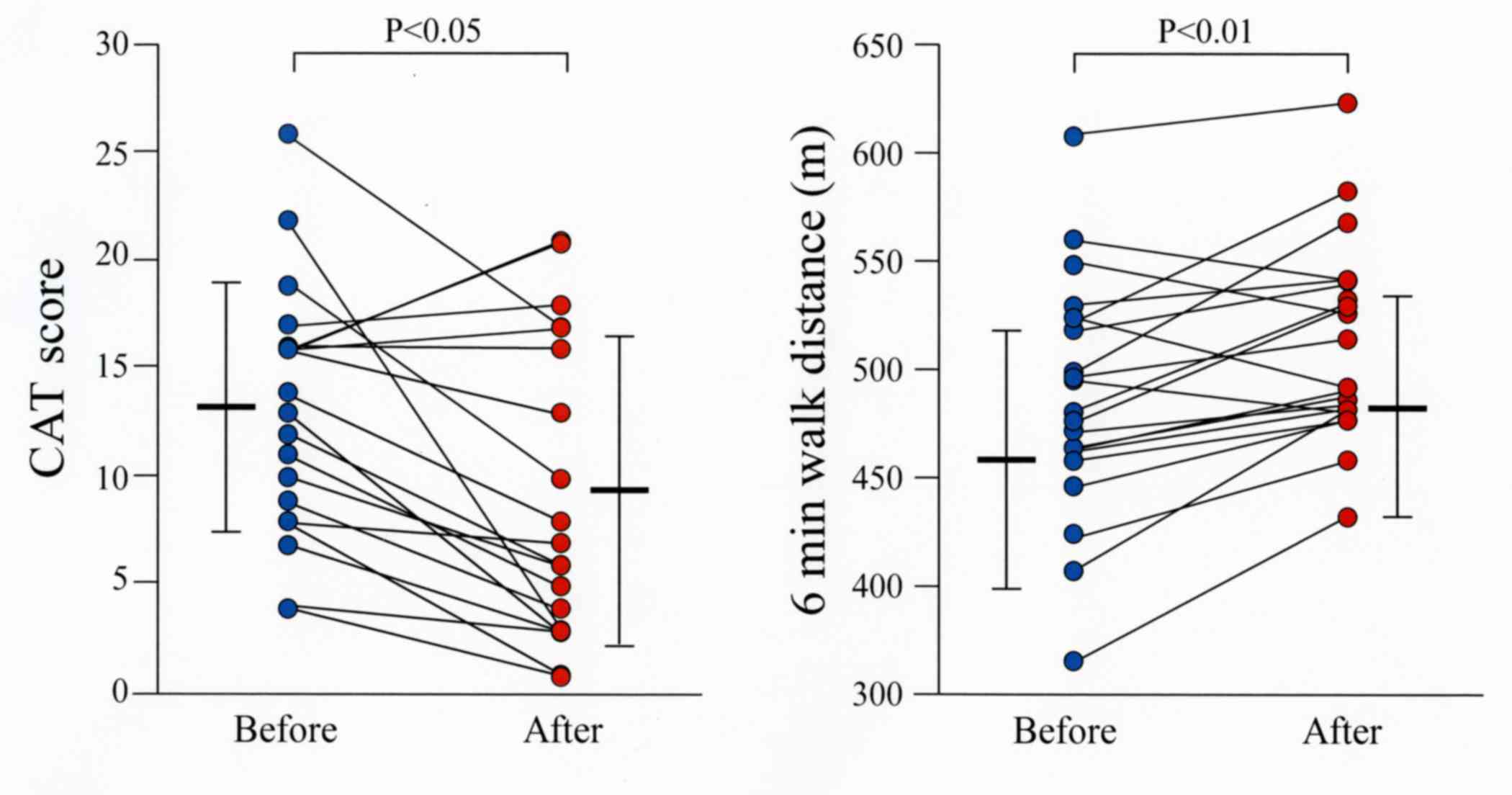
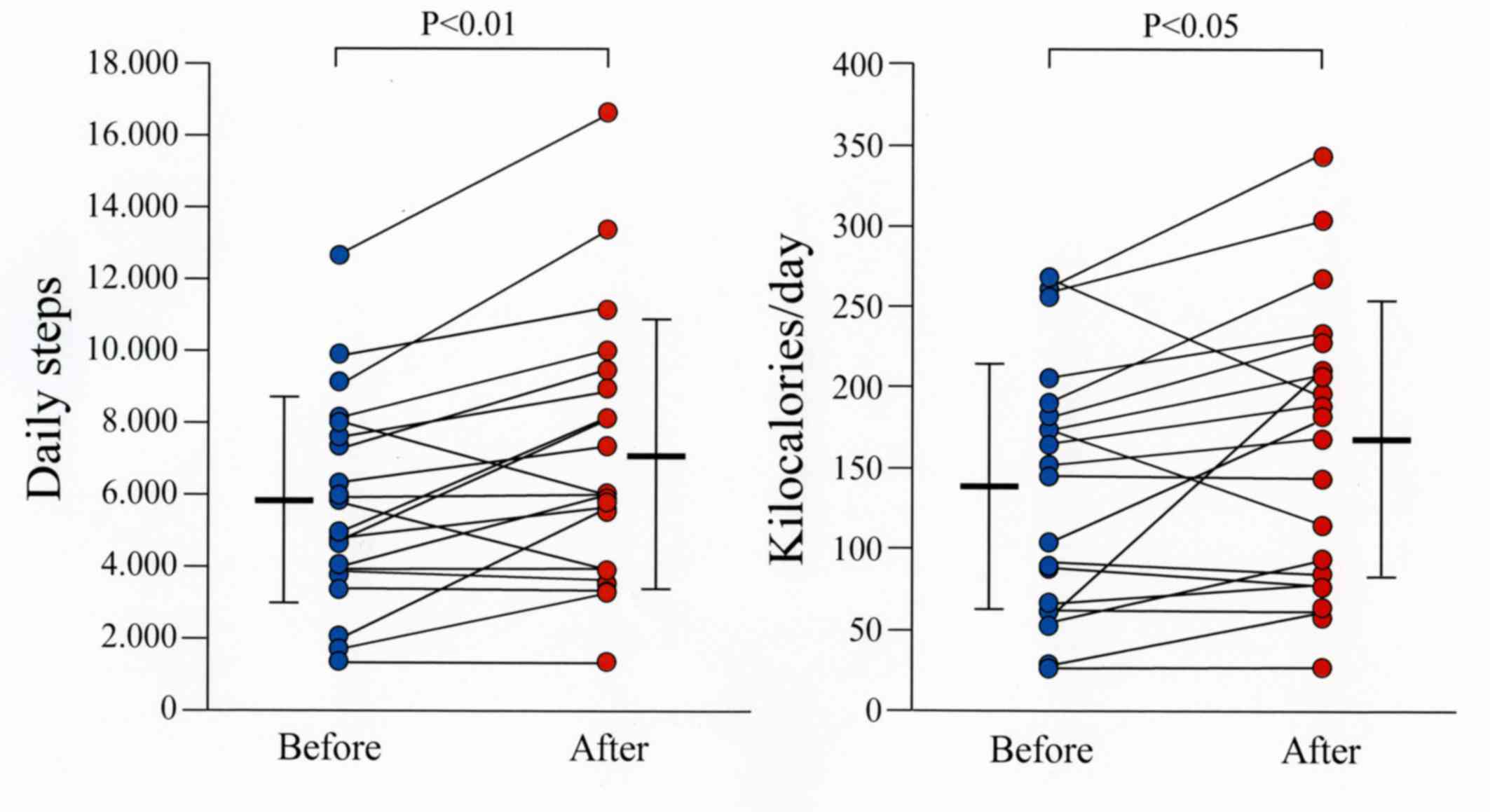
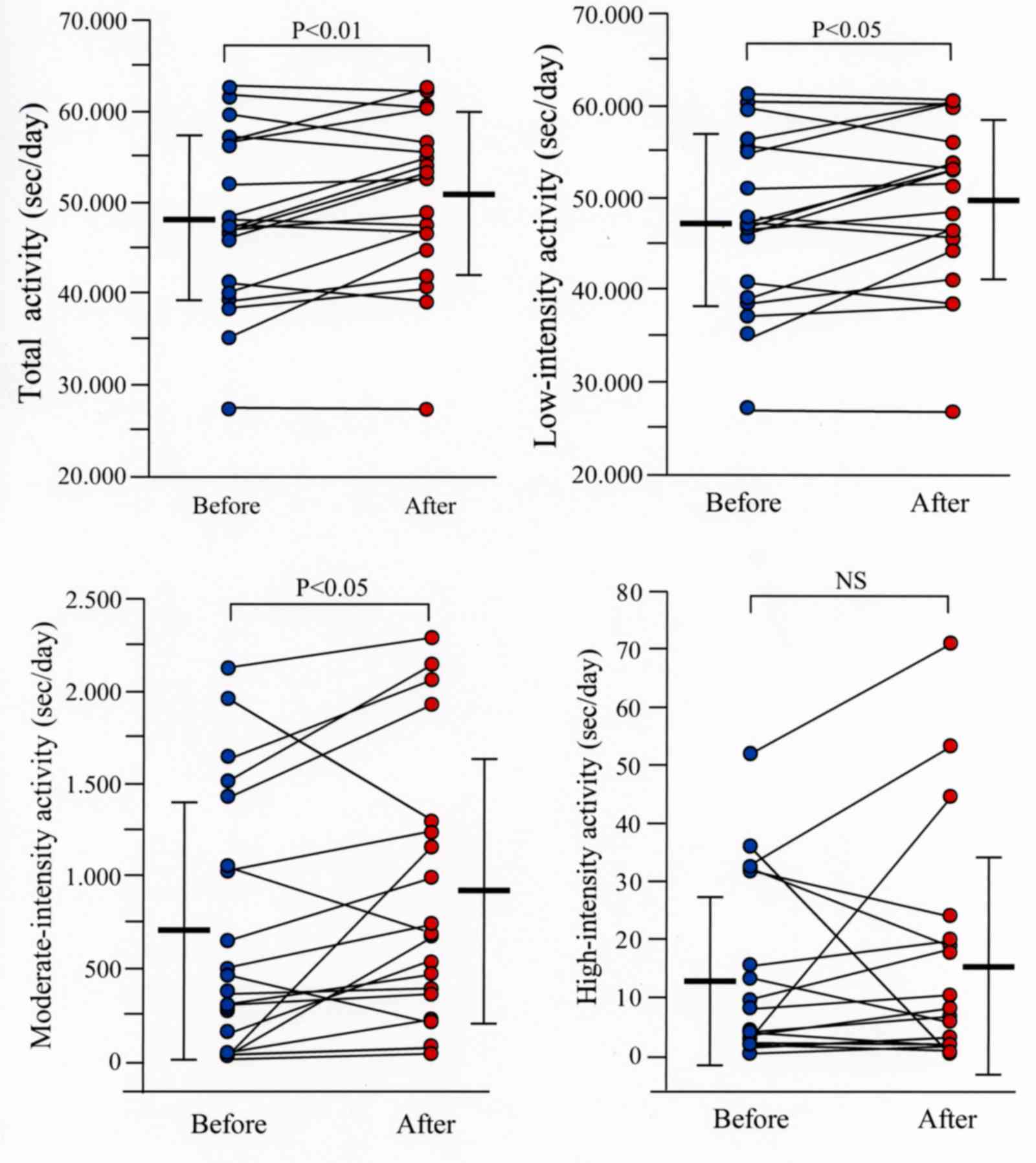
|
1
|
Kohl HW III, Craig CL, Lambert EV, Inoue
S, Alkandari JR, Leetongin G and Kahlmeier S: Lancet Physical
Activity Series Working Group: The pandemic of physical inactivity:
Global action for public health. Lancet. 380:294–305. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee IM, Shiroma EJ, Lobelo F, Puska P,
Blair SN and Katzmarzyk PT: Lancet Physical Activity Series Working
Group: Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable
diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life
expectancy. Lancet. 380:219–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Benzo RP, Chang CC, Farrell MH, Kaplan R,
