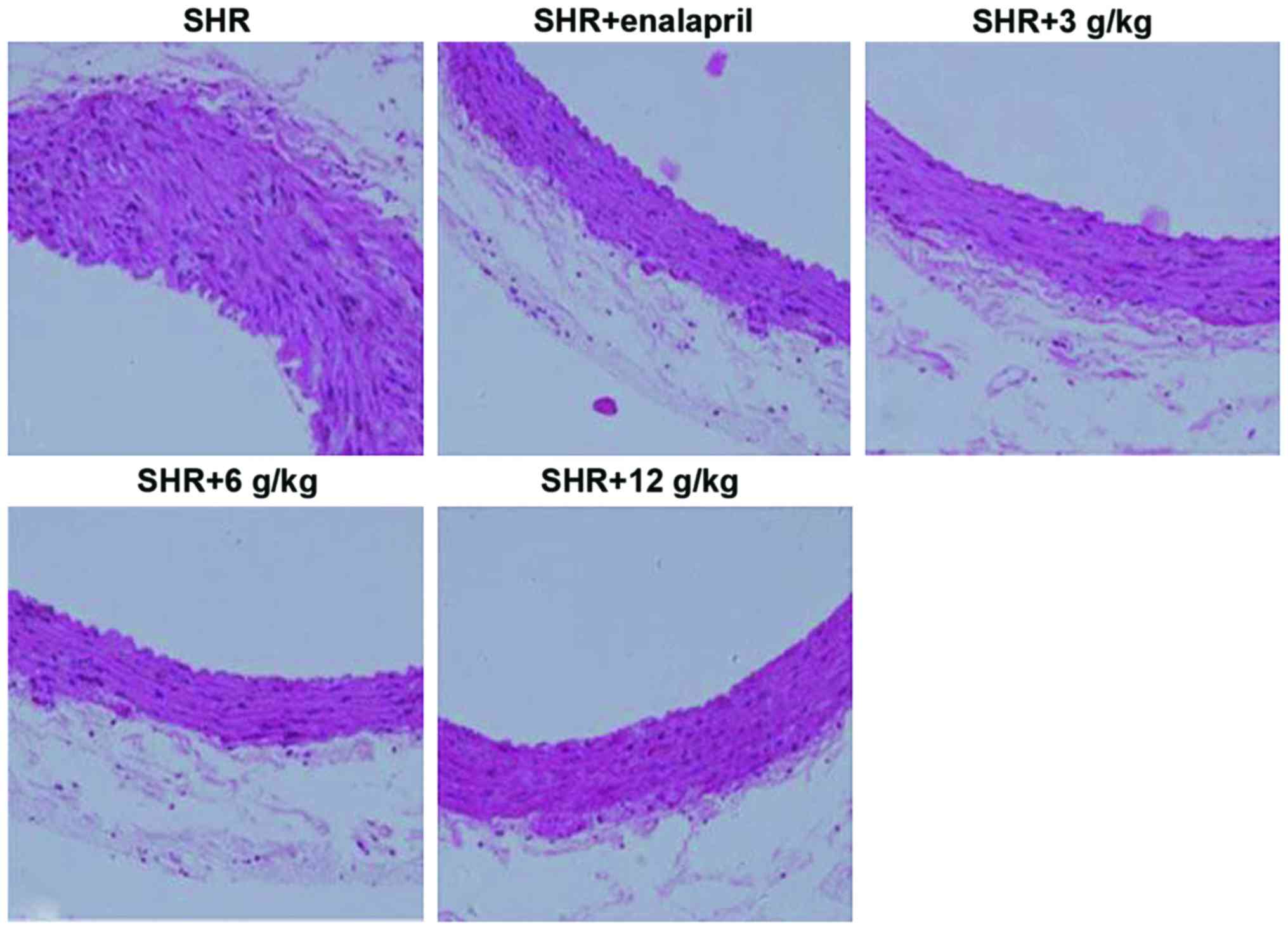
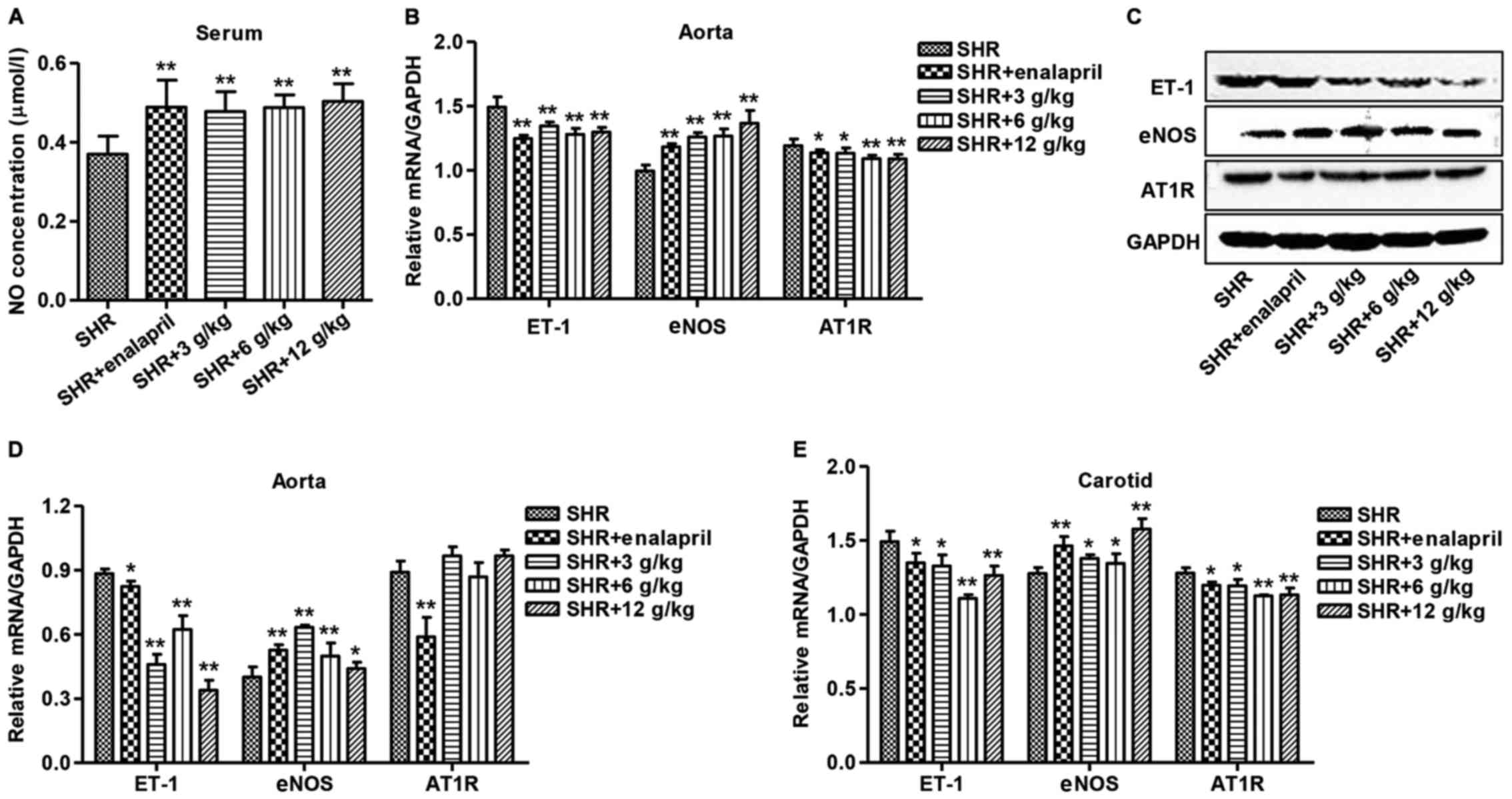
|
1
|
James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC,
Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, Lackland DT, LeFevre ML,
MacKenzie TD, Ogedegbe O, et al: 2014 Evidence-based guideline for
the management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the
panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
8). JAMA. 311:507–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Derosa G, Bonaventura A, Romano D, Bianchi
L, Fogari E, D'Angelo A and Maffioli P: Effects of
enalapril/lercanidipine combination on some emerging biomarkers in
cardiovascular risk stratification in hypertensive patients. J Clin
Pharm Ther. 39:277–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Antza C, Stabouli S and Kotsis V:
Combination therapy with lercanidipine and enalapril in the
management of the hypertensive patient: An update of the evidence.
Vasc Health Risk Manag. 12:443–451. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schiffrin EL: The vascular phenotypes in
hypertension: Relation with the natural history of hypertension. J
Am Soc Hypertens. 1:56–67. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lujan HL, Janbaih H and DiCarlo SE:
Structural remodeling of the heart and its premotor
cardioinhibitory vagal neurons following T(5) spinal cord
transection. J Appl Physiol (1985). 116:1148–1155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guerrero EI, Ardanaz N, Sevilla MA,
Arévalo MA and Montero MJ: Cardiovascular effects of nebivolol in
spontaneously hypertensive rats persist after treatment withdrawal.
J Hypertens. 24:151–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gómez-Roso M, Montero MJ, Carrón R and
Sevilla MA: Cardiovascular changes in spontaneously hypertensive
rats are improved by chronic treatment with zofenopril. Br J
Pharmacol. 158:1911–1921. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schiffrin EL: Vascular remodeling in
hypertension: Mechanisms and treatment. Hypertension. 59:367–374.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Higashi Y, Sasaki S, Nakagawa K, Ueda T,
Yoshimizu A, Kurisu S, Matsuura H, Kajiyama G and Oshima T: A
comparison of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, calcium
antagonists, beta-blockers and diuretic agents on reactive
hyperemia in patients with essential hypertension: A multicenter
study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 35:284–291. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmidt BM, Ribnicky DM, Lipsky PE and
Raskin I: Revisiting the ancient concept of botanical therapeutics.
