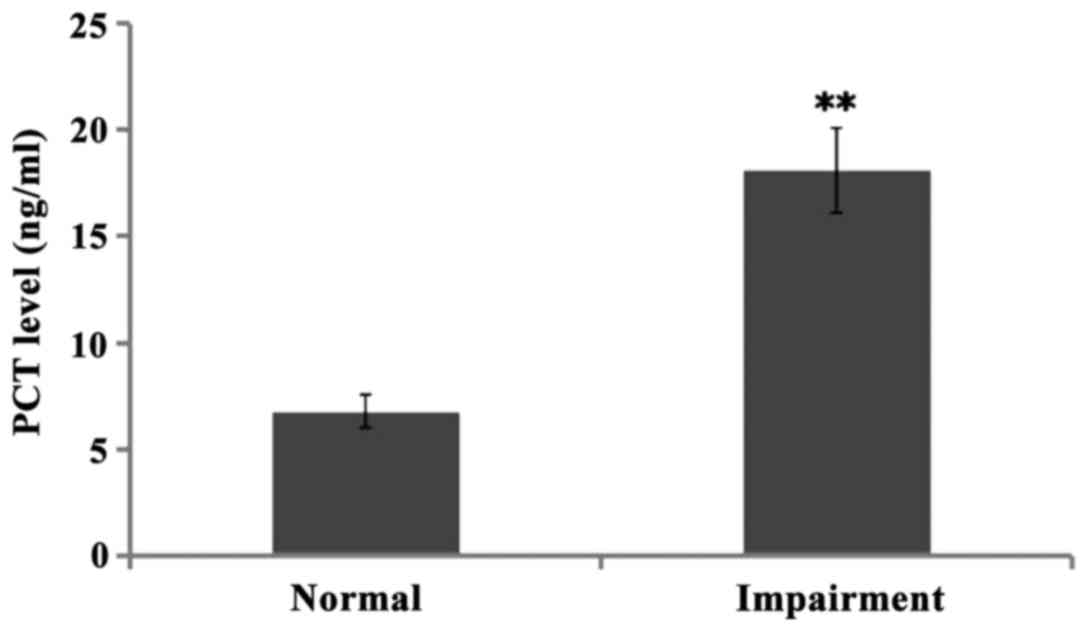
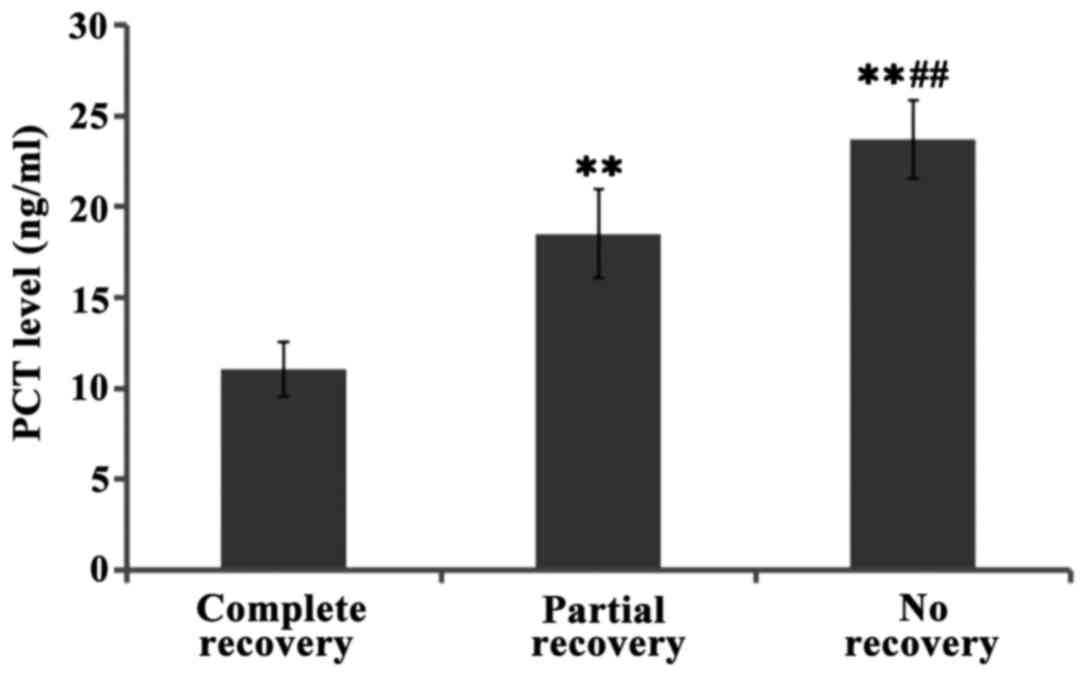
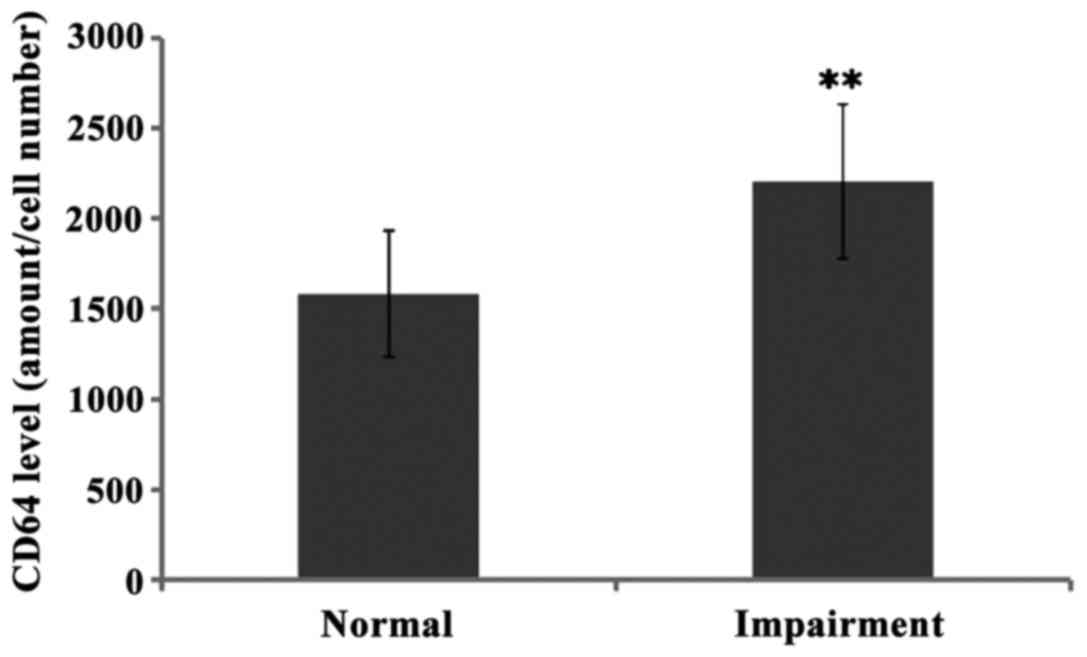