Ries A, Martinez FJ, Wise R, Make B and Sciurba F: NETT Research
Group: Physical activity, health status and risk of hospitalization
in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Respiration. 80:10–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garcia-Rio F, Rojo B, Casitas R, Lores V,
Madero R, Romero D, Galera R and Villasante C: Prognostic value of
the objective measurement of daily physical activity in patients
with COPD. Chest. 142:338–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pitta F, Troosters T, Probst VS, Spruit
MA, Decramer M and Gosselink R: Physical activity and
hospitalization for exacerbation of COPD. Chest. 129:536–544. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buhl R, Maltais F, Abrahams R, Bjermer L,
Derom E, Ferguson G, Fležar M, Hébert J, McGarvey L, Pizzichini E,
et al: Tiotropium and olodaterol fixed-dose combination versus
mono-components in COPD (GOLD 2–4). Eur Respir J. 45:969–979. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferguson GT, Fležar M, Korn S, Korducki L,
Grönke L, Abrahams R and Buhl R: Efficacy of tiotropium +
olodaterol in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
by initial disease severity and treatment intensity: A post hoc
analysis. Adv Ther. 32:523–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vestbo J, Edwards LD, Scanlon PD, Yates
JC, Agusti A, Bakke P, Calverley PM, Celli B, Coxson HO, Crim C, et
al: Changes in forced expiratory volume in 1 sec over time in COPD.
