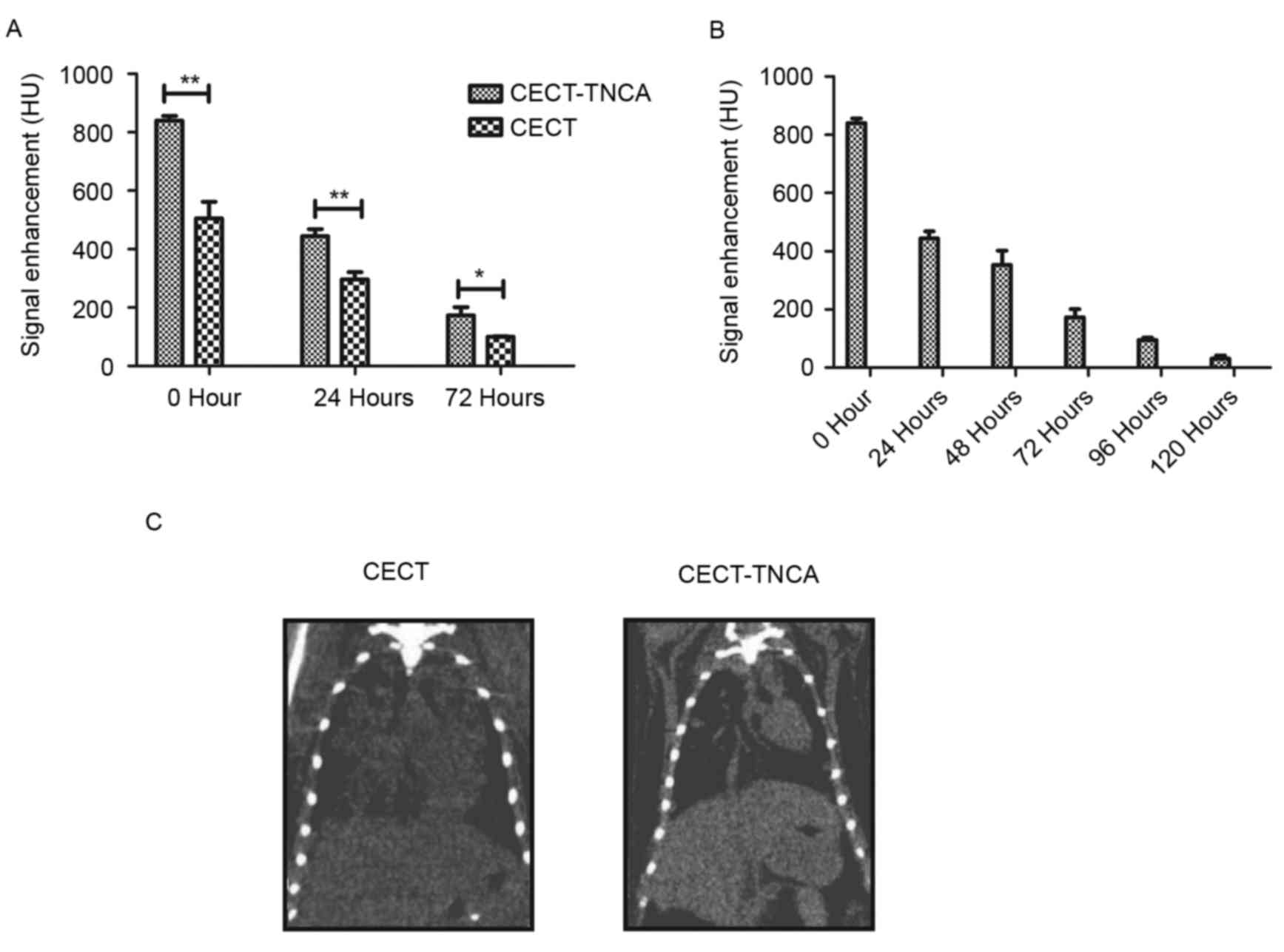
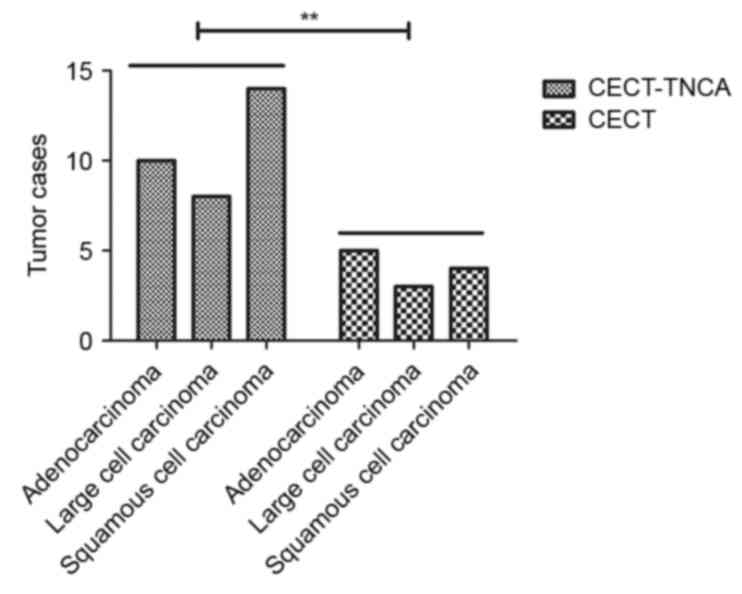
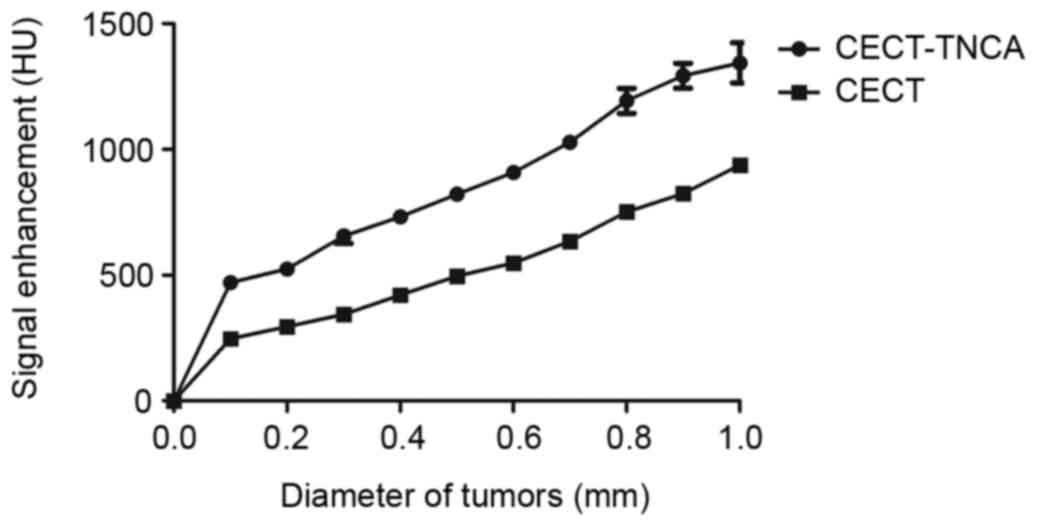
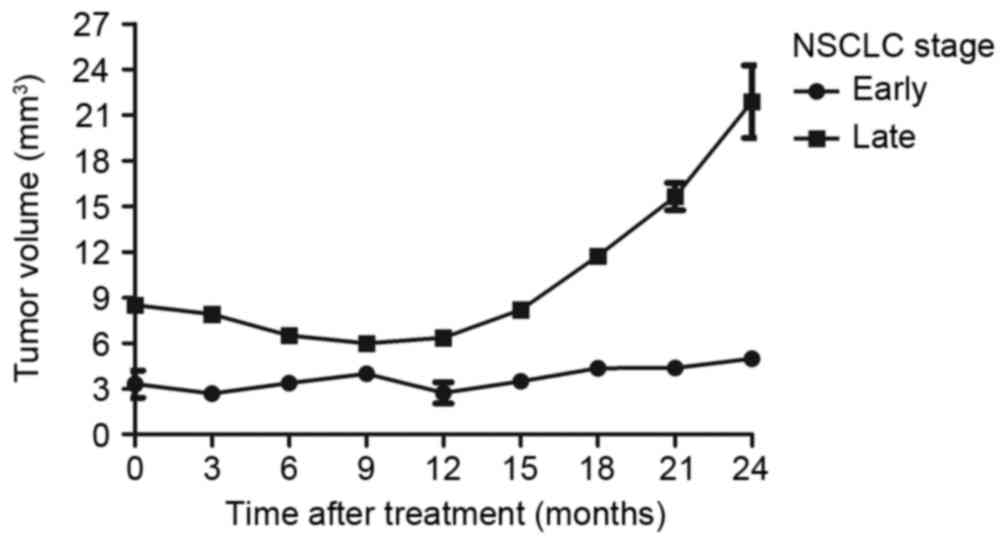
|
1
|
van der Wekken AJ, Saber A, Hiltermann TJ,
Kok K, van den Berg A and Groen HJ: Resistance mechanisms after
tyrosine kinase inhibitors afatinib and crizotinib in non-small
cell lung cancer, a review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 100:107–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Joseph SS, Yentz SE, Mikkilineni S, Nelson
C and Kalemkerian GP: Eyelid metastasis in non-small cell lung
cancer: Diagnosis and management. Am J Med. 129:e169–e172. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeCotiis C, Hu Y, Greenberg AK, Huie M,
Tsay JC, Pass H, Goldberg JD and Rom WN: Inflammatory cytokines and
non-small cell lung cancer in a CT-scan screening cohort:
Background review of the literature. Cancer Biomark. 16:219–233.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kepka L and Socha J: PET-CT use and the
occurrence of elective nodal failure in involved field radiotherapy
for non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Radiother
Oncol. 115:151–156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morinaga R, Okamoto I, Furuta K, Kawano Y,
Sekijima M, Dote K, Satou T, Nishio K, Fukuoka M and Nakagawa K:
Sequential occurrence of non-small cell and small cell lung cancer
with the same EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer. 58:411–413. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Khreish F, Hellwig D, Mathews J, Bücker A,
