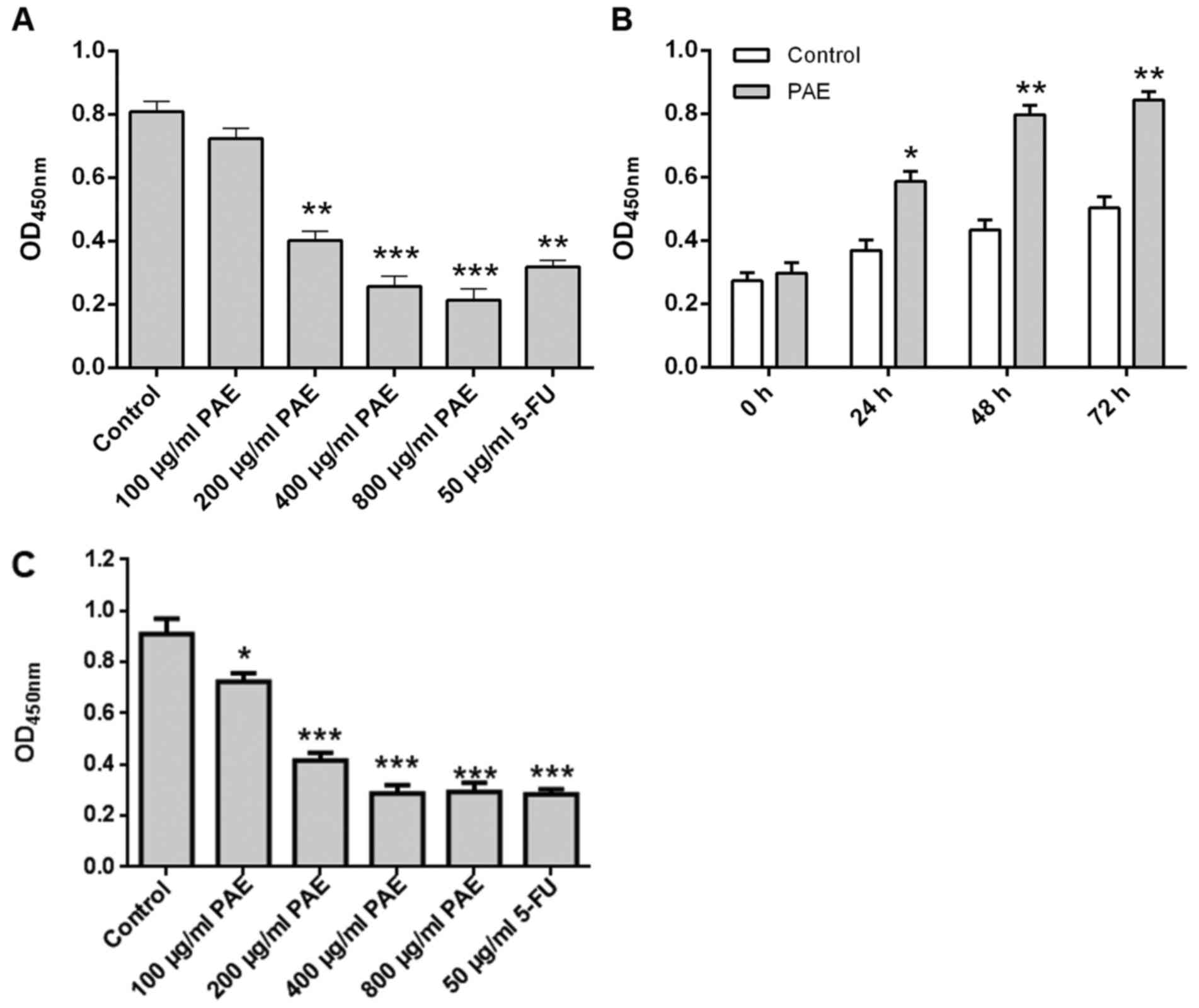
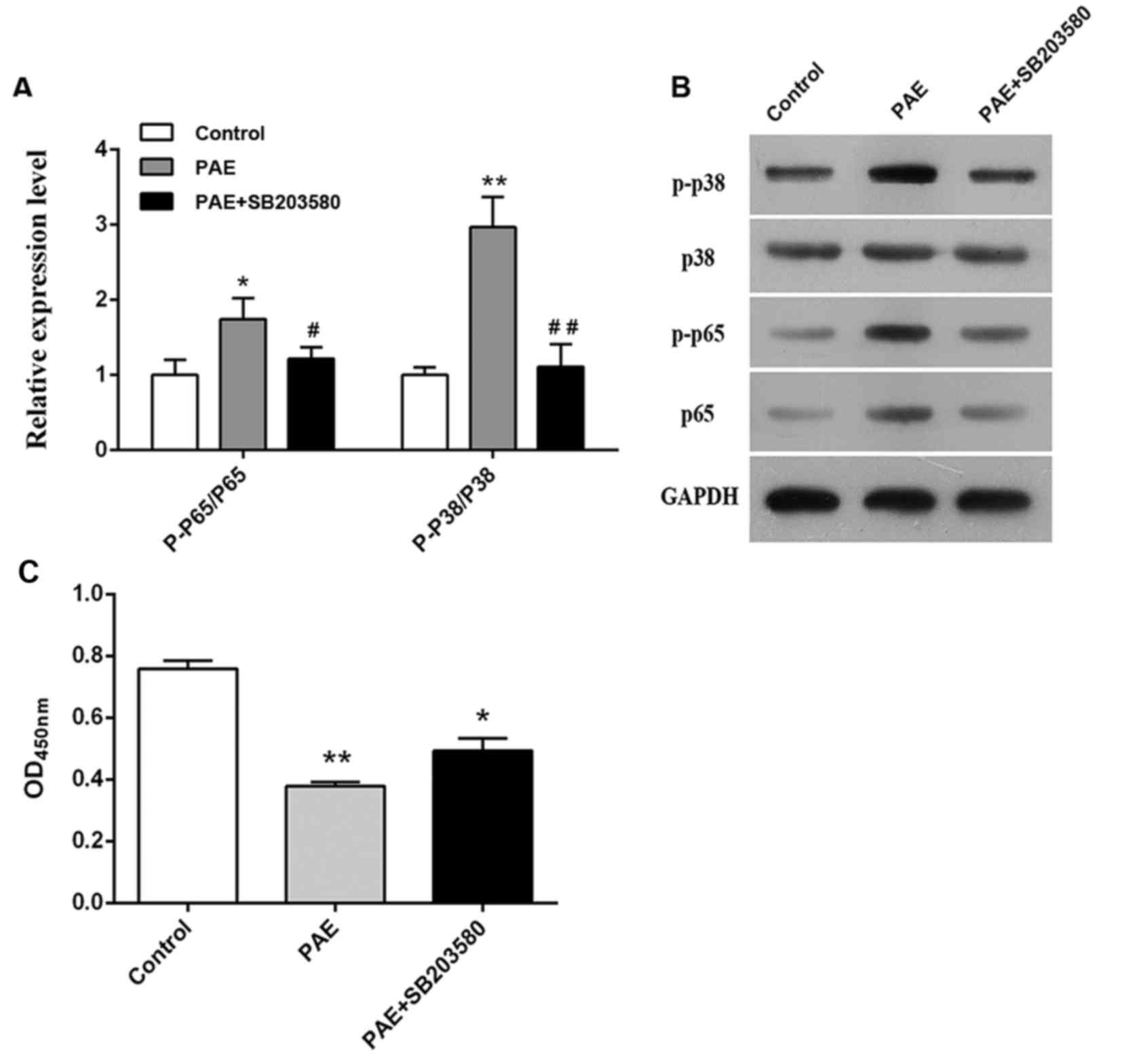
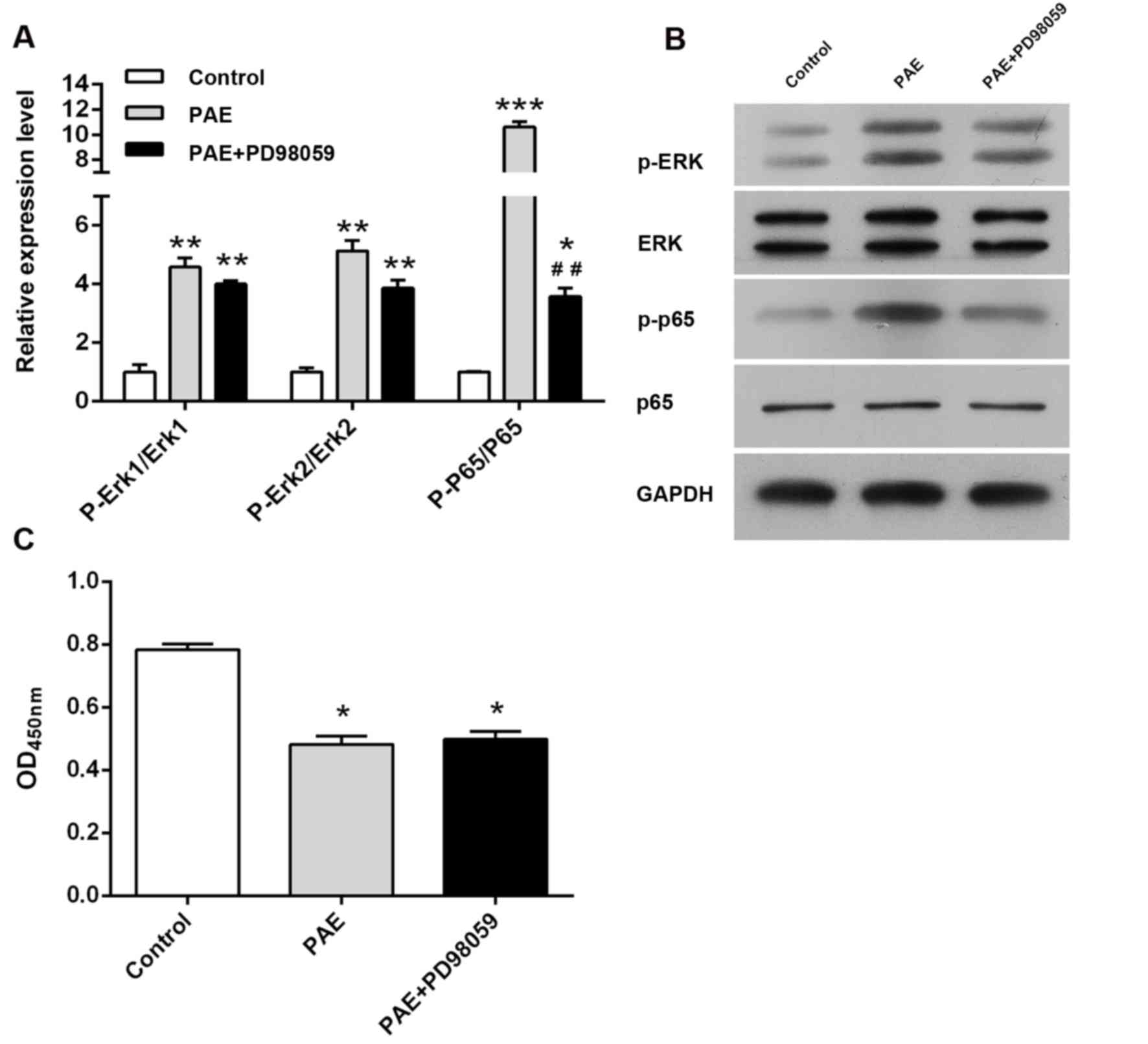
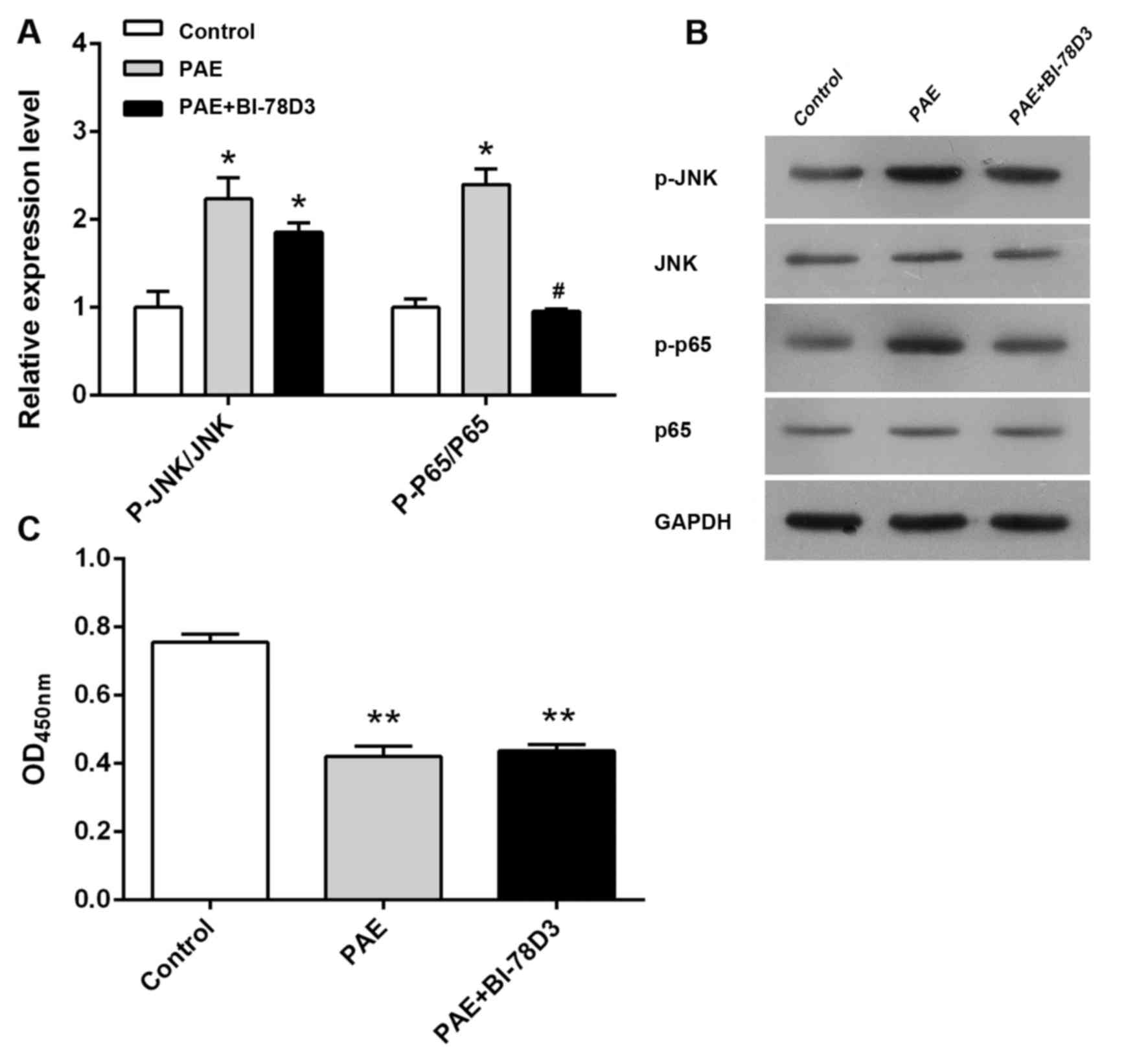
|
1
|
Fatima I, Chandra V, Saxena R, Sanghani Y,
Hajela K, Negi MP, Sankhwar PL, Jain SK and Dwivedi A:
2,3-diaryl-2H-1-benzopyran derivatives interfere with classical and
non-classical estrogen receptor signaling pathways, inhibit akt
activation and induce apoptosis in human endometrial cancer cells.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 348:198–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alteri R, Bertaut T, Brooks D, et al:
Cancer Facts and Figures 2016. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer
Society; 2016
|
|
3
|
Horan TC, Zompa MA, Seto CT, Kim KK, Moore
RG and Lange TS: Description of the cytotoxic effect of a novel
drug abietyl-isothiocyanate on endometrial cancer cell lines.
Invest New Drugs. 30:1460–1470. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fleming GF: Systemic chemotherapy for
uterine carcinoma: Metastatic and adjuvant. J Clin Oncol.
25:2983–2990. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singapore Cancer Network (SCAN)
Gynaecological Cancers Systemic Therapy Workgroup: Singapore cancer
network (SCAN) guidelines for the systemic therapy of endometrial
(uterine) cancer. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 44:434–439.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thigpen JT, Brady MF, Homesley HD,
Malfetano J, DuBeshter B, Burger RA and Liao S: Phase III trial of
doxorubicin with or without cisplatin in advanced endometrial
carcinoma: A gynecologic oncology group study. J Clin Oncol.
22:3902–3908. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li H and Narahara H: 15-Deoxy-Δ(12,
14)-prostaglandin j (2) induces growth inhibition, cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in human endometrial cancer cell lines. Int J
Mol Med. 31:778–788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu H, Li W, Wang T, Shu Y and Liu P:
Paeoniflorin suppress NF-κB activation through modulation of I
kappaB alpha and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in human
gastric carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 62:659–666. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang X, Duan X, Yang G, Zhang X, Deng L,
Zheng H, Deng C, Wen J, Wang N, Peng C, et al: Honokiol crosses BBB
and BCSFB, and inhibits brain tumor growth in rat 9L intracerebral
gliosarcoma model and human U251 xenograft glioma model. PLoS One.
