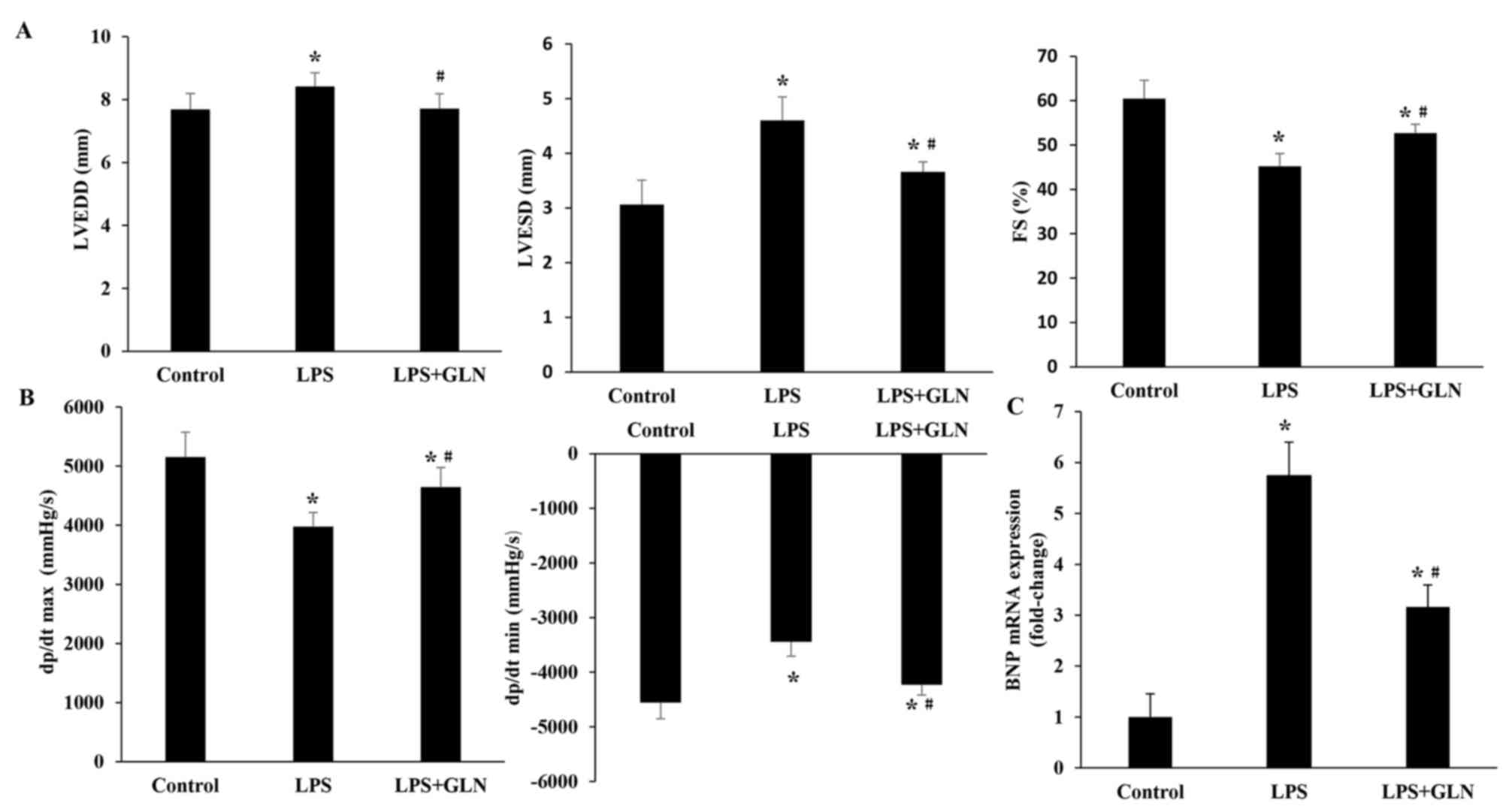
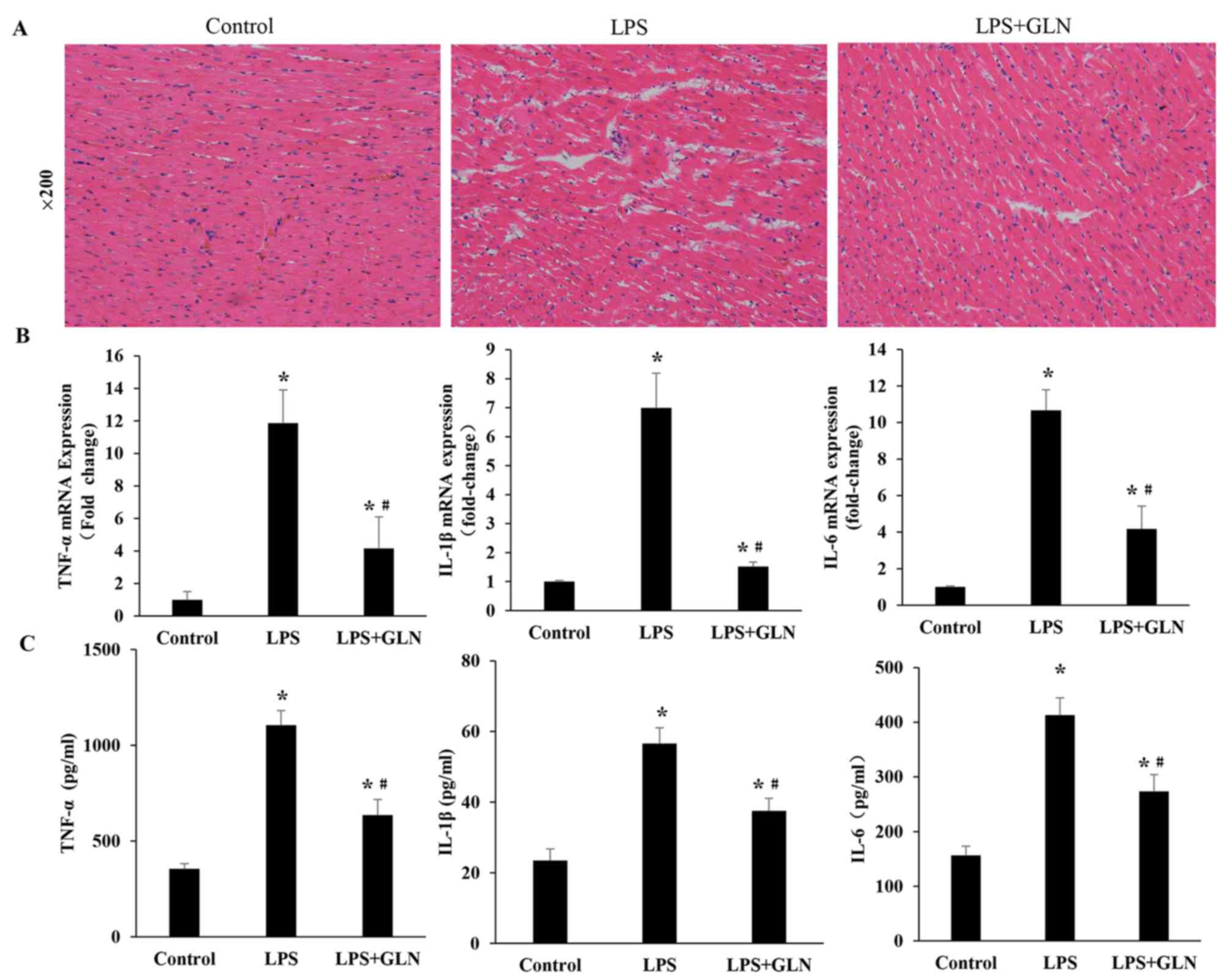
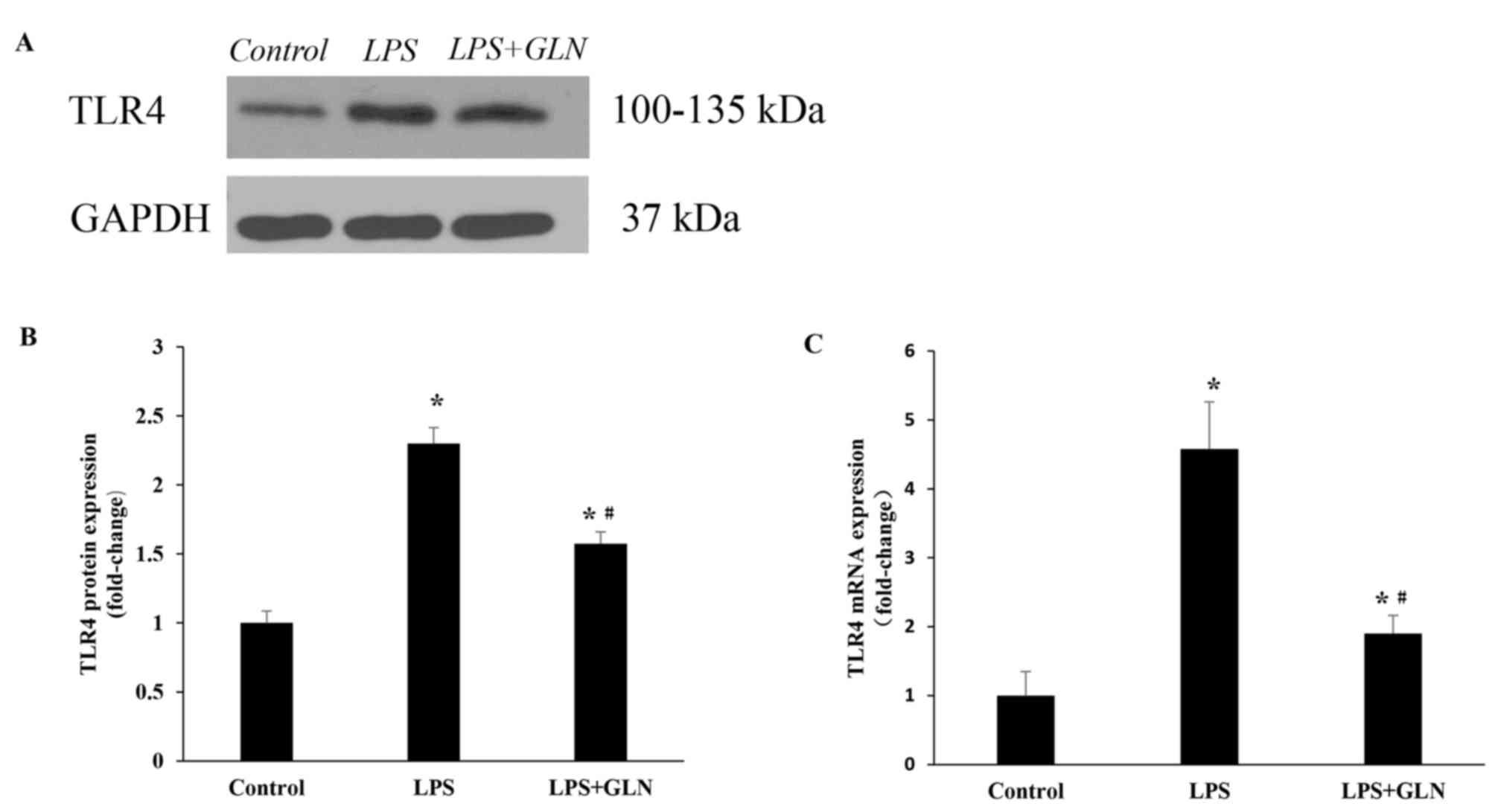
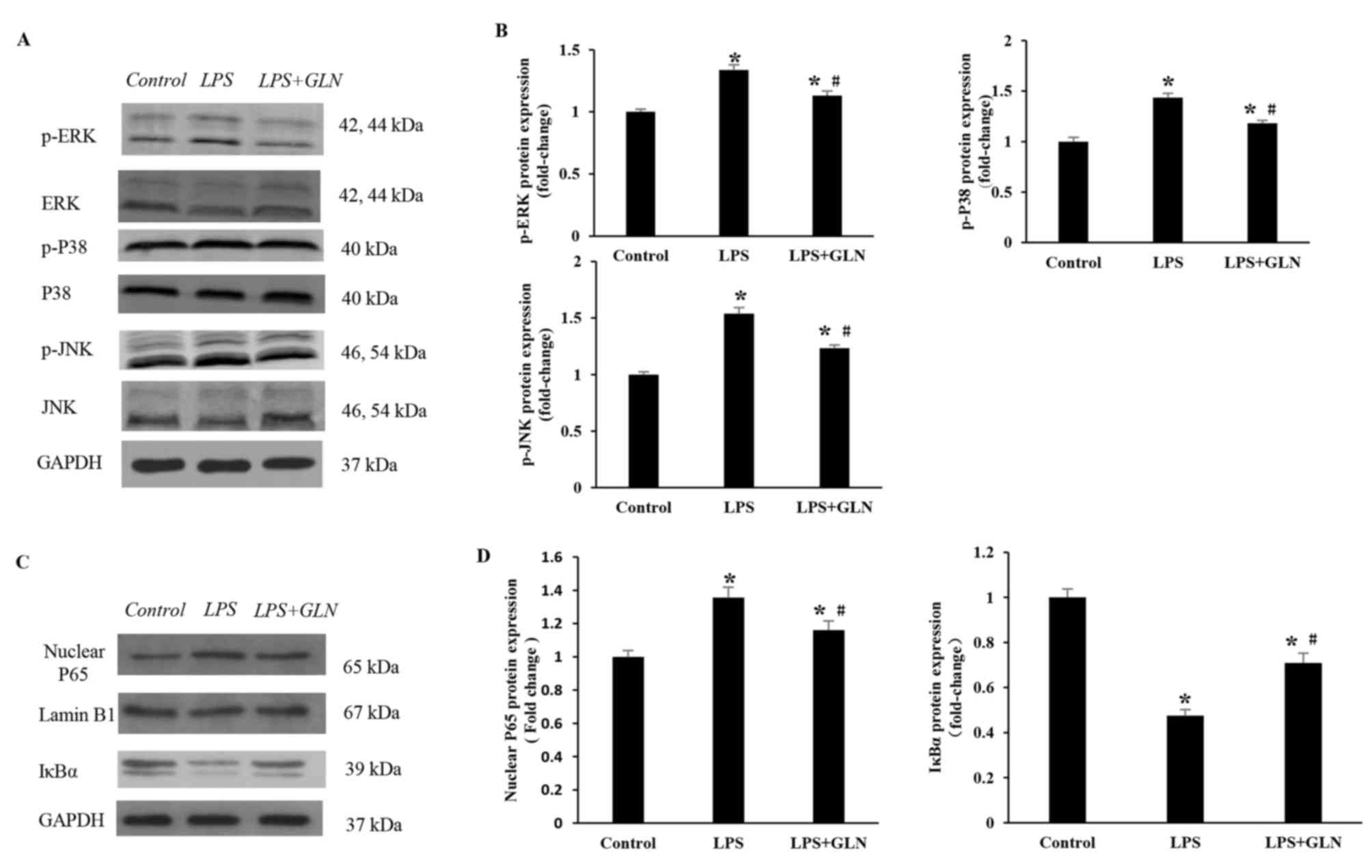
|
1
|
Kimmoun A, Ducrocq N and Levy B:
Mechanisms of vascular hyporesponsiveness in septic shock. Curr
Vasc Pharmacol. 11:139–149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao H, Zhang M, Zhou F, Cao W, Bi L, Xie
Y, Yang Q and Wang S: Cinnamaldehyde ameliorates LPS-induced
cardiac dysfunction via TLR4-NOX4 pathway: The regulation of
autophagy and ROS production. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 101:11–24. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Merx MW and Weber C: Sepsis and the heart.
