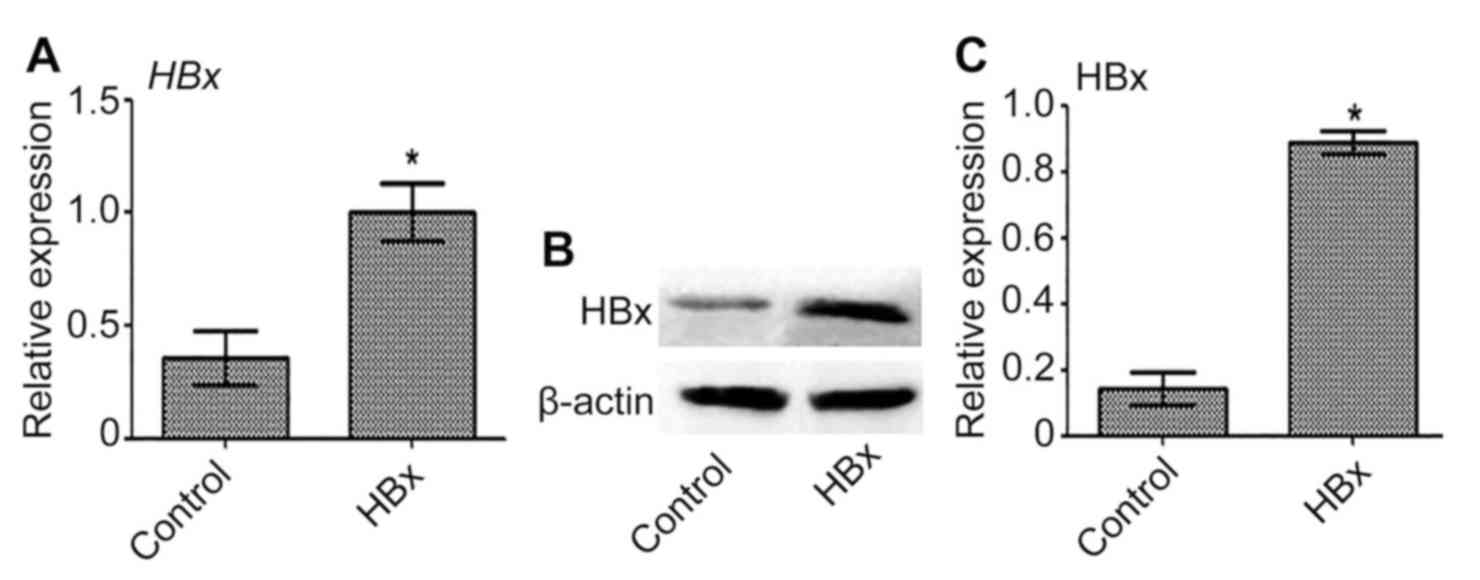
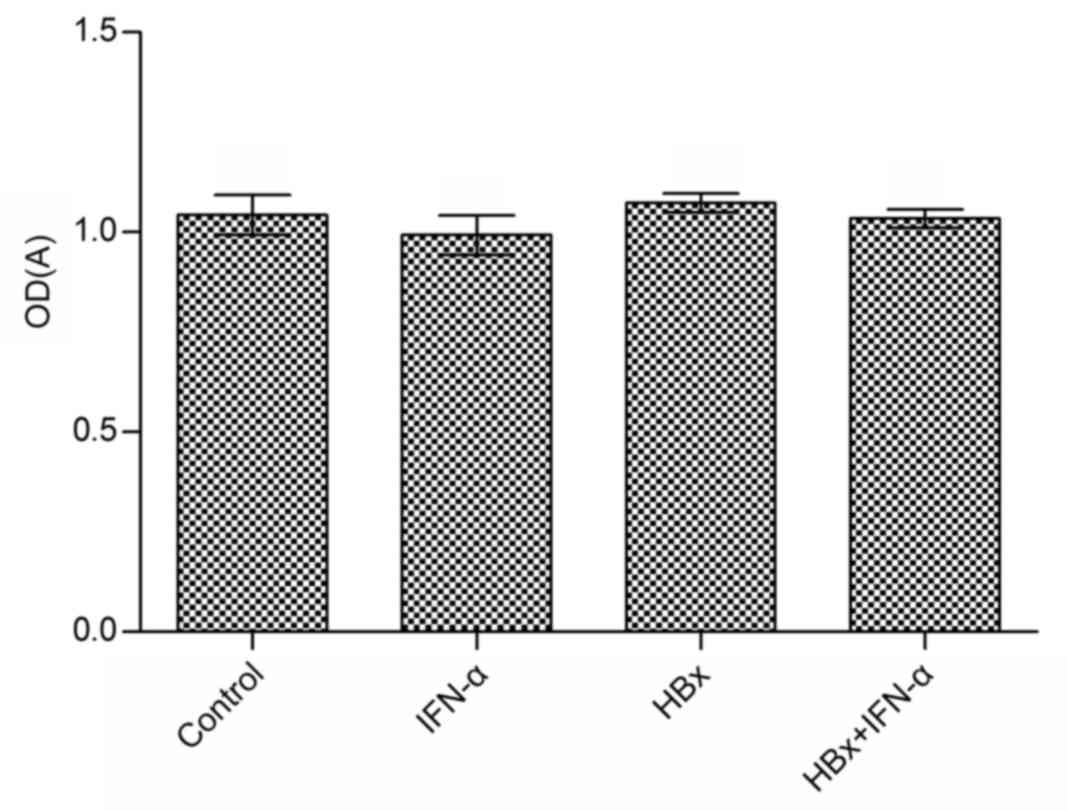
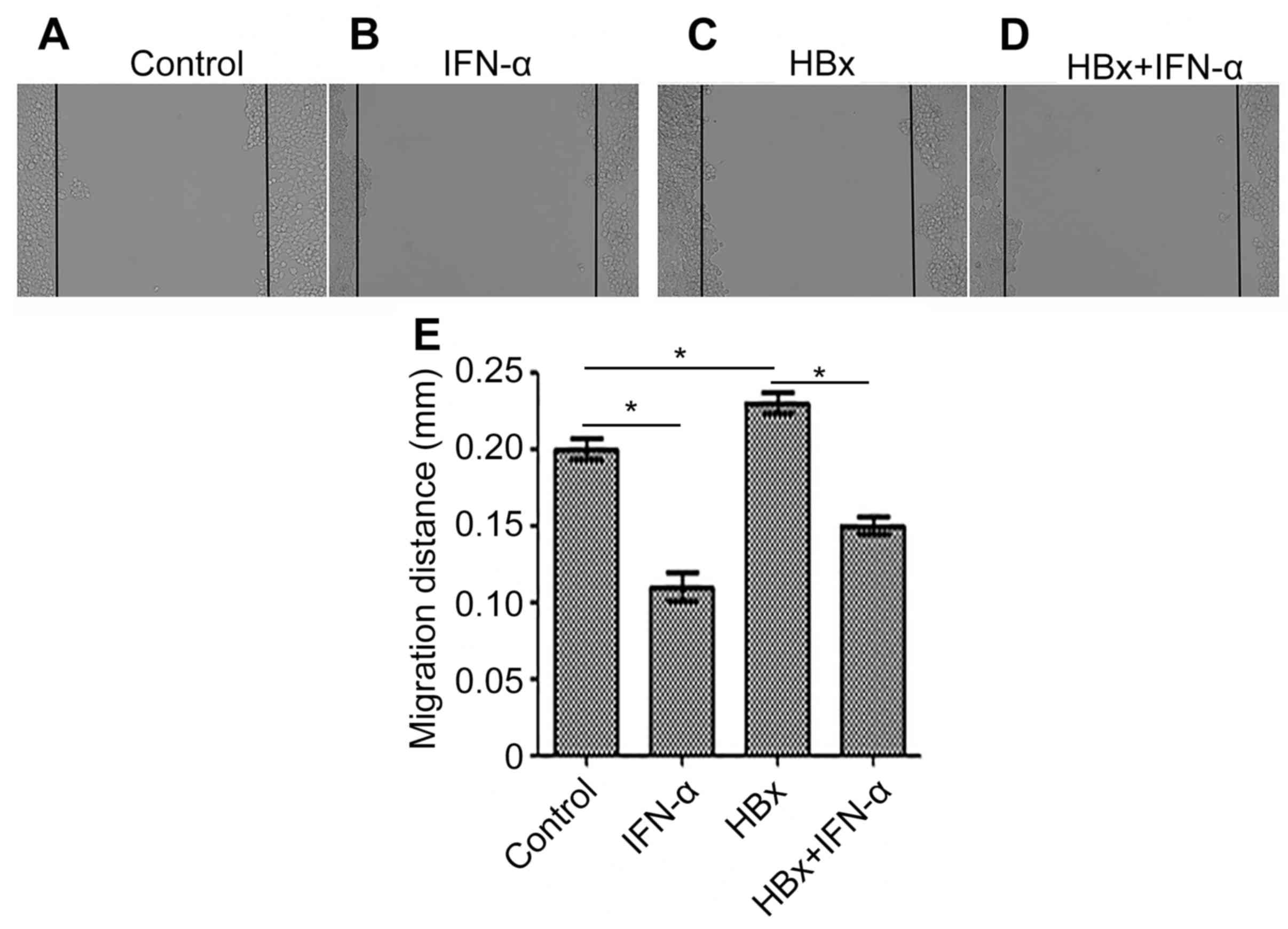
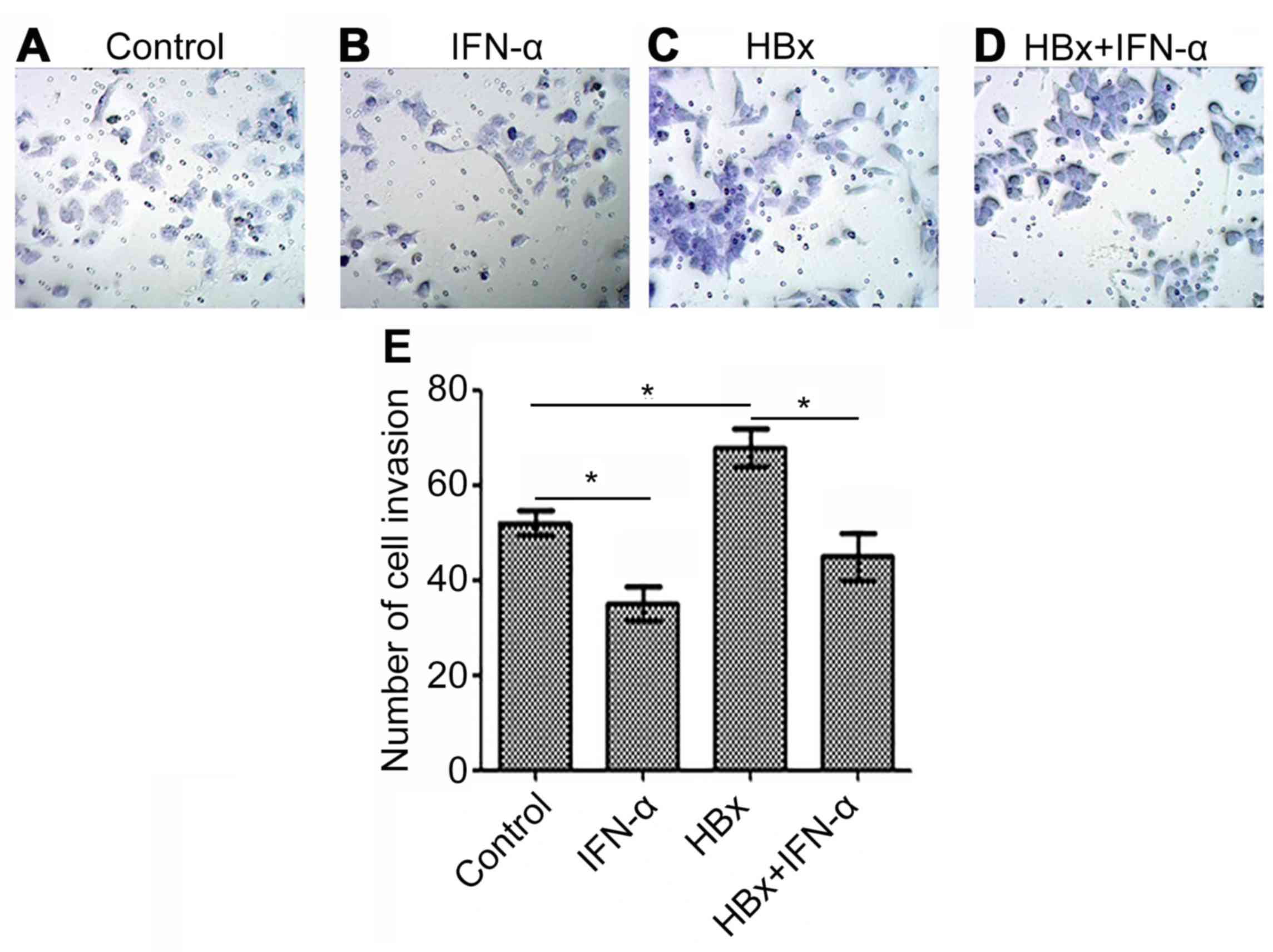
|
1
|
Lavanchy D: Hepatitis B virus
epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging
prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 11:97–107. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liaw YF and Chu CM: Hepatitis B virus
infection. Lancet. 373:582–592. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hooshyar A, Habibzadeh S, Ghasemi N,
Yazdanbod A, Sohrabi S, Maleki N and Amani F: Females have a lower
liver histopathological score in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B
than males. Arch Clin Infect Dis. 8:e179722013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang N and Bertoletti A: Advances in
therapeutics for chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Int. 10:277–285.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Zhao J, Chen L, Dong N, Ying Z,
Cai Z, Ji D, Zhang Y, Dong L, Li Y, et al: STAT1 modification
improves therapeutic effects of interferons on lung cancer cells. J
Transl Med. 13:2932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gerber SA, Yatsula B, Maier CL, Sadler TJ,
Whittaker LW and Pober JS: Interferon-gamma induces prolyl
hydroxylase (PHD)3 through a STAT1-dependent mechanism in human
endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1363–1369.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rehermann B and Bertoletti A:
Immunological aspects of antiviral therapy of chronic hepatitis B
virus and hepatitis C virus infections. Hepatology. 61:712–721.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bowick GC, Airo AM and Bente DA:
Expression of interferon-induced antiviral genes is delayed in a
STAT1 knockout mouse model of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever.
