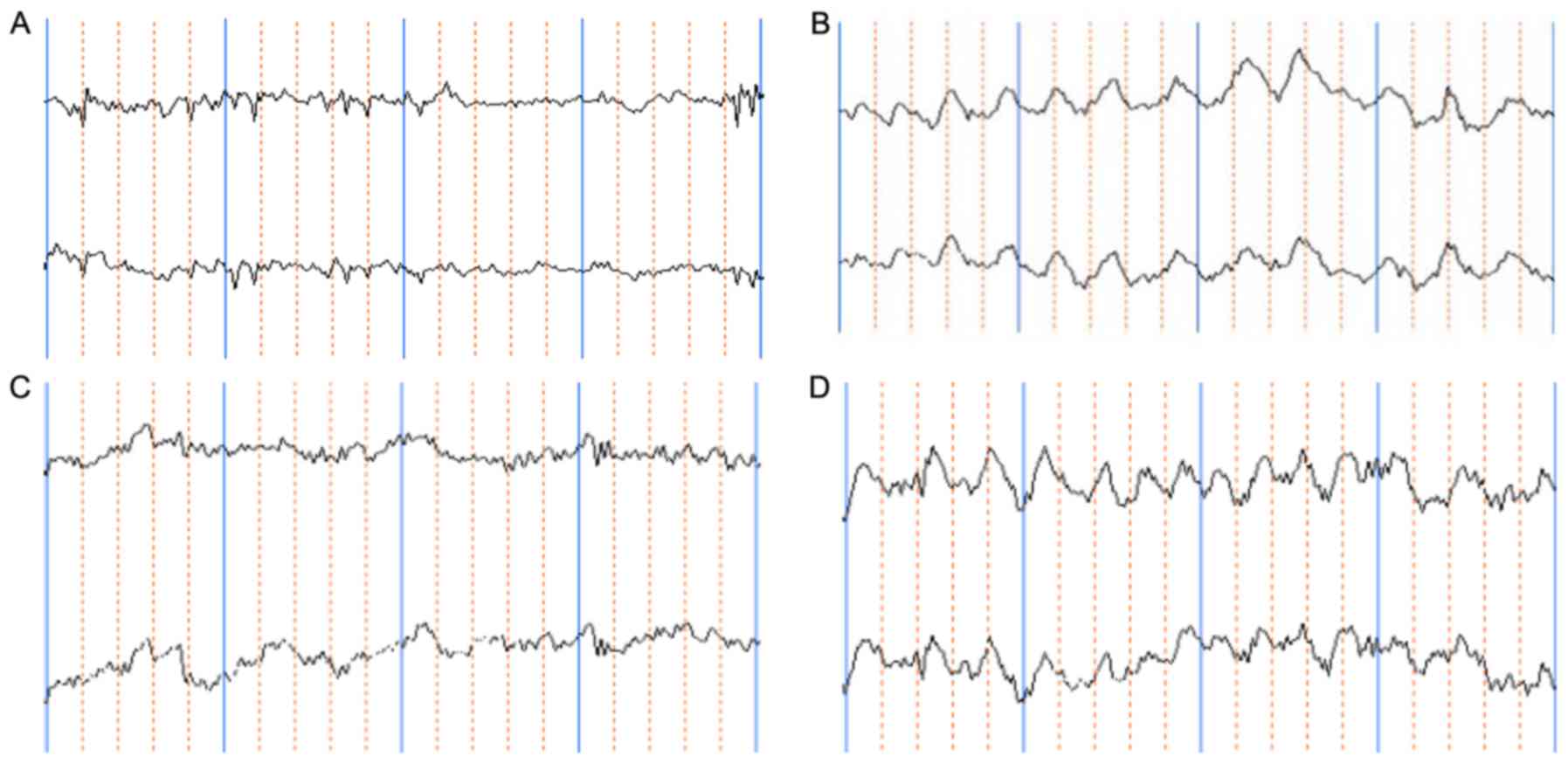
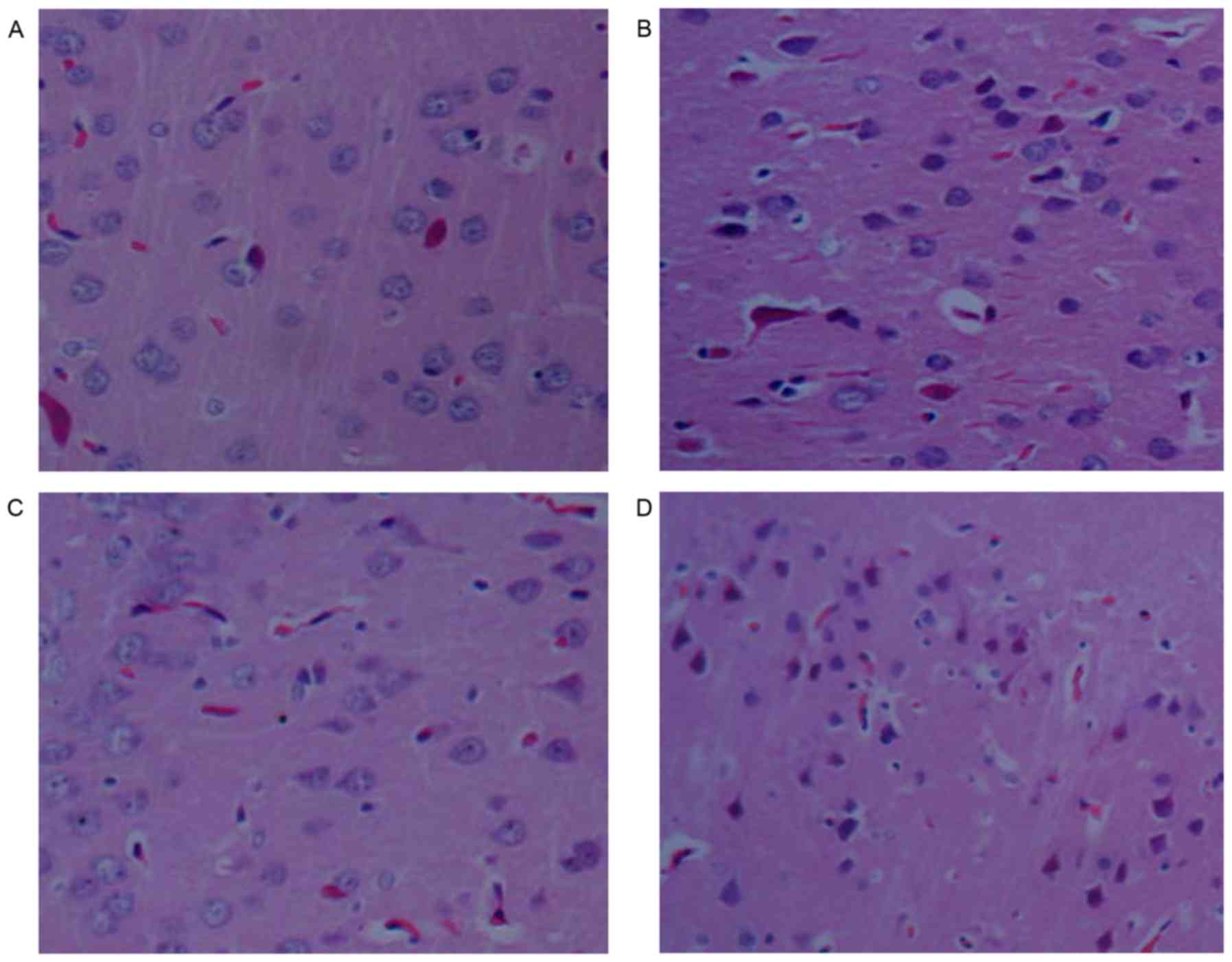
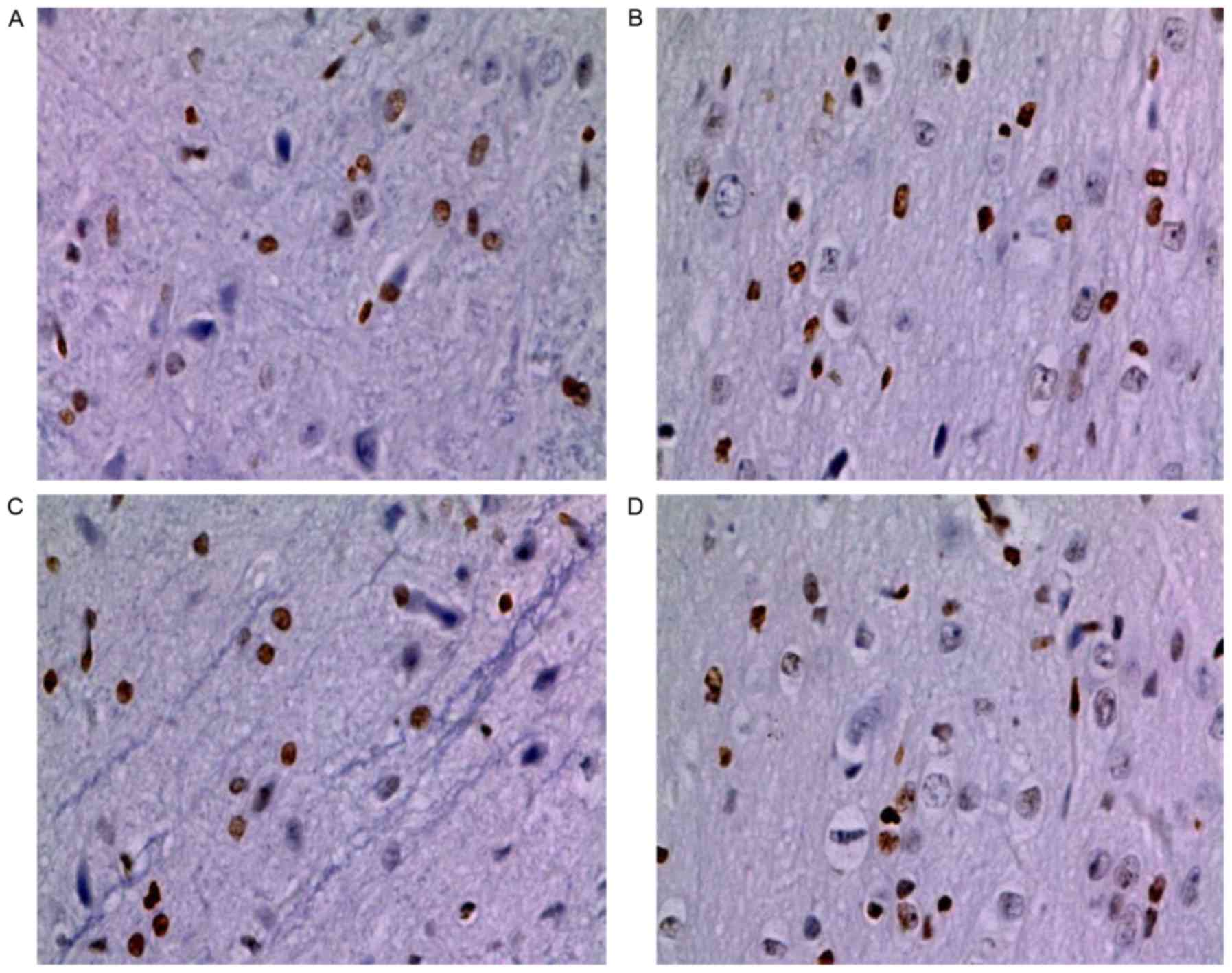
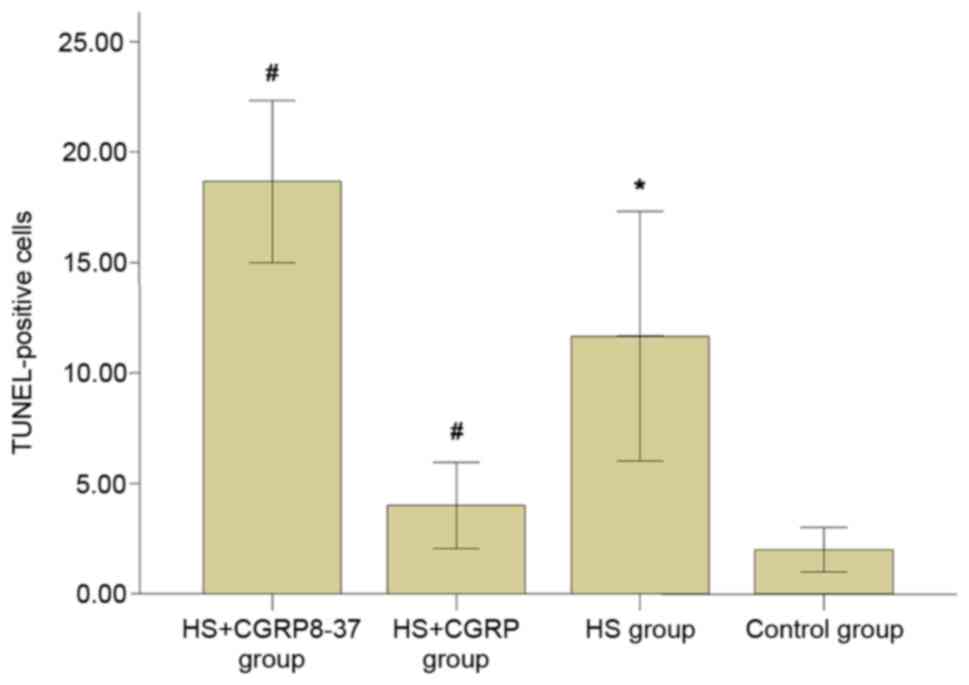
|
1
|
Leon LR: Hypothermia in systemic
inflammation: Role of cytokines. Front Biosci. 9:1877–1888. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brownlow MA, Dart AJ and Jeffcott LB:
Exertional heat illness: A review of the syndrome affecting racing
Thoroughbreds in hot and humid climates. Aust Vet J. 94:240–247.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Székely M, Carletto L and Garami A: The
pathophysiology of heat exposure. Temperature (Austin). 2:4522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang D, Zhang P, Wang Y, Han N, Tang C