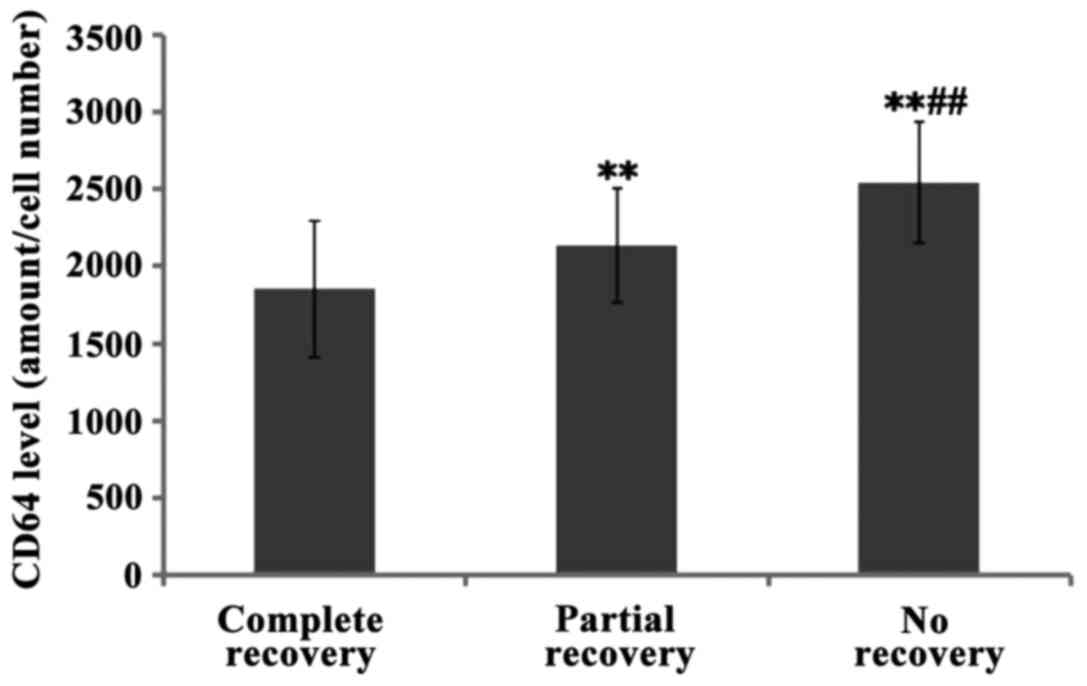
|
1
|
Kim KS: Pathogenesis of bacterial
meningitis: From bacteraemia to neuronal injury. Nat Rev Neurosci.
