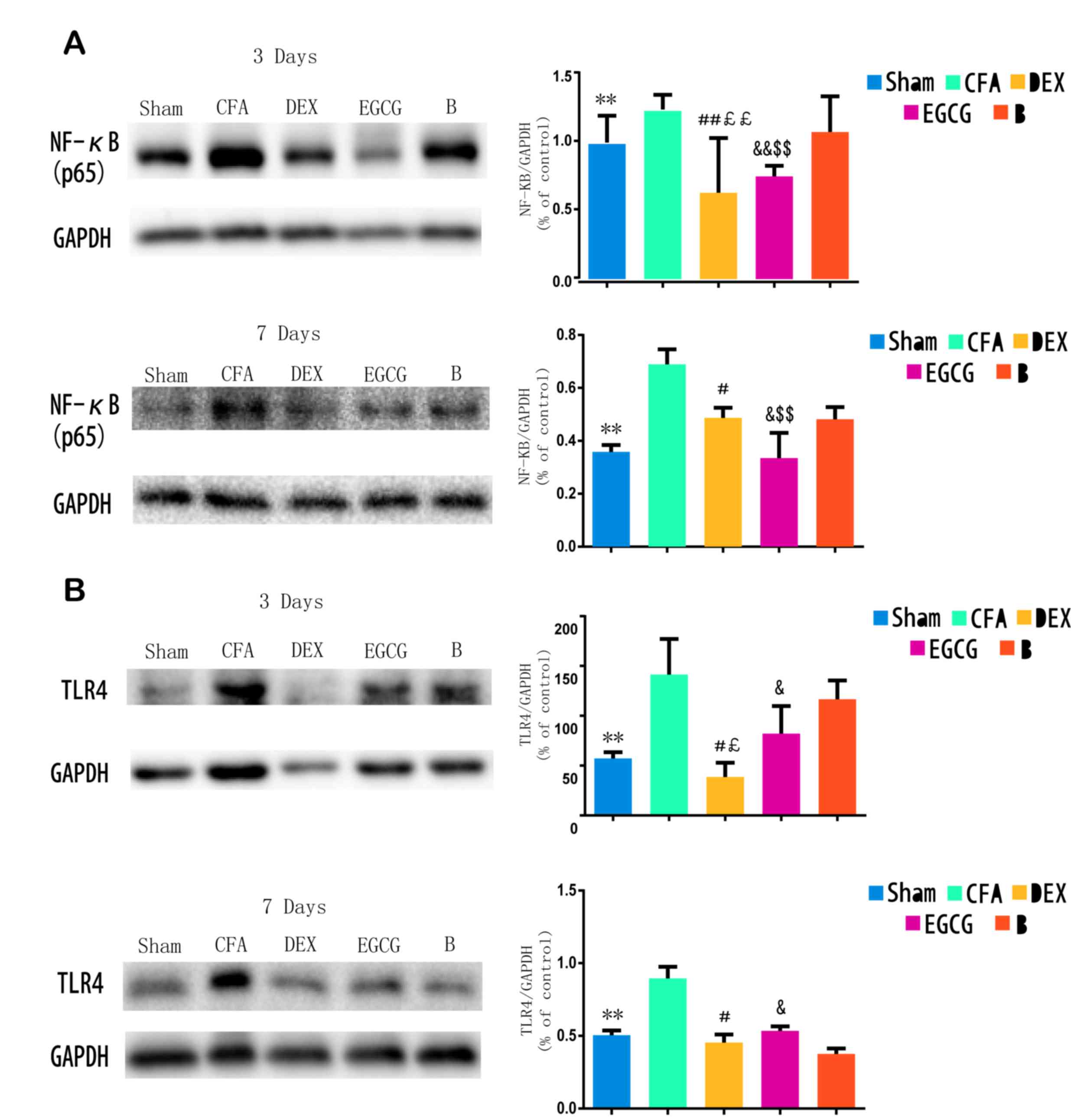
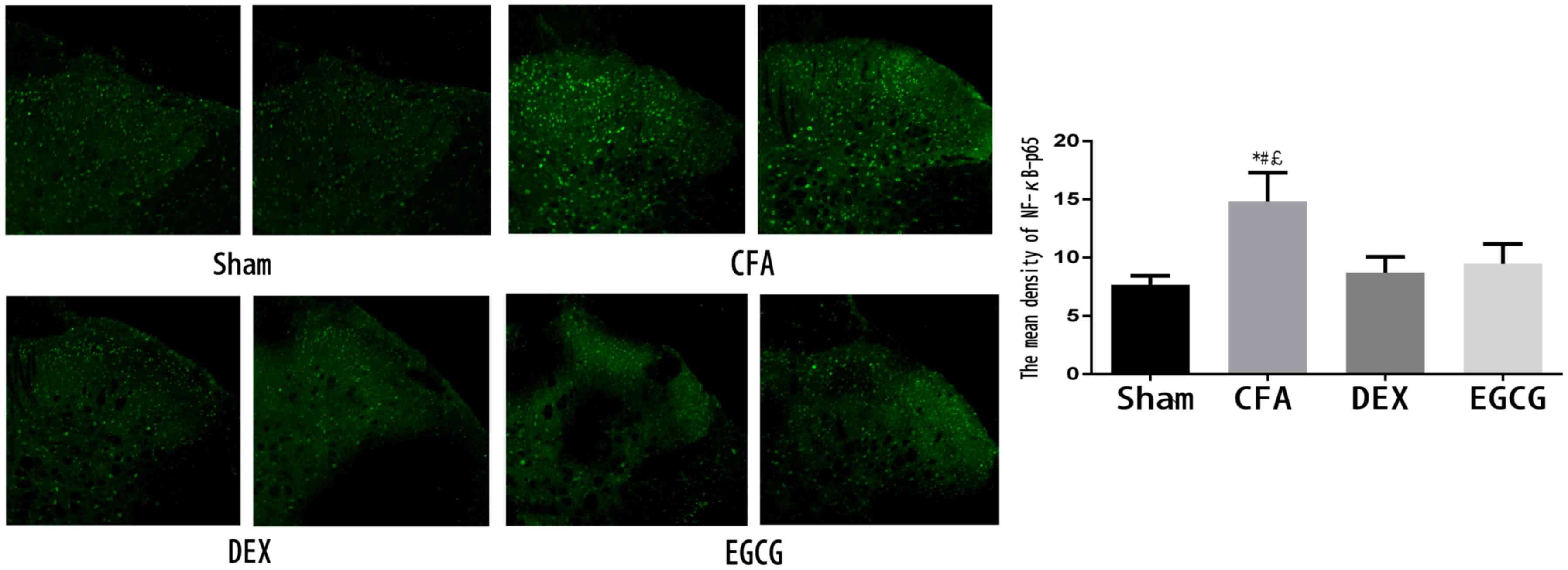
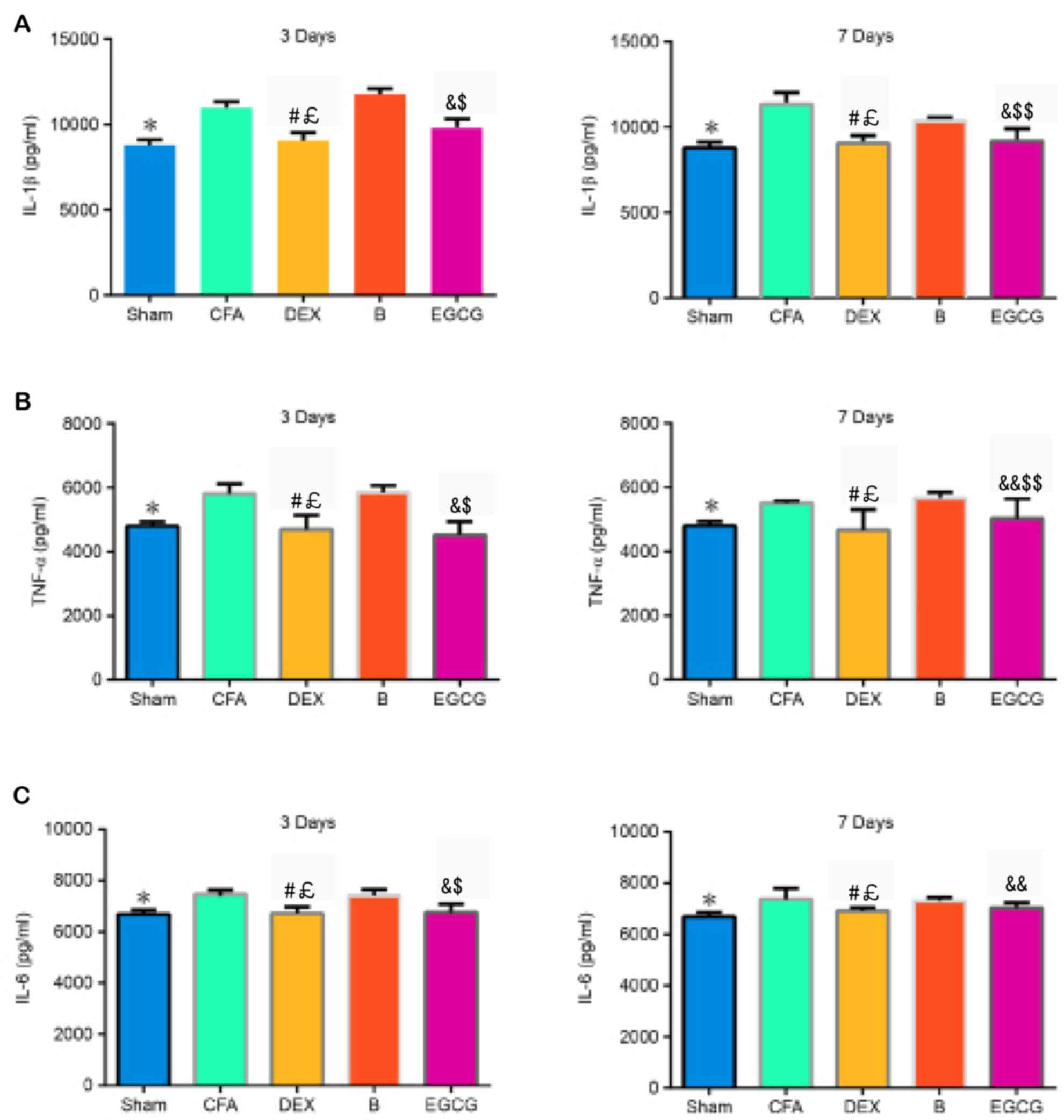
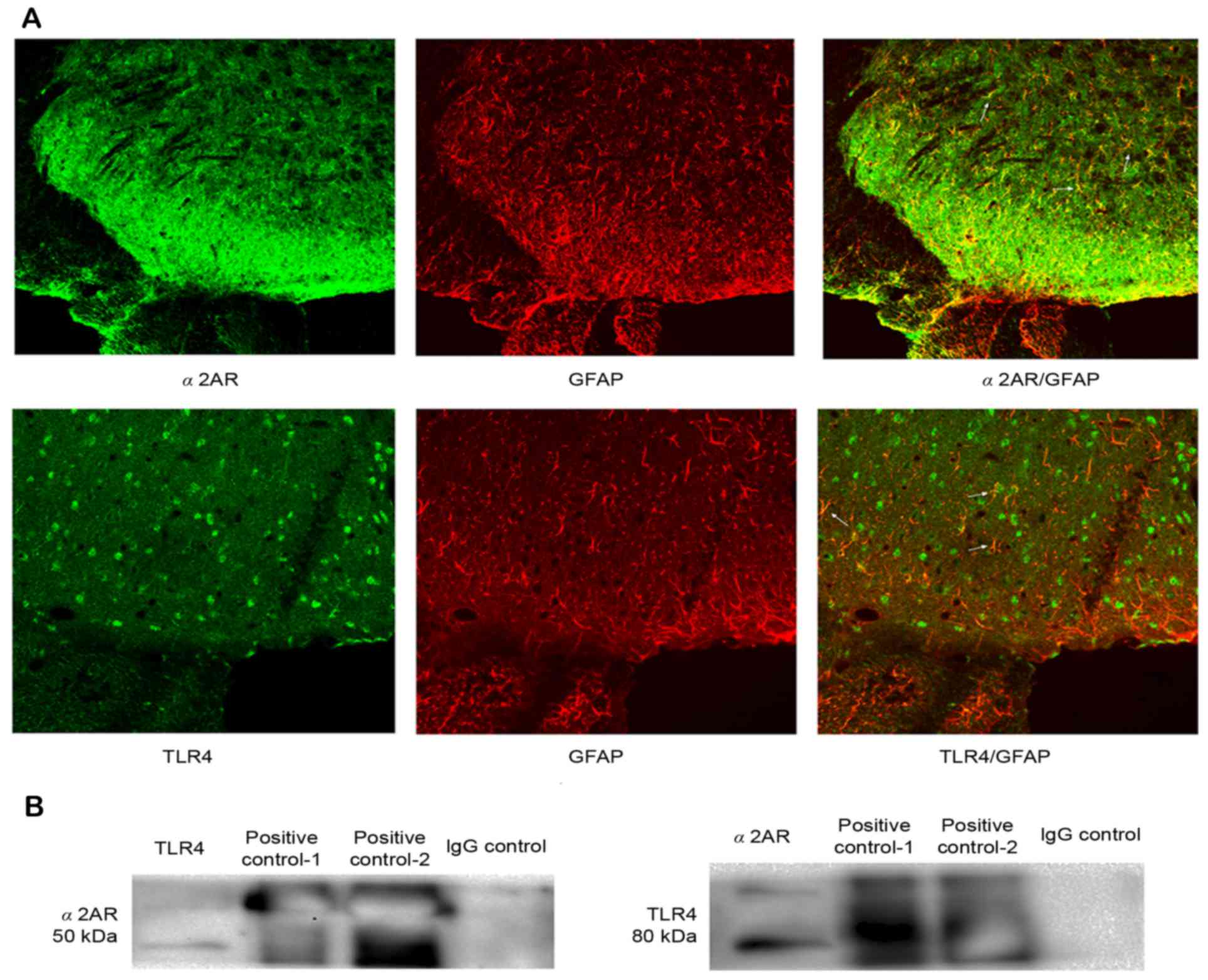
|
1
|
Schaible HG, Ebersberger A and Von Banchet
GS: Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 966:343–354.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu B, Zhang WS, Yang JL, Xu H, Deng XM and
Zhang YQ: Dexmedetomidine blocks thermal hyperalgesia and spinal
glial activation in rat model of monoarthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:523–530. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Virtanen R, Savola JM, Saano V and Nyman
L: Characterization of the selectivity, specificity and potency of
medetomidine as an alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol.
150:9–14. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shimode N, Fukuoka T, Tanimoto M, Tashiro
C, Tokunaga A and Noguchi K: The effects of dexmedetomidine and
halothane on Fos expression in the spinal dorsal horn using a rat
postoperative pain model. Neurosci Lett. 343:45–48. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Malmberg AB, Hedley LR, Jasper JR, Hunter
JC and Basbaum AI: Contribution of alpha(2) receptor subtypes to
nerve injury-induced pain and its regulation by dexmedetomidine. Br
J Pharmacol. 132:1827–1836. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu M, Kontinen VK and Kalso E: Effects of
radolmidine, a novel alpha2-adrenergic agonist compared with
dexmedetomidine in different pain models in the rat.