Circulation. 116:793–802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Teo JD, Macary PA and Tan KS: Pleiotropic
effects of Blastocystis spp. Subtypes 4 and 7 on ligand-specific
toll-like receptor signaling and NF-κB activation in a human
monocyte cell line. PLoS One. 9:e890362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li H, Yoon JH, Won HJ, Ji HS, Yuk HJ, Park
KH, Park HY and Jeong TS: Isotrifoliol inhibits pro-inflammatory
mediators by suppression of TLR/NF-κB and TLR/MAPK signaling in
LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 45:110–119. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao H, Zheng Q, Hu X, Shen H and Li F:
Betulin attenuates kidney injury in septic rats through inhibiting
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Life Sci. 144:185–193. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: Mechanisms of
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 35:1599–1608.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang F, Wang X, Pan L, Wang W, Li N and
Li J: Glutamine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury. Nutrition. 25:692–698. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jia CJ, Dai CL, Zhang X, Cui K, Xu F and
Xu YQ: Alanyl-glutamine dipeptide inhibits hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol.
12:1373–1378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou X, Wu X, Yin Y, Zhang C and He L:
Preventive oral supplementation with glutamine and arginine has
beneficial effects on the intestinal mucosa and inflammatory
cytokines in endotoxemic rats. Amino Acids. 43:813–821. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bayne K: Revised guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals available. American physiological
society. Physiologist. 39(199): 208–211. 1996.
|
|
12
|
Masson GS, Nair AR, Dange RB, Silva-Soares
PP, Michelini LC and Francis J: Toll-like receptor 4 promotes
autonomic dysfunction, inflammation and microglia activation in the
hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: Role of endoplasmic reticulum
stress. PLoS One. 10:e01228502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Plante E, Lachance D, Beaudoin J,
Champetier S, Roussel E, Arsenault M and Couet J: Comparative study
of vasodilators in an animal model of chronic volume overload
caused by severe aortic regurgitation. Circ Heart Fail. 2:25–32.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Plunkett A and Tong J: Sepsis in children.
BMJ. 350:h30172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NK, Machado
FR, Angus DC, Calandra T, Jaton K, Giulieri S, Delaloye J, Opal S,
et al: Sepsis: A roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis.
15:581–614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
De Geer L, Engvall J and Oscarsson A:
Strain echocardiography in septic shock-a comparison with systolic
and diastolic function parameters, cardiac biomarkers and outcome.
Crit Care. 19:1222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Avlas O, Fallach R, Shainberg A, Porat E
and Hochhauser E: Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation initiates an
inflammatory response that decreases cardiomyocyte contractility.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1895–1909. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He G, Zhang X, Chen Y, Chen J, Li L and
Xie Y: Isoalantolactone inhibits LPS-induced inflammation via NF-κB
inactivation in peritoneal macrophages and improves survival in
sepsis. Biomed Pharmacother. 90:598–607. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma F, Liu F, Ding L, You M, Yue H, Zhou Y
and Hou Y: Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin are associated
with down regulating microRNA-155 in LPS-treated macrophages and
mice. Pharm Biol. 55:1263–1273. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen ZB, Tang H, Liang YB, Yang W, Wu JG,
Hu XC, Li ZY, Zeng LJ and Ma ZF: Recombinant Trichinella spiralis
53-kDa protein activates M2 macrophages and attenuates the
LPS-induced damage of endotoxemia. Innate Immun. 22:419–432. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tian Y, Tao T, Zhu J, Zou Y, Wang J, Li J,
Bo L and Deng X: Soluble tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis
inducing ligand level as a predictor of severity of sepsis and the
risk of mortality in septic patients. PLoS One. 8:e822042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Copray JC, Mantingh I, Brouwer N, Biber K,
Küst BM, Liem RS, Huitinga I, Tilders FJ, Van Dam AM and Boddeke
HW: Expression of interleukin-1 beta in rat dorsal root ganglia. J
Neuroimmunol. 118:203–211. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Gonzalo-Calvo D, Neitzert K, Fernández
M, Vega-Naredo I, Caballero B, García-Macía M, Suárez FM,
Rodríguez-Colunga MJ, Solano JJ and Coto-Montes A: Differential
inflammatory responses in aging and disease: TNF-alpha and IL-6 as
possible biomarkers. Free Radic Biol Med. 49:733–737. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Waller Persson K, Colditz IG, Lun S and
Ostensson K: Cytokines in mammary lymph and milk during
endotoxin-induced bovine mastitis. Res Vet Sci. 74:31–36. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hou XL, Tong Q, Wang WQ, Shi CY, Xiong W,
Chen J, Liu X and Fang JG: Suppression of inflammatory responses by
dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid from ampelopsis grossedentata, via
inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J
Nat Prod. 78:1689–1696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pellegrino P, Falvella FS, Cheli S,
Perrotta C, Clementi E and Radice S: The role of Toll-like receptor
4 polymorphisms in vaccine immune response. Pharmacogenomics J.