and Jiang B: The influence of brain injury or peripheral nerve
injury on calcitonin gene-related peptide concentration variation
and fractures healing process. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil
Biotechnol. 37:85–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song Y, Bi L, Zhang Z, Huang Z, Hou W, Lu
X, Sun P and Han Y: Increased levels of calcitonin gene-related
peptide in serum accelerate fracture healing following traumatic
brain injury. Mol Med Rep. 5:432–438. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Z, Liu Q, Cai H, Xu C, Liu G and Li Z:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide prevents blood-brain barrier injury
and brain edema induced by focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion.
Regul Pept. 171:19–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu D, Chen B, Wang B and Ma D: The changes
in the morphology and distribution of substance P and
calcitonin-gene related peptide nerves in the anterior pituitary of
scalded rats. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 18:176–179. 2002.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Satoh M, Kuraishi Y and Kawamura M:
Effects of intrathecal antibodies to substance P, calcitonin
gene-related peptide and galanin on repeated cold stress-induced
hyperalgesia: Comparison with carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia.
Pain. 49:273–278. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Legat FJ, Jaiani LT, Wolf P, Wang M, Lang
R, Abraham T, Solomon AR, Armstrong CA, Glass JD and Ansel JC: The
role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in cutaneous
immunosuppression induced by repeated subinflammatory ultraviolet
irradiation exposure. Exp Dermatol. 13:242–250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bouchama A: Heatstroke: Facing the threat.
Crit Care Med. 34:1272–1273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leon LR and Helwig BG: Heat stroke: Role
of the systemic inflammatory response. J Appl Physiol (1985).
