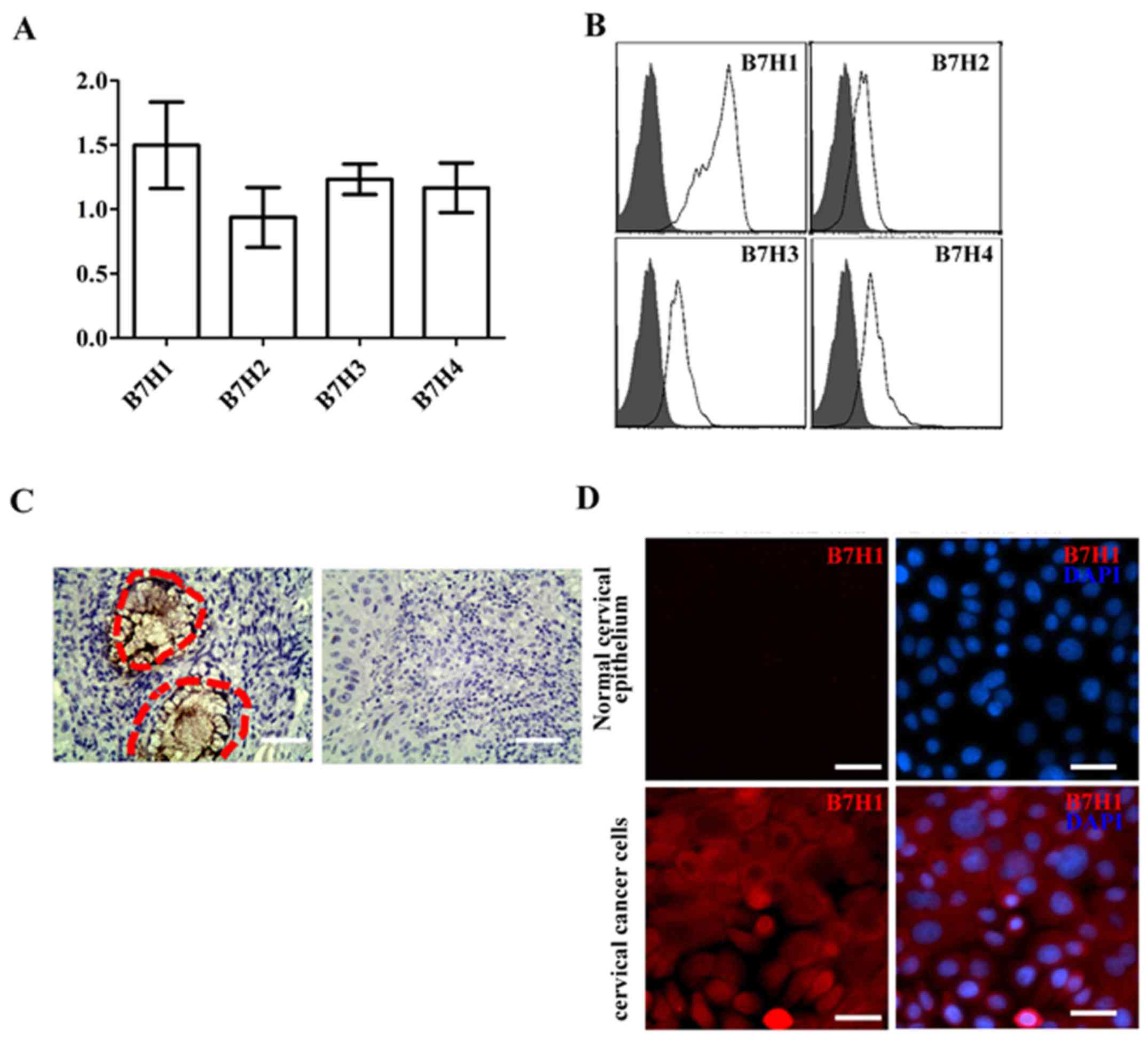
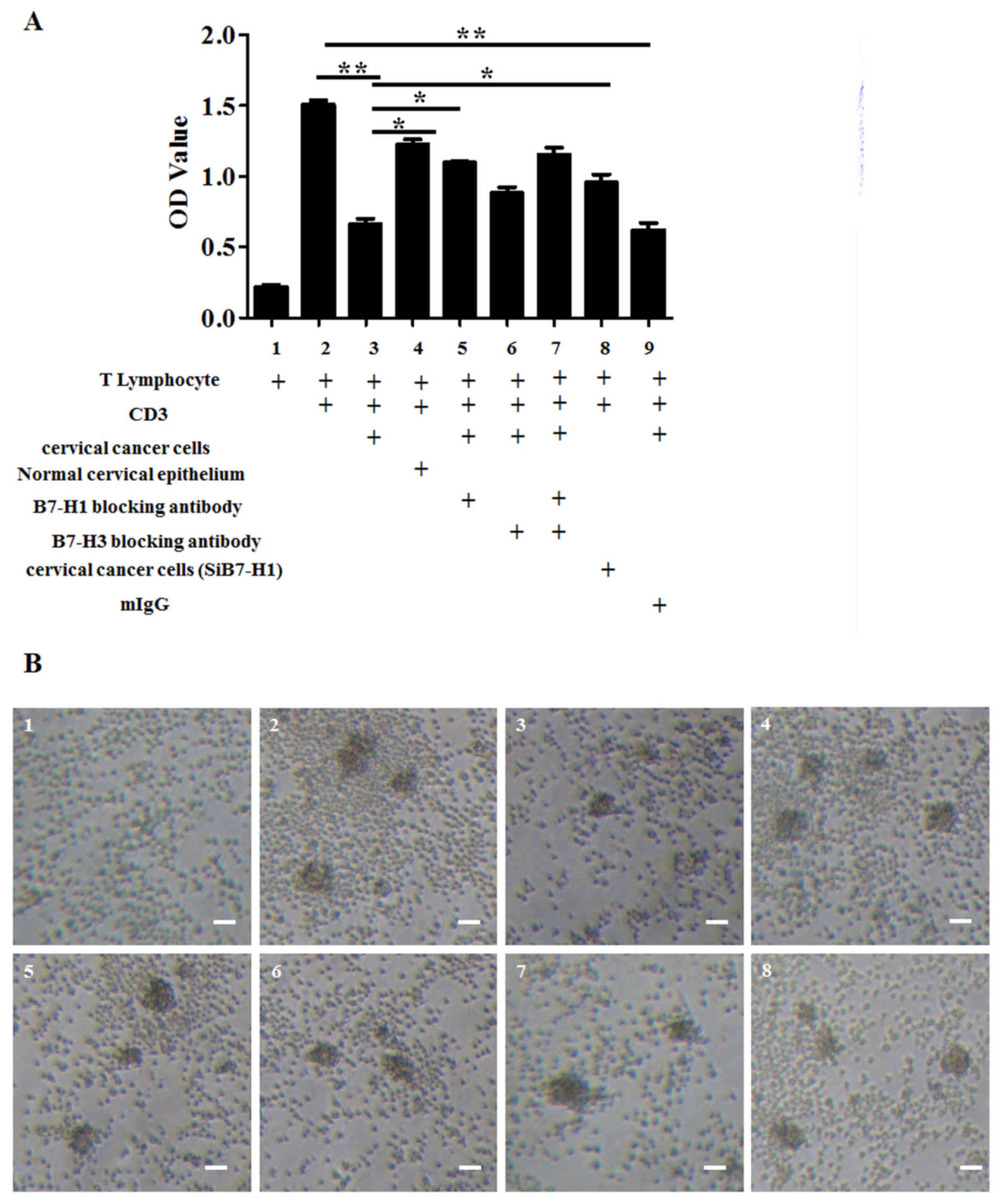
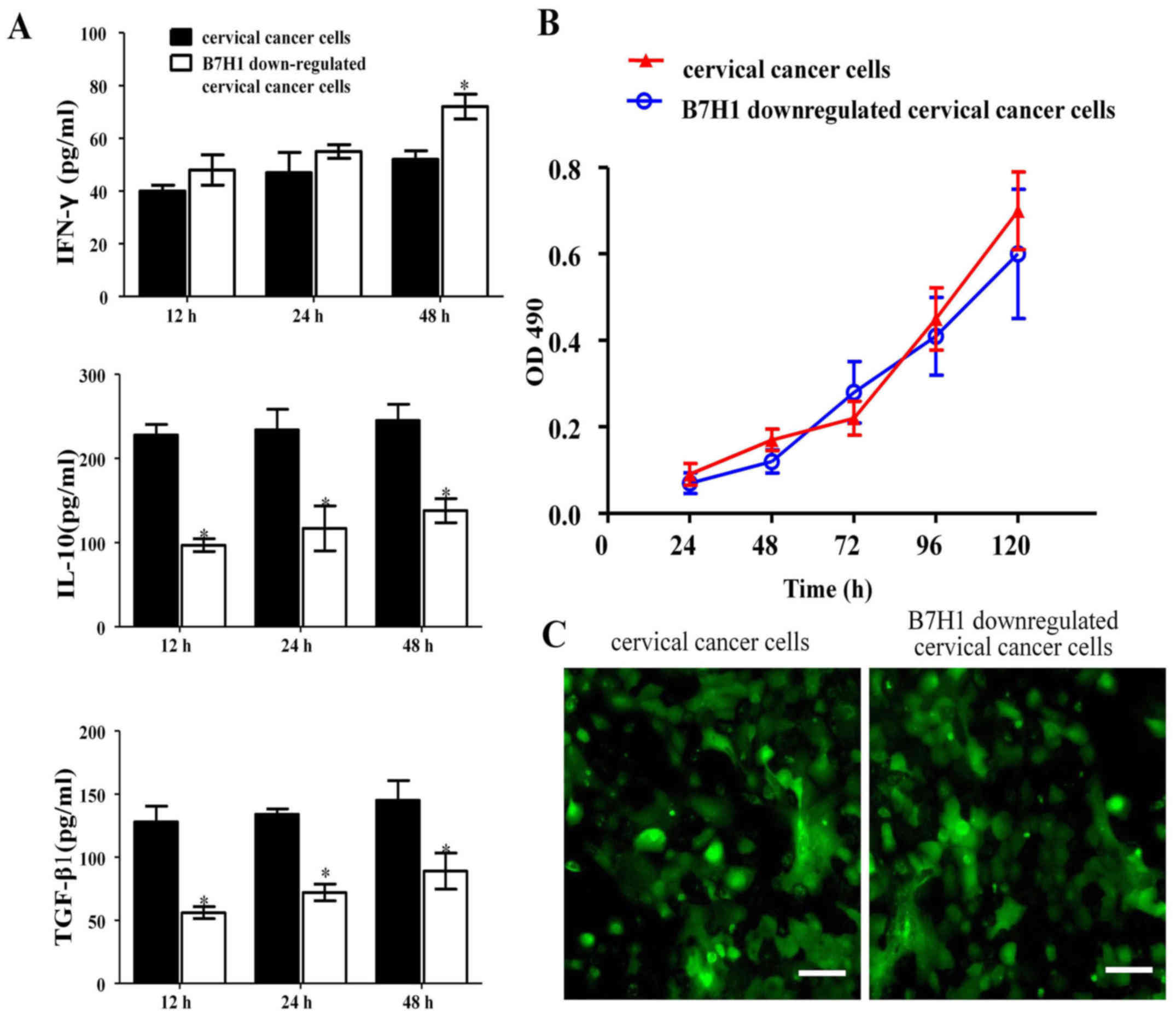
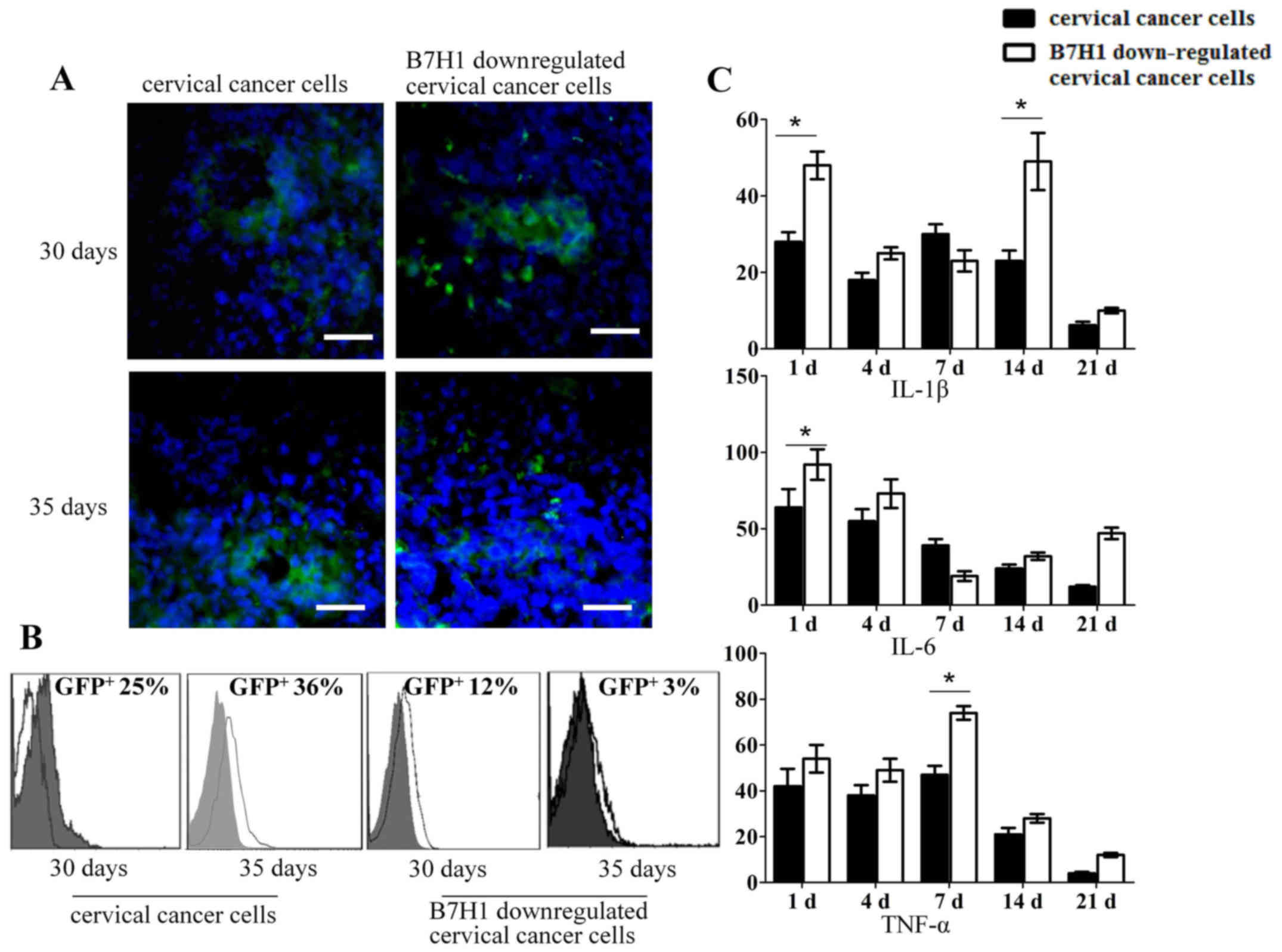
|
1
|
Hammes LS, Tekmal RR, Naud P, Edelweiss
MI, Kirma N, Valente PT, Syrjänen KJ and Cunha-Filho JS:
Macrophages, inflammation and risk of cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia (CIN) progression-clinicopathological correlation.
Gynecol Oncol. 105:157–165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu SY, Zheng RS, Zhao FH, Zhang SW, Chen
WQ and Qiao YL: Trend analysis of cervical cancer incidence and
mortality rates in Chinese women during 1989–2008. Zhongguo Yi Xue
Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 36:119–125. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu YY, Liang MR, Li LY and Zeng SY:
Analysis of 4223 hospitalized patients with cervical cancer during
1990–2007. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 43:433–436. 2008.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Human papillomavirus testing for triage of
women with cytologic evidence of low-grade squamous intraepithelial
lesions: Baseline data from a randomized trial. The Atypical
Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance/Low-Grade Squamous
Intraepithelial Lesions Triage Study (ALTS) Group. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 92:397–402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo XM, Song L, Wu JL, Liu Y, Di JL, Song
B, Zheng RM and Ma L: Analysis of the reported data of national
rural cervical cancer screening project from 2012 to 2013, China.
Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 50:346–350. 2016.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anisimov VN: Syndrome of accelerated aging
induced by carcinogenic environmental factors. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I
M Sechenova. 96:817–833. 2010.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stroh EL, Besa PC, Cox JD, Fuller LM and
Cabanillas FF: Treatment of patients with lymphomas of the uterus
or cervix with combination chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Cancer. 75:2392–2399. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park HJ, Chang AR, Seo Y, Cho CK, Jang WI,
Kim MS and Choi C: Stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent or
oligometastatic uterine cervix cancer: A cooperative study of the
Korean radiation oncology group (KROG 14–11). Anticancer Res.
35:5103–5110. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim KH, Dishongh R, Santin AD, Cannon MJ,
Bellone S and Nakagawa M: Recognition of a cervical cancer derived
tumor cell line by a human papillomavirus type 16 E6 52-61-specific
CD8 T cell clone. Cancer Immun. 6:92006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chew V, Toh HC and Abastado JP: Immune
microenvironment in tumor progression: Characteristics and
challenges for therapy. J Oncol. 2012:6084062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghebeh H, Mohammed S, Al-Omair A, Qattan
A, Lehe C, Al-Qudaihi G, Elkum N, Alshabanah M, Bin Amer S, Tulbah
A, et al: The B7-1 (PD-L1) T lymphocyte-inhibitory molecule is
expressed in breast cancer patients with infiltrating ductal
carcinoma: Correlation with important high-risk prognostic factors.
Neoplasia. 8:190–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, Okazaki
T, Tanaka Y, Yamaguchi K, Higuchi T, Yagi H, Takakura K, Minato N,
et al: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating
CD8+ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human
ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:3360–3365. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, Tsurui Y,
Hamada K, Ikeda N, Mizuno T, Yoriki R, Kashizuka H, Yane K, et al:
Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed
death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:2947–2953. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Dong
H, Lohse CM, Webster WS, Sengupta S, Frank I, Parker AS, Zincke H,
et al: Tumor B7-1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell
carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res.
66:3381–3385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang XG and
Xu N: Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1
ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical
significance. Acta Histochem. 108:19–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Wang T, Xu M, Xiao L, Luo Y, Huang
W, Zhang Y and Geng W: B7-H4 overexpression impairs the immune
response of T cells in human cervical carcinomas. Hum Immunol.
75:1203–1209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han S, Li Y, Zhang J, Liu L, Chen Q, Qian
Q, Li S and Zhang Y: Roles of immune inhibitory molecule B7-H4 in
cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:2308–2316. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu W, Shibata K, Koya Y, Kajiyama H,
Senga T, Yamashita M and Kikkawa F: B7-H4 overexpression correlates
with a poor prognosis for cervical cancer patients. Mol Clin Oncol.
2:219–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang W, He W, Shi Y, Gu H, Li M, Liu Z,
Feng Y, Zheng N, Xie C and Zhang Y: High expression of KIF20A Is
associated with poor overall survival and tumor progression in
Early-stage cervical squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
11:e01674492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pilz GA, Braun J, Ulrich C, Felka T,
Warstat K, Ruh M, Schewe B, Abele H, Larbi A and Aicher WK: Human
mesenchymal stromal cells express CD14 cross-reactive epitopes.
Cytometry A. 79:635–645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Herzenberg LA, Tung J, Moore WA,
Herzenberg LA and Parks DR: Interpreting flow cytometry data: A
guide for the perplexed. Nat Immunol. 7:681–685. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinto AE, Areia F, Pereira T, Cardoso P,
Aparício M, Silva GL, Ferreira MC and André S: Clinical relevance
of the reappraisal of negative hormone receptor expression in
breast cancer. Springerplus. 2:3752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fei F, Yu Y, Schmitt A, Rojewski MT, Chen
B, Greiner J, Götz M, Guillaume P, Döhner H, Bunjes D and Schmitt
M: Dasatinib exerts an immunosuppressive effect on CD8+
T cells specific for viral and leukemia antigens. Exp Hematol.