Kirsch CM and Grgic A: Simultaneous occurrence of typical carcinoid
and non-small-cell lung cancer in the same lung lobe: Value of
nuclear medicine. Clin Nucl Med. 36:481–483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Targowski T, Janda P, Owczarek W, Raczka
A, Jahnz-Rózyk K and Plusa T: Evaluation of occurrence frequency of
circulating p53 protein in serum of patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary diseases and non-small cell lung cancer. Pol
Merkur Lekarski. 28:265–267. 2010.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie FJ, Lu HY, Zheng QQ, Qin J, Gao Y,
Zhang YP, Hu X and Mao WM: The clinical pathological
characteristics and prognosis of FGFR1 gene amplification in
non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Onco Targets and Ther.
9:171–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Moro-Sibilot D, Smit E, de Castro Carpeno
J, Lesniewski-Kmak K, Aerts JG, Villatoro R, Kraaij K, Nacerddine
K, Dyachkova Y, Smith KT, et al: Non-small cell lung cancer
patients with brain metastases treated with first-line
platinum-doublet chemotherapy: Analysis from the European FRAME
study. Lung Cancer. 90:427–432. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lim SH, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K and
Ahn MJ: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small cell lung
cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 16:397–406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ulivi P, Mercatali L, Casoni GL, Scarpi E,
Bucchi L, Silvestrini R, Sanna S, Monteverde M, Amadori D, Poletti
