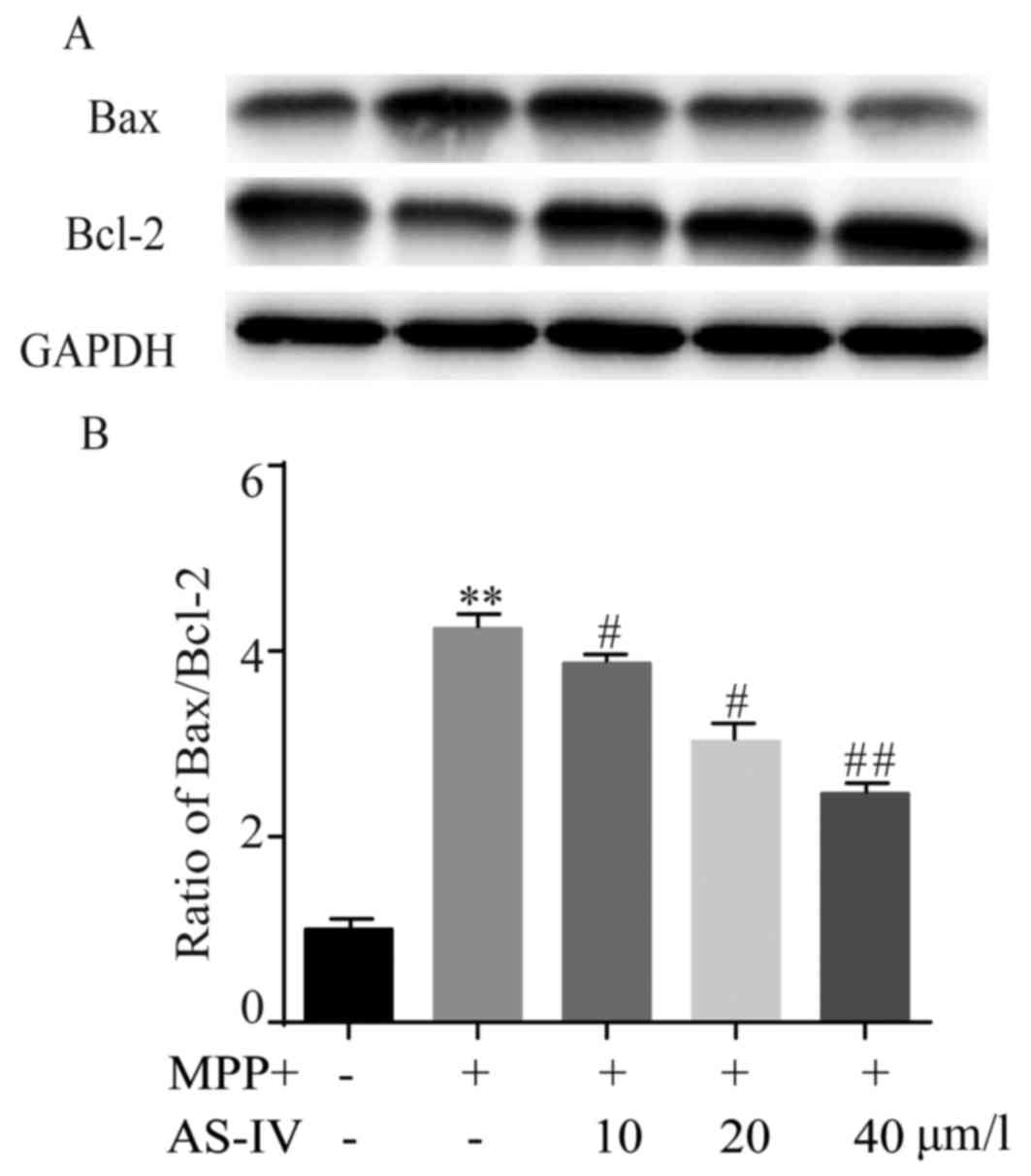
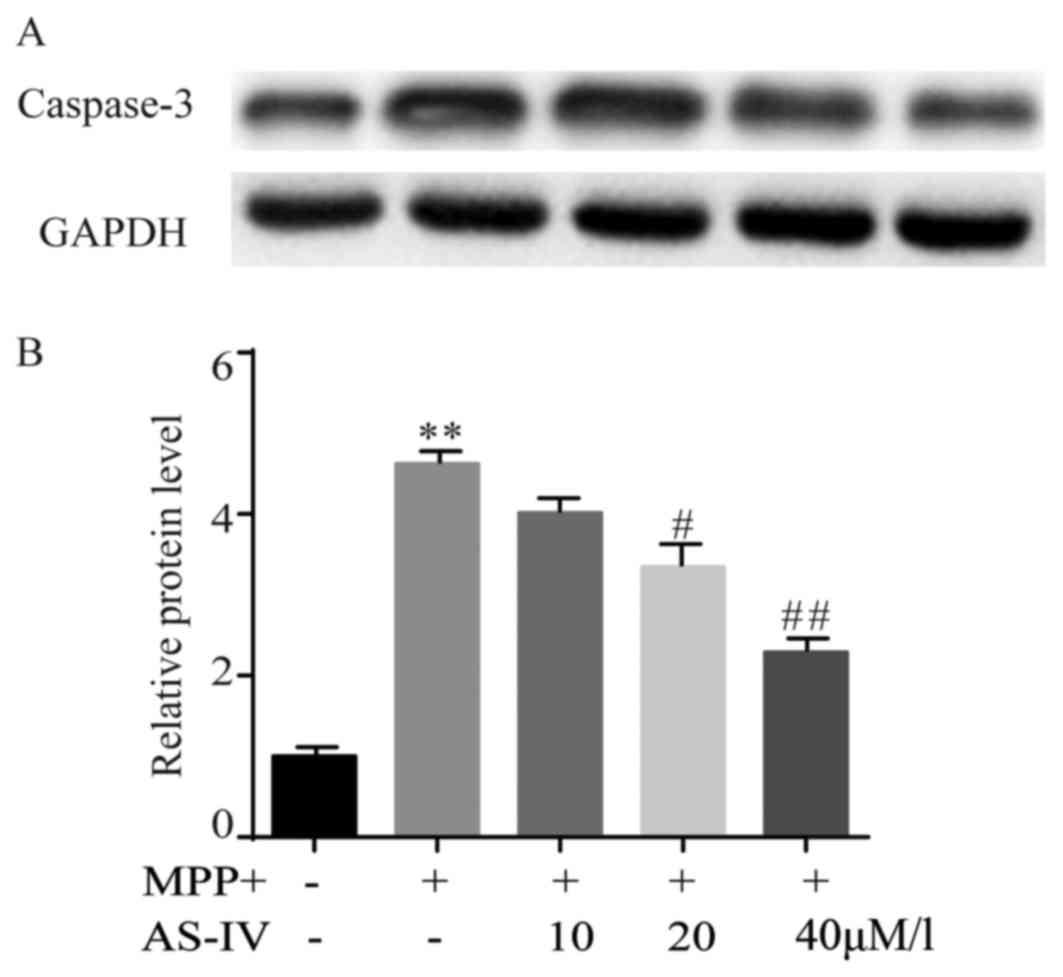
|
1
|
Franco-Iborra S, Vila M and Perier C: The
Parkinson disease mitochondrial hypothesis: Where are we at?
Neuroscientist. 22:266–277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Camilleri A and Vassallo N: The centrality
of mitochondria in the pathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson's
disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 20:591–602. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sanchez-Guajardo V, Tentillier N and
Romero-Ramos M: The relation between α-synuclein and microglia in
Parkinson's disease: Recent developments. Neuroscience. 302:47–58.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xie A, Gao J, Xu L and Meng D: Shared
mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and
Parkinson's disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014:6487802014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Takeuchi H, Mizuno T, Zhang G, Wang J,
Kawanokuchi J, Kuno R and Suzumura A: Neuritic beading induced by
activated microglia is an early feature of neuronal dysfunction
toward neuronal death by inhibition of mitochondrial respiration
and axonal transport. J Biol Chem. 280:10444–10454. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo Y, Qin Z, Hong Z, Zhang X, Ding D, Fu
JH, Zhang WD and Chen J: Astragaloside IV protects against ischemic
