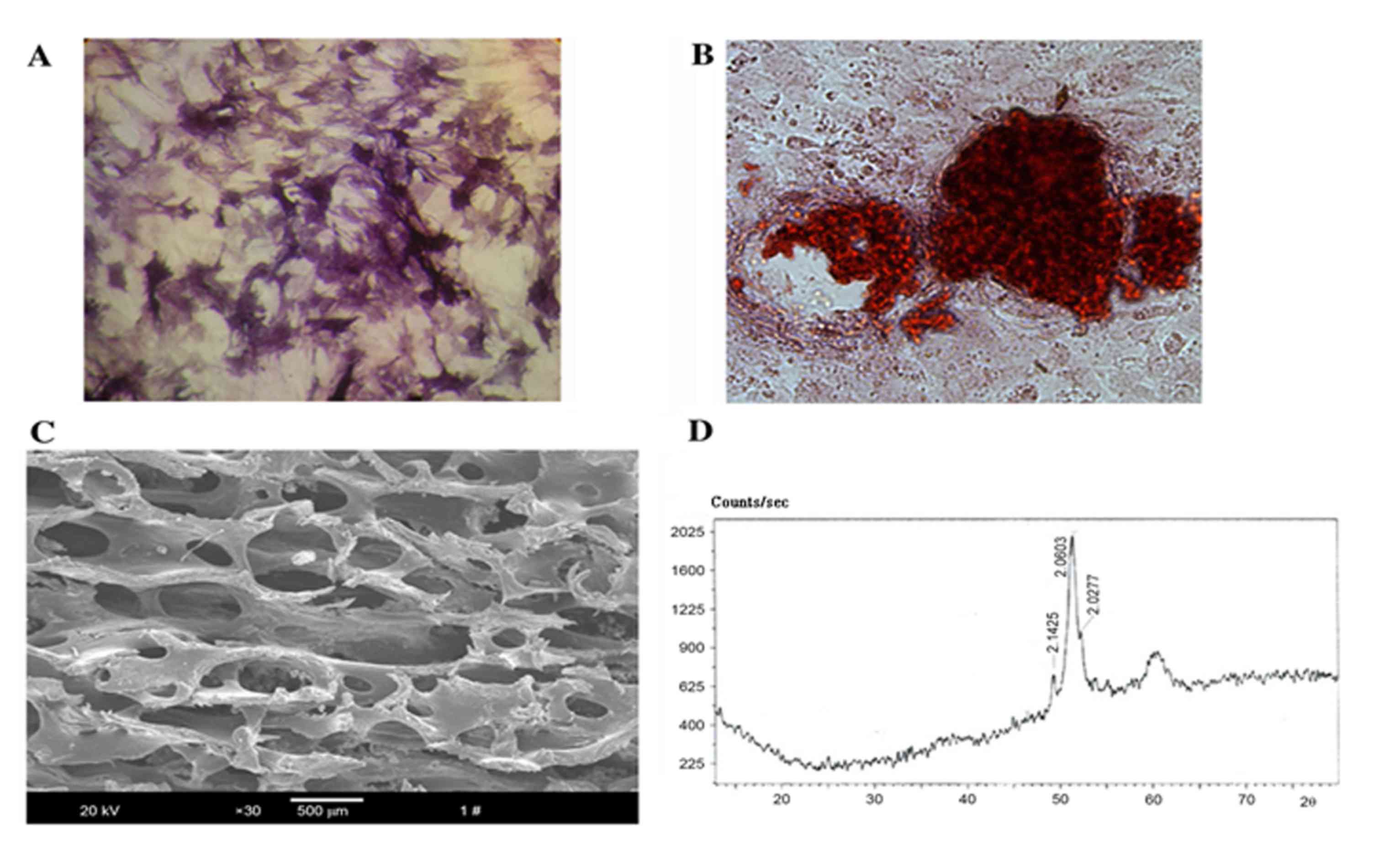
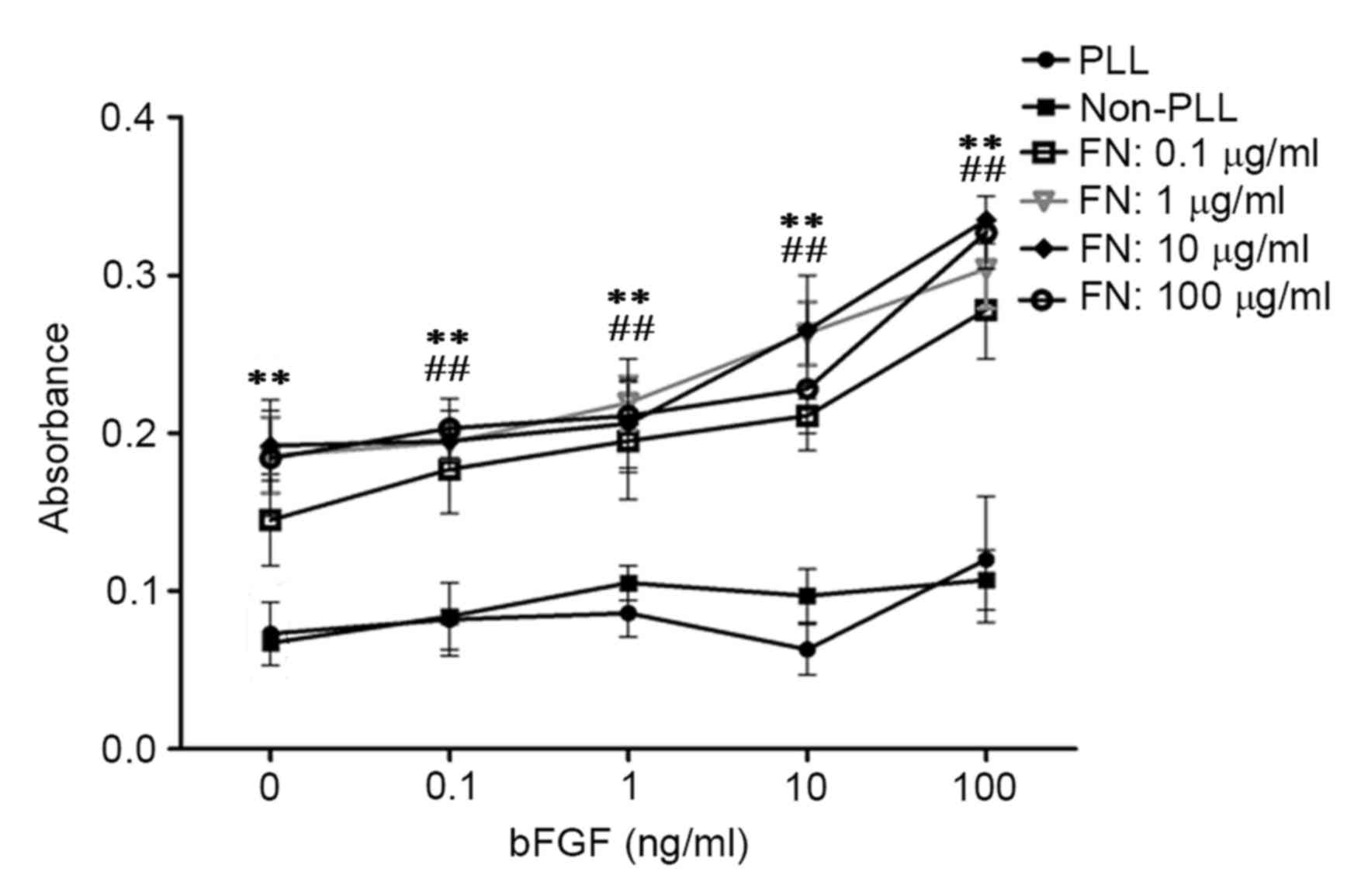
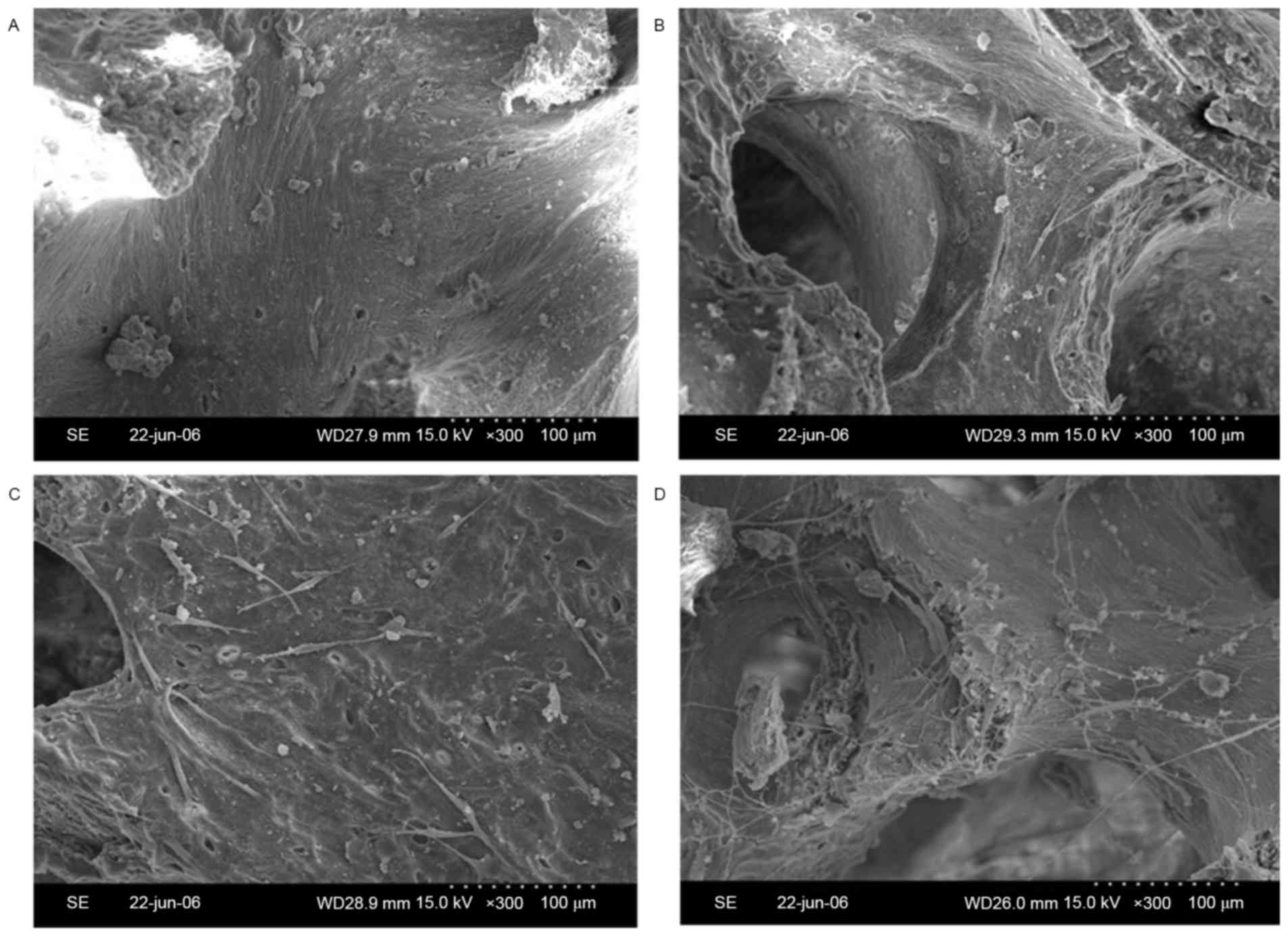
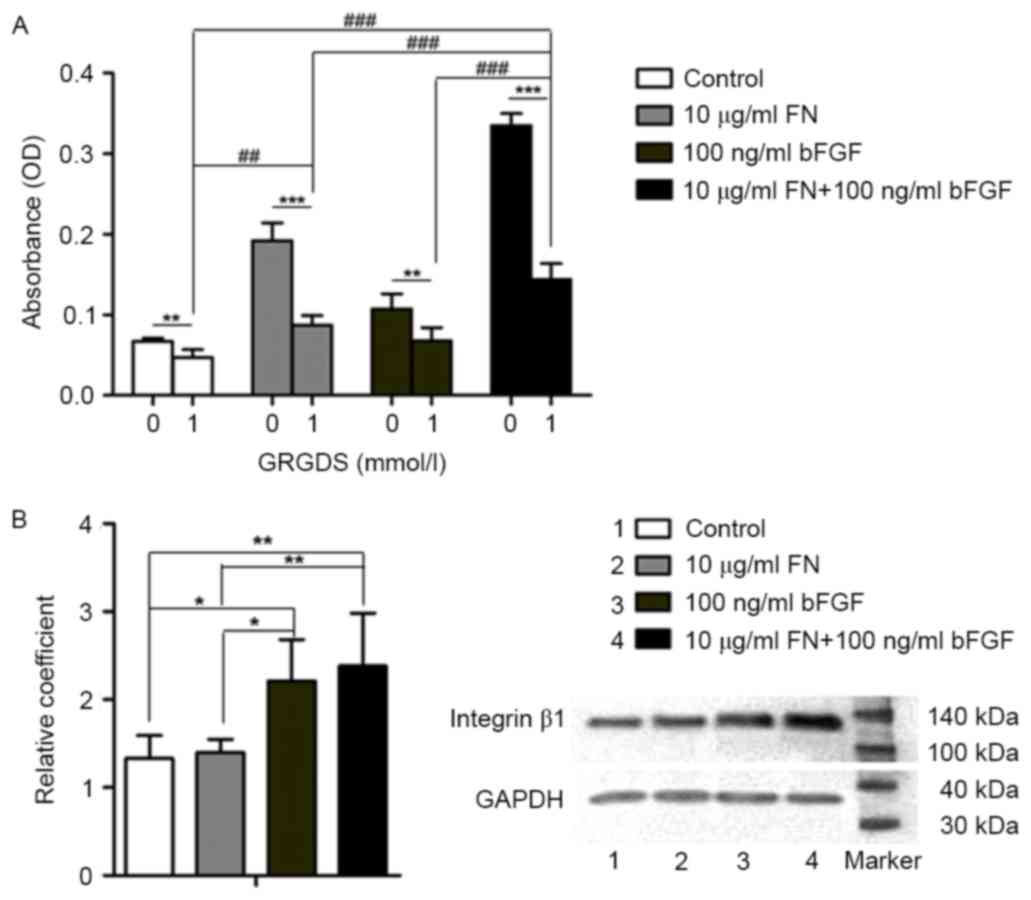
|
1
|
Liu F, Zhang X, Yu X, Xu Y, Feng T and Ren
D: In vitro study in stimulating the secretion of angiogenic growth
factors of strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate for bone tissue
engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 22:683–692. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang ZY, Teoh SH, Chong WS, Foo TT, Chng
YC, Choolani M and Chan J: A biaxial rotating bioreactor for the
culture of fetal mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue
engineering. Biomaterials. 30:2694–2704. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie H, Yang F, Deng L, Luo J, Qin T, Li X,