109:1980–1988. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bouchama A, Roberts G, Al Mohanna F,
El-Sayed R, Lach B, Chollet-Martin S, Ollivier V, Al Baradei R,
Loualich A, Nakeeb S, et al: Inflammatory, hemostatic, and clinical
changes in a baboon experimental model for heatstroke. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 98:697–705. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu ZF, Li BL, Tong HS, Tang YQ, Xu QL,
Guo JQ and Su L: Pathological changes in the lung and brain of mice
during heat stress and cooling treatment. World J Emerg Med.
2:50–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edvinsson L: The Journey to establish CGRP
as a migraine target: A retrospective view. Headache. 55:1249–1255.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schebesch KM, Herbst A, Bele S, Schödel P,
Brawanski A, Stoerr EM, Lohmeier A, Kagerbauer SM, Martin J and
Proescholdt M: Calcitonin-gene related peptide and cerebral
vasospasm. J Clin Neurosci. 20:584–586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kageneck C, Nixdorf-Bergweiler BE,
Messlinger K and Fischer MJ: Release of CGRP from mouse brainstem
slices indicates central inhibitory effect of triptans and
kynurenate. J Headache Pain. 15:72014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tian XH, Wang ZG, Meng H, Wang YH, Feng W,
Wei F, Huang ZC, Lin XN and Ren L: Tat peptide-decorated
gelatin-siloxane nanoparticles for delivery of CGRP transgene in
treatment of cerebral vasospasm. Int J Nanomedicine. 8:865–876.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De winter BY, Bredenoord AJ, Van Nassauw
L, De Man JG, De Schepper HU, Timmermans JP and Pelckmans PA:
Involvement of afferent neurons in the pathogenesis of
endotoxin-induced ileus in mice: Role of CGRP and TRPV1 receptors.
Eur J Pharmacol. 615:177–184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sinha RK: Electro-encephalogram
disturbances in different sleep-wake states following exposure to
high environmental heat. Med Biol Eng Comput. 42:282–287. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smillie SJ and Brain SD: Calcitonin
gene-related peptide (CGRP) and its role in hypertension.
Neuropeptides. 45:93–104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mai TH, Wu J, Diedrich A, Garland EM and
Robertson D: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in autonomic
cardiovascular regulation and vascular structure. J Am Soc
Hypertens. 8:286–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang ZH, Fang XB, Xi GM, Li WC, Ling HY
and Qu P: Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances CREB
phosphorylation and attenuates tau protein phosphorylation in rat
brain during focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Biomed
Pharmacother. 64:430–436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye F, Deng PY, Li D, Luo D, Li NS, Deng S,
Deng HW and Li YJ: Involvement of endothelial cell-derived CGRP in
heat stress-induced protection of endothelial function. Vascul
Pharmacol. 46:238–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kibayashi K, Nakao K and Shojo H:
Hyperthermia combined with ethanol administration induces c-fos
expression in the central amygdaloid nucleus of the mouse brain. A
possible mechanism of heatstroke under the influence of ethanol
intake. Int J Legal Med. 123:371–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ji J, Kline AE, Amoscato A, Samhan-Arias
AK, Sparvero LJ, Tyurin VA, Tyurina YY, Fink B, Manole MD, Puccio
AM, et al: Lipidomics identifies cardiolipin oxidation as a
mitochondrial target for redox therapy of brain injury. Nat
Neurosci. 15:1407–1413. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao RV, Hermel E, Castro-Obregon S, del
Rio G, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM and Bredesen DE: Coupling endoplasmic
reticulum stress to the cell death program. Mechanism of caspase
activation. J Biol Chem. 276:33869–33874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duan L, Lei H, Zhang Y, Wan B, Chang J,
Feng Q and Huang W: Calcitonin gene-related peptide improves
hypoxia-induced inflammation and apoptosis via nitric oxide in H9c2
cardiomyoblast cells. Cardiology. 133:44–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo CC, Huang CS, Ming YC, Chu SM and Chao
HC: Calcitonin gene-related peptide downregulates expression of
inducible nitride oxide synthase and caspase-3 after intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Pediatr Neonatol. 57:474–479.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|