brain injury in a murine model of transient focal ischemia.
Neurosci Lett. 363:218–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qiu YY, Zhu JX, Bian T, Gao F, Qian XF, Du
Q, Yuan MY, Sun H, Shi LZ and Yu MH: Protective effects of
astragaloside IV against ovalbumin-induced lung inflammation are
regulated/mediated by T-bet/GATA-3. Pharmacology. 94:51–59. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qiu L, Yin G, Cheng L, Fan Y, Xiao W, Yu
G, Xing M, Jia R, Sun R, Ma X, et al: Astragaloside IV ameliorates
acute pancreatitis in rats by inhibiting the activation of nuclear
factor-κB. Int J Mol Med. 35:625–636. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang WD, Zhang C, Liu RH, Li HL, Zhang
JT, Mao C, Moran S and Chen CL: Preclinical pharmacokinetics and
tissue distribution of a natural cardioprotective agent
astragaloside IV in rats and dogs. Life Sci. 79:808–815. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seifert G, Schilling K and Steinhauser C:
Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: A molecular
perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:194–206. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kobayashi K, Hayashi M, Nakano H, Fukutani
Y, Sasaki K, Shimazaki M and Koshino Y: Apoptosis of astrocytes
with enhanced lysosomal activity and oligodendrocytes in white
matter lesions in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol.
