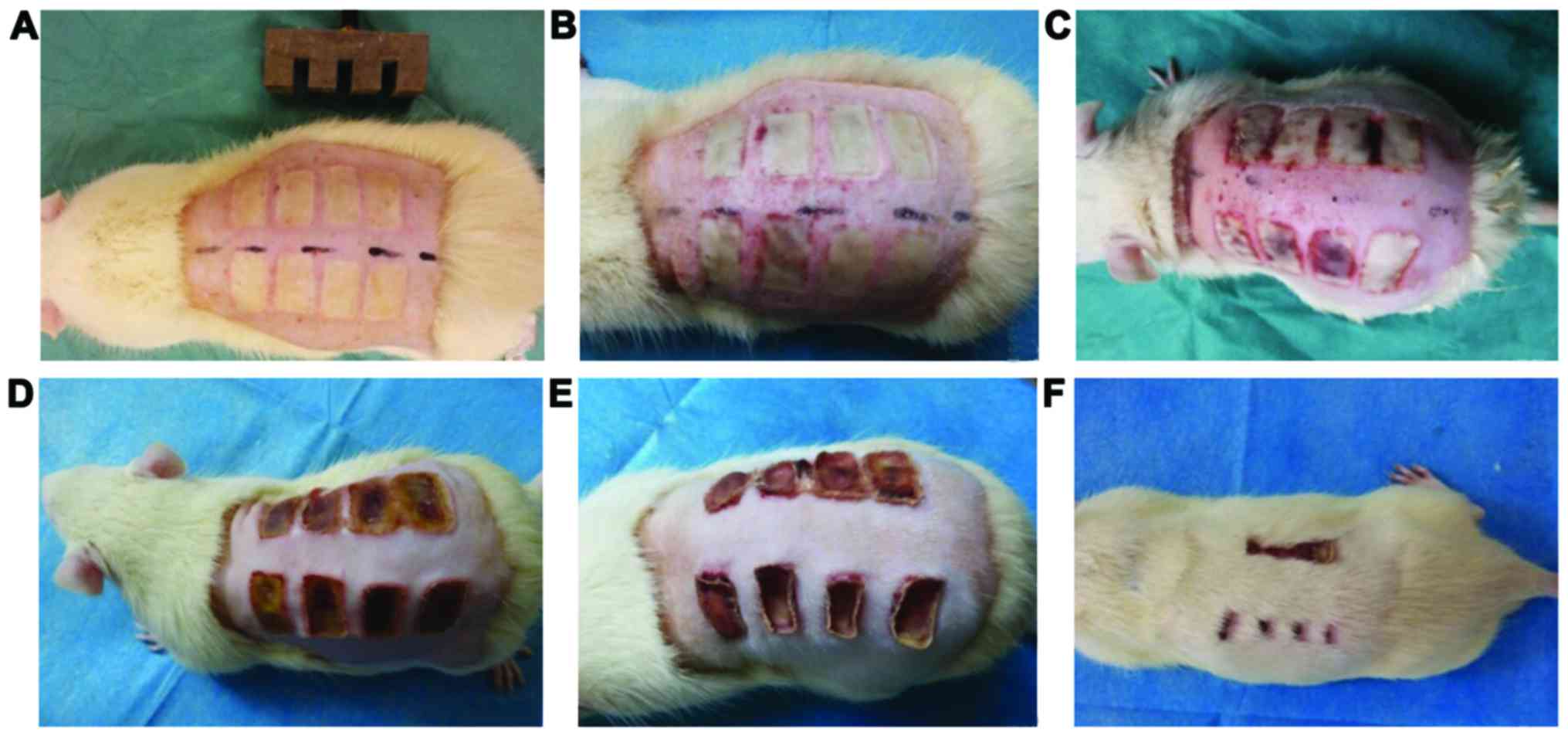
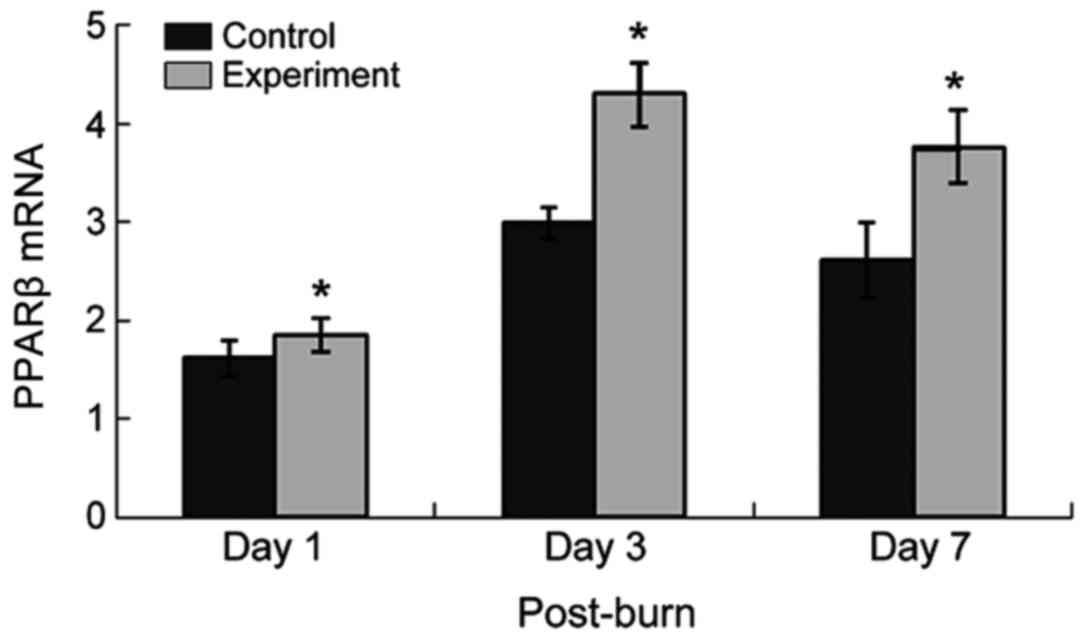
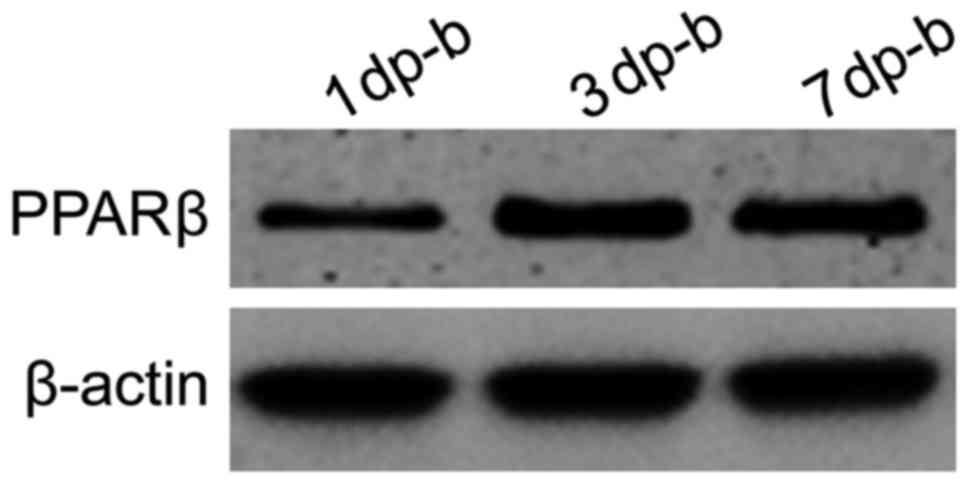
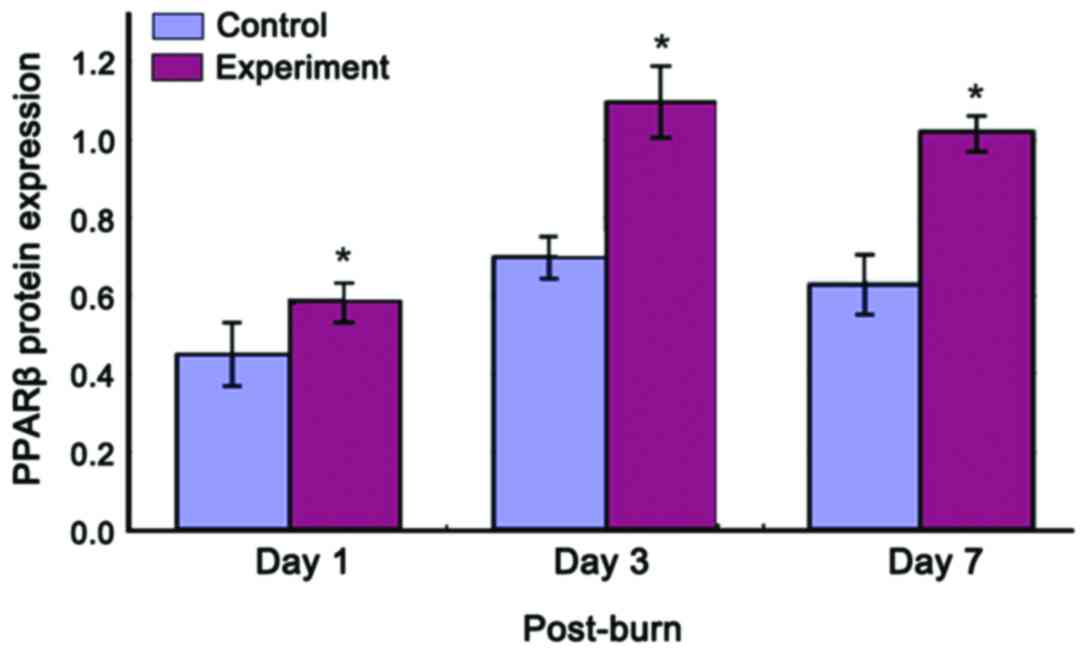
|
1
|
Keck M, Herndon DH, Kamolz LP, Frey M and
Jeschke MG: Pathophysiology of burns. Wien Med Wochenschr.
159:327–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goertz O, Vogelpohl J, Jettkant B,
Daigeler A, Steinau HU, Steinstraesser L and Langer S: Burn model
for in vivo investigations of microcirculatory changes. Eplasty.
9:e132009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nisanci M, Eski M, Sahin I, Ilgan S and
Isik S: Saving the zone of stasis in burns with activated protein
C: An experimental study in rats. Burns. 36:397–402. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jackson DM: The diagnosis of the depth of
burning. Br J Surg. 40:588–596. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zor F, Ozturk S, Deveci M, Karacalioglu O
