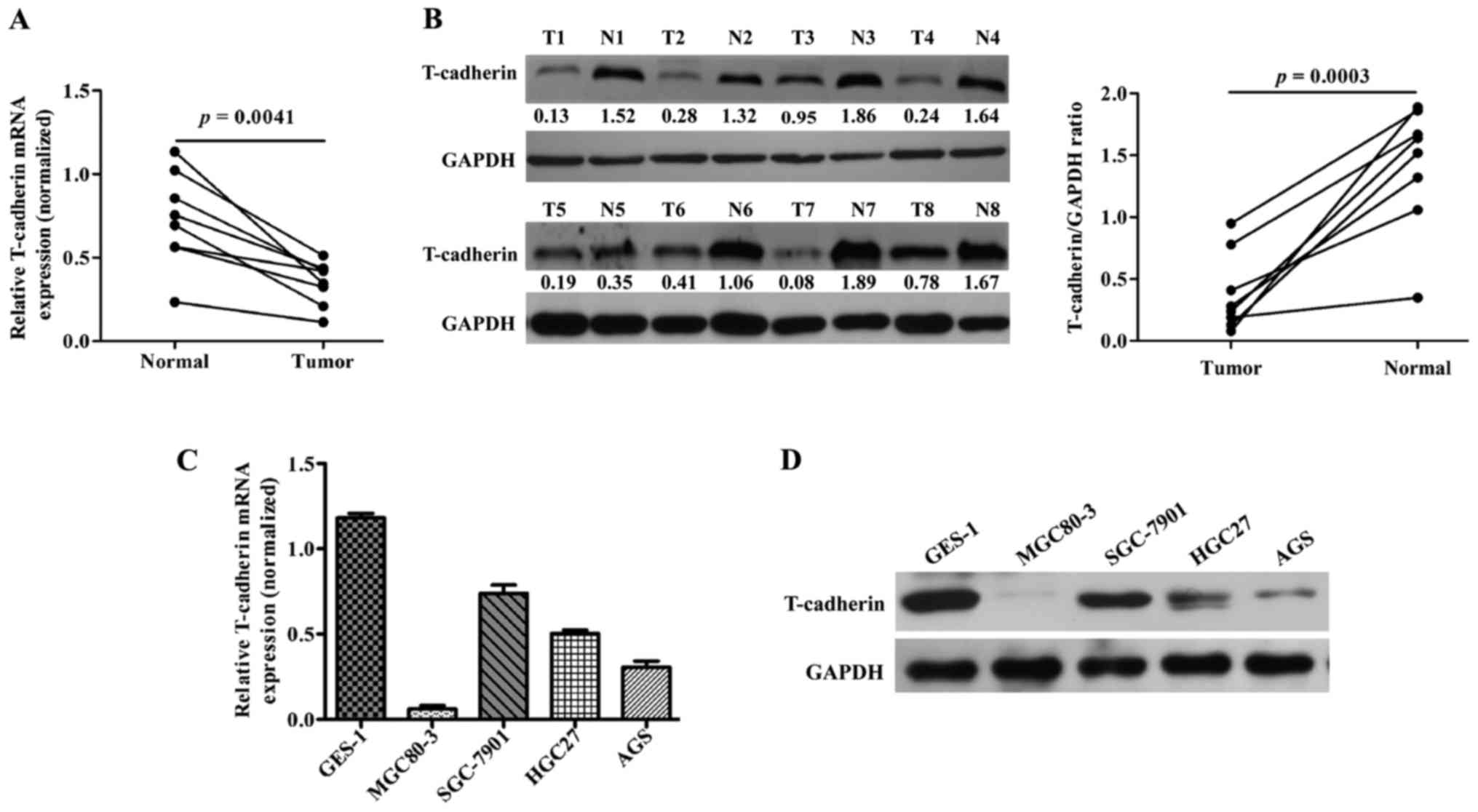
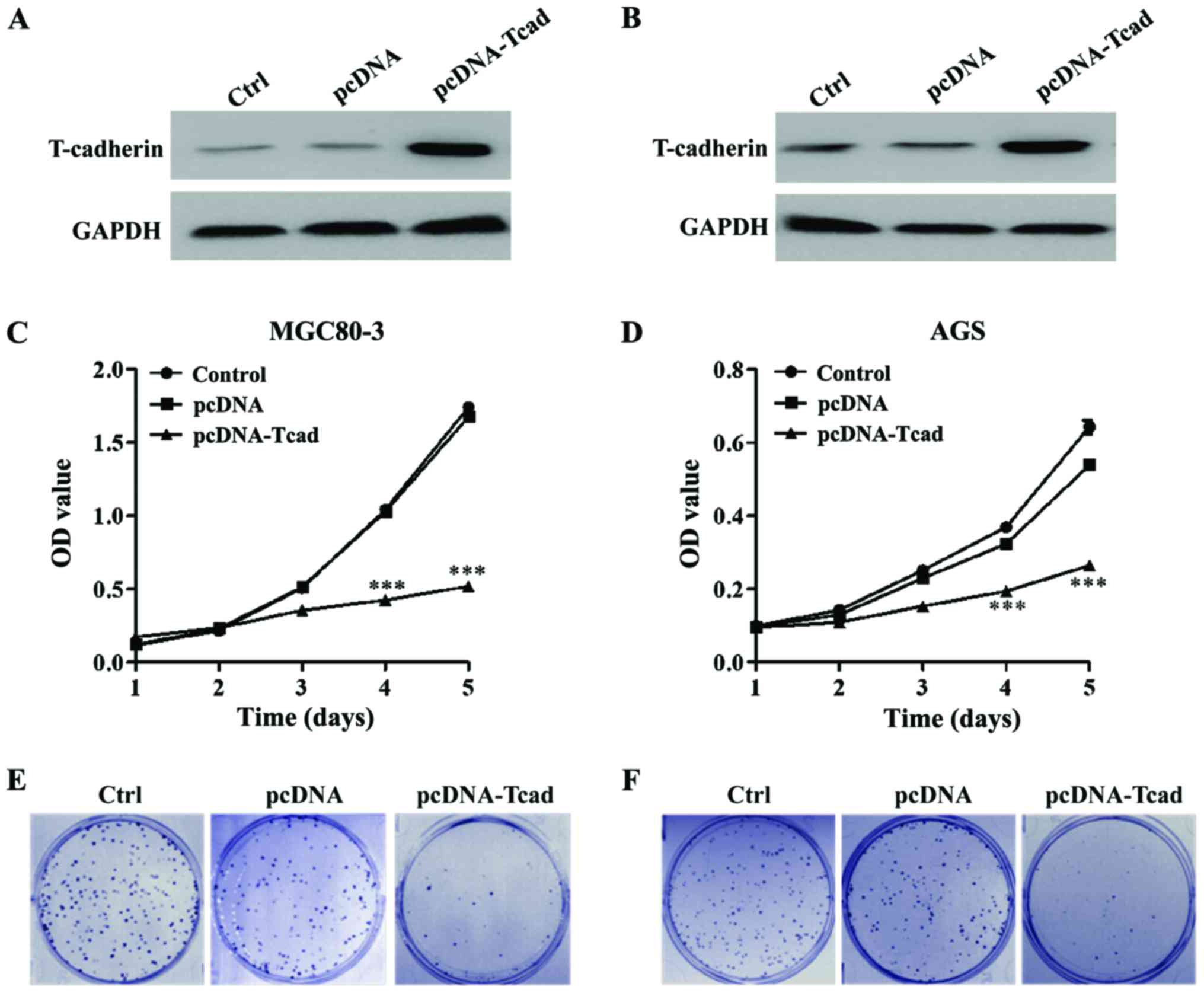
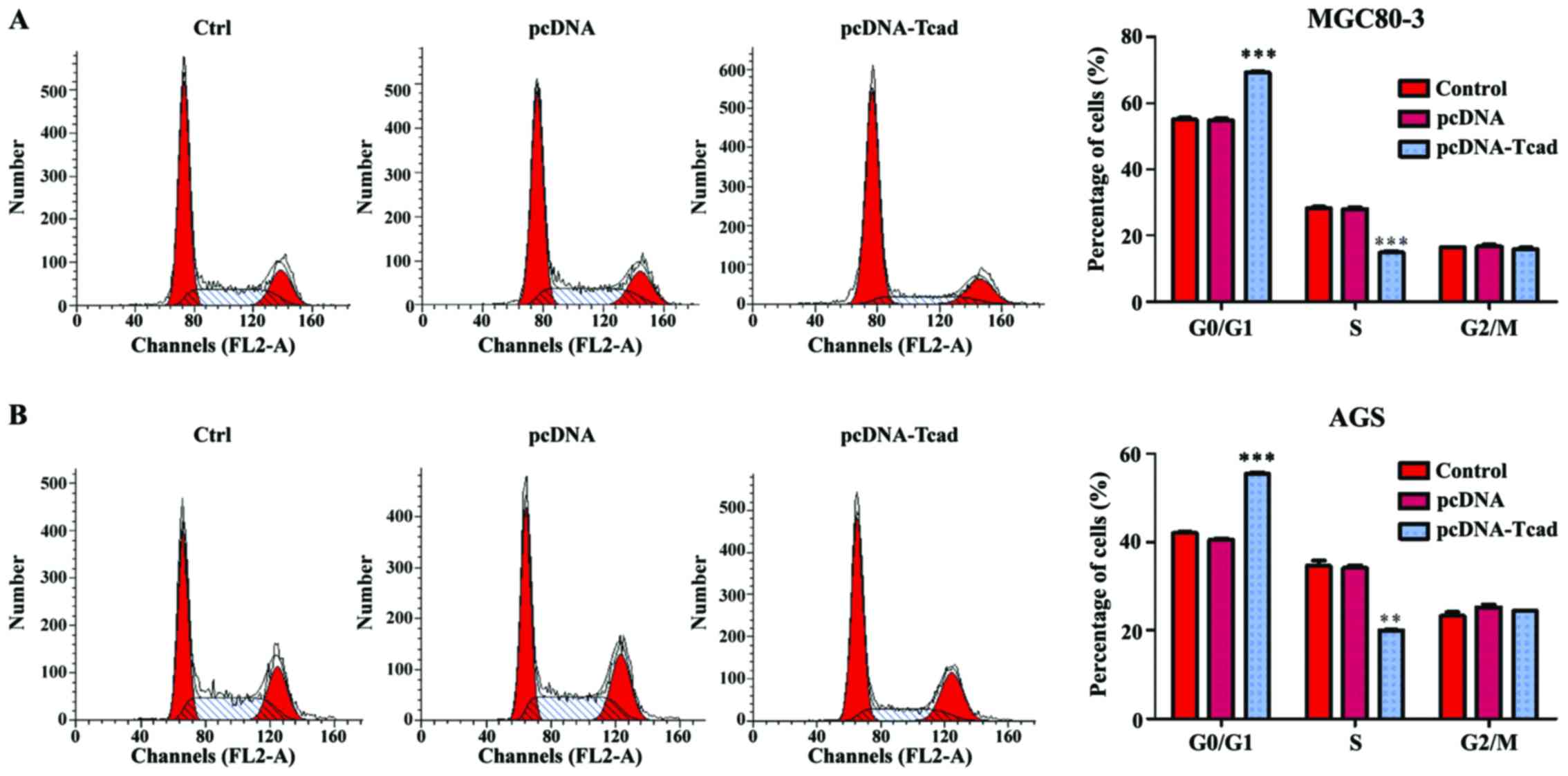
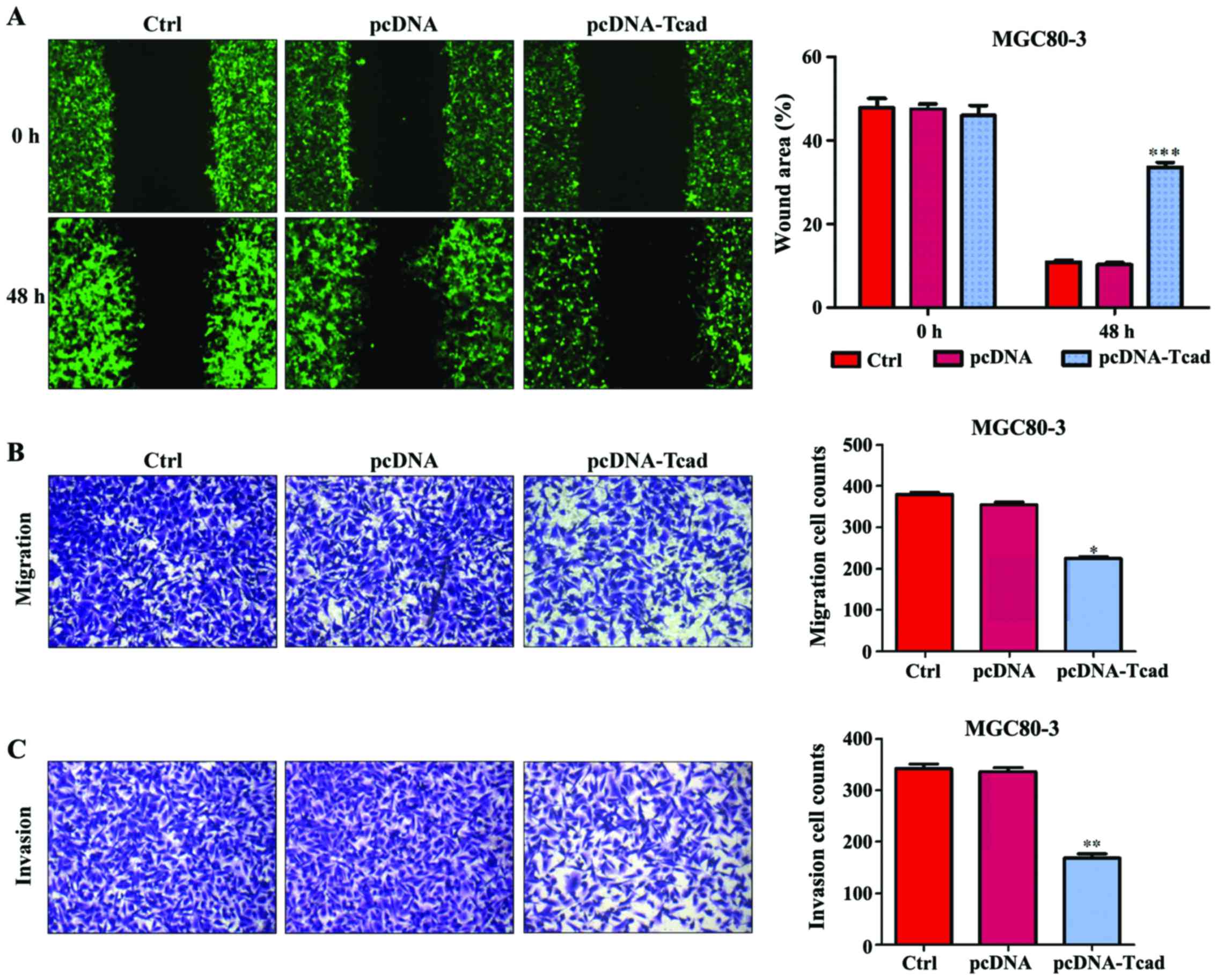
|
1
|
Piazuelo MB and Correa P: Gastric cáncer:
Overview. Colomb Med (Cali). 44:192–201. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sugano K: Screening of gastric cancer in
Asia. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 29:895–905. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xia P, Song CL, Liu JF, Wang D and Xu XY:
Prognostic value of circulating CD133(+) cells in patients with
gastric cancer. Cell Prolif. 48:311–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gigek CO, Chen ES, Calcagno DQ, Wisnieski
F, Burbano RR and Smith MA: Epigenetic mechanisms in gastric
cancer. Epigenomics. 4:279–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu W, Ye L, Zhang J, Yu P, Wang H, Ye Z
and Tian J: PFK15, a small molecule inhibitor of PFKFB3, induces
cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and inhibits invasion in gastric
cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01637682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yasui W, Sentani K, Sakamoto N, Anami K,
Naito Y and Oue N: Molecular pathology of gastric cancer: Research
and practice. Pathol Res Pract. 207:608–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baniak N, Senger JL, Ahmed S, Kanthan SC
and Kanthan R: Gastric biomarkers: A global review. World J Surg
Oncol. 14:2122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S and Takeichi M:
Transmembrane control of cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion.
