|
1
|
Krishnamoorthy S and Honn KV: Inflammation
and disease progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:481–491. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arulselvan P, Fard MT, Tan WS, Gothai S,
Fakurazi S, Norhaizan ME and Kumar SS: Role of antioxidants and
natural products in inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:52761302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Henson PM, Larsen GL, Henson JE, Newman
SL, Musson RA and Leslie CC: Resolution of pulmonary inflammation.
Fed Pro. 43:2799–2806. 1984.
|
|
4
|
Gautam R and Jachak SM: Recent
developments in anti-inflammatory natural products. Med Res Rev.
29:767–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parker KL and Schimmer BP: Genetics of the
development and function of the adrenal cortex. Rev Endocr Metab
Disord. 2:245–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ravipati AS, Zhang L, Koyyalamudi SR,
Jeong SC, Reddy N, Bartlett J, Smith PT, Shanmugam K, Münch G, Wu
MJ, et al: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of selected
Chinese medicinal plants and their relation with antioxidant
content. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:1732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim HY, Hwang KW and Park SY: Extracts of
Actinidia arguta stems inhibited LPS-induced inflammatory responses
through nuclear factor-κB pathway in Raw 264.7 cells. Nutr Res.
34:1008–1016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hou XL, Tong Q, Wang WQ, Shi CY, Xiong W,
Chen J, Liu X and Fang JG: Suppression of inflammatory responses by
dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid from Ampelopsis grossedentata, via
inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J
Nat Prod. 78:1689–1696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oh YC, Jeong YH, Kim T, Cho WK and Ma JY:
Anti-inflammatory effect of Artemisiae annuae herba in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 10
Suppl 3:S588–S595. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lamichhane R, Kim SG, Poudel A, Sharma D,
Lee KH and Jung HJ: Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo biological
activities of Cheilanthes albomarginata Clarke. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 14:3422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim DH, Kim ME and Lee JS: Inhibitory
effects of extract from G. lanceolata on LPS-induced production of
nitric oxide and IL-1β via down-regulation of MAPK in macrophages.
Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 175:657–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim H, Lee E, Lim T, Jung J and Lyu Y:
Inhibitory effect of Asparagus cochinchinensis on tumor necrosis
factor-alpha secretion from astrocytes. Int J Immunopharmacol.
20:153–162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee DY, Choo BK, Yoon T, Cheon MS, Lee HW,
Lee YA and Kim HK: Anti-inflammatory effects of Asparagus
cochinchinensis extract in acute and chronic cutaneous
inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. 121:28–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koo HN, Jeong HJ, Choi JY, Choi SD, Choi
TJ, Cheon YS, Kim KS, Kang BK, Park ST, Chang CH, et al: Inhibition
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis by Asparagus
cochlnchinensis in HepG2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 73:137–143. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiong D, Yu LX, Yan X, Guo C and Xiong Y:
Effects of root and stem extracts of Asparagus cochinchinensis on
biochemical indicators related to aging in the brain and liver of
mice. Am J Chinese Med. 39:719–726. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jung KH, Choi HL, Park S, Lee G, Kim M,
Min JK, Min BI and Bae H: The effects of the standardized herbal
formula PM014 on pulmonary inflammation and airway responsiveness
in a murine model of cockroach allergen-induced asthma. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:113–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elson LA and Morgan WTJ: A colorimetric
method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine.
Biochem J. 27:1824–1828. 1933. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaegawa H, Matsumoto H, Endo K, Satoh T,
Nonaka GI and Noshioka I: Inhibitory effects of tannins on
hyaluronidase activation and on the degranulation from rat
mesentery mast cells. Chem Pharm Bull. 33:5079–5082. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee KK, Kim JH, Cho JJ and Choi JD:
Inhibitory effects of 150 plant extracts on elastase activity and
their anti-inflammatory effects. Int J Cosmet Sci. 21:71–82. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singleton VL and Rossi JA: Colorimetry of
total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents.