N Engl J Med. 365:1184–1192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ,
Buist SA, Calverley P, Fukuchi Y, Jenkins C, Rodriguez-Roisin R,
van Weel C, et al: Global strategy for the diagnosis, management,
and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD
executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 176:532–555. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for
Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories: ATS statement: Guidelines
for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
166:111–117. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mackay AJ, Donaldson GC, Patel AR, Jones
PW, Hurst JR and Wedzicha JA: Usefulness of the Chronic Obstructive
Pulmonary Disease Assessment Test to evaluate severity of COPD
exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 185:1218–1224. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vaes AW, Garcia-Aymerich J, Marott JL,
Benet M, Groenen MT, Schnohr P, Franssen FM, Vestbo J, Wouters EF,
Lange P and Spruit MA: Changes in physical activity and all-cause
mortality in COPD. Eur Respir J. 44:1199–1209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dodd JW, Hogg L, Nolan J, Jefford H, Grant
A, Lord VM, Falzon C, Garrod R, Lee C, Polkey MI, et al: The COPD
assessment test (CAT): Response to pulmonary rehabilitation. A
multicentre, prospective study. Thorax. 66:425–429. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lacasse Y, Goldstein R, Lasserson TJ and
Martin S: Pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD003793. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Casaburi R and ZuWallack R: Pulmonary
rehabilitation for management of chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. N Engl J Med. 360:1329–1335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nici L, Donner C, Wouters E, Zuwallack R,
Ambrosino N, Bourbeau J, Carone M, Celli B, Engelen M, Fahy B, et
al: American thoracic society/european respiratory society
statement on pulmonary rehabilitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
173:1390–1413. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yohannes A, Stone R, Lowe D, Pursey N,
Buckingham R and Roberts C: Pulmonary rehabilitation in the United
Kingdom. Chron Respir Dis. 8:193–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davis AH: Exercise adherence in patients
with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: An exploration of
motivation and goals. Rehabil Nurs. 32:104–110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishijima Y, Minami S, Yamamoto S, Ogata
Y, Koba T, Futami S and Komuta K: Influence of indacaterol on daily
physical activity in patients with untreated chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 10:439–444.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Watz H, Krippner F, Kirsten A, Magnussen H
and Vogelmeier C: Indacaterol improves lung hyperinflation and
physical activity in patients with moderate chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease-a randomized, multicenter, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. BMC Pulm Med. 14:1582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mendoza L, Horta P, Espinoza J, Aguilera
M, Balmaceda N, Castro A, Ruiz M, Díaz O and Hopkinson NS:
Pedometers to enhance physical activity in COPD: A randomised
controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 45:347–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moy ML, Weston NA, Wilson EJ, Hess ML and
Richardson CR: A pilot study of an Internet walking program and
pedometer in COPD. Respir Med. 106:1342–1350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tabak M, Brusse-Keizer M, van der Valk P,
Hermens H and Vollenbroek-Hutten M: A telehealth program for
self-management of COPD exacerbations and promotion of an active
lifestyle: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Int J Chron
Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 9:935–944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wewel AR, Gellermann I, Schwertfeger I,
Morfeld M, Magnussen H and Jörres RA: Intervention by phone calls
raises domiciliary activity and exercise capacity in patients with
severe COPD. Respir Med. 102:20–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|