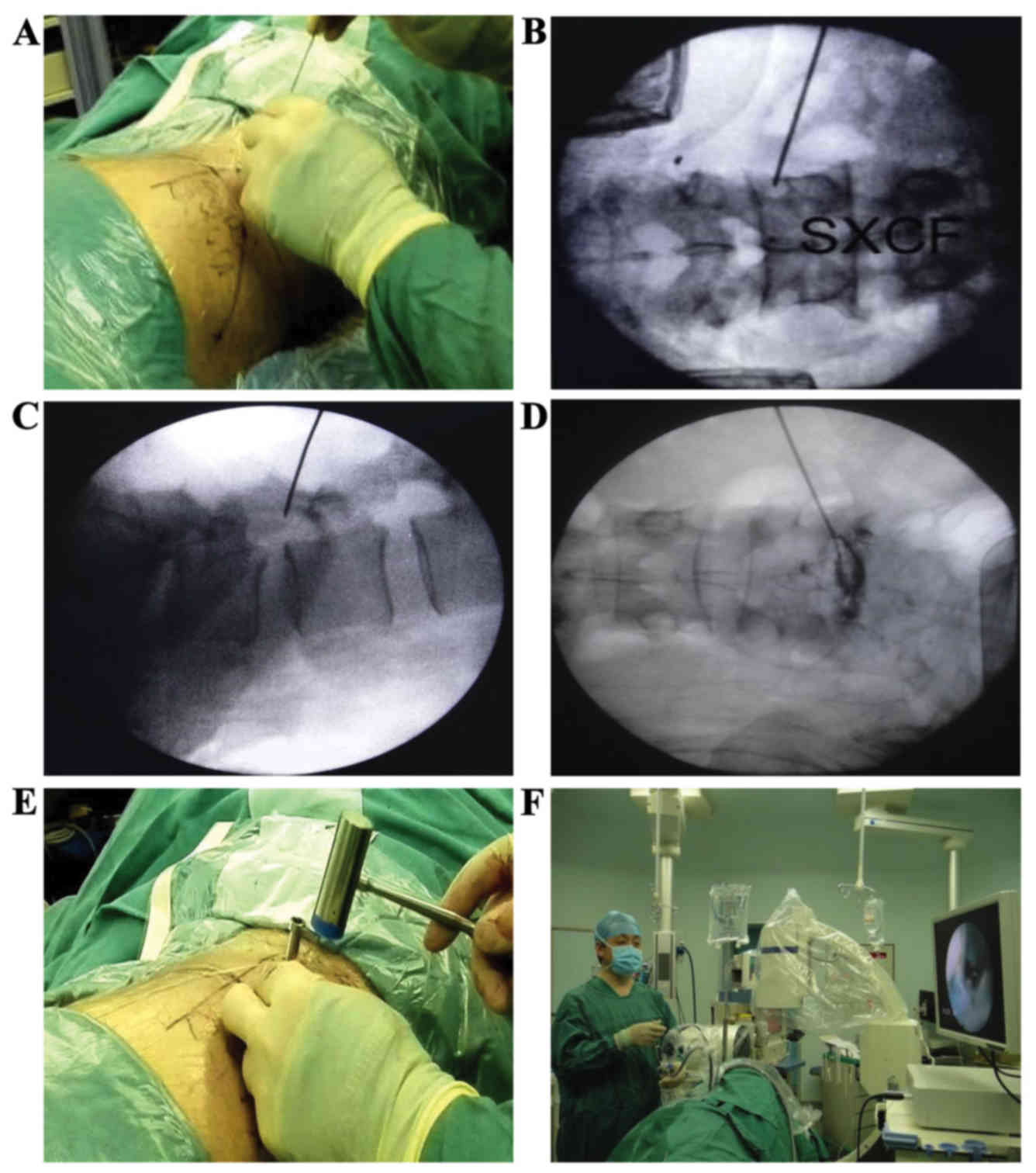
|
1
|
Zheng C, Wu F and Cai L: Transforaminal
percutaneous endoscopic discectomy in the treatment of far-lateral
lumbar disc herniations in children. Int Orthop. 40:1099–1102.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karamouzian S, Ebrahimi-Nejad A,
Shahsavarani S, Keikhosravi E, Shahba M and Ebrahimi F: Comparison
of two methods of epidural steroid injection in the treatment of
recurrent lumbar disc herniation. Asian Spine J. 8:646–652. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cong L, Zhu Y and Tu G: A meta-analysis of
endoscopic discectomy versus open discectomy for symptomatic lumbar
disk herniation. Eur Spine J. 25:134–143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jha SC, Tonogai I, Takata Y, Sakai T,
Higashino K, Matsuura T, Suzue N, Hamada D, Goto T, Nishisho T, et
al: Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for a huge herniated
disc causing acute cauda equina syndrome: A case report. J Med
Invest. 62:100–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang SJ, Chen BH, Wang P, Liu CS, Yu JM
and Ma XX: The effect of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy
under different anesthesia on pain and immunity of patients with
prolapse of lumbar intervertebral disc. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:2793–2799. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Löhr M, Lebenheim L, Berg F, Stenzel W,
Hescheler J, Molcanyi M, Ernestus RI and Bosche B: Gadolinium
enhancement in newly diagnosed patients with lumbar disc
herniations are associated with inflammatory peridiscal tissue
reactions – evidence of fragment degradation? Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 119:28–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dalbayrak S, Yaman O, Yilmaz M and Özer
AF: Transforaminal approach in lumbar disc herniations:
Transforaminal microdiscectomy (TFMD) technique. Turk Neurosurg.