Am J Enol Vitic. 16:144–158. 1965.
|
|
21
|
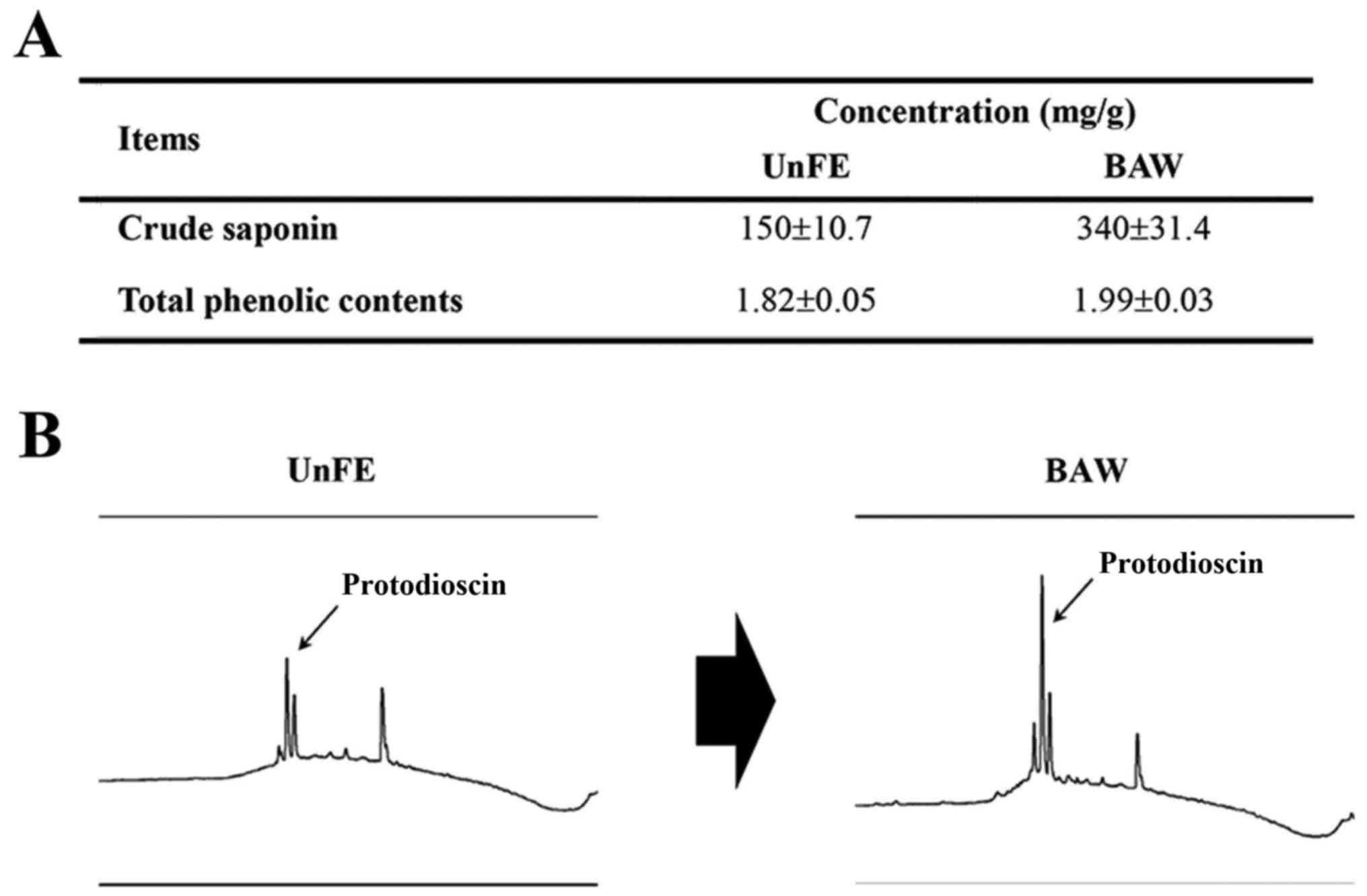
Hassan SM, Al Aqil AA and Attimarad M:
Determination of crude saponin and total flavonoids content in guar
meal. Adv Med Plant Res. 1:24–28. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Oh H, Ko EK, Kim DH, Jan KK, Park SE, Lee
HS and Kim YC: Secoiridoid glucosides with free radical scavenging
activity from the leaves of Syringa dilatata. Phytother Res.
17:417–419. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jie S, Xueji Z, Mark B and Harry F:
Measurement of nitric oxide production in biological systems by
using griess reaction assay. Sensors. 3:276–284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim JE, Park SH, Kwak MH, Go J, Koh EK,
Song SH, Sung JE, Lee HS, Hong JT and Hwang DY: Characterization of
changes in global genes expression in the distal colon of
loperamide-induced constipation SD rats in response to the laxative
effects of Liriope platyphylla. PLoS One. 10:e01296642015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ishimura N, Bronk SF and Gores GJ:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 in
mouse cholangiocytes promoting cell growth. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G88–G95. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rahman M: Medical application of
fermentation technology. Adv Mat Res. 810:127–157. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Oh YC, Cho WK, Jeong YH, Im GY, Yang MC
and Ma JY: Fermentation improves anti-inflammatory effect of
sipjeondaebotang on LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Am J Chin Med.