16:96–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li HR, Liu J, Zhang SL, Luo T, Wu F, Dong
JH, Guo YJ and Zhao L: Corilagin ameliorates the extreme
inflammatory status in sepsis through TLR4 signaling pathways. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 17:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frazier WJ, Xue J, Luce WA and Liu Y: MAPK
signaling drives inflammation in LPS-stimulated cardiomyocytes: The
route of crosstalk to G-protein-coupled receptors. PLoS One.
7:e500712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng S, Pan Y, Wang C, Liu Y, Shi M and
Ding G: HMGB1 turns renal tubular epithelial cells into
inflammatory promoters by interacting with TLR4 during sepsis. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 36:9–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Feng H, Guo W, Han J and Li XA: Role of
caveolin-1 and caveolae signaling in endotoxemia and sepsis. Life
Sci. 93:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang X, Nelin LD, Kuhlman JR, Meng X,
Welty SE and Liu Y: The role of MAP kinase phosphatase-1 in the
protective mechanism of dexamethasone against endotoxemia. Life
Sci. 83:671–680. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim SJ, Baek KS, Park HJ, Jung YH and Lee
SM: Compound 9a, a novel synthetic histone deacetylase inhibitor,
protects against septic injury in mice by suppressing MAPK
signalling. Br J Pharmacol. 173:1045–1057. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang M, Wang X, Bai B, Zhang R, Li Y and
Wang Y: Oxymatrine protects against sepsis-induced myocardial
injury via inhibition of the TNF-α/p38-MAPK/caspase-3 signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 14:551–559. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Morales MG, Olguín H, Di Capua G, Brandan
E, Simon F and Cabello-Verrugio C: Endotoxin-induced skeletal
muscle wasting is prevented by angiotensin-(1–7) through a p38
MAPK-dependent mechanism. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:461–476. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee S, Choi SY, Choo YY, Kim O, Tran PT,
Dao CT, Min BS and Lee JH: Sappanone A exhibits anti-inflammatory
effects via modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB. Int Immunopharmacol.
28:328–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lawrence T, Bebien M, Liu GY, Nizet V and
Karin M: IKKalpha limits macrophage NF-kappaB activation and
contributes to the resolution of inflammation. Nature.
434:1138–1143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang W, Hu X, Shen P, Zhang N and Fu Y:
Sodium houttuyfonate inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response via
suppressing TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway in bovine mammary
epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 107:12–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu XL, Zhao CH, Zhang H and Yao XL: iRhom2
is involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac injury in vivo
and in vitro through regulating inflammation response. Biomed
Pharmacother. 86:645–653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mariappan N, Elks CM, Sriramula S,
Guggilam A, Liu Z, Borkhsenious O and Francis J: NF-kappaB-induced
oxidative stress contributes to mitochondrial and cardiac
dysfunction in type II diabetes. Cardiovasc Res. 85:473–483. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ha T, Xia Y, Liu X, Lu C, Liu L, Kelley J,
Kalbfleisch J, Kao RL, Williams DL and Li C: Glucan phosphate
attenuates myocardial HMGB1 translocation in severe sepsis through
inhibiting NF-κB activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H848–H855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Lu Y, Ma L, Cao X, Xiao J, Chen
J, Jiao S, Gao Y, Liu C, Duan Z, et al: Activation of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in macrophages restrains
TLR4-NF-κB signaling and protects against endotoxin shock.
Immunity. 40:501–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vaez H, Najafi M, Rameshrad M, Toutounchi
NS, Garjani M, Barar J and Garjani A: AMPK activation by metformin
inhibits local innate immune responses in the isolated rat heart by
suppression of TLR 4-related pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
40:501–507. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|