Nat Chem Biol. 3:360–366. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou R, Li BG and Zhang GL: Chemical study
on Cyathula officinalis Kuan. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
7:245–252. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng H, Du X, Liu J, Han X, Cao X and Zeng
X: Novel polysaccharide from Radix Cyathulae officinalis
Kuan can improve immune response to ovalbumin in mice. Int J Biol
Macromol. 65:121–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park HY, Lim H, Kim HP and Kwon YS:
Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 by the root extract
of Cyathula officinalis Kuan and its constituents in
IL-1β-treated chondrocytes. Planta Med. 77:1528–1530. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu J, Xu J, Zhao XJ, Gao WY, Zhang SZ and
Guo YQ: A new heterocyclic compound from Cyathula
officinalis Kuan. Chin Chem Lett. 21:70–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ye P, Peng J and Liu J: The research
development of Cyathula officinalis kuan. Zhongguo Yaowu
Huaxue Zazhi. 35:51–53. 2007.
|
|
16
|
Han X, Shen S, Liu T, Du X, Cao X, Feng H
and Zeng X: Characterization and antioxidant activities of the
polysaccharides from Radix Cyathulae officinalis Kuan. Int J
Biol Macromol. 72:544–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner
P, Whelton PK and He J: Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of
worldwide data. Lancet. 365:217–223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu TT, Guo K, Chen HC, Lan CZ, Wang J,
Huang LL, Wang XH, Zhang Z and Gao S: Effects of traditional
Chinese medicine Xin-Ji-Er-Kang formula on 2K1C hypertensive rats:
Role of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 13:1732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ghiadoni L, Taddei S and Virdis A:
Hypertension and endothelial dysfunction: Therapeutic approach.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 10:42–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shantsila A and Shantsila E: Arterial
stiffening in hypertension: Beyond blood pressure levels. J Hum
Hypertens. 24:303–305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feihl F, Liaudet L, Levy BI and Waeber B:
Hypertension and microvascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res.
78:274–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao P, Xu TT, Lu J, Li L, Xu J, Hao DL,
Chen HZ and Liu DP: Overexpression of SIRT1 in vascular smooth
muscle cells attenuates angiotensin II-induced vascular remodeling
and hypertension in mice. J Mol Med (Berl). 92:347–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barrios V, Escobar C and Echarri R: Fixed
combinations in the management of hypertension: Perspectives on
lercanidipine-enalapril. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 4:847–853. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang H, Shen Z, Chu Y, Li Y, Li J, Wang
X, Yang W, Zhang X, Ju J, Xu J, et al: Serum metabolomics research
of the anti-hypertensive effects of Tengfu Jiangya tablet on
spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol
Biomed Life Sci. 1002:210–217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gordish KL, Kassem KM, Ortiz PA and
Beierwaltes WH: Moderate (20%) fructose-enriched diet stimulates
salt-sensitive hypertension with increased salt retention and
decreased renal nitric oxide. Physiol Rep. 5:52017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhai YL, Zhu L, Shi SF, Liu LJ, Lv JC and
Zhang H: Elevated soluble VEGF receptor sFlt-1 correlates with
endothelial injury in IgA nephropathy. PLoS One. 9:e1017792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wassmann S, Laufs U, Stamenkovic D, Linz
W, Stasch JP, Ahlbory K, Rösen R, Böhm M and Nickenig G: Raloxifene
improves endothelial dysfunction in hypertension by reduced
oxidative stress and enhanced nitric oxide production. Circulation.
105:2083–2091. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang MY, Chen J, Wang J, Xiao F, Zhang
HH, Zhang CR, Du DS, Cao YX, Shen LL and Zhu DN: Nitric oxide
modulates cardiovascular function in the rat by activating
adenosine A2A receptors and inhibiting acetylcholine release in the
rostral ventrolateral medulla. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
38:380–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang YM, Huang A, Kaley G and Sun D: eNOS
uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction in aged vessels. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 297:H1829–H1836. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Wang X, Hu F, Zhou B, Chen HB,
Zha D, Liu Y, Guo Y, Zheng L and Xiu J: A novel hydrodynamic
approach of drag-reducing polymers to improve left ventricular
hypertrophy and aortic remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Int J Nanomed. 11:6743–6751. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee TM, Lin MS, Chou TF, Tsai CH and Chang
NC: Effect of pravastatin on development of left ventricular
hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 289:H220–H227. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Amiri F, Virdis A, Neves MF, Iglarz M,
Seidah NG, Touyz RM, Reudelhuber TL and Schiffrin EL:
Endothelium-restricted overexpression of human endothelin-1 causes
vascular remodeling and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation.
110:2233–2240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Igase M, Strawn WB, Gallagher PE, Geary RL
and Ferrario CM: Angiotensin II AT1 receptors regulate ACE2 and
angiotensin-(1–7) expression in the aorta of spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
289:H1013–H1019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwai M, Nakaoka H, Senba I, Kanno H,
Moritani T and Horiuchi M: Possible involvement of
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and Mas activation in inhibitory
effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on vascular
remodeling. Hypertension. 60:137–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|