Zhou GQ and Yang Z: The performance of a bone-derived scaffold
material in the repair of critical bone defects in a rhesus monkey
model. Biomaterials. 28:3314–3324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee S, Lee DS, Choi I, Le Pham BH and Jang
JH: Design of an osteoinductive extracellular fibronectin matrix
protein for bone tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 16:7672–7681.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pegueroles M, Aparicio C, Bosio M, Engel
E, Gil FJ, Planell JA and Altankov G: Spatial organization of
osteoblast fibronectin matrix on titanium surfaces: Effects of
roughness, chemical heterogeneity and surface energy. Acta
Biomater. 6:291–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calderwood DA, Shattil SJ and Ginsberg MH:
Integrins and actin filaments: Reciprocal regulation of cell
adhesion and signaling. J Biol Chem. 275:22607–22610. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brunner M, Millon-Frémillon A, Chevalier
G, Nakchbandi IA, Mosher D, Block MR, Albigès-Rizo C and Bouvard D:
Osteoblast mineralization requires beta1 integrin/ICAP-1-dependent
fibronectin deposition. J Cell Biol. 194:307–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bentmann A, Kawelke N, Moss D, Zentgraf H,
Bala Y, Berger I, Gasser JA and Nakchbandi IA: Circulating
fibronectin affects bone matrix, whereas osteoblast fibronectin
modulates osteoblast function. J Bone Miner Res. 25:706–715.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He L, Lin Y, Hu X, Zhang Y and Wu H: A
comparative study of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich
plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of
rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol Endod. 108:707–713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Houseman BT and Mrksich M: The
microenvironment of immobilized Arg-Gly-Asp peptides is an
important determinant of cell adhesion. Biomaterials. 22:943–955.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin H, Zygourakis K, Farach-Carson MC,
Yaszemski MJ and Mikos AG: Attachment, proliferation, and migration
of marrow stromal osteoblasts cultured on biomimetic hydrogels
modified with an osteopontin-derived peptide. Biomaterials.
