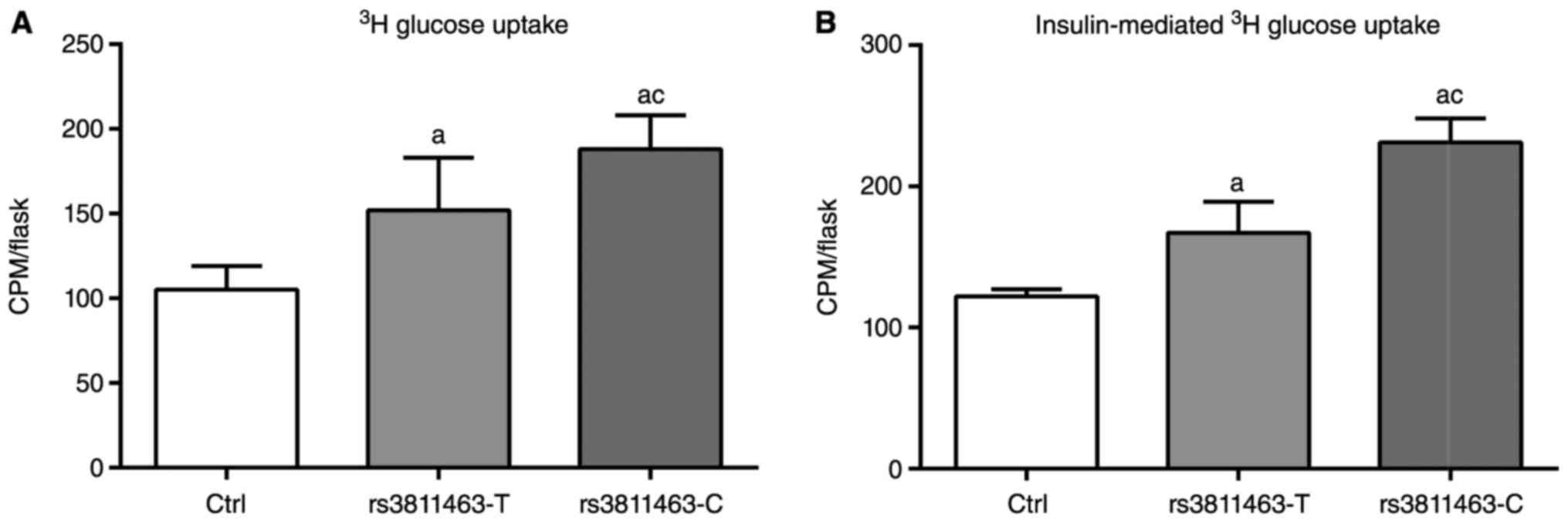
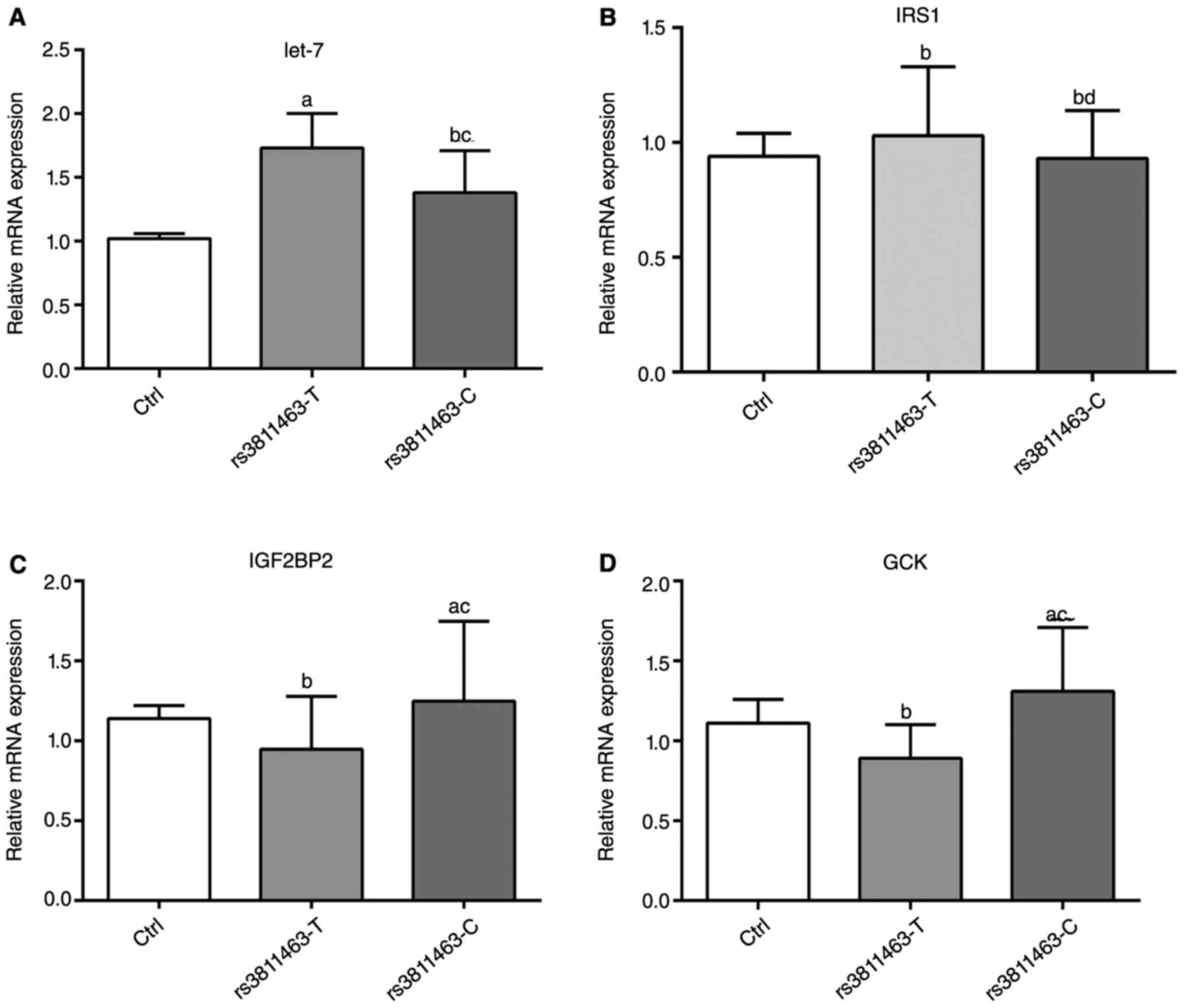
|
1
|
Russo LM, Nobles C, Ertel KA, Chasan-Taber
L and Whitcomb BW: Physical activity interventions in pregnancy and
risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 125:576–582. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang C and Ning Y: Effect of dietary and
lifestyle factors on the risk of gestational diabetes: Review of
epidemiologic evidence. Am J Clin Nutr. 94 6 Suppl:1975S–1979S.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bowers K, Tobias DK, Yeung E, Hu FB and
Zhang C: A prospective study of prepregnancy dietary fat intake and
risk of gestational diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 95:446–453. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Donin AS, Nightingale CM, Owen CG,
Rudnicka AR, Jebb SA, Ambrosini GL, Stephen AM, Cook DG and Whincup
PH: Dietary energy intake is associated with type 2 diabetes risk
markers in children. Diabetes Care. 37:116–123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nicoloso MS, Sun H, Spizzo R, Kim H,
Wickramasinghe P, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Ferdin J, Kunej T, Xiao L,
et al: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms inside microRNA target sites
influence tumor susceptibility. Cancer Res. 70:2789–2798. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nguyen LH and Zhu H: Lin28 and let-7 in
cell metabolism and cancer. Transl Pediatr. 4:4–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun X, Liu J, Xu C, Tang SC and Ren H: The
insights of Let-7 miRNAs in oncogenesis and stem cell potency. J
Cell Mol Med. 20:1779–1788. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Viswanathan SR, Daley GQ and Gregory RI:
Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science.
320:97–100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu H, Shyh-Chang N, Segrè AV, Shinoda G,
Shah SP, Einhorn WS, Takeuchi A, Engreitz JM, Hagan JP, Kharas MG,
et al: The Lin28/let-7 axis regulates glucose metabolism. Cell.
147:81–94. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen AX, Yu KD, Fan L, Li JY, Yang C,
Huang AJ and Shao ZM: Germline genetic variants disturbing the
Let-7/LIN28 double-negative feedback loop alter breast cancer
susceptibility. PLoS Genet. 7:e10022592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J, Zhang L, Fan R, Guo N, Xiong C,
Wang L, Jin S, Li W and Lu J: The polymorphism in the let-7