Semin Cell Biol. 4:175–181. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takeichi M: Cadherin cell adhesion
receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 251:1451–1455.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wheelock MJ and Johnson KR: Cadherins as
modulators of cellular phenotype. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
19:207–235. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takeichi M: Cadherins in cancer:
Implications for invasion and metastasis. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
5:806–811. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mayer B, Johnson JP, Leitl F, Jauch KW,
Heiss MM, Schildberg FW, Birchmeier W and Funke I: E-cadherin
expression in primary and metastatic gastric cancer:
Down-regulation correlates with cellular dedifferentiation and
glandular disintegration. Cancer Res. 53:1690–1695. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bringuier PP, Umbas R, Schaafsma HE,
Karthaus HF, Debruyne FM and Schalken JA: Decreased E-cadherin
immunoreactivity correlates with poor survival in patients with
bladder tumors. Cancer Res. 53:3241–3245. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oka H, Shiozaki H, Kobayashi K, Inoue M,
Tahara H, Kobayashi T, Takatsuka Y, Matsuyoshi N, Hirano S,
Takeichi M, et al: Expression of E-cadherin cell adhesion molecules
in human breast cancer tissues and its relationship to metastasis.
Cancer Res. 53:1696–1701. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Angst BD, Marcozzi C and Magee AI: The
cadherin superfamily: Diversity in form and function. J Cell Sci.
114:629–641. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takeuchi T and Ohtsuki Y: Recent progress
in T-cadherin (CDH13, H-cadherin) research. Histol Histopathol.
16:1287–1293. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Philippova M, Joshi MB, Kyriakakis E,
Pfaff D, Erne P and Resink TJ: A guide and guard: The many faces of
T-cadherin. Cell Signal. 21:1035–1044. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Andreeva AV and Kutuzov MA: Cadherin 13 in
cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 49:775–790. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee SW: H-cadherin, a novel cadherin with
growth inhibitory functions and diminished expression in human
breast cancer. Nat Med. 2:776–782. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang XD, Wang BE, Soriano R, Zha J, Zhang
Z, Modrusan Z, Cunha GR and Gao WQ: Expression profiling of the
mouse prostate after castration and hormone replacement:
Implication of H-cadherin in prostate tumorigenesis.
Differentiation. 75:219–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pfaff D, Philippova M, Kyriakakis E,
Maslova K, Rupp K, Buechner SA, Iezzi G, Spagnoli GC, Erne P and
Resink TJ: Paradoxical effects of T-cadherin on squamous cell
carcinoma: Up- and down-regulation increase xenograft growth by
distinct mechanisms. J Pathol. 225:512–524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Y, Dai Y and Huo J: Decreased
expression of T-cadherin is associated with gastric cancer
prognosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1294–1298. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mori Y, Matsunaga M, Abe T, Fukushige S,
Miura K, Sunamura M, Shiiba K, Sato M, Nukiwa T and Horii A:
Chromosome band 16q24 is frequently deleted in human gastric
cancer. Br J Cancer. 80:556–562. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lindblom A, Rotstein S, Skoog L,
Nordenskjöld M and Larsson C: Deletions on chromosome 16 in primary
familial breast carcinomas are associated with development of
distant metastases. Cancer Res. 53:3707–3711. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carter BS, Ewing CM, Ward WS, Treiger BF,
Aalders TW, Schalken JA, Epstein JI and Isaacs WB: Allelic loss of
chromosomes 16q and 10q in human prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 87:8751–8755. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen T, Sahin A and Aldaz CM: Deletion map
of chromosome 16q in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast:
Refining a putative tumor suppressor gene region. Cancer Res.
