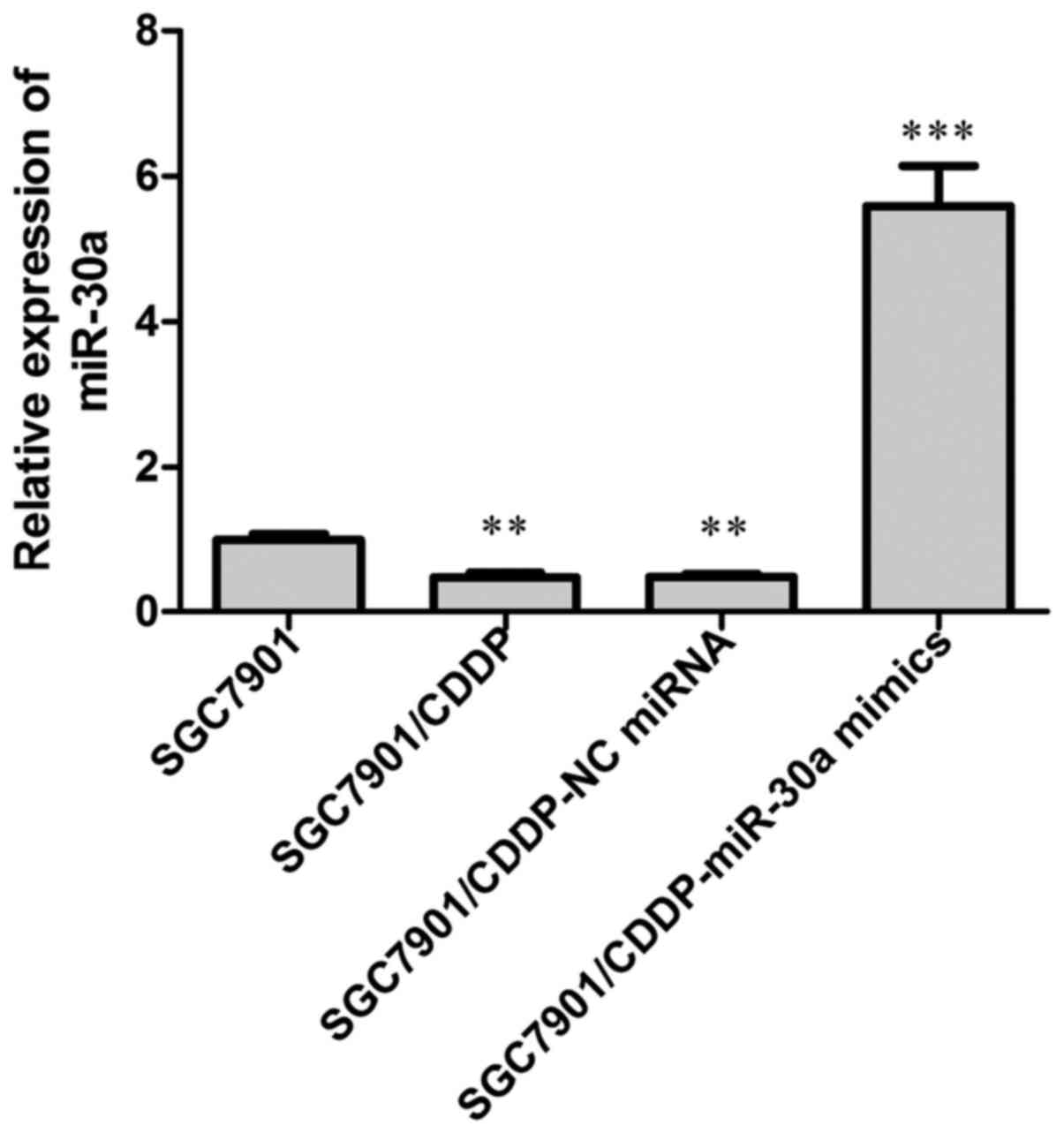