Anesthesiology. 93:473–481. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee HG, Choi JI, Kim YO and Yoon MH: The
role of alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtype in the antiallodynic effect of
intraplantar dexmedetomidine in a rat spinal nerve ligation model.
Neurosci Lett 557 Pt B. 1–122. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Paqueron X, Conklin D and Eisenach JC:
Plasticity in action of intrathecal clonidine to mechanical but not
thermal nociception after peripheral nerve injury. Anesthesiology.
99:199–204. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pertovaara A and Wei H: Attenuation of
ascending nociceptive signals to the rostroventromedial medulla
induced by a novel alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, MPV-2426, following
intrathecal application in neuropathic rats. Anesthesiology.
92:1082–1092. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Neill L: The Toll/interleukin-1 receptor
domain: A molecular switch for inflammation and host defence.
Biochem Soc Trans. 28:557–563. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akira S and Takeda K: Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:499–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baeuerle PA and Henkel T: Function and
activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol.
12:141–179. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watkins LR, Milligan ED and Maier SF:
Glial activation: A driving force for pathological pain. Trends
Neurosci. 24:450–455. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsuda M, Inoue K and Salter MW:
Neuropathic pain and spinal microglia: A big problem from molecules
in ‘small’ glia. Trends Neurosci. 28:101–107. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao H and Zhang YQ: Spinal glial
activation contributes to pathological pain states. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 32:972–983. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gwak YS, Kang J, Unabia GC and Hulsebosch
CE: Spatial and temporal activation of spinal glial cells: Role of
gliopathy in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury
in rats. Exp Neurol. 234:362–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Milligan ED, Twining C, Chacur M,
Biedenkapp J, O'Connor K, Poole S, Tracey K, Martin D, Maier SF and
Watkins LR: Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate
mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci. 23:1026–1040.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ledeboer A, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Frank
MG, Mahony JH, Maier SF and Watkins LR: Minocycline attenuates
mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat
models of pain facilitation. Pain. 115:71–83. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Pan HL, Zhao
ZQ and Zhang YQ: New evidence for the involvement of spinal
fractalkine receptor in pain facilitation and spinal glial
activation in rat model of monoarthritis. Pain. 129:64–75. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shan S, Qi-Liang MY, Hong C, Tingting L,
Mei H, Haili P, Yan-Qing W, Zhi-Qi Z and Yu-Qiu Z: Is functional
state of spinal microglia involved in the anti-allodynic and
anti-hyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture in rat model of
monoarthritis? Neurobiol Dis. 26:558–568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Zhao ZQ and
Zhang YQ: Evidence for suppression of electroacupuncture on spinal
glial activation and behavioral hypersensitivity in a rat model of
monoarthritis. Brain Res Bull. 75:83–93. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun S, Chen WL, Wang PF, Zhao ZQ and Zhang
YQ: Disruption of glial function enhances electroacupuncture
analgesia in arthritic rats. Exp Neurol. 198:294–302. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mori K, Ozaki E, Zhang B, Yang L, Yokoyama
A, Takeda I, Maeda N, Sakanaka M and Tanaka J: Effects of
norepinephrine on rat cultured microglial cells that express
alpha1, alpha2, beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptors.
Neuropharmacology. 43:1026–1034. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng L, Yu AC, Fung KY, Prévot V and Hertz
L: Alpha-adrenergic stimulation of ERK phosphorylation in
astrocytes is alpha(2)-specific and may be mediated by
transactivation. Brain Res. 978:65–71. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Heal DJ, Butler SA, Prow MR and Buckett
WR: Quantification of presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat
brain after short-term DSP-4 lesioning. Eur J Pharmacol. 249:37–41.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Conway EL, Gundlach AL and Craven JA:
Temporal changes in glial fibrillary acidic protein messenger RNA
and [3H]PK11195 binding in relation to imidazoline-I2-receptor and
alpha 2-adrenoceptor binding in the hippocampus following transient
global forebrain ischaemia in the rat. Neuroscience. 82:805–817.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li SS, Zhang WS, Ji D, Zhou YL, Li H, Yang
JL, Xiong YC, Zhang YQ and Xu H: Involvement of spinal microglia
and interleukin-18 in the anti-nociceptive effect of
dexmedetomidine in rats subjected to CCI. Neurosci Lett. 560:21–25.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu JJ, Walla BC, Diaz MF, Fuller GN and
Gutstein HB: Intermittent lumbar puncture in rats: A novel method
for the experimental study of opioid tolerance. Anesth Analg.