25:895–906. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan Q, Kubo T, Doi K, Morita K, Takeshita
R, Katoh S, Shiba T, Gong P and Akagawa Y: Effect of combined
application of bFGF and inorganic polyphosphate on bioactivities of
osteoblasts and initial bone regeneration. Acta Biomater.
5:1716–1724. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li P, Bai Y, Yin G, Pu X, Huang Z, Liao X,
Chen X and Yao Y: Synergistic and sequential effects of BMP-2, bFGF
and VEGF on osteogenic differentiation of rat osteoblasts. J Bone
Miner Metab. 32:627–635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang DZ, Hou W, Zhou Q, Zhang M, Holz J,
Sheu TJ, Li TF, Cheng SD, Shi Q, Harris SE, et al: Osthole
stimulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation by
activation of beta-catenin-BMP signaling. J Bone Miner Res.
25:1234–1245. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Trivedi R, Kumar S, Kumar A, Siddiqui JA,
Swarnkar G, Gupta V, Kendurker A, Dwivedi AK, Romero JR and
Chattopadhyay N: Kaempferol has osteogenic effect in ovariectomized
adult sprague-dawley rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 289:85–93. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huo K, Zhang X, Wang H, Zhao L, Liu X and
Chu PK: Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effects on titanium
surfaces modified with Zn-incorporated nanotube arrays.
Biomaterials. 34:3467–3478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao D, Xie XH, Wang XL, Wan C, Lee YW,
Chen SH, Pei DQ, Wang YX, Li G and Qin L: Icaritin, an exogenous
phytomolecule, enhances osteogenesis but not angiogenesis-an in
vitro efficacy study. PLoS One. 7:e412642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang ZY, Teoh SH, Chong MS, Schantz JT,
Fisk NM, Choolani MA and Chan J: Superior osteogenic capacity for
bone tissue engineering of fetal compared with perinatal and adult
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells. 27:126–137. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin YC, Brayfield CA, Gerlach JC, Rubin JP
and Marra KG: Peptide modification of polyethersulfone surfaces to
improve adipose-derived stem cell adhesion. Acta Biomater.
5:1416–1424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mariscal-Muñoz E, Costa CA, Tavares HS,
Bianchi J, Hebling J, Machado JP, Lerner UH and Souza PP:
Osteoblast differentiation is enhanced by a nano-to-micro hybrid
titanium surface created by Yb: YAG laser irradiation. Clin Oral
Investig. 20:503–511. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang YW, Wu Q and Chen GQ: Attachment,
proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts on random
biopolyester poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)
scaffolds. Biomaterials. 25:669–675. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li T, Li H, Li T, Fan J, Zhao RC and Weng
X: MicroRNA expression profile of dexamethasone-induced human bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic
differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 115:1683–1691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hendesi H, Barbe MF, Safadi FF, Monroy MA
and Popoff SN: Integrin mediated adhesion of osteoblasts to
connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) induces cytoskeleton
reorganization and cell differentiation. PLoS One. 10:e01153252015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishida K and Haudenschild DR: Interactions
between FGF21 and BMP-2 in osteogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 432:677–682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yoshimoto H, Shin YM, Terai H and Vacanti
JP: A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its
potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 24:2077–2082.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang H, Li Y, Zuo Y, Li J, Ma S and Cheng
L: Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of biomimetic
nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide composite scaffolds for bone tissue
engineering. Biomaterials. 28:3338–3348. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ribeiro N, Sousa SR and Monteiro FJ:
Influence of crystallite size of nanophased hydroxyapatite on
fibronectin and osteonectin adsorption and on MC3T3-E1 osteoblast
adhesion and morphology. J Colloid Interface Sci. 351:398–406.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moursi AM, Globus RK and Damsky CH:
Interactions between integrin receptors and fibronectin are
required for calvarial osteoblast differentiation in vitro. J Cell
Sci. 110:2187–2196. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lim JY, Taylor AF, Li Z, Vogler EA and
Donahue HJ: Integrin expression and osteopontin regulation in human
fetal osteoblastic cells mediated by substratum surface
characteristics. Tissue Eng. 11:19–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang CH, Yang RS, Huang TH, Liu SH and Fu
WM: Enhancement of fibronectin fibrillogenesis and bone formation
by basic fibroblast growth factor via protein kinase c-dependent
pathway in rat osteoblasts. Mol Pharmacol. 66:440–449.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|