Virol J. 9:1222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
von Marschall Z, Scholz A, Cramer T,
Schäfer G, Schirner M, Oberg K, Wiedenmann B, Höcker M and Rosewicz
S: Effects of interferon alpha on vascular endothelial growth
factor gene transcription and tumor angiogenesis. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 95:437–448. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fazio N and Oberg K: Prospective,
randomized, multicenter trial on the antiproliferative effect of
lanreotide, interferon alfa and their combination for therapy of
metastatic neuroendocrine gastroenteropancreatic tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 22:573–575. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Palma M, Mazzieri R, Politi LS, Pucci
F, Zonari E, Sitia G, Mazzoleni S, Moi D, Venneri MA, Indraccolo S,
et al: Tumor-targeted interferon-alpha delivery by Tie2-expressing
monocytes inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Cell.
14:299–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JY, Song EH, Lee HJ, Oh YK, Choi KH,
Yu DY, Park SI, Seong JK and Kim WH: HBx-induced hepatic steatosis
and apoptosis are regulated by TNFR1- and NF-kappaB-dependent
pathways. J Mol Biol. 397:917–931. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang HY, Yang SL, Liang HF and Li CH: HBx
protein promotes oval cell proliferation by up-regulation of cyclin
D1 via activation of the MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:3507–3518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murakami S: Hepatitis B virus X protein: A
multifunctional viral regulator. J Gastroenterol. 36:651–660. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T and
Jay G: HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in
transgenic mice. Nature. 351:317–320. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lara-Pezzi E, Gomez-Gaviro MV, Galvez BG,
Mira E, Iñiguez MA, Fresno M, Martínez AC, Arroyo AG and
López-Cabrera M: The hepatitis B virus X protein promotes tumor
cell invasion by inducing membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1
and cyclooxygenase-2 expression. J Clin Invest. 110:1831–1838.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanaka Y, Kanai F, Kawakami T, Tateishi K,
Ijichi H, Kawabe T, Arakawa Y, Kawakami T, Nishimura T, Shirakata
Y, et al: Interaction of the hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) with
heat shock protein 60 enhances HBx-mediated apoptosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 318:461–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Liu S, Hu T, Liu S, He Y and Sun
S: Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B
enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin
expression. Hepatology. 50:490–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lizee G, Aerts JL, Gonzales MI, Chinnasamy
N, Morgan RA and Topalian SL: Real-time quantitative reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction as a method for determining
lentiviral vector titers and measuring transgene expression. Hum
Gene Ther. 14:497–507. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Frodsham AJ, Zhang L, Dumpis U, Taib NA,
Best S, Durham A, Hennig BJ, Hellier S, Knapp S, Wright M, et al:
Class II cytokine receptor gene cluster is a major locus for
hepatitis B persistence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 9148–9153.