40:813–831. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bose S, Jeon S, Eom T, Song MY and Kim H:
Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo protective effects of
unfermented and fermented Rhizoma coptidis formulations against
lipopolysaccharide insult. Food Chem. 135:452–459. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Giriwono PE, Shirakawa H, Hokazono H, Goto
T and Komai M: Fermented barley extract supplementation maintained
antioxidative defense suppressing lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory liver injury in rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
75:1971–1976. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao PG: Modern Chinese Materia Medica.
Chemical Industry Press; Beijing: pp. 1502002
|
|
31
|
Liu YZ, Qu FY and Zhang PX: EfBFct of
chloroform extract of Tiandong on the brain antioxidation of
D-galactose-induced senile mice. Heilongjiang Med Pharm. 24:7–8.
2001.
|
|
32
|
Ni JM, Zhao R and Wang R: Comparison on
amino acid content in prepared and unprepared Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 23:182–183. 1992.
|
|
33
|
Tenji K and Junzo S: Studies on the
constituents of Asparagi Radix. I. On the structures of furostanol
oligosides of Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr. Chem Pharm
Bull. 27:3086–3094. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liang ZZ, Aquino R, De Simone F, Dini A,
Schettino O and Pizza C: Oligofurostanosides from Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Planta Med. 54:344–346. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang YC, Huang SY and Shi JG: Two new
furostanol glycosides from Asparagus cochinchinensis. Chin Chem
Lett. 13:1185–1188. 2002.
|
|
36
|
Cong PZ and Keman S: Handbook of
analytical chemistry-mass volume. Chemical Industry Publishing
House; Beijing: pp. 296–298. 2000
|
|
37
|
Gong YH: 13C NMR chemical shifts of
natural organic compounds. Yunnan Science and Technology Publishing
House; Kunming: pp. 2521986
|
|
38
|
Yang MH: Steroidal sapogenins of
dioscorea. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 12:43–44. 1981.
|
|
39
|
Xu CL, Chen HS and Tan XQ: Studies on the
active constituents of Asparagi radix. Nat Prod Res Dev.
17:128–130. 2005.
|
|
40
|
Shen Y, Chen HS and Wang Q: Studies on
chemical constituents of Asparagus cochinchinensis. J Second Med
Univ. 28:1241–1244. 2007.
|
|
41
|
Shen Y, Xu CL, Xuan WD, Li HL, Liu RH, Xu
XK and Chen HS: A new furostanol saponin from Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Arch Pharm Res. 34:1587–1591. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li XN, Chu C, Cheng DP, Tong SQ and Yan
JZ: Norlignans from Asparagus cochinchinensis. Nat Prod Commun.
7:1357–1358. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu GL, Hao Q, Li RT and Li HZ: Steroidal
saponins from the roots of Asparagus cochinchinensis. Chin J Nat
Med. 12:213–217. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Oh YC, Cho WK, Oh JH, Im GY, Jeong YH,
Yang MC and Ma JY: Fermentation by Lactobacillus enhances
anti-inflammatory effect of Oyaksungisan on LPS-stimulated RAW
264.7 mouse macrophage cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bose S, Song MY, Nam JK, Lee MJ and Kim H:
In vitro and in vivo protective effects of fermented preparations
of dietary herbs against lipopolysaccharide insult. Food Chem.
134:758–765. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jung HJ, Choi H, Lim HW, Shin D, Kim H,
Kwon B, Lee JE, Park EH and Lim CJ: Enhancement of
anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive actions of red ginseng
extract by fermentation. J Pharm Pharmacol. 64:756–762. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee WH, Wu HM, Lee CG, Sung DI, Song HJ,
Matsui T, Kim HB and Kim SG: Specific oligopeptides in fermented
soybean extract inhibit NF-κB-dependent iNOS and cytokine induction
by toll-like receptor ligands. J Med Food. 17:1239–1246. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Endo K, Yoon BI, Pairojkul C, Demetris AJ
and Sirica AE: ERBB-2 overexpression and cyclooxygenase-2
up-regulation in human cholangiocarcinoma and risk conditions.
