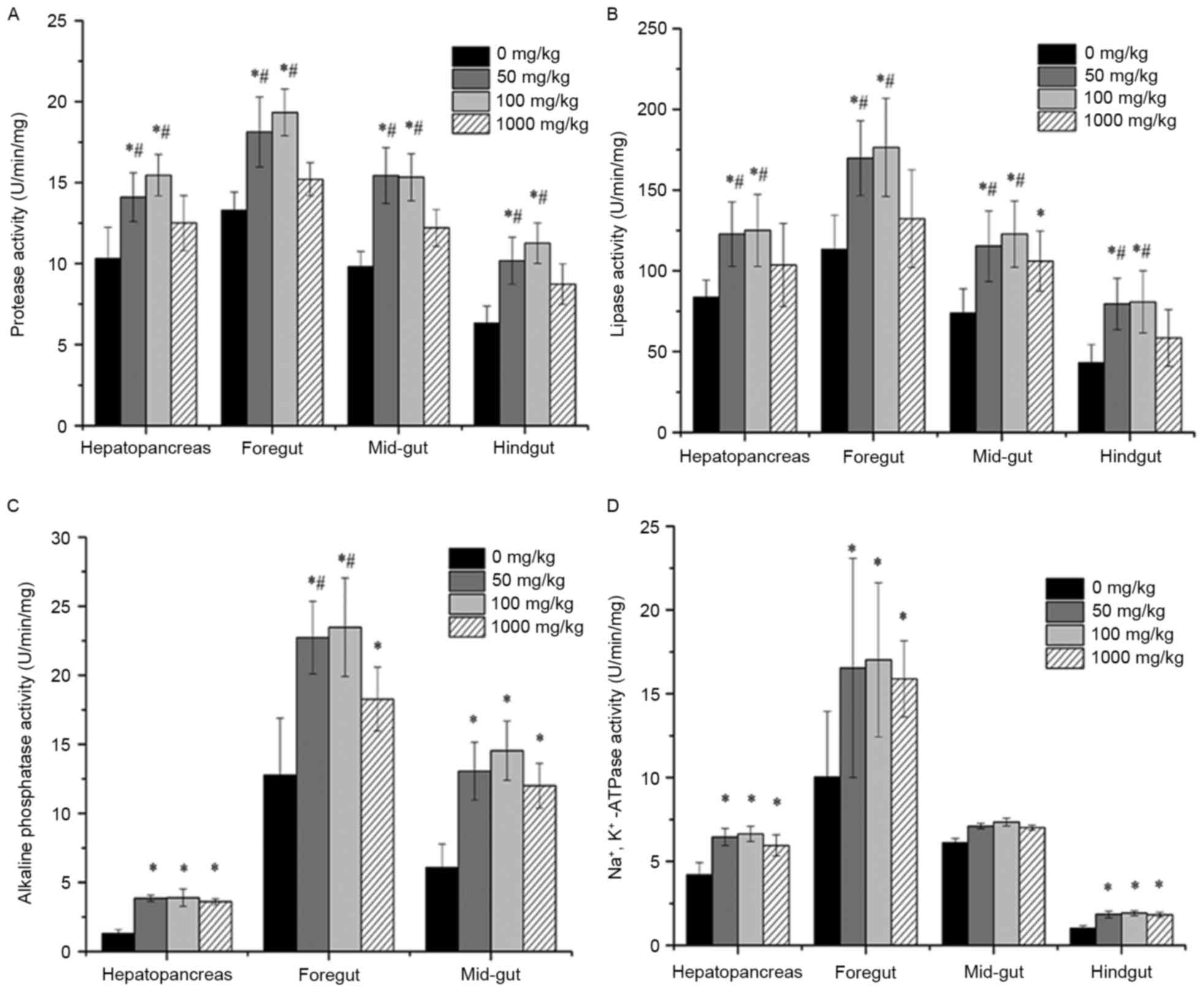
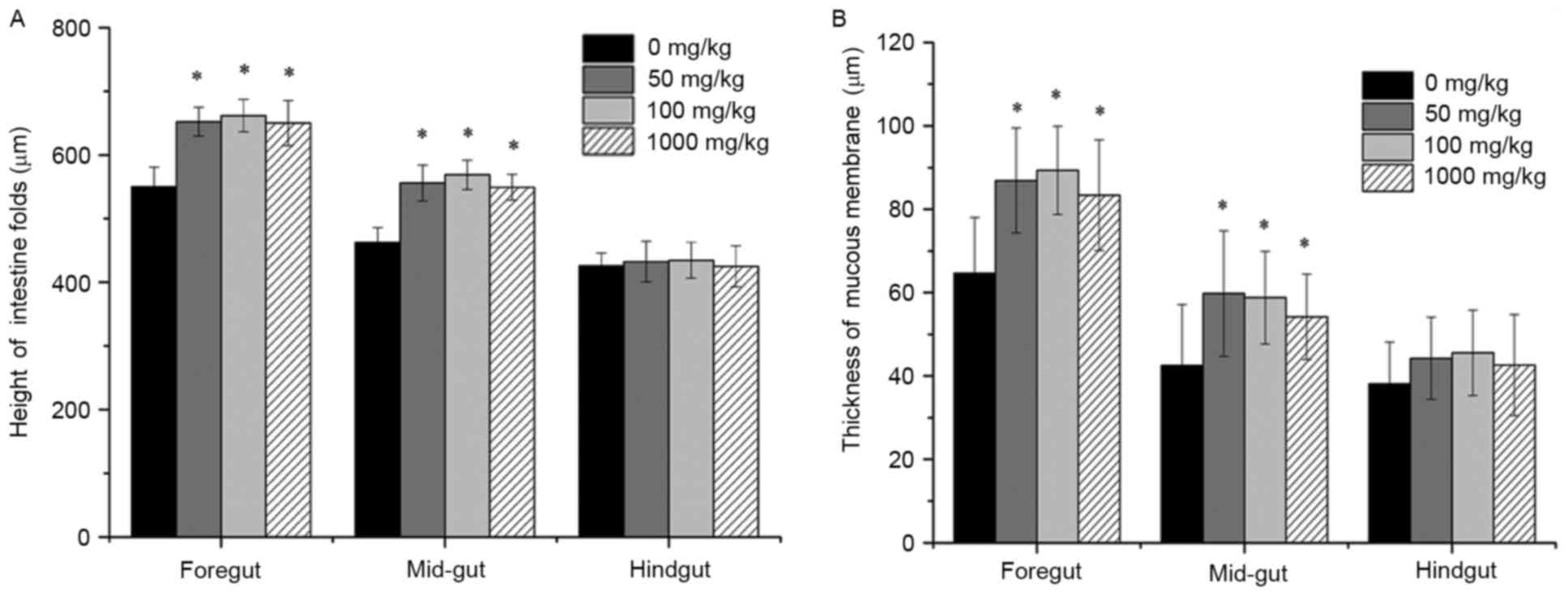
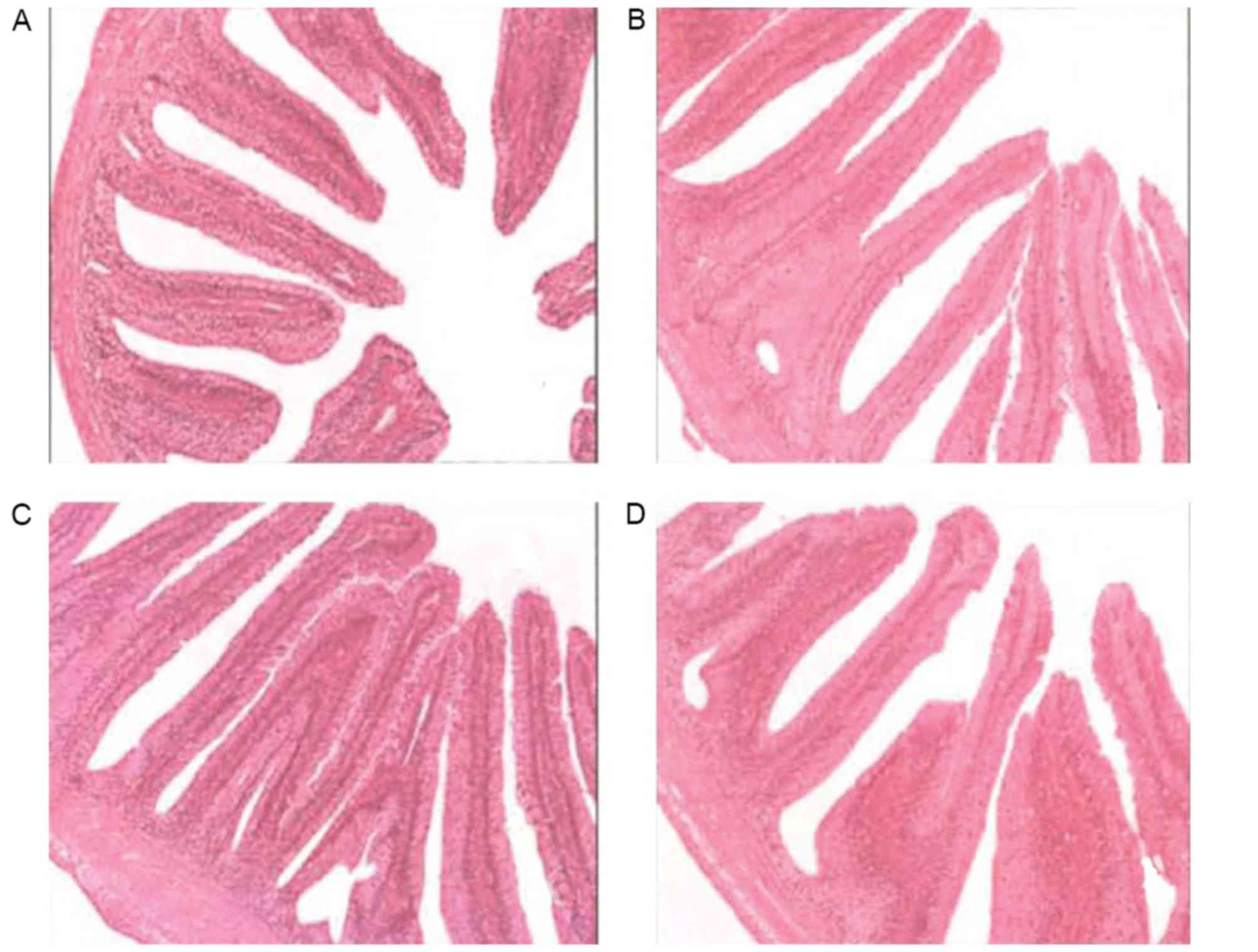
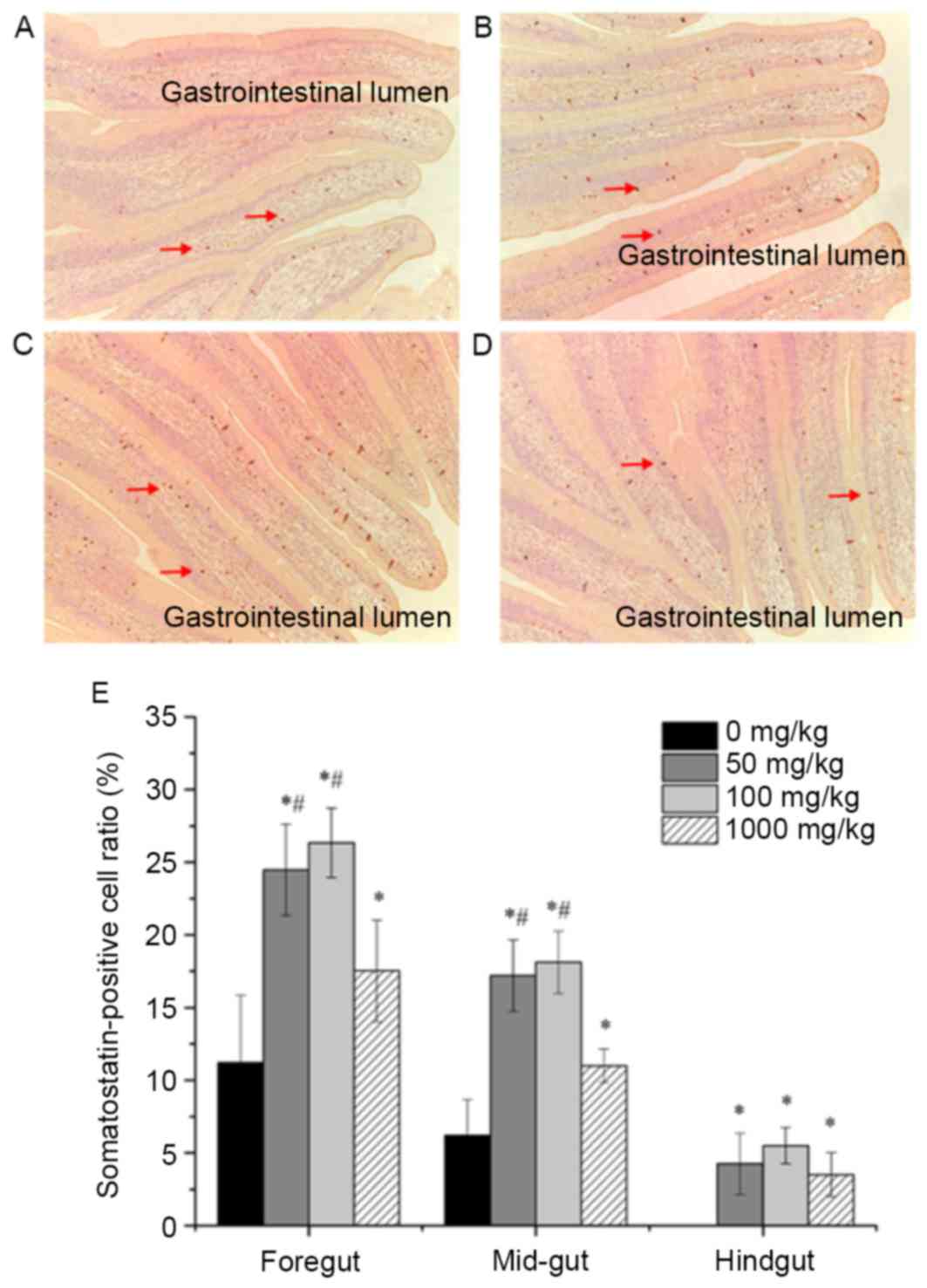
|
1
|
Yu W, Simmons-Menchaca M, Gapor A, Sanders
BG and Kline K: Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
by tocopherols and tocotrienols. Nutr Cancer. 33:26–32. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blaner WS: Vitamin E: The enigmatic one! J
Lipid Res. 54:2293–2294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Niki E: Role of vitamin E as a