2006, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou J, Smith DK, Lu L, Poon VK, Ng F,
Chen DQ, Huang JD, Yuen KY, Cao KY and Zheng BJ: A non-synonymous
single nucleotide polymorphism in IFNAR1 affects susceptibility to
chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat. 16:45–52. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han Q, Zhang C, Zhang J and Tian Z:
Involvement of activation of PKR in HBx-siRNA-mediated innate
immune effects on HBV inhibition. PLoS One. 6:e279312011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park IH, Kwon YC, Ryu WS and Ahn BY:
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by ligand-mediated
activation of RNase L. Antiviral Res. 104:118–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Wei L, Jiang D, Wang JH,
Rao HY, Zhu L, Chen HS, Fei R and Cong X: Role of ISGF3 in
modulating the anti-hepatitis B virus activity of interferon-alpha
in vitro. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1747–1761. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA,
Hutin YJ and Bell BP: The contributions of hepatitis B virus and
hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer
worldwide. J Hepatol. 45:529–538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kong J, Kong F, Gao J, Zhang Q, Dong S, Gu
F, Ke S, Pan B, Shen Q, Sun H, et al: YC-1 enhances the anti-tumor
activity of sorafenib through inhibition of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Mol Cancer. 13:72014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang
JP, Jonas MM and Murad MH: American Association for the Study of
Liver Diseases: AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis
B. Hepatology. 63:261–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuen MF, Ahn SH, Chen DS, Chen PJ,
Dusheiko GM, Hou JL, Maddrey WC, Mizokami M, Seto WK, Zoulim F, et
al: Chronic hepatitis b virus infection: Disease revisit and
management recommendations. J Clin Gastroenterol. 50:286–294. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F,
Pediconi N, Volz T, Pollicino T, Petersen J, Raimondo G, Dandri M
and Levrero M: IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in
cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic
regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest.
122:529–537. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lai CL and Yuen MF: Prevention of
hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma with antiviral
therapy. Hepatology. 57:399–408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Robek MD, Boyd BS and Chisari FV: Lambda
interferon inhibits hepatitis B and C virus replication. J Virol.
79:3851–3854. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Piratvisuth T: Reviews for APASL
guidelines: Immunomodulator therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol
Int. 2:140–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sprengers D and Janssen HL:
Immunomodulatory therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 19:17–26. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Uzé G, Di Marco S, Mouchel-Vielh E,
Monneron D, Bandu MT, Horisberger MA, Dorques A, Lutfalla G and
Mogensen KE: Domains of interaction between alpha interferon and
its receptor components. J Mol Biol. 243:245–257. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peltekian C, Gordien E, Garreau F,
Meas-Yedid V, Soussan P, Willams V, Chaix ML, Olivo-Marin JC,
Bréchot C and Kremsdorf D: Human MxA protein participates to the
interferon-related inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in
female transgenic mice. J Hepatol. 43:965–972. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Su L and David M: Distinct mechanisms of
STAT phosphorylation via the interferon-alpha/beta receptor.
Selective inhibition of STAT3 and STAT5 by piceatannol. J Biol
Chem. 275:12661–12666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rani MR, Leaman DW, Han Y, Leung S, Croze
E, Fish EN, Wolfman A and Ransohoff RM: Catalytically active TYK2
is essential for interferon-beta-mediated phosphorylation of STAT3
and interferon-alpha receptor-1 (IFNAR-1) but not for activation of
phosphoinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 274:32507–32511. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ward SV and Samuel CE: The PKR kinase
promoter binds both Sp1 and Sp3, but only Sp3 functions as part of
the interferon-inducible complex with ISGF-3 proteins. Virology.
313:553–566. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
George CX, Das S and Samuel CE:
Organization of the mouse RNA-specific adenosine deaminase Adar1
gene 5′-region and demonstration of STAT1-independent,
STAT2-dependent transcriptional activation by interferon. Virology.
380:338–343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Goh KC, Haque SJ and Williams BR: p38 MAP
kinase is required for STAT1 serine phosphorylation and
transcriptional activation induced by interferons. EMBO J.
18:5601–5608. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang X and Chan C: Repression of PKR
mediates palmitate-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells through
regulation of Bcl-2. Cell Res. 19:469–486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chai Y, Huang HL, Hu DJ, Luo X, Tao QS,
Zhang XL and Zhang SQ: IL-29 and IFN-α regulate the expression of
MxA, 2′,5′-OAS and PKR genes in association with the activation of
Raf-MEK-ERK and PI3K-AKT signal pathways in HepG2.2.15 cells. Mol
Biol Rep. 38:139–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guan SH, Lu M, Grünewald P, Roggendorf M,
Gerken G and Schlaak JF: Interferon-alpha response in chronic
hepatitis B-transfected HepG2.2.15 cells is partially restored by
lamivudine treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 13:228–235. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mathews JD, McCaw CT, McVernon J, McBryde
ES and McCaw JM: A biological model for influenza transmission:
Pandemic planning implications of asymptomatic infection and
immunity. PLoS One. 2:e12202007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ren S, Yu H, Zhang H, Liu Y, Huang Y, Ma
L, Wei L, Wu H and Chen XY: Polymorphisms of interferon-inducible
genes OAS associated with interferon-α treatment response in
chronic HBV infection. Antiviral Res. 89:232–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|