and Sengezer M: Saving the zone of stasis: Is glutathione
effective? Burns. 31:972–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eski M, Ozer F, Firat C, Alhan D, Arslan
N, Senturk T and Işik S: Cerium nitrate treatment prevents
progressive tissue necrosis in the zone of stasis following burn.
Burns. 38:283–289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Noratto G, Martino HS, Simbo S, Byrne D
and Mertens-Talcott SU: Consumption of polyphenol-rich peach and
plum juice prevents risk factors for obesity-related metabolic
disorders and cardiovascular disease in Zucker rats. J Nutr
Biochem. 26:633–641. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wagner KD and Wagner N: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) acts as
regulator of metabolism linked to multiple cellular functions.
Pharmacol Ther. 125:423–435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao PL, Chen L, Dobrzański TP, Zhu B, Kang
BH, Müller R, Gonzalez FJ and Peters JM: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-β/δ inhibits human neuroblastoma
cell tumorigenesis by inducing p53- and SOX2-mediated cell
differentiation. Mol Carcinog. 56:1472–1483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Akay R, Kamisli O, Kahraman A, Oner S and
Tecellioglu M: Evaluation of aqueductal CSF flow dynamics with
phase contrast cine MR imaging in idiopathic intracranial
hypertension patients: Preliminary results. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 19:3475–3479. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan H, Chen J and Peng X: Recombinant
human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor hydrogel
promotes healing of deep partial thickness burn wounds. Burns.