V and Zoli W: Multiple marker detection in peripheral blood for
NSCLC diagnosis. PloS One. 8:e574012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mroczko B, Szmitkowski M and Czygier M:
Granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in diagnosis and
monitoring of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Pol Arch Med
Wewn. 103:163–168. 2000.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Muller B, Bovet M, Yin Y, Stichel D, Malz
M, González-Vallinas M, Middleton A, Ehemann V, Schmitt J, Muley T,
et al: Concomitant expression of far upstream element (FUSE)
binding protein (FBP) interacting repressor (FIR) and its splice
variants induce migration and invasion of non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) cells. J Pathol. 237:390–401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Q, Yue J, Zhang C, Gu X, Chen H and
Xu L: Inactivation of M2 AChR/NF-κB signaling axis reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and suppresses migration
and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Oncotarget.
6:29335–29346. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim DS, Park KM, Won YS, Kim JY, Lee JK,
Kim JG, Oh ST, Jung SS and Kang WK: Occurrence and prognosis of
symptomatic venous thromboembolism in colorectal cancer surgery
patients. Vasc Specialist Int. 30:49–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thunnissen E, Kerr KM, Herth FJ,
Lantuejoul S, Papotti M, Rintoul RC, Rossi G, Skov BG, Weynand B,
Bubendorf L, et al: The challenge of NSCLC diagnosis and predictive
analysis on small samples. Practical approach of a working group.
