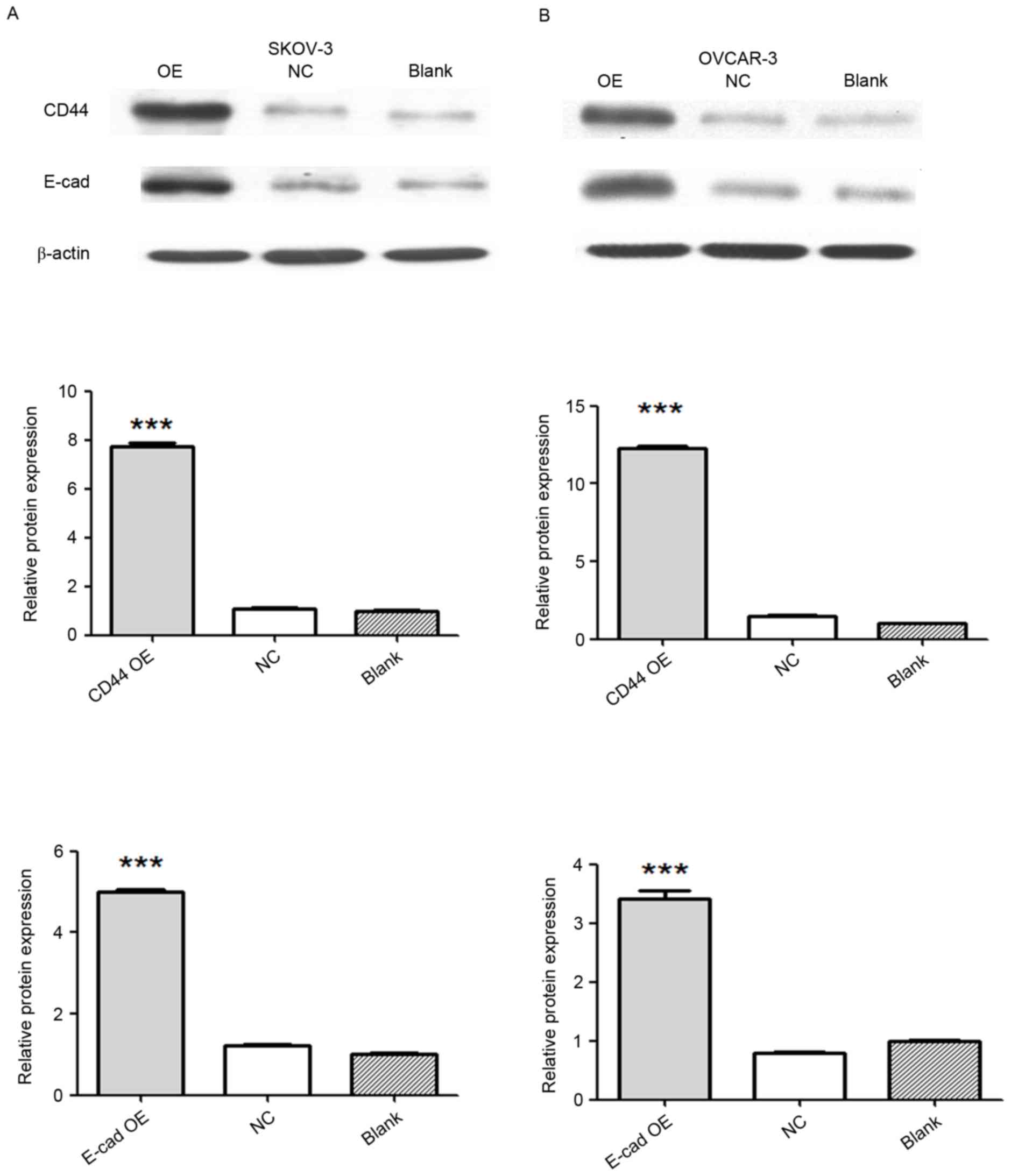
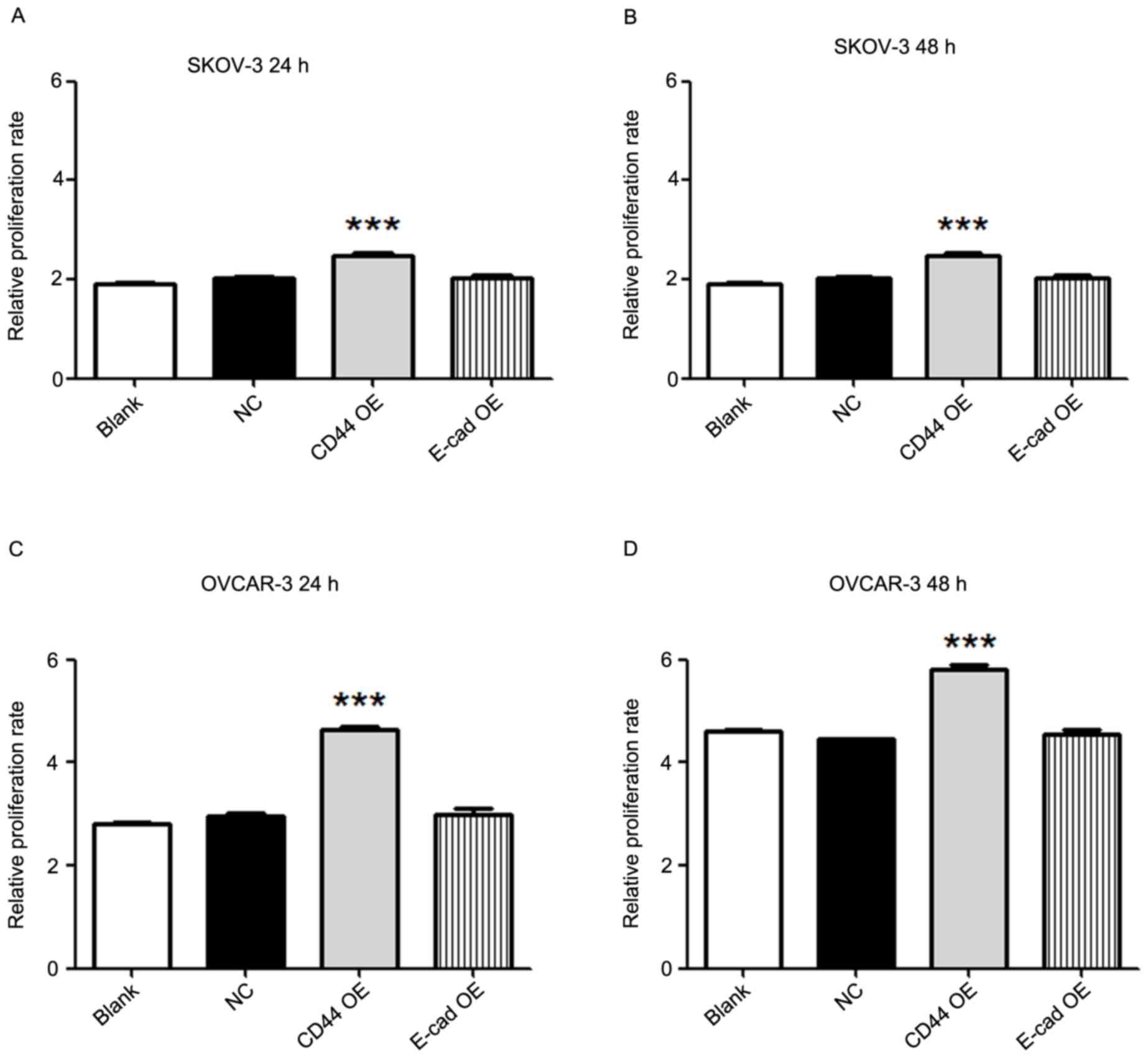
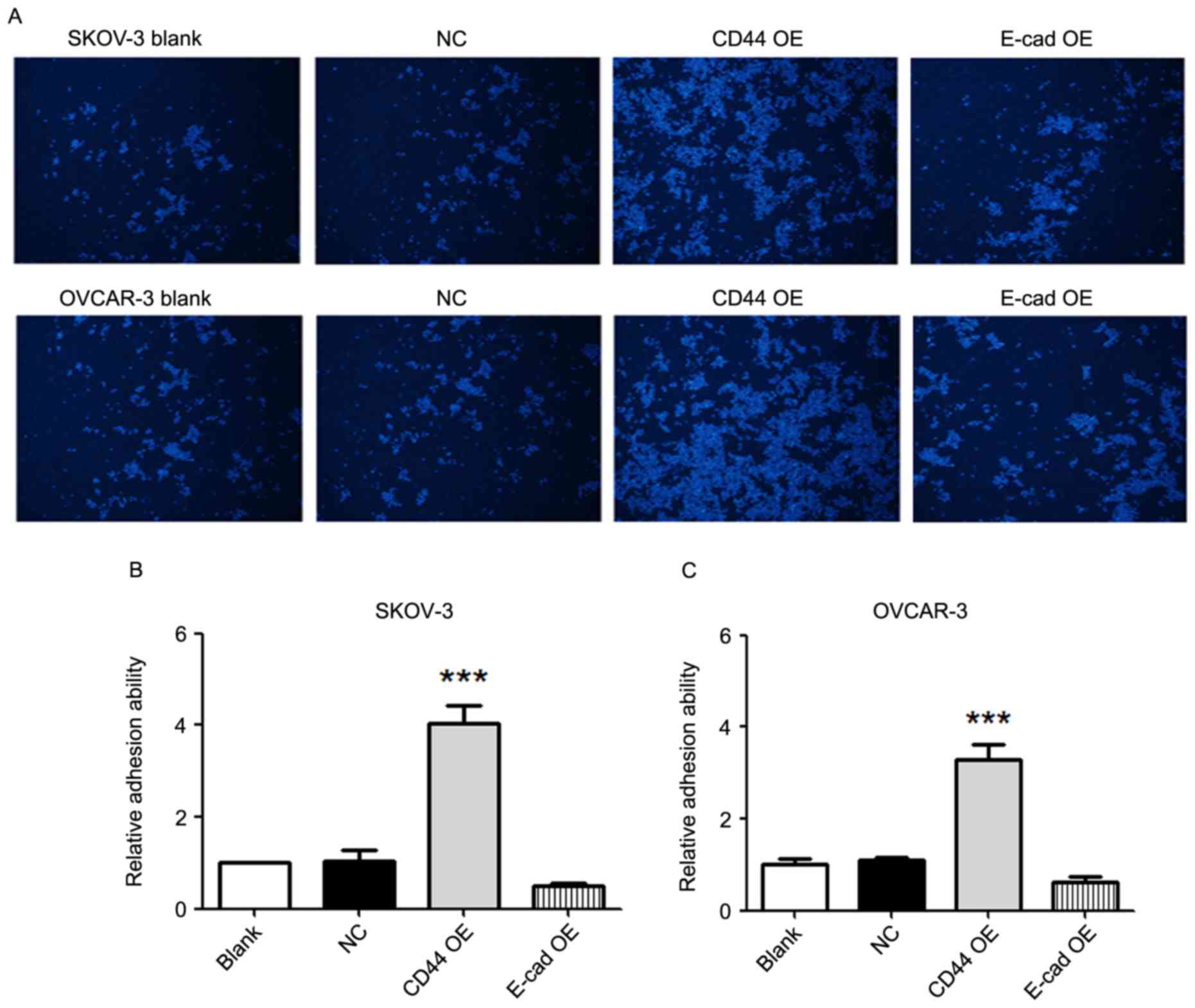
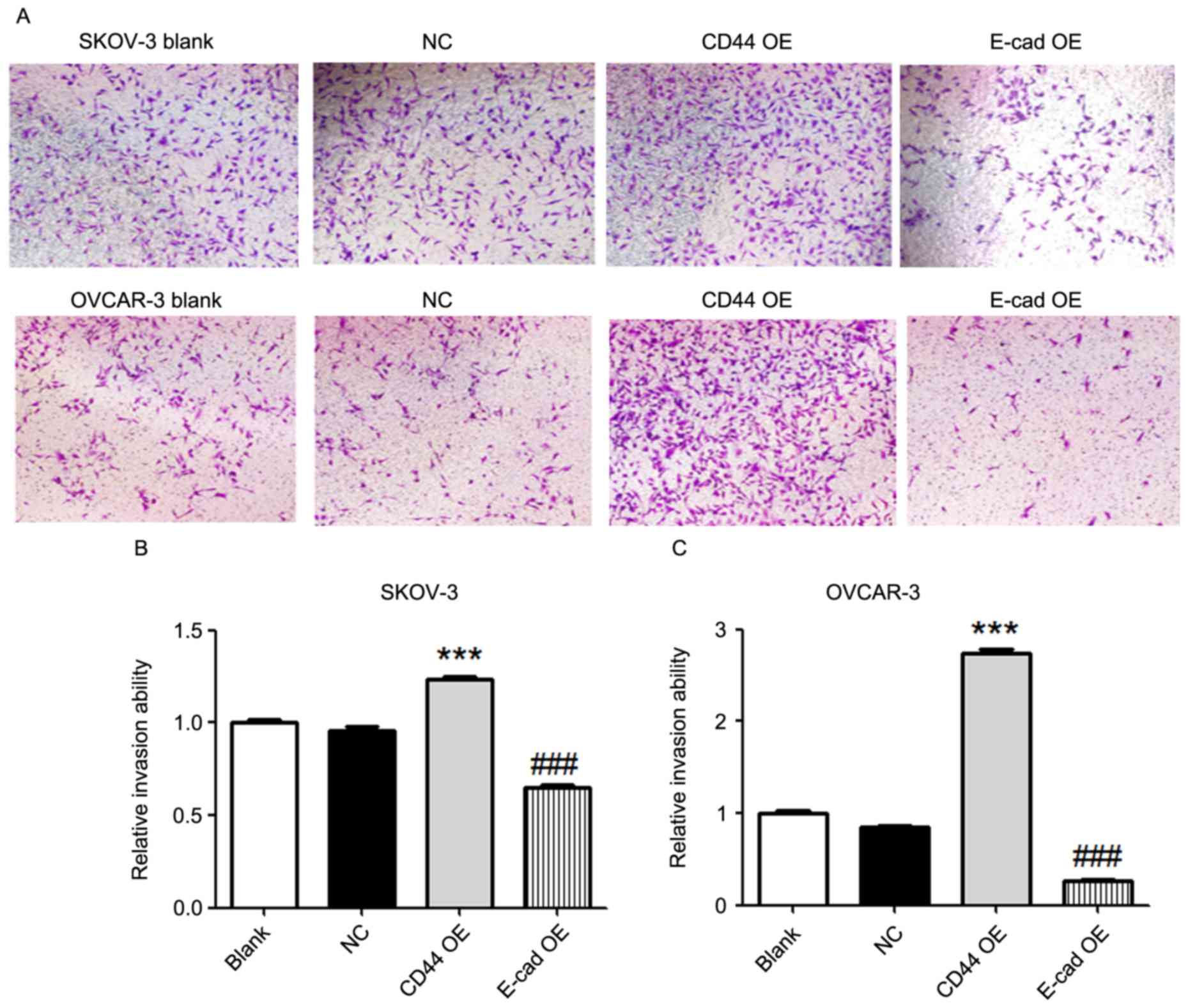
|
1
|
Auersperg N, Wong AS, Choi KC, Kang SK and
Leung PC: Ovarian surface epithelium: Biology, endocrinology, and
pathology. Endocr Rev. 22:255–288. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jia Q, Feng M, Wang Y and Xue S: Gastric
cancer cells in collagen gel matrix: Three-dimensional growth and
differential expression of adhesion molecules (CD44s, CD54,
E-cadherin). J Biomed Mater Res A. 84:917–925. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karan Križanac D, Krasić Arapović A,
Skočibušić S, Pintarić I, Trgo G and Tomić S: CD44 Immunoexpression
is unfavorable predictor in ovarian serous cancer. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. Aug 3–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
5
|
Shi YY and Jiang H: Prognostic role of the
cancer stem cell marker CD44 in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis.