lipid-soluble peroxyl radical scavenger: in vitro and in vivo
evidence. Free Radic Biol Med. 66:3–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sen CK, Khanna S and Roy S: Tocotrienols:
Vitamin E beyond tocopherols. Life Sci. 78:2088–2098. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McDowell LR: The vitaminsFish nutrition
Academic Press, San Diego, California. Vitamin E Academic Press;
London: pp. 93–131. 1989
|
|
6
|
Halver JE: The vitamins. Fish nutrition
Academic Press; San Diego, California: pp. 61–141. 2002
|
|
7
|
Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Prasad S and
Kannappan R: Tocotrienols, the vitamin E of the 21st century: Its
potential against cancer and other chronic diseases. Biochem
Pharmacol. 80:1613–1631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salinthone S, Kerns AR, Tsang V and Carr
DW: α-Tocopherol (vitamin E) stimulates cyclic AMP production in
human peripheral mononuclear cells and alters immune function. Mol
Immunol. 53:173–178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang Y, Zhou Y, Zhong Y, Gao X and Tan T:
Effect of vitamin E on reproductive functions and anti-oxidant
activity of adolescent male mice exposed to bisphenol A. Wei Sheng
Yan Jiu. 42:18–22. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sau Sk, Paul BN, Mohanta KN and Mohanty
SN: Dietary vitamin E requirement, fish performance and carcass
composition of rohu (Labeo rohita) fry. Aquaculture.