Lung Cancer. 76:1–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Geng J, Sun J, Lin Q, Gu J, Zhao Y, Zhang
H, Feng X, He Y, Wang W, Zhou X and Yu J: Methylation status of
NEUROG2 and NID2 improves the diagnosis of stage I NSCLC. Oncol
Lett. 3:901–906. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peters S, Adjei AA, Gridelli C, Reck M,
Kerr K and Felip E: ESMO Guidelines Working Group: Metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical practice
guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 23
Suppl 7:vii56–vii64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jafri SH, Shi R and Mills G: Advance lung
cancer inflammation index (ALI) at diagnosis is a prognostic marker
in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A
retrospective review. BMC Cancer. 13:1582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vilmar AC, Santoni-Rugiu E and Sørensen
JB: ERCC1 and histopathology in advanced NSCLC patients randomized
in a large multicenter phase III trial. Ann Oncol. 21:1817–1824.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
National Lung Screening Trial Research
Team, . Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD,
Fagerstrom RM, Gareen IF, Gatsonis C, Marcus PM and Sicks JD:
Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic
screening. N Engl J Med. 365:395–409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saldias PF, Díaz PJ, Rain MC, Illanes CP,
Díaz TR and Díaz PO: Early detection of lung cancer using computed
tomography among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Rev Med Chil. 144:202–210. 2016.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rubin GD: Lung nodule and cancer detection
in computed tomography screening. J Thorac Imaging. 30:130–138.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seigneurin A, Field JK, Gachet A and Duffy
SW: A systematic review of the characteristics associated with
recall rates, detection rates and positive predictive values of
computed tomography screening for lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
25:781–791. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sudarski S, Henzler T and Schoenberg SO:
Post-therapeutic positron emission tomography/computed tomography
for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer recurrence.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2:295–303. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hagberg GE, Mamedov I, Power A, Beyerlein
M, Merkle H, Kiselev VG, Dhingra K, Kubìček V, Angelovski G and
Logothetis NK: Diffusion properties of conventional and
calcium-sensitive MRI contrast agents in the rat cerebral cortex.
Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 9:71–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Turetschek K, Preda A, Novikov V, Brasch
RC, Weinmann HJ, Wunderbaldinger P and Roberts TP: Tumor
microvascular changes in antiangiogenic treatment: Assessment by
magnetic resonance contrast media of different molecular weights. J
Magn Reson Imaging. 20:138–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Samei E, Saunders RS, Badea CT, Ghaghada
KB, Hedlund LW, Qi Y, Yuan H, Bentley RC and Mukundan S Jr:
Micro-CT imaging of breast tumors in rodents using a liposomal,
nanoparticle contrast agent. Int J Nanomedicine. 4:277–282. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Palekar RU, Jallouk AP, Lanza GM, Pan H
and Wickline SA: Molecular imaging of atherosclerosis with
nanoparticle-based fluorinated MRI contrast agents. Nanomedicine
(Lond). 10:1817–1832. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oghabian MA and Farahbakhsh NM: Potential
use of nanoparticle based contrast agents in MRI: A molecular
imaging perspective. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 6:203–213. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho EC, Glaus C, Chen J, Welch MJ and Xia
Y: Inorganic nanoparticle-based contrast agents for molecular
imaging. Trends Mol Med. 16:561–573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakamoto Y, Ishimori T, Sano K, Temma T,
Ueda M, Saji H and Togashi K: Clinical efficacy of dual-phase
scanning using (68)Ga-DOTATOC-PET/CT in the detection of
neuroendocrine tumours. Clin Radiol. 71:1069.e1–e5. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen CL, Hu GY, Mei Q, Qiu H, Long GX and
Hu GQ: Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted ultra-small
superparamagnetic iron oxide particles for magnetic resonance
molecular imaging of lung cancer cells in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl).
125:2322–2328. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yasugi M, Takigawa N, Ochi N, Ohashi K,
Harada D, Ninomiya T, Murakami T, Honda Y, Ichihara E, Tanimoto M
and Kiura K: Everolimus prolonged survival in transgenic mice with
EGFR-driven lung tumors. Exp Cell Res. 326:201–209. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fenton-Ambrose L and Kazerooni EA:
Preventative care: Lung-cancer screens now worth the cost. Nature.
514:352014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kulkarni S, Vella ET, Coakley N, Cheng S,
Gregg R, Ung YC and Ellis PM: The use of systemic treatment in the
maintenance of patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A
systematic review. J Thorac Oncol. 11:989–1002. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yoshiba S, Jansen M, Matsushima N, Chen S
and Mendell J: Population pharmacokinetic analysis of patritumab, a
HER3 inhibitor, in subjects with advanced non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) or solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
77:987–996. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Weller A, O'Brien ME, Ahmed M, Popat S,
Bhosle J, McDonald F, Yap TA, Du Y, Vlahos I and deSouza NM:
Mechanism and non-mechanism based imaging biomarkers for assessing
biological response to treatment in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur
J Cancer. 59:65–78. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim SH, Cho BC, Choi HJ, Chung KY, Kim DJ,
Park MS, Kim SK, Chang J, Shin SJ, Sohn JH and Kim JH: The number
of residual metastatic lymph nodes following neoadjuvant
chemotherapy predicts survival in patients with stage III NSCLC.