Hepatology. 36:439–450. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jaiswal M, LaRusso NF, Burgart LJ and
Gores GJ: Inflammatory cytokines induce DNA damage and inhibit DNA
repair in cholangiocarcinoma cells by a nitric oxide-dependent
mechanism. Cancer Res. 60:184–190. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hemish J, Nakaya N, Mittal V and
Enikolopov G: Nitric oxide activates diverse signaling pathways to
regulate gene expression. J Biol Chem. 278:42321–42329. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
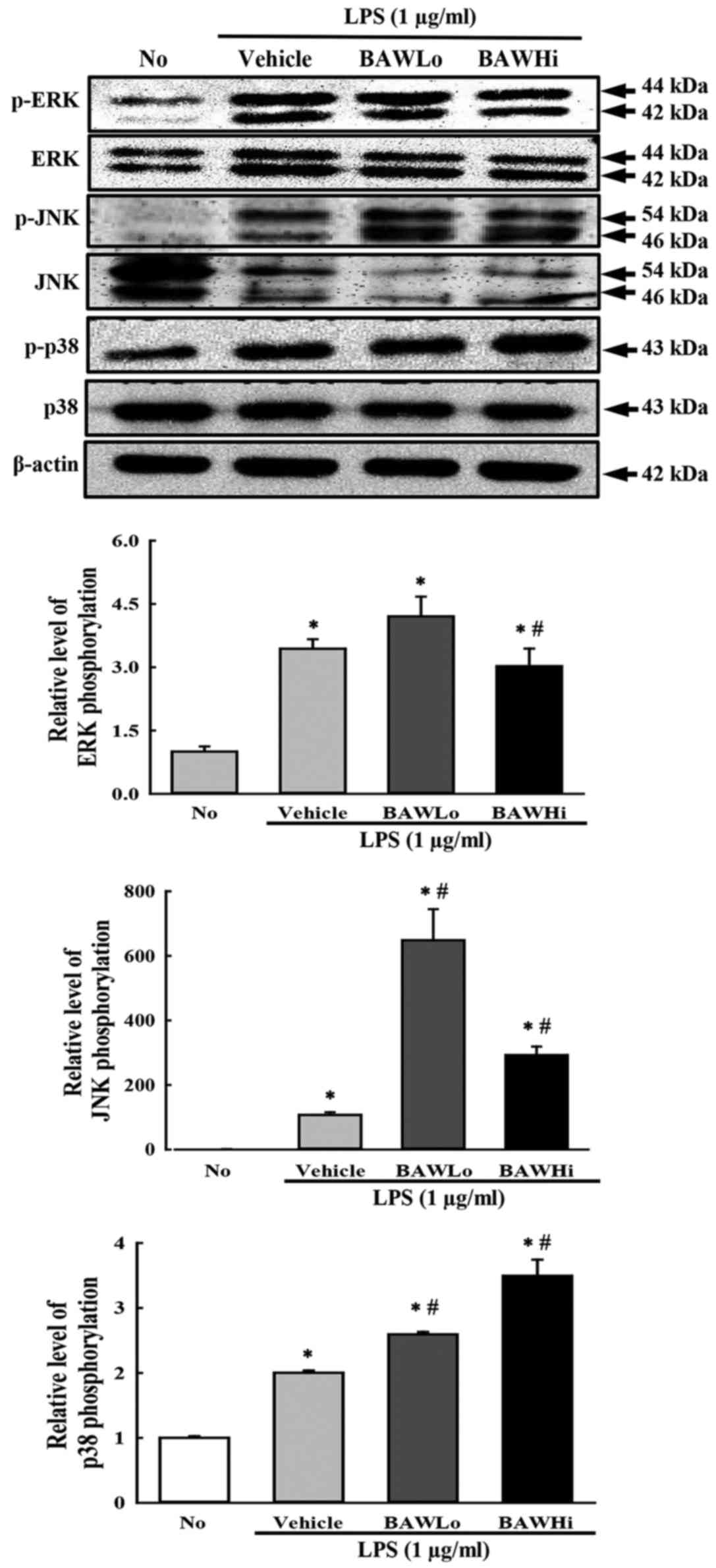
Berghe W Vanden, Plaisance S, Boone E,
Debosscher K, Schmitz ML, Fiers W and Haegeman G: p38 and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways are required for nuclear factor-kappaB p65
transactivation mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem.
273:3285–3290. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|