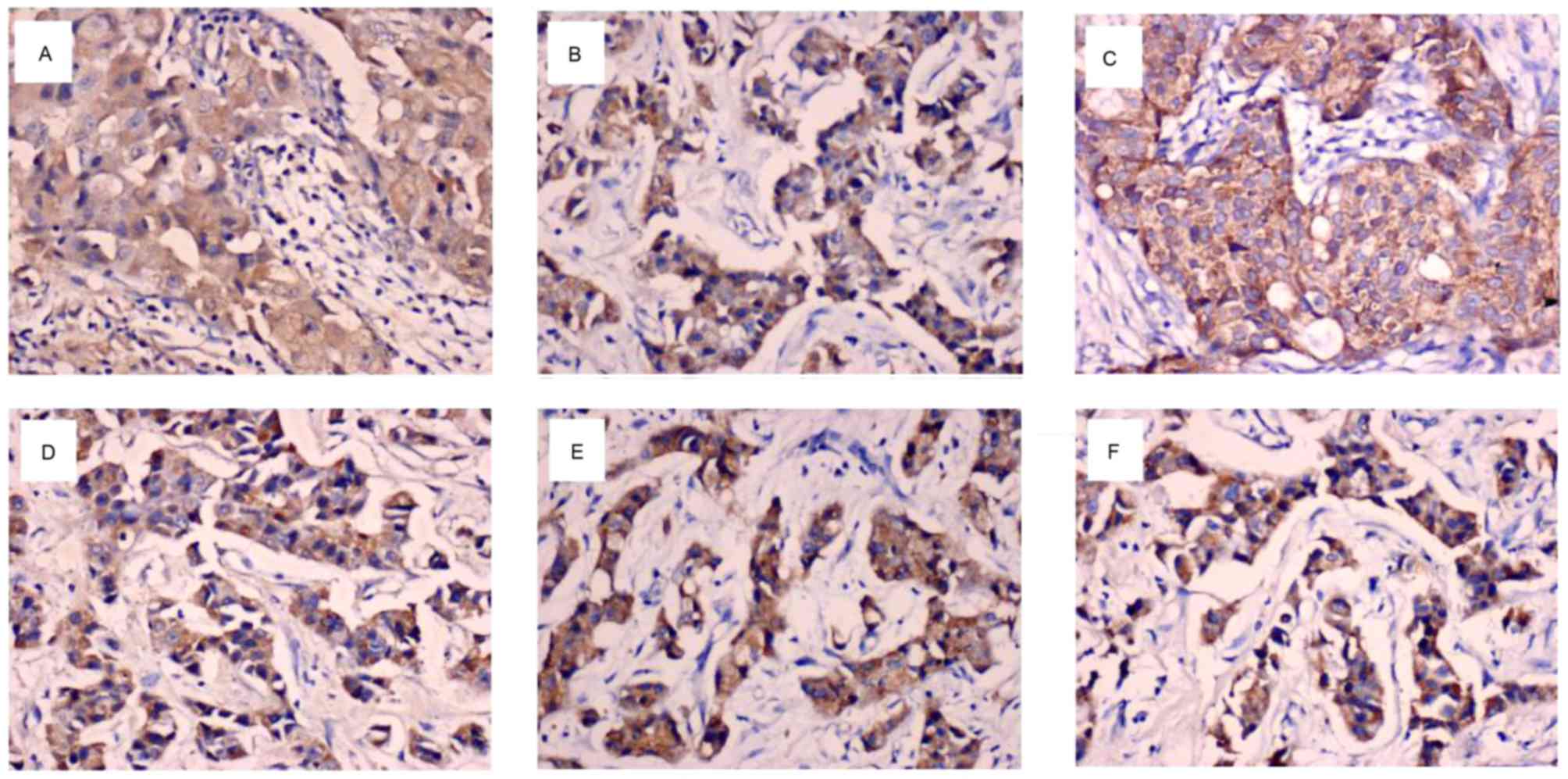
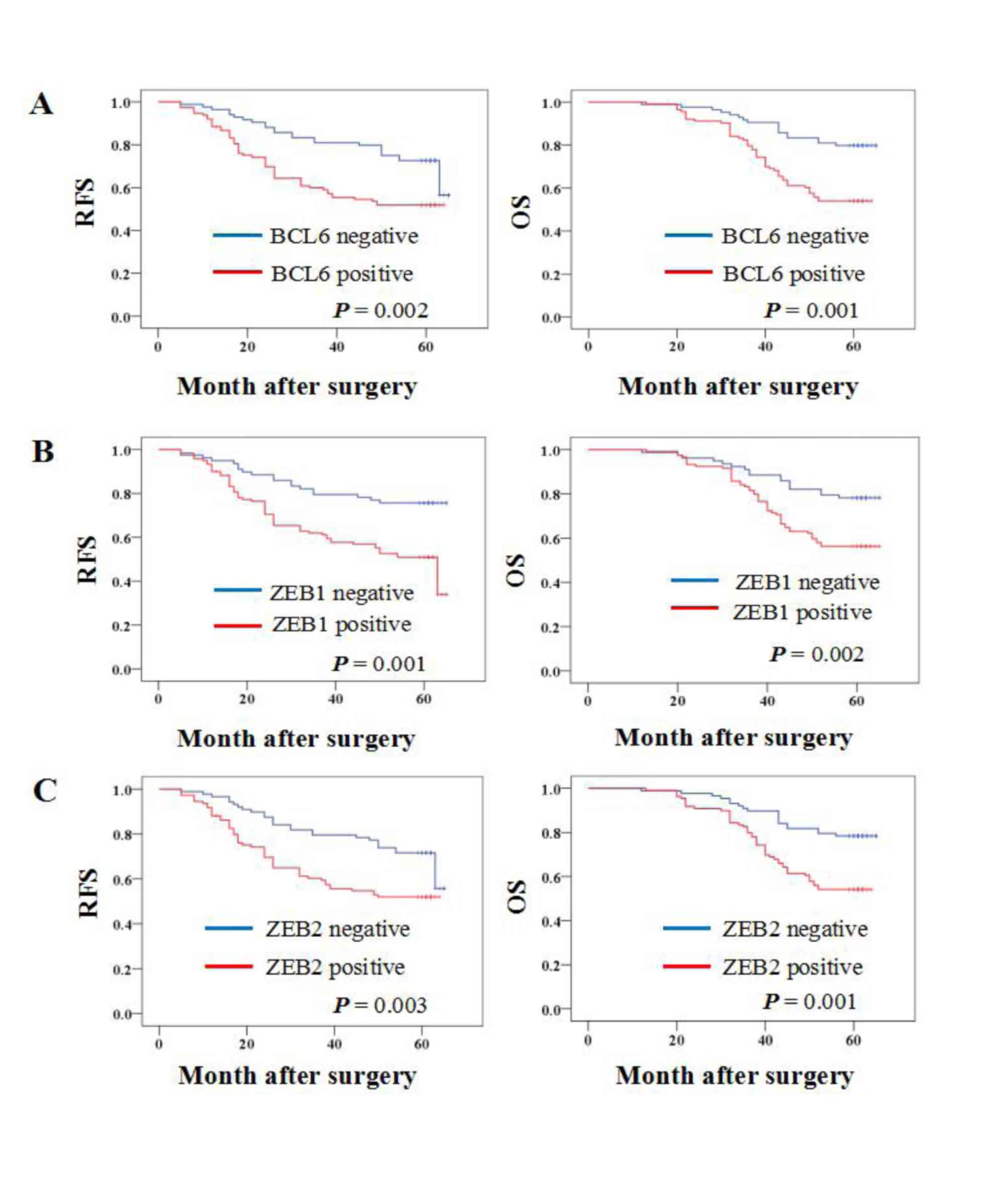
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nola S, Sin S, Bonin F, Lidereau R and
Driouch K: A methodological approach to unravel organ-specific
breast cancer metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
17:135–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Q, Liu X, Yan H, He YH, Ye S, Cheng XW,
Zhu GL, Wu WY, Wang XN, Kong XJ, et al: B-cell lymphoma 6 protein
stimulates oncogenicity of human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
14:4182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yan H, Zhao M, Huang S, Chen P, Wu WY,
Huang J, Wu ZS and Wu Q: Prolactin inhibits BCL6 expression in
breast cancer cells through a microRNA-339-5p-dependent pathway. J
Breast Cancer. 19:26–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Walker SR, Liu S, Xiang M, Nicolais M,
Hatzi K, Giannopoulou E, Elemento O, Cerchietti L, Melnick A and
Frank DA: The transcriptional modulator BCL6 as a molecular target
for breast cancer therapy. Oncogene. 34:1073–1082. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shaffer AL, Yu X, He Y, Boldrick J, Chan
EP and Staudt LM: BCL-6 represses genes that function in lymphocyte
differentiation, inflammation, and cell cycle control. Immunity.
