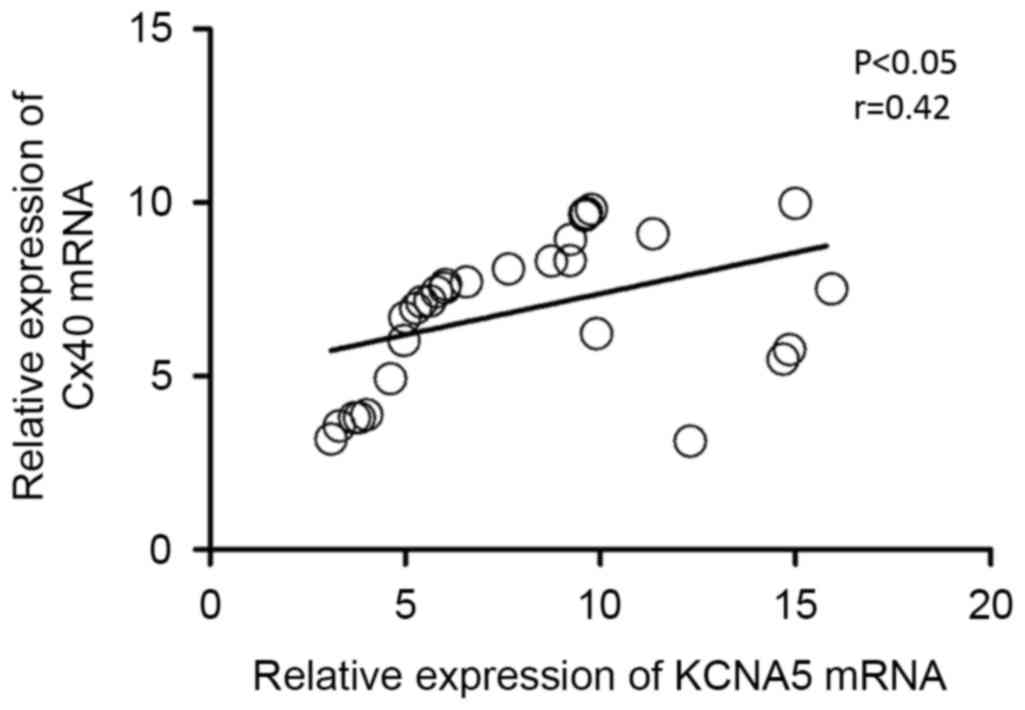
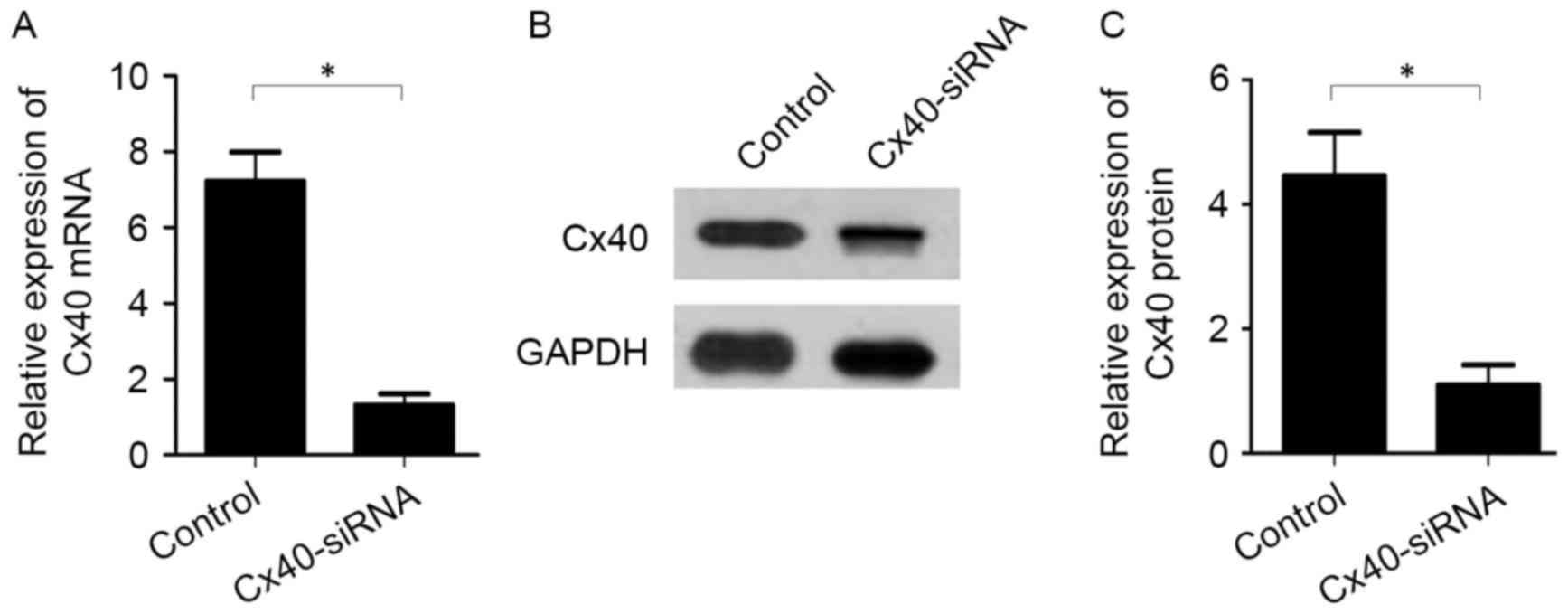
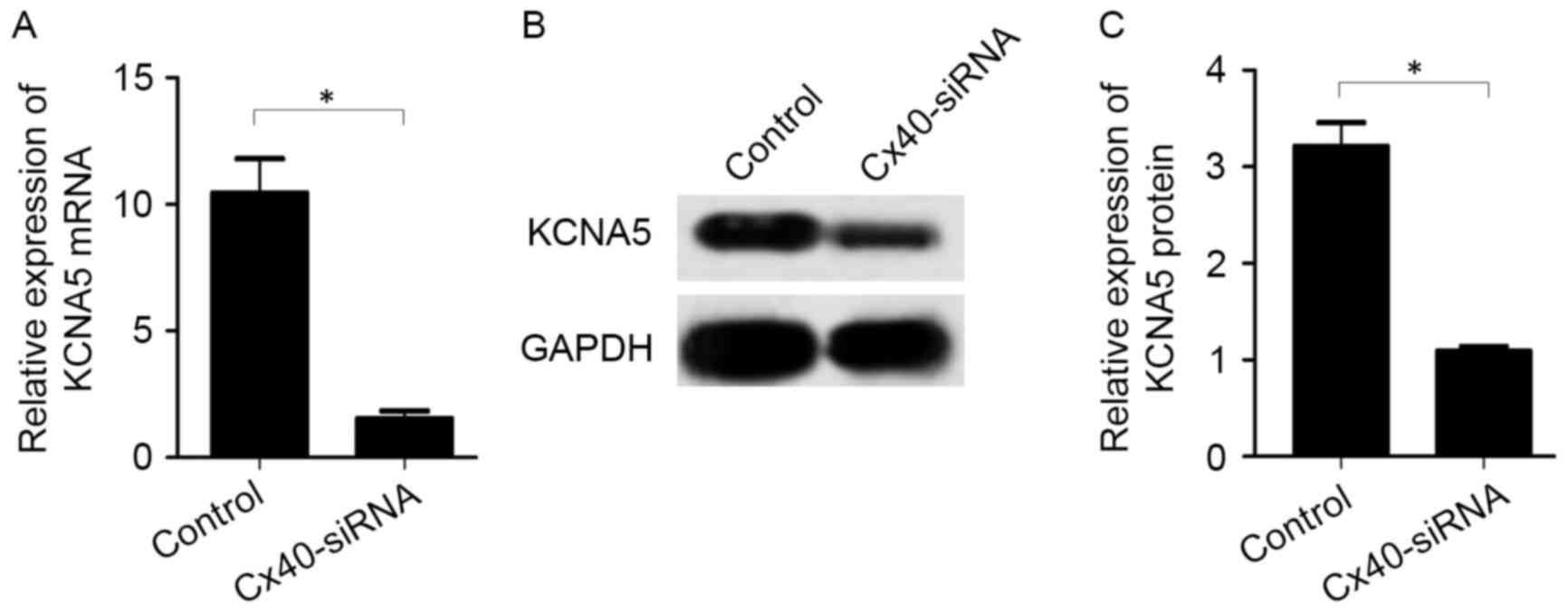