38:877–881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rho CR, Park MY and Kang S: Effects of
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating (GM-CSF) factor on
corneal epithelial cells in corneal wound healing model. PLoS One.
10:e01380202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Regas FC and Ehrlich HP: Elucidating the
vascular response to burns with a new rat model. J Trauma.
32:557–563. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singer AJ, McClain SA, Taira BR, Guerriero
JL and Zong W: Apoptosis and necrosis in the ischemic zone adjacent
to third degree burns. Acad Emerg Med. 15:549–554. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan L, Minghua C, Feifei D, Runxiu W,
Ziqiang L, Chengyue M and Wenbo J: Study of the use of recombinant
human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor hydrogel
externally to treat residual wounds of extensive deep
partial-thickness burn. Burns. 41:1086–1091. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smith CH, Allen MH, Groves RW and Barker
JN: Effect of granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor on
Langerhans cells in normal and healthy atopic subjects. Br J
Dermatol. 139:239–246. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Da Costa RM, Jesus Ribeiro FM, Aniceto C
and Mendes M: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
dose-ranging study of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating
factor in patients with chronic venous leg ulcers. Wound Repair
Regen. 7:17–25. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Chen J and Han C: A multicenter
clinical trial of recombinant human GM-CSF hydrogel for the
treatment of deep second-degree burns. Wound Repair Regen.
17:685–689. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kobayashi SD, Braughton KR, Whitney AR,
Voyich JM, Schwan TG, Musser JM and DeLeo FR: Bacterial pathogens
modulate an apoptosis differentiation program in human neutrophils.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:10948–10953. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu JS, Fang Y, Yao M, Yu WR and Du J:
Effects of rhGM-CSF on scalding wound healing and
neovascularization in rats. J Bengbu Med Coll. 37:17–19. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Seegers HC, Hood VC, Kidd BL, Cruwys SC
and Walsh DA: Enhancement of angiogenesis by endogenous substance P
release and neurokinin-1 receptors during neurogenic inflammation.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 306:8–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zuo C, Liang P and Huang X: Role of
PPARbeta in fibroblast response to heat injury. Indian J Biochem
Biophys. 49:219–227. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tyagi S, Gupta P, Saini AS, Kaushal C and
Sharma S: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: A family
of nuclear receptors role in various diseases. J Adv Pharm Technol
Res. 2:236–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Di-Poï N, Michalik L, Tan NS, Desvergne B
and Wahli W: The anti-apoptotic role of PPARbeta contributes to
efficient skin wound healing. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
85:257–265. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Piqueras L, Reynolds AR, Hodivala-Dilke
KM, Alfranca A, Redondo JM, Hatae T, Tanabe T, Warner TD and
Bishop-Bailey D: Activation of PPARbeta/delta induces endothelial
cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:63–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Attianese Giordano GM and Desvergne B:
Integrative and systemic approaches for evaluating PPARβ/δ (PPARD)
function. Nucl Recept Signal. 13:e0012015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Di-Poï N, Tan NS, Michalik L, Wahli W and
Desvergne B: Antiapoptotic role of PPARbeta in keratinocytes via
transcriptional control of the Akt1 signaling pathway. Mol Cell.
10:721–733. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liou JY, Lee S, Ghelani D,
Matijevic-Aleksic N and Wu KK: Protection of endothelial survival
by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta mediated 14-3-3
upregulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:1481–1487. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bishop-Bailey D: PPARs and angiogenesis.
Biochem Soc Trans. 39:1601–1605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gravante G, Palmieri MB, Esposito G,
Delogu D, Santeusanio G, Filingeri V and Montone A: Apoptotic cells
are present in ischemic zones of deep partial-thickness burns. J
Burn Care Res. 27:688–693. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|