56:5605–5609. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei B, Shi H, Lu X, Shi A, Cheng Y and
Dong L: Association between the expression of T-cadherin and
vascular endothelial growth factor and the prognosis of patients
with gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 12:2075–2081. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pfaff D, Philippova M, Buechner SA,
Maslova K, Mathys T, Erne P and Resink TJ: T-cadherin loss induces
an invasive phenotype in human keratinocytes and squamous cell
carcinoma (SCC) cells in vitro and is associated with malignant
transformation of cutaneous SCC in vivo. Br J Dermatol.
163:353–363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bosserhoff AK, Ellmann L, Quast AS, Eberle
J, Boyle GM and Kuphal S: Loss of T-cadherin (CDH-13) regulates AKT
signaling and desensitizes cells to apoptosis in melanoma. Mol
Carcinog. 53:635–647. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Philippova M, Pfaff D, Kyriakakis E,
Buechner SA, Iezzi G, Spagnoli GC, Schoenenberger AW, Erne P and
Resink TJ: T-cadherin loss promotes experimental metastasis of
squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 49:2048–2058. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ivanov D, Philippova M, Allenspach R, Erne
P and Resink T: T-cadherin upregulation correlates with cell-cycle
progression and promotes proliferation of vascular cells.
Cardiovasc Res. 64:132–143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhong Y, Lopez-Barcons L, Haigentz M Jr,
Ling YH and Perez-Soler R: Exogenous expression of H-cadherin in
CHO cells regulates contact inhibition of cell growth by inducing
p21 expression. Int J Oncol. 24:1573–1579. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mukoyama Y, Zhou S, Miyachi Y and
Matsuyoshi N: T-cadherin negatively regulates the proliferation of
cutaneous squamous carcinoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 124:833–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang ZY, Wu Y, Hedrick N and Gutmann DH:
T-cadherin-mediated cell growth regulation involves G2 phase arrest
and requires p21(CIP1/WAF1) expression. Mol Cell Biol. 23:566–578.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hermiston ML and Gordon JI: Inflammatory
bowel disease and adenomas in mice expressing a dominant negative
N-cadherin. Science. 270:1203–1207. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Behrens J: The role of cell adhesion
molecules in cancer invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 24:175–184. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pecina-Slaus N: Tumor suppressor gene
E-cadherin and its role in normal and malignant cells. Cancer Cell
Int. 3:172003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Venza M, Visalli M, Catalano T, Biondo C,
Beninati C, Teti D and Venza I: DNA methylation-induced E-cadherin
silencing is correlated with the clinicopathological features of
melanoma. Oncol Rep. 35:2451–2460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tamura G, Yin J, Wang S, Fleisher AS, Zou
T, Abraham JM, Kong D, Smolinski KN, Wilson KT, James SP, et al:
E-Cadherin gene promoter hypermethylation in primary human gastric
carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:569–573. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hibi K, Kodera Y, Ito K, Akiyama S and
Nakao A: Methylation pattern of CDH13 gene in digestive tract
cancers. Br J Cancer. 91:1139–1142. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schoumacher M, Goldman RD, Louvard D and
Vignjevic DM: Actin, microtubules and vimentin intermediate
filaments cooperate for elongation of invadopodia. J Cell Biol.
189:541–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|