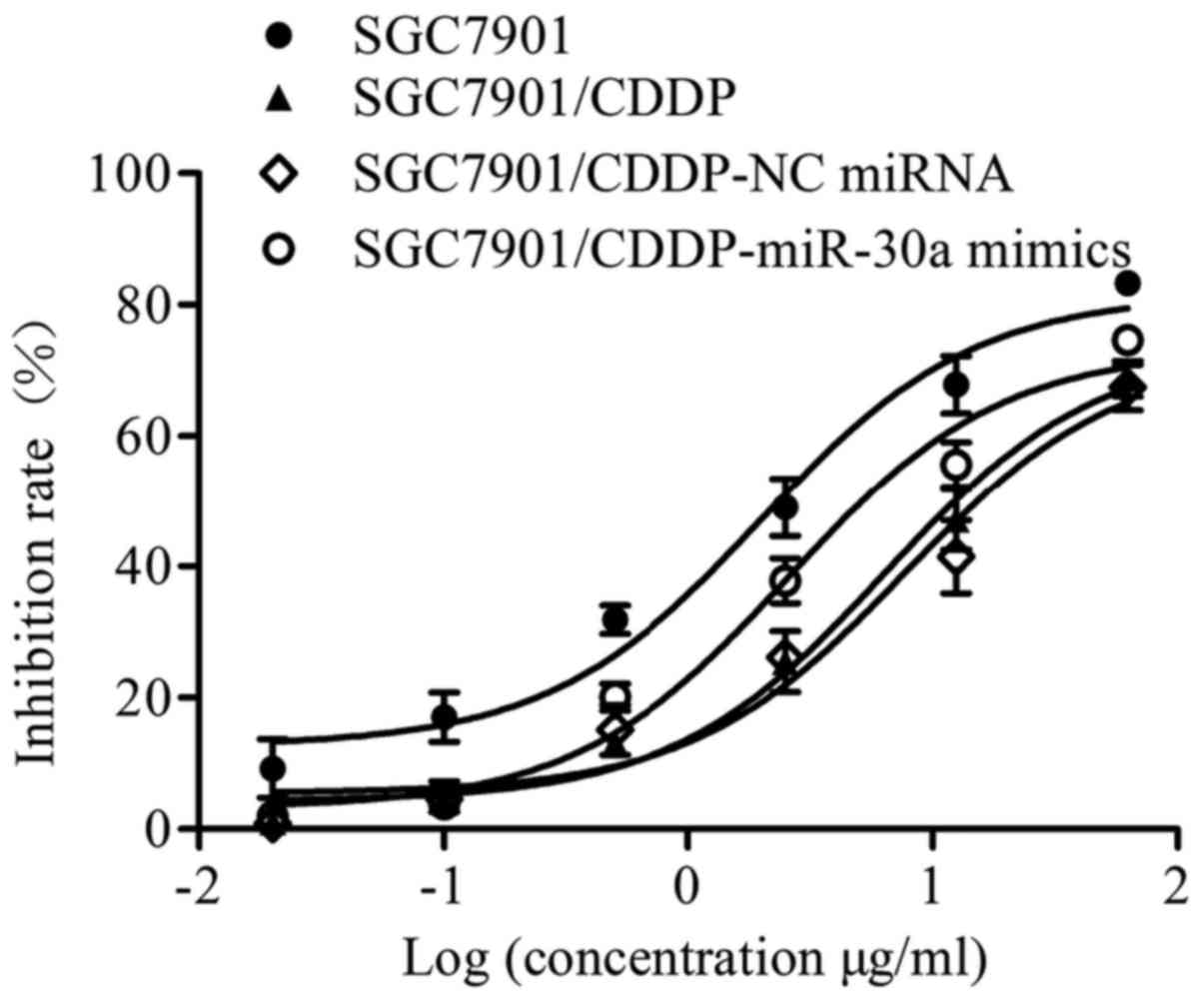