4:376–385. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mook-Kanamori BB, Geldhoff M, van der Poll
T and van de Beek D: Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of
pneumococcal meningitis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 24:557–591. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Sánchez PJ, Faix RG,
Poindexter BB, Van Meurs KP, Bizzarro MJ, Goldberg RN, Frantz ID
III, Hale EC, et al: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of
Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network: Early
onset neonatal sepsis: The burden of group B Streptococcal and
E. coli disease continues. Pediatrics. 127:817–826. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ku LC, Boggess KA and Cohen-Wolkowiez M:
Bacterial meningitis in infants. Clin Perinatol. 42:29–45. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim KS: Neonatal bacterial meningitis.
Neoreviews. 16:e535–e543. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
May M, Daley AJ, Donath S and Isaacs D:
Australasian Study Group for Neonatal Infections: Early onset
neonatal meningitis in Australia and New Zealand, 1992–2002. Arch
Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 90:F324–F327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaufman D, Zanelli S, Cantey JB and
Sánchez PJ: Neonatal meningitis: current treatment
optionsNeurology: Neonatology Questions and Controversies. Perlman
JMD: 2nd edition. Elsevier; Amsterdam: pp. 181–201. 2012
|
|
8
|
Holt DE, Halket S, de Louvois J and Harvey
D: Neonatal meningitis in England and Wales: 10 years on. Arch Dis
Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 84:F85–F89. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reading R: Meningitis in infancy in
England and Wales: Follow up at age 5 years. Child Care Health Dev.
28:533–536. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Stevens JP, Eames M, Kent A, Halket S,
Holt D and Harvey D: Long term outcome of neonatal meningitis. Arch
Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 88:F179–F184. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Furyk JS, Swann O and Molyneux E:
Systematic review: Neonatal meningitis in the developing world.
Trop Med Int Health. 16:672–679. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grimwood K: Legacy of bacterial meningitis
in infancy. Many children continue to suffer functionally important
deficits. BMJ. 323:523–524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klinger G, Chin CN, Beyene J and Perlman
M: Predicting the outcome of neonatal bacterial meningitis.
Pediatrics. 106:477–482. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bargui F, D'Agostino I, Mariani-Kurkdjian
P, Alberti C, Doit C, Bellier N, Morin L, Galli Gibertini G, Smail
A, Zanin A, et al: Factors influencing neurological outcome of
children with bacterial meningitis at the emergency department. Eur
J Pediatr. 171:1365–1371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ravetch JV: Fc receptors: Rubor redux.
Cell. 78:553–560. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fossati G, Bucknall RC and Edwards SW:
Fcgamma receptors in autoimmune diseases. Eur J Clin Invest.
31:821–831. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Du J, Li L, Dou Y, Li P, Chen R and Liu H:
Diagnostic utility of neutrophil CD64 as a marker for early-onset
sepsis in preterm neonates. PLoS One. 9:e1026472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chung JW, Park CJ, Cha CH, Cho YU, Jang S,
Chi HS, Seo EJ, Lee JH, Lee JH, Lee KH, et al: A combination of
CD15/CD10, CD64/CD33, CD16/CD13 or CD11b flow cytometric
granulocyte panels is sensitive and specific for diagnosis of
myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 42:271–280.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeune Simonin-Le K, Le Jeune A, Jouneau S,
Belleguic C, Roux PF, Jaguin M, Dimanche-Boitre MT, Lecureur V,
Leclercq C, Desrues B, et al: Impaired functions of macrophage from
cystic fibrosis patients: CD11b, TLR-5 decrease and sCD14,
inflammatory cytokines increase. PLoS One. 8:e756672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Konstantinidis T, Cassimos D, Gioka T,
Tsigalou C, Parasidis T, Alexandropoulou I, Nikolaidis C,
Kampouromiti G, Constantinidis T, Chatzimichael A, et al: Can
procalcitonin in cerebrospinal fluid be a diagnostic tool for
meningitis? J Clin Lab Anal. 29:169–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abdelkader NA, Mahmoud WA and Saber SM:
Serum procalcitonin in Egyptian patients with acute meningitis and
a negative direct cerebrospinal fluid examination. J Infect Public
Health. 7:106–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi HJ: Procalcitonin in diagnosis of
post-operative bacterial meningitis: A promising but limited role.
Infect Chemother. 45:346–348. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Viallon A, Desseigne N, Marjollet O,
Birynczyk A, Belin M, Guyomarch S, Borg J, Pozetto B, Bertrand JC
and Zeni F: Meningitis in adult patients with a negative direct
cerebrospinal fluid examination: value of cytochemical markers for
differential diagnosis. Crit Care. 15:R1362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|