6:e184902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang S, Zhu W, Zhang Y, Shu Y and Liu P:
Paeoniflorin modulates multidrug resistance of a human gastric
cancer cell line via the inhibition of NF-κB activation. Mol Med
Rep. 5:351–356. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nie XH, Ou-yang J, Xing Y, Li DY, Dong XY,
Liu RE and Xu RX: Paeoniflorin inhibits human glioma cells via
STAT3 degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:5611–5622. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Dou W, Zhang E, Sun A, Ding L,
Wei X, Chou G, Mani S and Wang Z: Paeoniflorin abrogates
DSS-induced colitis via a TLR4-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 306:G27–G36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gan Y, Cui X, Ma T, Liu Y, Li A and Huang
M: Paeoniflorin upregulates β-defensin-2 expression in human
bronchial epithelial cell through the p38 MAPK, ERK, and NF-κB
signaling pathways. Inflammation. 37:1468–1475. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee B, Shin YW, Bae EA, Han SJ, Kim JS,
Kang SS and Kim DH: Antiallergic effect of the root of Paeonia
lactiflora and its constituents paeoniflorin and paeonol. Arch
Pharm Res. 31:445–450. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen T, Guo ZP, Wang L, Qin S, Cao N, Li
MM, Jia RZ and Wang TT: Paeoniflorin suppresses vascular damage and
the expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1 in a mouse model of
cutaneous arthus reaction. Exp Dermatol. 22:453–457. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu H, Wei W, Song L, Zhang L, Chen Y and
Hu X: Paeoniflorin induced immune tolerance of mesenteric lymph
node lymphocytes via enhancing beta 2-adrenergic receptor
desensitization in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 7:662–673. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He DY and Dai SM: Anti-inflammatory and
immunomodulatory effects of Paeonia lactiflora pall., a
traditional chinese herbal medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2:102011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dong H, Li R, Yu C, Xu T, Zhang X and Dong
M: Paeoniflorin inhibition of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis
in PC12 cells via suppressing reactive oxygen species-mediated
pkcdelta/NF-κB pathway. Neuroscience. 285:70–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hung JY, Yang CJ, Tsai YM, Huang HW and
Huang MS: Antiproliferative activity of paeoniflorin is through
cell cycle arrest and the FAS/FAS ligand-mediated apoptotic pathway
in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 35:141–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu JT, He W, Song SS and Wei W:
Paeoniflorin inhibited the tumor invasion and metastasis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bratisl Lek Listy. 115:427–433.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Zhou H, Wang CX, Li YS, Xie HY,
Luo JD and Zhou Y: Paeoniflorin inhibits growth of human colorectal
carcinoma HT 29 cells in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:1560–1567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Qi Z, Wei Z, Liu S, Wang P, Chen Y
and Zhao Y: Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and induces
apoptosis of human glioma cells via microRNA-16 upregulation and
matrix metalloproteinase-9 downregulation. Mol Med Rep.
12:2735–2740. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim JY, Lee SG, Chung JY, Kim YJ, Park JE,
Oh S, Lee SY, Choi HJ, Yoo YH and Kim JM: 7,
12-Dimethylbenzanthracene induces apoptosis in RL95-2 human
endometrial cancer cells: Ligand-selective activation of cytochrome
P450 1B1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 260:124–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li W, Fan M, Chen Y, Zhao Q, Song C, Yan
Y, Jin Y, Huang Z, Lin C and Wu J: Melatonin induces cell apoptosis
in AGS cells through the activation of JNK and P38 MAPK and the
suppression of nuclear factor-Kappa B: A novel therapeutic
implication for gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:2323–2338.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khandrika L, Lieberman R, Koul S, Kumar B,
Maroni P, Chandhoke R, Meacham RB and Koul HK: Hypoxia-associated
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated androgen receptor
activation and increased HIF-1alpha levels contribute to emergence
of an aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer. Oncogene.
28:1248–1260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai PW, Shiah SG, Lin MT, Wu CW and Kuo
ML: Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor C in breast
cancer cells by heregulin-beta 1. A critical role of p38/nuclear
factor-kappa B signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 278:5750–5759. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iyoda K, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Toyama T,
Yakushijin T, Sakakibara M, Takehara T, Fujimoto J, Hori M, Wands
JR and Hayashi N: Involvement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 97:3017–3026.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koul HK, Pal M and Koul S: Role of p38 MAP
kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes Cancer.
4:342–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Greten FR and Karin M: The IKK/NF-kappaB
activation pathway-a target for prevention and treatment of cancer.
Cancer Lett. 206:193–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Wu M, Jiang H, Hao J, Zhang Q,
Zhu Q, Saren G, Zhang Y, Meng X and Yue X: Angiotensin II
upregulates endothelial lipase expression via the NF-kappa B and
MAPK signaling pathways. PLoS One. 9:e1076342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Van Waes C: Nuclear factor-kappa B in
development, prevention and therapy of cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:1076–1082. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li J, Jia H, Xie L, Wang X, Wang X, He H,
Lin Y and Hu L: Association of constitutive nuclear factor-KappaB
activation with aggressive aspects and poor prognosis in cervical
cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:1421–1426. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|