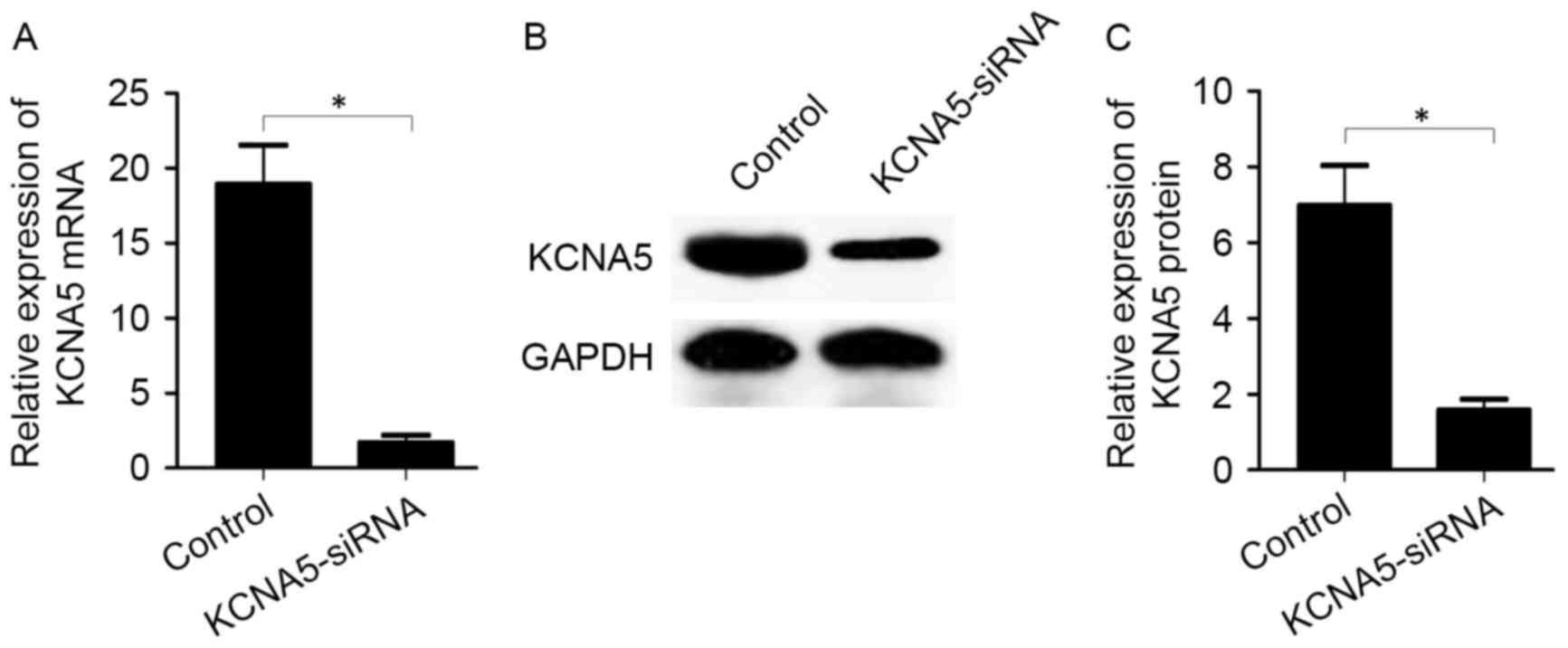
|
1
|
Frustaci A, Chimenti C, Bellocci F,
Morgante E, Russo MA and Maseri A: Histological substrate of atrial
biopsies in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Circulation.
