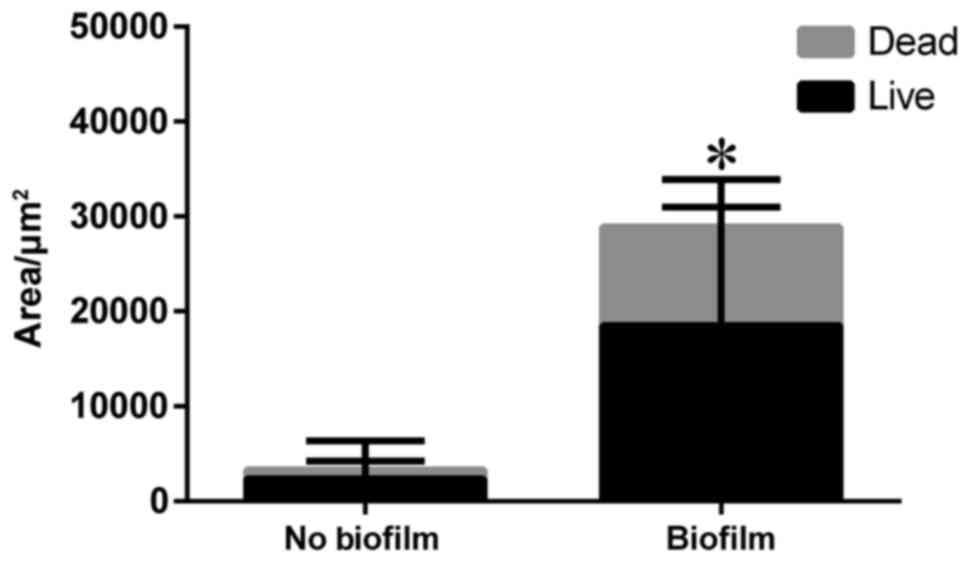
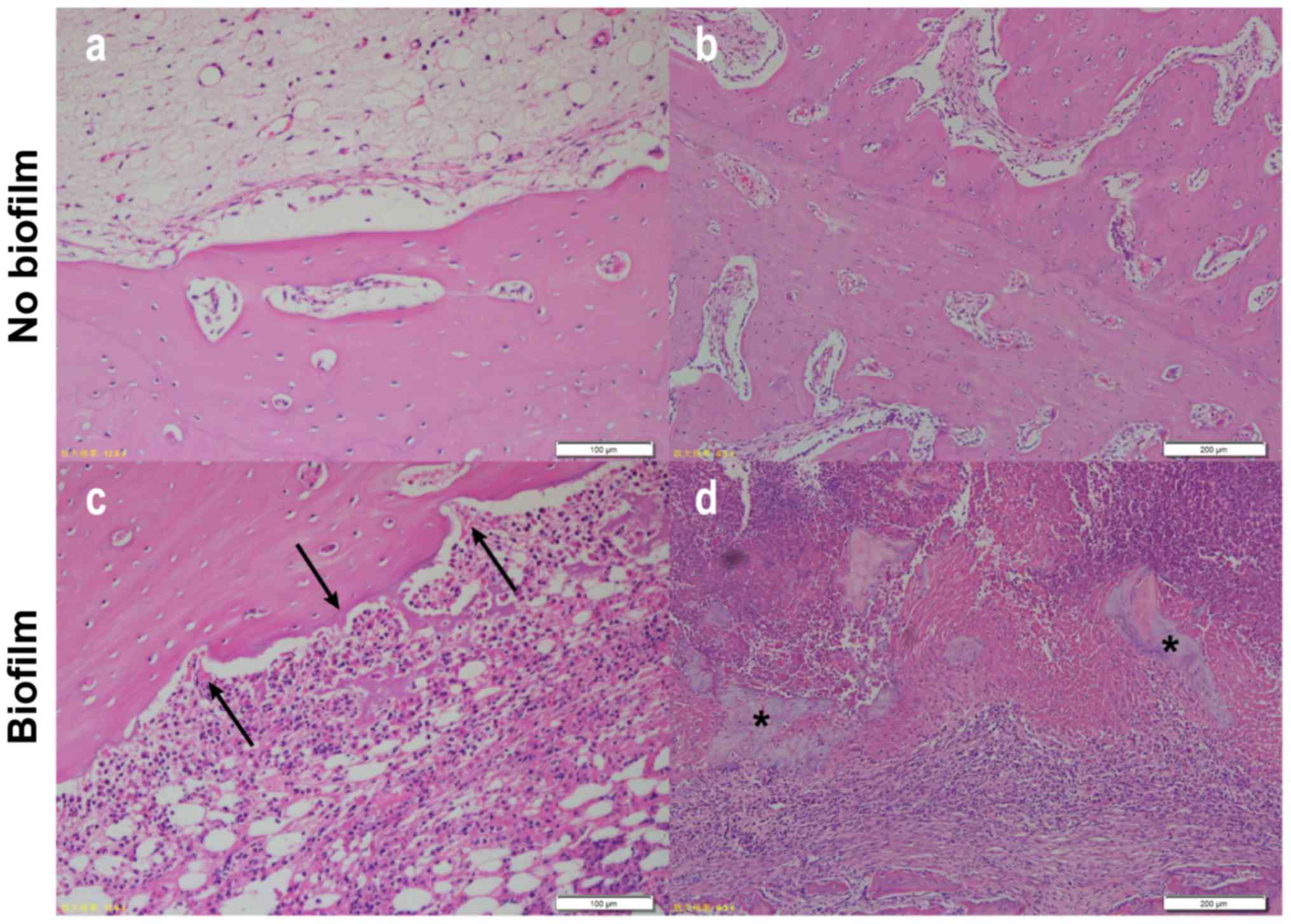
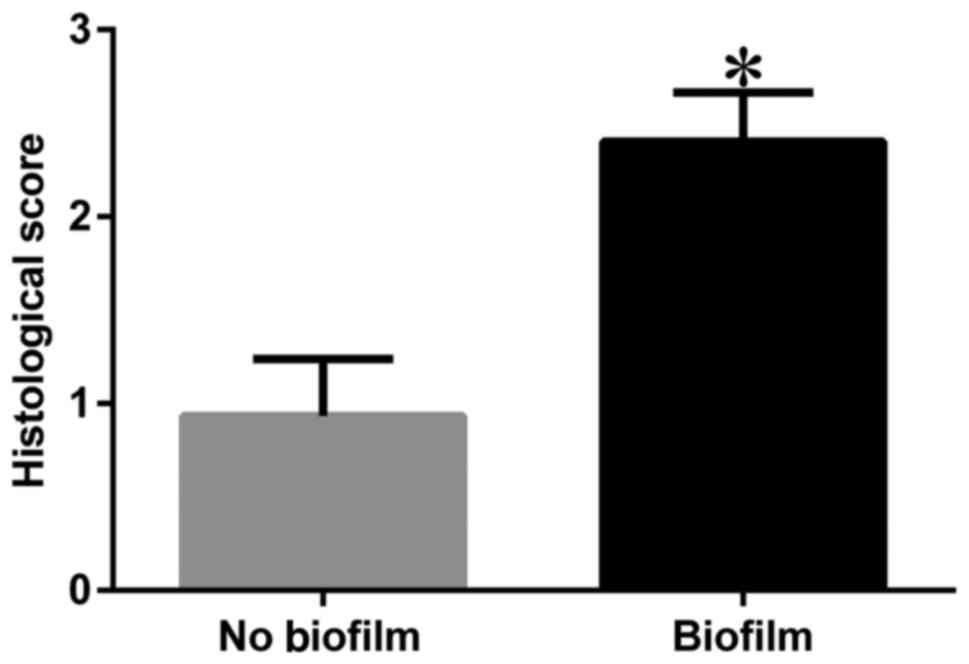
|
1
|
Arciola CR, Campoccia D, Ehrlich GD and
Montanaro L: Biofilm-based implant infections in orthopaedics. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 830:29–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Metsemakers WJ, Kuehl R, Moriarty TF,
Richards RG, Verhofstad MH, Borens O, Kates S and Morgenstern M:
Infection after fracture fixation: Current surgical and
microbiological concepts. Injury. Sep 11–2016.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Worlock P, Slack R, Harvey L and Mawhinney
R: An experimental model of post-traumatic osteomyelitis in
rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 69:235–244. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reizner W, Hunter JG, O'Malley NT,
Southgate RD, Schwarz EM and Kates SL: A systematic review of
animal models for Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Eur Cell
Mater. 27:196–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Donné J and Dewilde S: The challenging
world of biofilm physiology. Adv Microb Physiol. 67:235–292. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Costerton JW: Cystic fibrosis pathogenesis
and the role of biofilms in persistent infection. Trends Microbiol.
9:50–52. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Montanaro L, Speziale P, Campoccia D,
Ravaioli S, Cangini I, Pietrocola G, Giannini S and Arciola CR:
Scenery of Staphylococcus implant infections in orthopedics. Future
Microbiol. 6:1329–1349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trampuz A and Zimmerli W: Diagnosis and
treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices.