25:29–35. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Dou Q, Hu S, Liu J, Kong Q, Zeng J
and Song Y: Treatment of cauda equina syndrome caused by lumbar
disc herniation with percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy.
Acta Neurol Belg. 116:185–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kogias E, Franco Jimenez P, Klingler JH
and Hubbe U: Minimally invasive redo discectomy for recurrent
lumbar disc herniations. J Clin Neurosci. 22:1382–1386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gotecha S, Ranade D, Patil SV, Chugh A,
Kotecha M, Sharma S and Punia P: The role of transforaminal
percutaneous endoscopic discectomy in lumbar disc herniations. J
Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 7:217–223. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mroz TE, Lubelski D, Williams SK, O'Rourke
C, Obuchowski NA, Wang JC, Steinmetz MP, Melillo AJ, Benzel EC,
Modic MT, et al: Differences in the surgical treatment of recurrent
lumbar disc herniation among spine surgeons in the United States.
Spine J. 14:2334–2343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jang JS, An SH and Lee SH: Transforaminal
percutaneous endoscopic discectomy in the treatment of foraminal
and extraforaminal lumbar disc herniations. J Spinal Disord Tech.
19:338–343. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kamper SJ, Ostelo RW, Rubinstein SM,
Nellensteijn JM, Peul WC, Arts MP and van Tulder MW: Minimally
invasive surgery for lumbar disc herniation: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 23:1021–1043. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kerr D, Zhao W and Lurie JD: What are
long-term predictors of outcomes for lumbar disc herniation? A
randomized and observational study. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
473:1920–1930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Golinvaux NS, Bohl DD, Basques BA, Yacob A
and Grauer JN: Comparison of the lumbar disc herniation patients
randomized in SPORT to 6,846 discectomy patients from NSQIP:
Demographics, perioperative variables, and complications correlate
well. Spine J. 15:685–691. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshimoto M, Iwase T, Takebayashi T, Ida K
and Yamashita T: Microendoscopic discectomy for far lateral lumbar
disk herniation: Less surgical invasiveness and minimum 2-year
follow-up results. J Spinal Disord Tech. 27:E1–E7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamashita K, Higashino K, Sakai T, Takata
Y, Abe M, Morimoto M, Nagamachi A and Sairyo K: Revision
percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy under the local
anesthesia for the recurrent lumbar herniated nucleus pulposus in a
high class athlete: A Case Report. J Med Invest. 63:135–139. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kapetanakis S, Giovannopoulou E,
Charitoudis G and Kazakos K: Transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic
discectomy for lumbar disc herniation in Parkinson's disease: A
Case-Control Study. Asian Spine J. 10:671–677. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Strömqvist F, Strömqvist B, Jönsson B and
Karlsson MK: Gender differences in patients scheduled for lumbar
disc herniation surgery: A National Register Study including 15,631
operations. Eur Spine J. 25:162–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Motor S, Ozturk S, Ozcan O, Gurpinar AB,
Can Y, Yuksel R, Yenin JZ, Seraslan G and Ozturk OH: Evaluation of
total antioxidant status, total oxidant status and oxidative stress
index in patients with alopecia areata. Int J Clin Exp Med.
7:1089–1093. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|