Genet Mol Res. doi: 10.4238/gmr.15038325.
|
|
6
|
Sosulski A, Horn H, Zhang L, Coletti C,
Vathipadiekal V, Castro CM, Birrer MJ, Nagano O, Saya H, Lage K, et
al: CD44 Splice Variant v8-10 as a marker of serous ovarian cancer
prognosis. PLoS One. 11:e01565952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Elzarkaa AA, Sabaa BE, Abdelkhalik D,
Mansour H, Melis M, Shaalan W, Farouk M, Malik E and Soliman AA:
Clinical relevance of CD44 surface expression in advanced stage
serous epithelial ovarian cancer: A prospective study. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 142:949–958. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Juan W, Shan K, Na W, Rong-Miao Z and Yan
L: The associations of genetic variants in E-cadherin gene with
clinical outcome of epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 26:1601–1607. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trillsch F, Kuerti S, Eulenburg C, Burandt
E, Woelber L, Prieske K, Eylmann K, Oliveira-Ferrer L,
Milde-Langosch K and Mahner S: E-Cadherin fragments as potential
mediators for peritoneal metastasis in advanced epithelial ovarian
cancer. Br J Cancer. 114:213–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Henic E, Noskova V, Høyer-Hansen G,
Hansson S and Casslén B: Estradiol attenuates EGF-induced rapid
uPAR mobilization and cell migration via the G-protein-coupled
receptor 30 in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
19:214–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banerjee S and Kaye SB: New strategies in
the treatment of ovarian cancer: Current clinical perspectives and
future potential. Clin Cancer Res. 19:961–968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lengyel E: Ovarian cancer development and
metastasis. Am J Pathol. 177:1053–1064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vos MC, Hollemans E, Ezendam N, Feijen H,
Boll D, Pijlman B, van der Putten H, Klinkhamer P, van Kuppevelt
TH, van der Wurff AA and Massuger LF: MMP-14 and CD44 in
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in ovarian cancer. J
Ovarian Res. 9:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao Y, Foster R, Yang X, Feng Y, Shen JK,
Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Amiji MM and Duan Z: Up-regulation of CD44
in the development of metastasis, recurrence and drug resistance of
ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 6:9313–9326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu KH, Tsai HW, Lin PW, Hsu YS, Shan YS
and Lu PJ: Osteopontin expression is an independent adverse
prognostic factor in resectable gastrointestinal stromal tumor and
its interaction with CD44 promotes tumor proliferation. Ann Surg
Oncol. 17:3043–3052. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu B, Sondag GR, Malcuit C, Kim MH and
Safadi FF: Macrophage-Associated Osteoactivin/GPNMB Mediates
Mesenchymal stem cell survival, proliferation, and migration via a
CD44-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 117:1511–1521. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nam K, Oh S, Lee KM, Yoo SA and Shin I:
CD44 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via
modulation of c-Src transcription in human breast cancer cells.
Cell Signal. 27:1882–1894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miše BP, Telesmanić VD, Tomić S, Šundov D,
Čapkun V and Vrdoljak E: Correlation between E-cadherin
Immunoexpression and efficacy of first line platinum-based
chemotherapy in advanced high grade serous ovarian cancer. Pathol
Oncol Res. 21:347–356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu X, Cheng JC, Klausen C, Fan Q, Chang
HM, So WK and Leung PC: Transforming growth factor-α induces human
ovarian cancer cell invasion by down-regulating E-cadherin in a
Snail-independent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 461:128–135.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao J, Klausen C, Qiu X, Cheng JC, Chang
HM and Leung PC: Betacellulin induces Slug-mediated down-regulation
of E-cadherin and cell migration in ovarian cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:28881–28890. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|