Lung Cancer. 60:393–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Satouchi M, Negoro S, Funada Y, Urata Y,
Shimada T, Yoshimura S, Kotani Y, Sakuma T, Watanabe H, Adachi S,
et al: Predictive factors associated with prolonged survival in
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated
with gefitinib. Br J Cancer. 96:1191–1196. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Soldan K, Pooley FD, Hansen J, Andersen A,
Chang-Claude J, Ferro G, Ohgaki H, Skov BG, Cherrie JW, Saracci R
and Boffetta P: Lung fibre burden in lung cancer cases employed in
the rock and slag wool industry. Ann Occup Hyg. 50:241–248.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garcia Duenas OF, Villanueva Kerckoff H,
Olvera Rico H and Plascencia Lira J: Benign peritoneal cystic
mesothelioma as differential diagnose of an ovarian dependant
tumor. Case report and review of the literature. Ginecol Obstet
Mex. 75:111–114. 2007.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Garg PK, Deo SV, Kumar R, Shukla NK,
Thulkar S, Gogia A, Sharma DN and Mathur SR: Staging PET-CT
scanning provides superior detection of lymph nodes and distant
metastases than traditional imaging in locally advanced breast
cancer. World J Surg. 40:2036–2042. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nogami Y, Banno K, Irie H, Iida M, Masugi
Y, Murakami K and Aoki D: Efficacy of 18-FDG PET-CT dual-phase
scanning for detection of lymph node metastasis in gynecological
cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:2247–2253. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Davison CA, Chapman SE, Sasser TA, Wathen
C, Diener J, Schafer ZT and Leevy WM: Multimodal optical, X-ray CT
and SPECT imaging of a mouse model of breast cancer lung
metastasis. Curr Mol Med. 13:368–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Genestreti G, Burgio MA, Matteucci F,
Piciucchi S, Scarpi E, Monti M, Bucchi L, Parisi E, Crociani L,
Gurioli C, et al: Endobronchial/Endoesophageal Ultrasound
(EBUS/EUS) guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) and 18F-FDG PET/CT
scanning in restaging of locally advanced non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) Treated with Chemo-radiotherapy: A
Mono-institutional pilot experience. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
14:721–727. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Manowitz A, Sedlar M, Griffon M, Miller A,
Miller J and Markowitz S: Use of BMI guidelines and individual dose
tracking to minimize radiation exposure from low-dose helical chest
CT scanning in a lung cancer screening program. Acad Radiol.
19:84–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rini BI and Atkins MB: Resistance to
targeted therapy in renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol.
10:992–1000. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Eichelberg C, Junker K, Ljungberg B and
Moch H: Diagnostic and prognostic molecular markers for renal cell
carcinoma: A critical appraisal of the current state of research
and clinical applicability. Eur Urol. 55:851–863. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hutson TE: Targeted therapies for the
treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Clinical evidence.
Oncologist. 16 Suppl 2:S14–S22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Nishio M, Horai T, Horiike A, Nokihara H,
Yamamoto N, Takahashi T, Murakami H, Yamamoto N, Koizumi F, Nishio
K, et al: Phase 1 study of lenvatinib combined with carboplatin and
paclitaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J
Cancer. 109:538–544. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Achenbach S, Paul JF, Laurent F, Becker
HC, Rengo M, Caudron J, Leschka S, Vignaux O, Knobloch G, Benea G,
et al: Erratum to: Comparative assessment of image quality for
coronary CT angiography with iobitridol and two contrast agents
with higher iodine concentrations: Iopromide and iomeprol. A
multicentre randomized double-blind trial. Eur Radiol. 27:8312017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mannheim JG, Schlichthaerle T, Kuebler L,
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kohlhofer U, Kneilling M and Pichler BJ:
Comparison of small animal CT contrast agents. Contrast Media Mol
Imaging. 11:272–284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Honoris L, Zhong Y, Chu E, Rosenthal D, Li
D, Lam F and Budoff MJ: Comparison of contrast enhancement, image
quality and tolerability in Coronary CT angiography using 4
contrast agents: A prospective randomized trial. Int J Cardiol.
186:126–128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|