240:359–368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Thorarinsson R, Landolt ML, Elliott DG,
Pascho RJ and Hardy RW: Effect of dietary vitamin E and selenium on
growth, survival and the prevalence of Renibacterium
salmoninarum infection in chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus
tshawytscha). Aquaculture. 121:343–358. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee KJ and Dabrowski K: Interaction
between vitamins C and E affects their tissue concentrations,
growth, lipid oxidation, and deficiency symptoms in yellow perch
(Perca flavescens). Br J Nutr. 89:589–596. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai SC and Lee KJ: Different levels of
dietary DL-α-tocopheryl acetate affect the vitamin E status of
juvenile Korean rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Aquaculture.
161:405–414. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang CH and Lin WY: Effects of dietary
vitamin E level on growth and tissue lipid peroxidation of
soft-shelled turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis (Wiegmann). Aquac
Res. 35:948–954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Paul B, Sarkar S and Mohanty SN: Dietary
vitamin E requirement of mrigal, Cirrhinus mrigala fry.
Aquaculture. 242:529–536. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Keenan E, Warner S, Crowe A and Courtney
M: Length, Weight and Yield in Channel Catfish. Lake Diane, MI:
arXiv preprint arXiv:1102.4623. 2011
|
|
17
|
Jobling M: National Research Council
(NRC): Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. Aquac Int.
20:601–602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gatlin DM, Bai SC and Erickson MC: Effects
of dietary vitamin E and synthetic antioxidants on composition and
storage quality of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus.
Aquaculture. 106:323–332. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bai SC and Gatlin DM: Dietary vitamin E
concentration and duration of feeding affect tissue α-tocopherol
concentrations of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus).
Aquaculture. 113:129–135. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li MH, Wise DJ and Robinson EH: Effect of
dietary vitamin C on weight gain, tissue ascorbate concentration,
stress response and disease resistance of channel catfish
ictalurus punctatus1. J World Aquac Soc. 29:1–8.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Patel YC: Somatostatin and its receptor
family. Front Neuroendocrinol. 20:157–198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Diakatou E, Kaltsas G, Tzivras M, Kanakis
G, Papaliodi E and Kontogeorgos G: Somatostatin and dopamine
receptor profile of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors:
An immunohistochemical study. Endocr Pathol. 22:24–30. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sheridan MA and Hagemeister AL:
Somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in fish growth. Gen Comp
Endocrinol. 167:360–365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Council NR: Nutrient requirements of fish.
Washington: National Academy; 1993
|
|
25
|
Wen J, Morrissey PA, Buckley DJ and Pja S:
Supranutritional vitamin E supplementation in pigs: Influence on
subcellular deposition of α-tocopherol and on oxidative stability
by conventional and derivative spectrophotometry. Meat Science.
