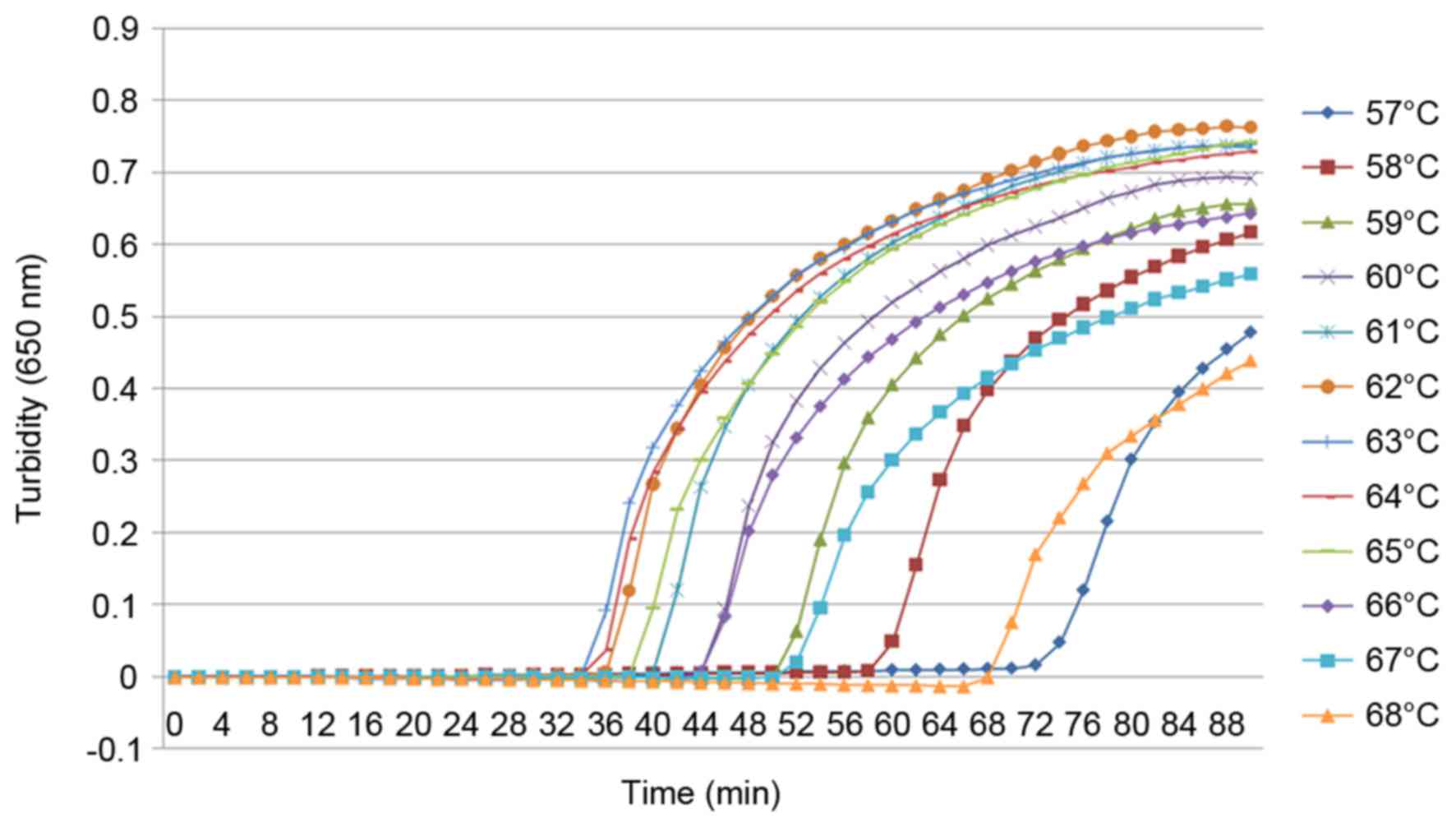
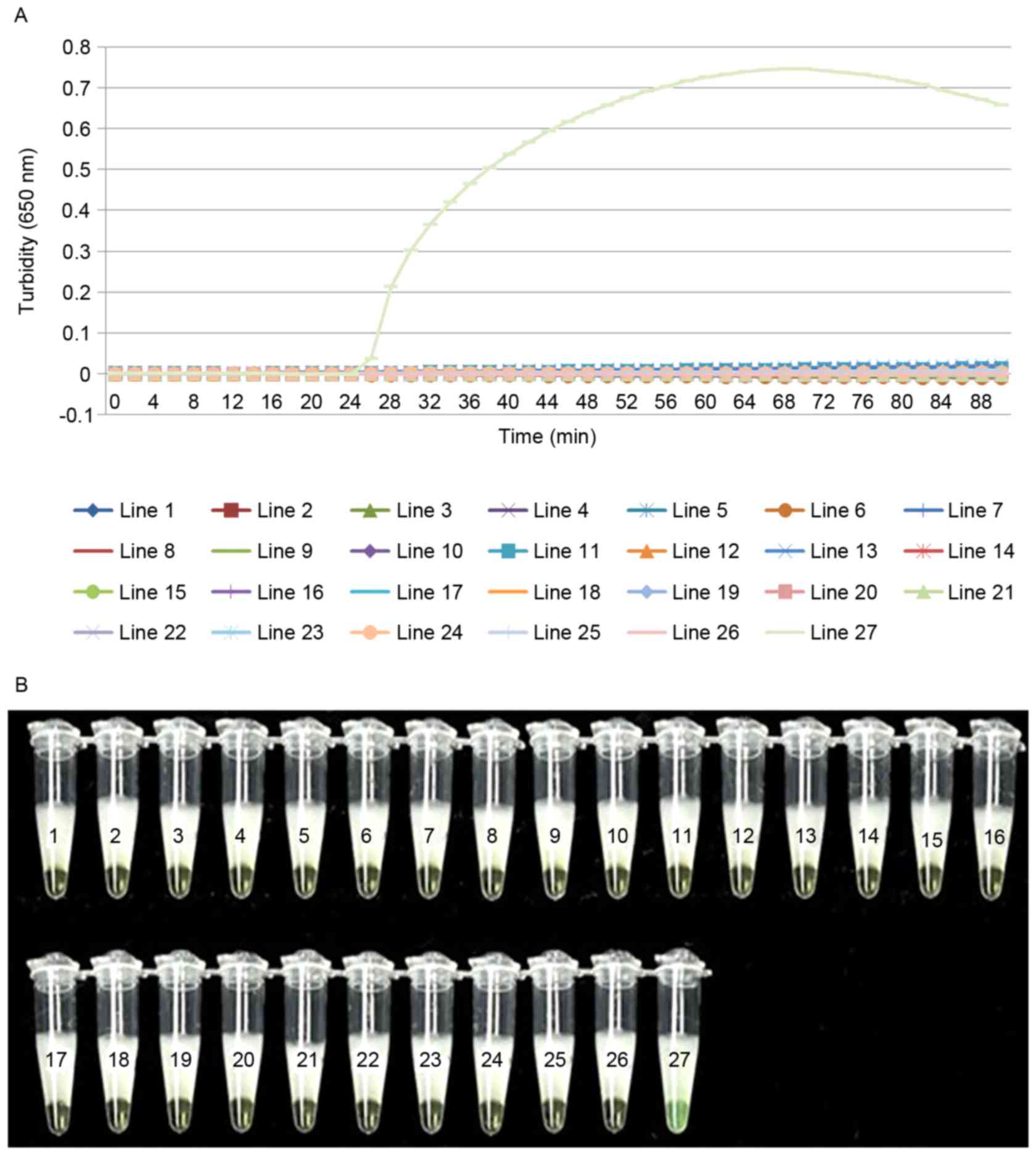
|
1
|
Doosti A and Mokhtari-Farsani A: Study of
the frequency of Clostridium difficile tcdA, tcdB, cdtA and cdtB
genes in feces of Calves in south west of Iran. Ann Clin Microbiol
Antimicrob. 13:212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Norén T, Unemo M, Magnusson C, Eiserman M
and Matussek A: Evaluation of the rapid loop-mediated isothermal
amplification assay Illumigene for diagnosis of Clostridium
difficile in an outbreak situation. APMIS. 122:155–160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boyanton BL Jr, Sural P, Loomis CR, Pesta
C, Gonzalez-Krellwitz L, Robinson-Dunn B and Riska P: Loop-mediated
isothermal amplification compared to real-time PCR and enzyme
immunoassay for toxigenic Clostridium difficile detection. J Clin
Microbiol. 50:640–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim J, Seo MR, Kang JO, Choi TY and Pai H:
Clinical and Microbiologic characteristics of Clostridium difficile
infection caused by binary toxin producing strain in Korea. Infect
Chemother. 45:175–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Papatheodorou P, Hornuss D, Nölke T,
Hemmasi S, Castonguay J, Picchianti M and Aktories K: Clostridium
difficile binary toxin CDT induces clustering of the
lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor into lipid rafts. MBio.