Injury. 37 Suppl 2:S59–S66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Williams DL and Costerton JW: Using
biofilms as initial inocula in animal models of biofilm-related
infections. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 100:1163–1169.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Williams DL, Haymond BS, Woodbury KL, Beck
JP, Moore DE, Epperson RT and Bloebaum RD: Experimental model of
biofilm implant-related osteomyelitis to test combination
biomaterials using biofilms as initial inocula. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 100:1888–1900. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Trampuz A, Piper KE, Jacobson MJ, Hanssen
AD, Unni KK, Osmon DR, Mandrekar JN, Cockerill FR, Steckelberg JM,
Greenleaf JF and Patel R: Sonication of removed hip and knee
prostheses for diagnosis of infection. N Engl J Med. 357:654–663.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Monsen T, Lövgren E, Widerström M and
Wallinder L: In vitro effect of ultrasound on bacteria and
suggested protocol for sonication and diagnosis of prosthetic
infections. J Clin Microbiol. 47:2496–2501. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rochford ET, Sabaté Brescó M, Zeiter S,
Kluge K, Poulsson A, Ziegler M, Richards RG, O'Mahony L and
Moriarty TF: Monitoring immune responses in a mouse model of
fracture fixation with and without Staphylococcus aureus
osteomyelitis. Bone. 83:82–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Glass GE, Chan JK, Freidin A, Feldmann M,
Horwood NJ and Nanchahal J: TNF-alpha promotes fracture repair by
augmenting the recruitment and differentiation of muscle-derived
stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1585–1590. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kishor C, Mishra RR, Saraf SK, Kumar M,
Srivastav AK and Nath G: Phage therapy of staphylococcal chronic
osteomyelitis in experimental animal model. Indian J Med Res.
143:87–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Odekerken JC, Arts JJ, Surtel DA,
Walenkamp GH and Welting TJ: A rabbit osteomyelitis model for the
longitudinal assessment of early post-operative implant infections.
J Orthop Surg Res. 8:382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moriarty TF, Campoccia D, Nees SK, Boure
LP and Richards RG: In vivo evaluation of the effect of
intramedullary nail microtopography on the development of local
infection in rabbits. Int J Artif Organs. 33:667–675.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Norden CW: Experimental osteomyelitis. I.
A description of the model. J Infect Dis. 122:410–418. 1970.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shiels SM, Bedigrew KM and Wenke JC:
Development of a hematogenous implant-related infection in a rat
model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 16:2552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arens S, Kraft C, Schlegel U, Printzen G,
Perren SM and Hansis M: Susceptibility to local infection in
biological internal fixation. Experimental study of open vs
minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in rabbits. Arch Orthop
Trauma Surg. 119:82–85. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alt V, Lips KS, Henkenbehrens C, Muhrer D,
Cavalcanti Oliveira MC, Sommer U, Thormann U, Szalay G, Heiss C, et
al: A new animal model for implant-related infected non-unions
after intramedullary fixation of the tibia in rats with fluorescent
in situ hybridization of bacteria in bone infection. Bone.
48:1146–1153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Svensson S, Trobos M, Hoffman M, Norlindh
B, Petronis S, Lausmaa J, Suska F and Thomsen P: A novel soft
tissue model for biomaterial-associated infection and
inflammation-Bacteriological, morphological and molecular
observations. Biomaterials. 41:106–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
dos Reis JA Jr, de Carvalho FB, Trindade
RF, de Assis PN, de Almeida PF and Pinheiro AL: A new preclinical
approach for treating chronic osteomyelitis induced by
Staphylococcus aureus: In vitro and in vivo study on photodynamic
antimicrobial therapy (PAmT). Laser Med Sci. 29:789–795. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gnanadhas DP, Elango M, Janardhanraj S,
Srinandan CS, Datey A, Strugnell RA, Gopalan J and Chakravortty D:
Successful treatment of biofilm infections using shock waves
combined with antibiotic therapy. Sci Rep. 5:174402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wimpenny J, Manz W and Szewzyk U:
Heterogeneity in biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 24:661–671. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Christensen GD, Simpson WA, Younger JJ,
Baddour LM, Barrett FF, Melton DM and Beachey EH: Adherence of
coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates:
A quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical
devices. J Clin Microbiol. 22:996–1006. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vassena C, Fenu S, Giuliani F, Fantetti L,
Roncucci G, Simonutti G, Romanò CL, De Francesco R and Drago L:
Photodynamic antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of RLP068/Cl
against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa forming
biofilms on prosthetic material. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 44:47–55.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Drago L, Agrappi S, Bortolin M, Toscano M,
Romanò C and De Vecchi E: How to study biofilms after microbial
colonization of materials used in orthopaedic implants. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:2932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|