13:199–212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Logarajah S, Hunter P, Kraman M, Steele D,
Lakhani S, Bobrow L, Venkitaraman A and Wagner S: BCL-6 is
expressed in breast cancer and prevents mammary epithelial
differentiation. Oncogene. 22:5572–5578. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier
B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H and Foisner R:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Comijin J, Berx G, Vermassen P,
Verschueren K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D
and van Roy F: The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein
SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell.
7:1267–1278. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu JM, Sun W, Hua F, Xie J, Lin H, Zhou DD
and Hu ZW: BCL6 induces EMT by promoting the ZEB1-mediated
transcription repression of E-cadherin in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 365:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tavassoli FA and Devilee P: World Health
Organization Classification Of Tumors: Pathology And Genetics Of
Tumors Of The Breast And Female Genital Organs. Lyon: IARC Press;
pp. 13–59. 2003
|
|
15
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: TNM
classification of malignant tumours. 6th. New York: Wiley; 2002
|
|
16
|
Yoder BJ, Tso E, Skacel M, Pettay J, Tarr
S, Budd T, Tubbs RR, Adams JC and Hicks DG: The expression of
fascin, an actin-bundling motility protein, correlates with hormone
receptor-negative breast cancer and a more aggressive clinical
course. Clin Cancer Res. 11:186–192. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M,
McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M,
Fitzgibbons P, et al: Recommendations for human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of
Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical
practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 31:3997–4013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pinto AE, André S, Silva G, Vieira S,
Santos AC, Dias S and Soares J: BCL-6 oncoprotein in breast cancer:
Loss of expression in disease progression. Pathobiology.
76:235–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kurahara H, Takao S, Maemura K, Mataki Y,
Kuwahata T, Maeda K, Ding Q, Sakoda M, Iino S, Ishigami S, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal-epithelial
transition via regulation of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2 expression in
pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol. 105:655–661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Basso K and Dalla-Favera R: Roles of BCL6
in normal and transformed germinal center B cells. Immunol Rev.
247:172–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duan S, Cermak L, Pagan JK, Rossi M,
Martinengo C, di Celle PF, Chapuy B, Shipp M, Chiarle R and Pagano
M: FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in
diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Nature. 481:90–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bos R, van Diest PJ, van der Groep P,
Greijer AE, Hermsen MA, Heijnen I, Meijer GA, Baak JP, Pinedo HM,
van der Wall E and Shvarts A: Protein expression of B-cell lymphoma
gene 6 (BCL-6) in invasive breast cancer is associated with cyclin
D1 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha). Oncogene.
22:8948–8951. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xue M, Pang H, Li X, Li H, Pan J and Chen
W: Long non-coding RNA urothelial cancer-associated 1 promotes
bladder cancer cell migration and invasion by way of the
hsa-miR-145-ZEB1/2-FSCN1 pathway. Cancer Sci. 107:18–27. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu DI, Liu L, Ren C, Kong D, Zhang P, Jin
X, Wang T and Zhang G: Epithelial-mesenchymal interconversions and
the regulatory function of the ZEB family during the development
and progression of ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 11:1463–1468.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bates RC and Mercurio AM: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer
progression. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:365–370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xue C, Plieth D, Venkov C, Xu C and
Neilson EG: The gatekeeper effect of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition regulates the frequency of breast cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 63:3386–3394. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lossos IS, Jones CD, Warnke R, Natkunam Y,
Kaizer H, Zehnder JL, Tibshirani R and Levy R: Expression of a
single gene, BCL-6, strongly predicts survival in patients with
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 98:945–951. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jia B, Liu H, Kong Q and Li B:
Overexpression of ZEB1 associated with metastasis and invasion in
patients with gastric carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 366:223–229.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prislei S, Martinelli E, Zannoni GF,
Petrillo M, Filippetti F, Mariani M, Mozzetti S, Raspaglio G,
Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role and prognostic significance of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition factor ZEB2 in ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:18966–18979. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brabletz S, Bajdak K, Meidhof S, Burk U,
Niedermann G, Firat E, Wellner U, Dimmler A, Faller G, Schubert J
and Brabletz T: The ZEB1/miR-200 feedback loop controls Notch
signalling in cancer cells. EMBO J. 30:770–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nishijima N, Seike M, Soeno C, Chiba M,
Miyanaga A, Noro R, Sugano T, Matsumoto M, Kubota K and Gemma A:
MiR-200/ZEB axis regulates sensitivity to nintedanib in non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 48:937–944. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Smith E, Bert AG,
Wright JA, Roslan S, Morris M, Wyatt L, Farshid G, Lim YY, et al:
An autocrine TGF-beta/ZEB/miR-200 signaling network regulates
establishment and maintenance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Mol Biol Cell. 22:1686–1698. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|