4:e00244–e00213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gerding DN, Johnson S, Rupnik M and
Aktories K: Clostridium difficile binary toxin CDT: Mechanism,
epidemiology, and potential clinical importance. Gut Microbes.
5:15–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Silva RO, Santos RL, Pires PS, Pereira LC,
Pereira ST, Duarte MC, de Assis RA and Lobato FC: Detection of
toxins A/B and isolation of Clostridium difficile and Clostridium
perfringens from dogs in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Braz J Microbiol.
44:133–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa
T, Watanabe K, Amino N and Hase T: Loop-mediated isothermal
amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:E632000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JB, Han AR, Park EY, Kim JY, Cho W,
Lee J, Seo EK and Lee KT: Inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2 and
cytokines expression by poncirin through the NF-kappaB inactivation
in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:2345–2351. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gandelman O, Jackson R, Kiddle G and Tisi
L: Loop-mediated amplification accelerated by stem primers. Int J
Mol Sci. 12:9108–9124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu C, Jiang DN, Xiang GM, Luo FK, Liu LL,
Yu JC and Pu XY: DNA detection of Clostridium difficile infection
based on real-time resistance measurement. Genet Mol Res.
12:3296–3304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mori Y, Nagamine K, Tomita N and Notomi T:
Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by
turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 289:150–154. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gavin MA, Rasmussen JP, Fontenot JD, Vasta
V, Manganiello VC, Beavo JA and Rudensky AY: Foxp3-dependent
programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation. Nature.
445:771–775. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pollock NR: Ultrasensitive detection and
quantification of toxins for optimized diagnosis of Clostridium
difficile infection. J Clin Microbiol. 54:259–264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hicke B, Pasko C, Groves B, Ager E, Corpuz
M, Frech G, Munns D, Smith W, Warcup A, Denys G, et al: Automated
detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile in clinical samples:
Isothermal tcdB amplification coupled to array-based detection. J
Clin Microbiol. 50:2681–2687. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mansour SM, Ali H, Chase CC and Cepica A:
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for diagnosis of 18 World
Organization for Animal Health (OIE) notifiable viral diseases of
ruminants, swine and poultry. Anim Health Res Rev. 16:89–106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang L, Li J, Bi Y, Xu L and Liu W:
Development and application of a reverse transcription
loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection
of Duck hepatitis A virus type 1. Virus Genes. 45:585–589. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hirayama H, Kageyama S, Moriyasu S, Sawai
K and Minamihashi A: Embryo sexing and sex chromosomal chimerism
analysis by loop-mediated isothermal amplification in cattle and
water buffaloes. J Reprod Dev. 59:321–326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seki M, Yamashita Y, Torigoe H, Tsuda H,
Sato S and Maeno M: Loop-mediated isothermal amplification method
targeting the lytA gene for detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
J Clin Microbiol. 43:1581–1586. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim DW, Kilgore PE, Kim EJ, Kim SA, Anh
DD, Dong BQ, Kim JS and Seki M: The enhanced pneumococcal LAMP
assay: A clinical tool for the diagnosis of meningitis due to
Streptococcus pneumoniae. PLoS One. 7:e429542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|