targeted region of the Lin28 gene is associated with increased risk
of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 375:53–57. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johnson AM and Olefsky JM: The origins and
drivers of insulin resistance. Cell. 152:673–684. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Veerapur VP, Prabhakar KR, Kandadi MR,
Srinivasan KK and Unnikrishnan MK: Antidiabetic effect of Dodonaea
viscosa aerial parts in high fat diet and low dose
streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats: A mechanistic
approach. Pharm Biol. 48:1137–1148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang HC and Guarente L: SIRT1 and other
sirtuins in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:138–145. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
El-Mahmoudy A, Shimizu Y, Shiina T,
Matsuyama H, El-Sayed M and Takewaki T: Successful abrogation by
thymoquinone against induction of diabetes mellitus with
streptozotocin via nitric oxide inhibitory mechanism. Int
Immunopharmacol. 5:195–207. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mondol V and Pasquinelli AE: Let's make it
happen: The role of let-7 microRNA in development. Curr Top Dev
Biol. 99:1–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thornton JE and Gregory RI: How does lin28
let-7 control development and disease? Trends Cell Biol.
22:474–482. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frost RJ and Olson EN: Control of glucose
homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by the Let-7 family of
microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:pp. 21075–21080. 2011;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang C, Bao W, Rong Y, Yang H, Bowers K,
Yeung E and Kiely M: Genetic variants and the risk of gestational
diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Hum Reprod Update.
19:376–390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Petrie JR, Pearson ER and Sutherland C:
Implications of genome wide association studies for the
understanding of type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. Biochem
Pharmacol. 81:471–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rutanen J, Yaluri N, Modi S, Pihlajamäki
J, Vänttinen M, Itkonen P, Kainulainen S, Yamamoto H, Lagouge M,
Sinclair DA, et al: SIRT1 mRNA expression may be associated with
energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 59:829–835.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|