96:1180–1184. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Le Heuzey JY, Breithardt G, Camm J, Crijns
H, Dorian P, Kowey PR, Merioua I, Prystowsky EN, Schwartz PJ,
Torp-Pedersen C and Weintraub W: The RecordAF study: Design,
baseline data, and profile of patients according to chosen
treatment strategy for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol.
105:687–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou Z and Hu D: An epidemiological study
on the prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the Chinese population
of mainland China. J Epidemiol. 18:209–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verheijck EE, van Kempen MJ, Veereschild
M, Lurvink J, Jongsma HJ and Bouman LN: Electrophysiological
features of the mouse sinoatrial node in relation to connexin
distribution. Cardiovasc Res. 52:40–50. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jalife J, Morley GE and Vaidya D:
Connexins and impulse propagation in the mouse heart. J Cardiovasc
Electrophysiol. 10:1649–1663. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Allessie M, Ausma J and Schotten U:
Electrical, contractile and structural remodeling during atrial
fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 54:230–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kumar NM and Gilula NB: The gap junction
communication channel. Cell. 84:381–388. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Goodenough DA and Paul DL: Beyond the gap:
Functions of unpaired connexon channels. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
4:285–294. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schram G, Pourrier M, Melnyk P and Nattel
S: Differential distribution of cardiac ion channel expression as a
basis for regional specialization in electrical function. Circ Res.
90:939–950. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brundel BJ, Van Gelder IC, Henning RH,
Tuinenburg AE, Deelman LE, Tieleman RG, Grandjean JG, van Gilst WH
and Crijns HJ: Gene expression of proteins influencing the calcium
homeostasis in patients with persistent and paroxysmal atrial
fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 42:443–454. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olson TM, Alekseev AE, Liu XK, Park S,
Zingman LV, Bienengraeber M, Sattiraju S, Ballew JD, Jahangir A and
Terzic A: Kv1.5 channelopathy due to KCNA5 loss-of-function
mutation causes human atrial fibrillation. Hum Mol Genet.
15:2185–2191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gollob MH, Jones DL, Krahn AD, Danis L,
Gong XQ, Shao Q, Liu X, Veinot JP, Tang AS, Stewart AF, et al:
Somatic mutations in the connexin 40 gene (GJA5) in atrial
fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 354:2677–2688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xia M, Jin Q, Bendahhou S, He Y, Larroque
MM, Chen Y, Zhou Q, Yang Y, Liu Y, Liu B, et al: A Kir2.1
gain-of-function mutation underlies familial atrial fibrillation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 332:1012–1019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Li J, Lin X, Yang Y, Hong K, Wang
L, Liu J, Li L, Yan D, Liang D, et al: Novel KCNA5 loss-of-function
mutations responsible for atrial fibrillation. J Hum Genet.
54:277–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Christophersen IE, Olesen MS, Liang B,
Andersen MN, Larsen AP, Nielsen JB, Haunsø S, Olesen SP, Tveit A,
Svendsen JH and Schmitt N: Genetic variation in KCNA5: Impact on
the atrial-specific potassium current IKur in patients with lone
atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 34:1517–1525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wickenden AD: K(+) channels as therapeutic
drug targets. Pharmacol Ther. 94:157–182. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wulff H, Castle NA and Pardo LA:
Voltage-gated potassium channels as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:982–1001. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
King TJ and Bertram JS: Connexins as
targets for cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1719:146–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ravens U, Poulet C, Wettwer E and Knaut M:
Atrial selectivity of antiarrhythmic drugs. J Physiol.