28:238–251. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Szydlowska K, Zawadzka M and Kaminska B:
Neuroprotectant FK506 inhibits glutamate-induced apoptosis of
astrocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 99:965–975. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee J, Ziering A, Heineman SD and Berger
L: Piperidine derivatives; 2-phenyl- and 2-phenylalkyl-piperidines.
J Org Chem. 12:885–893. 1947. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pereira E A C and Aziz T Z: Parkinson's
disease and primate research: past, present, and future.
Postgraduate medical journal. 82:293–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Porras G, Li Q and Bezard E: Modeling
Parkinson's disease in primates: the MPTP model. Cold Spring Harbor
perspectives in medicine. 2:a0093082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seniuk NA, Tatton WG and Greenwood CE:
Dose-dependent destruction of the coeruleus-cortical and
nigral-striatal projections by MPTP. Brain Res. 527:7–20. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hantraye P, Varastet M, Peschanski M,
Riche D, Cesaro P, Willer JC and Maziere M: Stable parkinsonian
syndrome and uneven loss of striatal dopamine fibres following
chronic MPTP administration in baboons. Neuroscience. 53:169–178.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Przedborski S and Jackson-Lewis V:
Mechanisms of MPTP toxicity. Mov Disord. 13 Suppl 1:S35–S38.
1998.
|
|
19
|
Dauer W and Przedborski S: Parkinson's
disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron. 39:889–909. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogawa N, Hirose Y, Ohara S, Ono T and
Watanabe Y: A sireple quantitative hradykinesia test in MPIP
treated mice. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 50:435–441.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kubara H, Higuchi Y and Tadokoro S:
Effects of central depressants on rota-rod and action performances
in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol. 27:117–126. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Donnan GA, Willjs GL, Kaczmarczyk SJ and
Rowe P: Motor function in the l,
methyl-4-phenyl-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine treated mouse. J Neurol
Sci. 77:185–191. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dickens M, Rogers JS, Cavanagh J, Raitano
A, Xia Z, Halpern JR, Greenberg ME, Sawyers CL and Davis RJ: A
cytoplasmic inhibitor of the JNK signal transduction pathway.
Science. 277:693–696. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saporito MS, Thomas BA and Scott RW: MPTP
activates c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) and its upstream
regulatory kinase MKK4 in nigrostriatal neurons in vivo. J
Neurochem. 75:1200–1208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia XG, Harding T, Weller M, Bieneman A,
Uney JB and Schulz JB: Gene transfer of the JNK interacting
protein-1 protects dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP model of
Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:pp. 10433–10438.
2001, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lotharius J, Falsig J, van Beek J, Payne
S, Dringen R, Brundin P and Leist M: Progressive degeneration of
human mesencephalic neuron-derived cells triggered by
dopamine-dependent oxidative stress is dependent on the
mixed-lineage kinase pathway. J Neurosci. 25:6329–6342. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Findley HW, Gu L, Yeager AM and Zhou M:
Expression and regulation of Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, and Bax correlate with
p53 status and sensitivity to apoptosis in childhood acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 89:2986–2993. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mandir AS, Przedborski S, JacksonLewis V,
Wang ZQ, Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Smulson ME, Hoffman BE, Guastella
DB, Dawson VL and Dawson TM: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation
mediates 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
(MPTP)-induced parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:pp.
5774–5779. 1999, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
O'Malley KL, Liu J, Lotharius J and Holtz
W: Targeted expression of BCL-2 attenuates MPP+ but not 6-OHDA
induced cell death in dopaminergic neurons. Neurobiol Dis.
14:43–51. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Blum D, Torch S, Lambeng N, Nissou M,
Benabid AL, Sadoul R and Verna JM: Molecular pathways involved in
the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP: Contribution to the
apoptotic theory in Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol.
65:135–172. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Salvesen GS: Caspases: Opening the boxes
and interpreting the arrows. Cell Death Differ. 9:3–5. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B,
Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ and
Los M: Apoptosis and cancer: Mutations within caspase genes. J Med
Genet. 46:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang ZG, Wu L, Wang JL, Yang JD, Zhang J,
Zhang J, Li LH, Xia Y, Yao LB, Qin HZ and Gao GD: Astragaloside IV
prevents MPP+-induced SH-SY5Y cell death via the inhibition of
Bax-mediated pathways and ROS production. Mol Cell Biochem.
364:209–216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|