36:1297–1308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zou Q, Jin J, Xiao Y, Zhou X, Hu H, Cheng
X, Kazimi N, Ullrich SE and Sun SC: T Cell Intrinsic USP15
deficiency promotes excessive IFN-γ production and an
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in MCA-induced
fibrosarcoma. Cell Rep. 13:2470–2479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan M, Himoudi N, Pule M, Sebire N, Poon
E, Blair A, Williams O and Anderson J: Development of cellular
immune responses against PAX5, a novel target for cancer
immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 68:8058–8065. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen YM, He X, Deng HX, Xie YP, Wang CT,
Wei YQ and Zhao X: Overexpression of the hBiot2 gene is associated
with development of human cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 25:75–80.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Riella LV, Paterson AM, Sharpe AH and
Chandraker A: Role of the PD-1 pathway in the immune response. Am J
Transplant. 12:2575–2587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo Z, Wang H, Meng F, Li J and Zhang S:
Combined trabectedin and anti-PD1 antibody produces a synergistic
antitumor effect in a murine model of ovarian cancer. J Transl Med.
13:2472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weinstock M and McDermott DF: Emerging
role for novel immunotherapy agents in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma: From bench to bedside. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book.
2015:e291–e297. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang YT, Zhao XY, Zhao XS, Xu LP, Zhang
XH, Wang Y, Liu KY, Chang YJ and Huang XJ: The impact of donor
characteristics on the immune cell composition of mixture
allografts of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor-mobilized
marrow harvests and peripheral blood harvests. Transfusion.
55:2874–2881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wilson CL, Murphy LB, Leslie J, Kendrick
S, French J, Fox CR, Sheerin NS, Fisher A, Robinson JH, Tiniakos
DG, et al: Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 1 (UCHL1) A novel
functional marker for liver myofibroblasts and a therapeutic target
in chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 63:1421–1428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xie ZY, Chen YW, Fu XL, Yang CY and Wu YZ:
Expression of B7-H1 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells from
chronic hepatitis B patients. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
27:1635–1637. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin X and Xie C: TH-AB-BRB-04: Dosimetric
and clinical benefits of conformal radiotherapy plus volumetric
modulated arc therapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung
cancer. Med Phys. 42:37042015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Harshman LC, Choueiri TK, Drake C and Hodi
Stephen F Jr: Subverting the B7-H1/PD-1 pathway in advanced
melanoma and kidney cancer. Cancer J. 20:272–280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Wang GD, Guo ZY, Wei M,
Meng YL, Yang AG and Wen WH: B7-H1 expression is associated with
poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma and regulates the
proliferation and invasion of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e760122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Thompson RH, Gillett MD, Cheville JC,
Lohse CM, Dong H, Webster WS, Krejci KG, Lobo JR, Sengupta S, Chen
L, et al: Costimulatory B7-H1 in renal cell carcinoma patients:
Indicator of tumor aggressiveness and potential therapeutic target.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:17174–17179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pfankuchen DB, Stölting DP, Schlesinger M,
Royer HD and Bendas G: Low molecular weight heparin tinzaparin
antagonizes cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 97:147–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Arora S, Tyagi
N, Singh S, Andrews J, McClellan S, Wang B and Singh AP:
MicroRNA-345 induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through
potentiation of caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Br J
Cancer. 113:660–668. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Karabulut M, Alis H, Afsar CU, Karabulut
S, Kocatas A, Oguz H and Aykan NF: Serum neural precursor
cell-expressed, developmentally down regulated 9 (NEDD9) level may
have a prognostic role in patients with gastric cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 73:140–146. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen Q and Fang X, Jiang C, Yao N and Fang
X: Thrombospondin promoted anti-tumor of adenovirus-mediated
calreticulin in breast cancer: Relationship with anti-CD47. Biomed
Pharmacother. 73:109–115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mirza N, Duque MA, Dominguez AL, Schrum
AG, Dong H and Lustgarten J: B7-H1 expression on old CD8+ T cells
negatively regulates the activation of immune responses in aged
animals. J Immunol. 184:5466–5474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|