591:4087–4097. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Losa D, Chanson M and Crespin S: Connexins
as therapeutic targets in lung disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
15:989–1002. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bronis K, Metaxa S, Koulouris S and
Manolis AS: Vernakalant: Review of a novel atrial selective
antiarrhythmic agent and its place in current treatment of atrial
fibrillation. Hosp Chron. 7:171–181. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Roy D, Pratt CM, Torp-Pedersen C, Wyse DG,
Toft E, Juul-Moller S, Nielsen T, Rasmussen SL, Stiell IG, Coutu B,
et al: Vernakalant hydrochloride for rapid conversion of atrial
fibrillation: A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Circulation. 117:1518–1525. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dries DL, Exner DV, Gersh BJ, Domanski MJ,
Waclawiw MA and Stevenson LW: Atrial fibrillation is associated
with an increased risk for mortality and heart failure progression
in patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic left ventricular
systolic dysfunction: a retrospective analysis of the SOLVD trials.
Studies of left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol.
32:695–703. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van der Velden HM, Ausma J, Rook MB,
Hellemons AJ, van Veen TA, Allessie MA and Jongsma HJ: Gap
junctional remodeling in relation to stabilization of atrial
fibrillation in the goat. Cardiovasc Res. 46:476–486. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ou XH, Li ML, Liu R, Fan XR, Mao L, Fan
XH, Yang Y and Zeng XR: Remodeling of Kv1.5 channel in right atria
from Han Chinese patients with atrial fibrillation. Med Sci Monit.
21:1207–1213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burstein B and Nattel S: Atrial fibrosis:
Mechanisms and clinical relevance in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 51:802–809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Casaclang-Verzosa G, Gersh BJ and Tsang
TS: Structural and functional remodeling of the left atrium:
Clinical and therapeutic implications for atrial fibrillation. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 51:1–11. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang P, Su J and Mende U: Cross talk
between cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts: From multiscale
investigative approaches to mechanisms and functional consequences.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 303:H1385–H1396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Söhl G and Willecke K: Gap junctions and
the connexin protein family. Cardiovasc Res. 62:228–232. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Camelliti P, Borg TK and Kohl P:
Structural and functional characterisation of cardiac fibroblasts.
Cardiovasc Res. 65:40–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carnes CA, Chung MK, Nakayama T, Nakayama
H, Baliga RS, Piao S, Kanderian A, Pavia S, Hamlin RL, McCarthy PM,
et al: Ascorbate attenuates atrial pacing-induced peroxynitrite
formation and electrical remodeling and decreases the incidence of
postoperative atrial fibrillation. Circ Res. 89:e32–e38. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pongs O: Voltage-gated potassium channels:
From hyperexcitability to excitement. FEBS Lett. 452:31–35. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Everett TH, Li H, Mangrum JM, McRury ID,
Mitchell MA, Redick JA and Haines DE: Electrical, morphological,
and ultrastructural remodeling and reverse remodeling in a canine
model of chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 102:1454–1460.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB,
Silbershatz H, Kannel WB and Levy D: Impact of atrial fibrillation
on the risk of death the Framingham heart study. Circulation.
98:946–952. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Allessie MA, Boyden PA, Camm AJ, Kléber
AG, Lab MJ, Legato MJ, Rosen MR, Schwartz PJ, Spooner PM, Van
Wagoner DR and Waldo AL: Pathophysiology and prevention of atrial
fibrillation. Circulation. 103:769–777. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morillo CA, Klein GJ, Jones DL and
Guiraudon CM: Chronic rapid atrial pacing. Structural, functional,
and electrophysiological characteristics of a new model of
sustained atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 91:1588–1595. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|