47:301–310. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kühlwein H, Merrifield DL, Rawling MD,
Foey AD and Davies SJ: Effects of dietary β-(1,3)(1,6)-D-glucan
supplementation on growth performance, intestinal morphology and
haemato-immunological profile of mirror carp (Cyprinus
carpio L.). J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. 98:279–289. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Falahatkar B, Amlashi AS and Conte F:
Effect of dietary vitamin E on cortisol and glucose responses to
handling stress in juvenile beluga Huso huso. J Aquat Anim
Health. 24:11–16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taveekijakarn P, Miyazaki T, Matsumoto M
and Arai S: Study on vitamin E deficiency in amago salmon. Bull Fac
Biores Mie Univ. 16:17–24. 1996.
|
|
29
|
Wassef E, El Masry MH and Mikhail FR:
Growth enhancement and muscle structure of striped mullet, Mugil
cephalus L., fingerlings by feeding algal meal-based diets. Aquac
Res. 32:315–322. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
De Silva SS and Anderson TA: Fish
nutrition in aquaculture. Springer Science Business Media; 1994
|
|
31
|
Olli JJ and Krogdahi Å: Nutritive value of
four soybean products as protein sources in diets for rainbow trout
(Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) reared in fresh water. Acta
Agric Scand A Anim Sci. 44:185–192. 1994.
|
|
32
|
Farhangi M and Carter CG: Growth,
physiological and immunological responses of rainbow trout
(Oncorhynchus mykiss) to different dietary inclusion levels
of dehulled lupin (Lupinus angustifolius). Aquac Res.
32:329–340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Galgani F and Ceccaldi HJ: Effet de
l'incorporation de farines de soja et de poisson dans l'aliment sur
la croissance et les enzymes digestives de Penaeus vannamei. Aquat
Living Resour. 1:181–187. 1988.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kumlu M and Jones D: The effect of live
and artificial diets on growth, survival and trypsin activity in
larvae of Penaeus indicus. J World Aquac Soc. 26:406–415.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cuvier-Péres A and Kestemont P:
Development of some digestive enzymes in Eurasian perch larvae
Perca fluviatilis. Fish Physiol Biochem. 24:279–285. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wood SR, Zhao Q, Smith LH and Daniels CK:
Altered morphology in cultured rat intestinal epithelial IEC-6
cells is associated with alkaline phosphatase expression. Tissue
Cell. 35:47–58. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rhoads JM, Chen W, Chu P, Berschneider HM,
Argenzio RA and Paradiso AM: L-glutamine and L-asparagine stimulate
Na+-H+ exchange in porcine jejunal
enterocytes. Am J Physiol. 266:G828–G838. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yan L and Qiu-Zhou X: Dietary glutamine
supplementation improves structure and function of intestine of
juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Aquaculture.
256:389–394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin X and Peter RE: Somatostatins and
their receptors in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol.
129:543–550. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Reichlin S: Somatostatin. N Engl J Med.
309:1495–1501. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee JH, Ku SK, Park KD and Lee HS:
Immunohistochemical study of the gastrointestinal endocrine cells
in the Korean aucha perch. J Fish Biol. 65:170–181. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pan QS, Fang ZP and Huang FJ:
Identification, localization and morphology of APUD cells in
gastroenteropancreatic system of stomach-containing teleosts. World
J Gastroenterol. 6:842–847. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hobart P, Crawford R, Shen L, Pictet R and
Rutter WJ: Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding two
distinct somatostatin precursors found in the endocrine pancreas of
anglerfish. Nature. 288:137–141. 1980. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moore CA, Kittilson JD, Ehrman MM and
Sheridan MA: Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) possess two
somatostatin mRNAs that are differentially expressed. Am J Physiol.
277:R1553–R1561. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hanssen L, Hanssen KF and Myren J:
Inhibition of secretin release and pancreatic bicarbonate secretion
by somatostatin infusion in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 12:391–394.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dollinger HC, Raptis S and Pfeiffer EF:
Effects of somatostatin on exocrine and endocrine pancreatic
function stimulated by intestinal hormones in man. Horm Metab Res.
8:74–78. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|