103:714–720. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chu YX, Zhang YQ and Zhao ZQ: Involvement
of microglia and interleukin-18 in the induction of long-term
potentiation of spinal nociceptive responses induced by tetanic
sciatic stimulation. Neurosci Bull. 28:49–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang JL, Xu B, Li SS, Zhang WS, Xu H, Deng
XM and Zhang YQ: Gabapentin reduces CX3CL1 signaling and blocks
spinal microglial activation in monoarthritic rats. Mol Brain.
5:182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Unnerstall JR, Kopajtic TA and Kuhar MJ:
Distribution of alpha 2 agonist binding sites in the rat and human
central nervous system: Analysis of some functional, anatomic
correlates of the pharmacologic effects of clonidine and related
adrenergic agents. Brain Res. 319:69–101. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu L, Ji F, Liang J, He H, Fu Y and Cao
M: Inhibition by dexmedetomidine of the activation of spinal dorsal
horn glias and the intracellular ERK signaling pathway induced by
nerve injury. Brain Res. 1427:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Buerkle H and Yaksh TL: Pharmacological
evidence for different alpha 2-adrenergic receptor sites mediating
analgesia and sedation in the rat. Br J Anaesth. 81:208–215. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu B, Zhang WS, Yang JL, Lû N, Deng XM, Xu
H and Zhang YQ: Evidence for suppression of spinal glial activation
by dexmedetomidine in a rat model of monoarthritis. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 37:e158–e166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Y, Liu Y, Huang H, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Lu F
and Zhou C, Huang L, Li X and Zhou C: Dexmedetomidine inhibits
inflammatory reaction in lung tissues of septic rats by suppressing
TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:5621542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bettoni I, Comelli F, Rossini C, Granucci
F, Giagnoni G, Peri F and Costa B: Glial TLR4 receptor as new
target to treat neuropathic pain: Efficacy of a new receptor
antagonist in a model of peripheral nerve injury in mice. Glia.
56:1312–1319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saito O, Svensson CI, Buczynski MW, Wegner
K, Hua XY, Codeluppi S, Schaloske RH, Deems RA, Dennis EA and Yaksh
TL: Spinal glial TLR4-mediated nociception and production of
prostaglandin E(2) and TNF. Br J Pharmacol. 160:1754–1764. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu GJ, Chen TL, Ueng YF and Chen RM:
Ketamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6
gene expressions in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages
through suppression of toll-like receptor 4-mediated c-Jun
N-terminal kinase phosphorylation and activator protein-1
activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 228:105–113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feng Y and Longmore GD: The LIM protein
Ajuba influences interleukin-1-induced NF-kappaB activation by
affecting the assembly and activity of the protein kinase
Czeta/p62/TRAF6 signaling complex. Mol Cell Biol. 25:4010–4022.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wright JG and Christman JW: The role of
nuclear factor kappa B in the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases:
Implications for therapy. Am J Respir Med. 2:211–219. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu Y, Li W and Zhou C, Lu F, Gao T, Liu Y,
Cao J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Zhou C: Ketamine inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced astrocytes activation by suppressing
TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 30:609–617. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Baeuerle PA and Baltimore D: I kappa B: A
specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science.
242:540–546. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Grilli M, Chiu JJ and Lenardo MJ: NF-kappa
B and Rel: Participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory
system. Int Rev Cytol. 143:1–62. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|