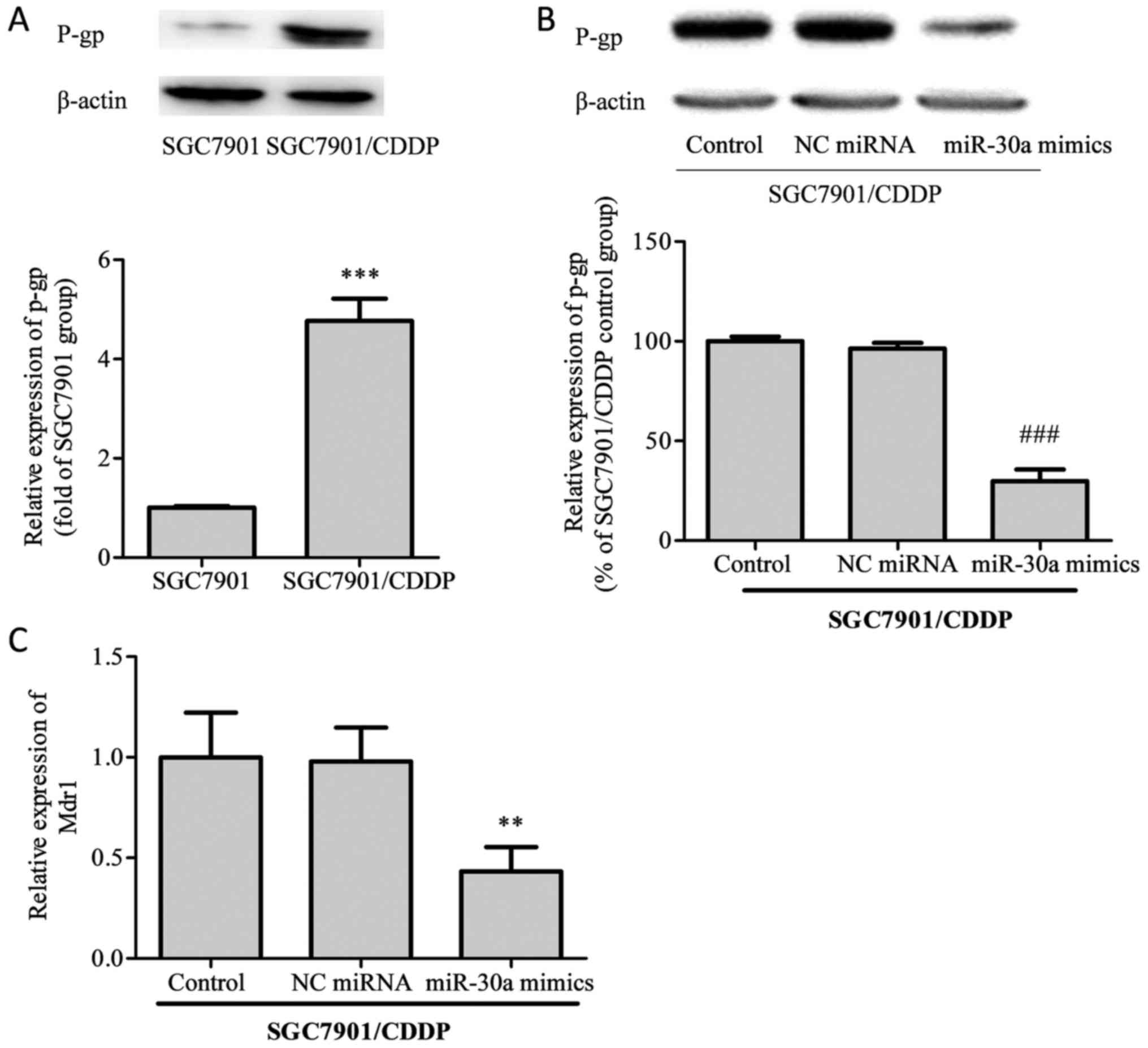
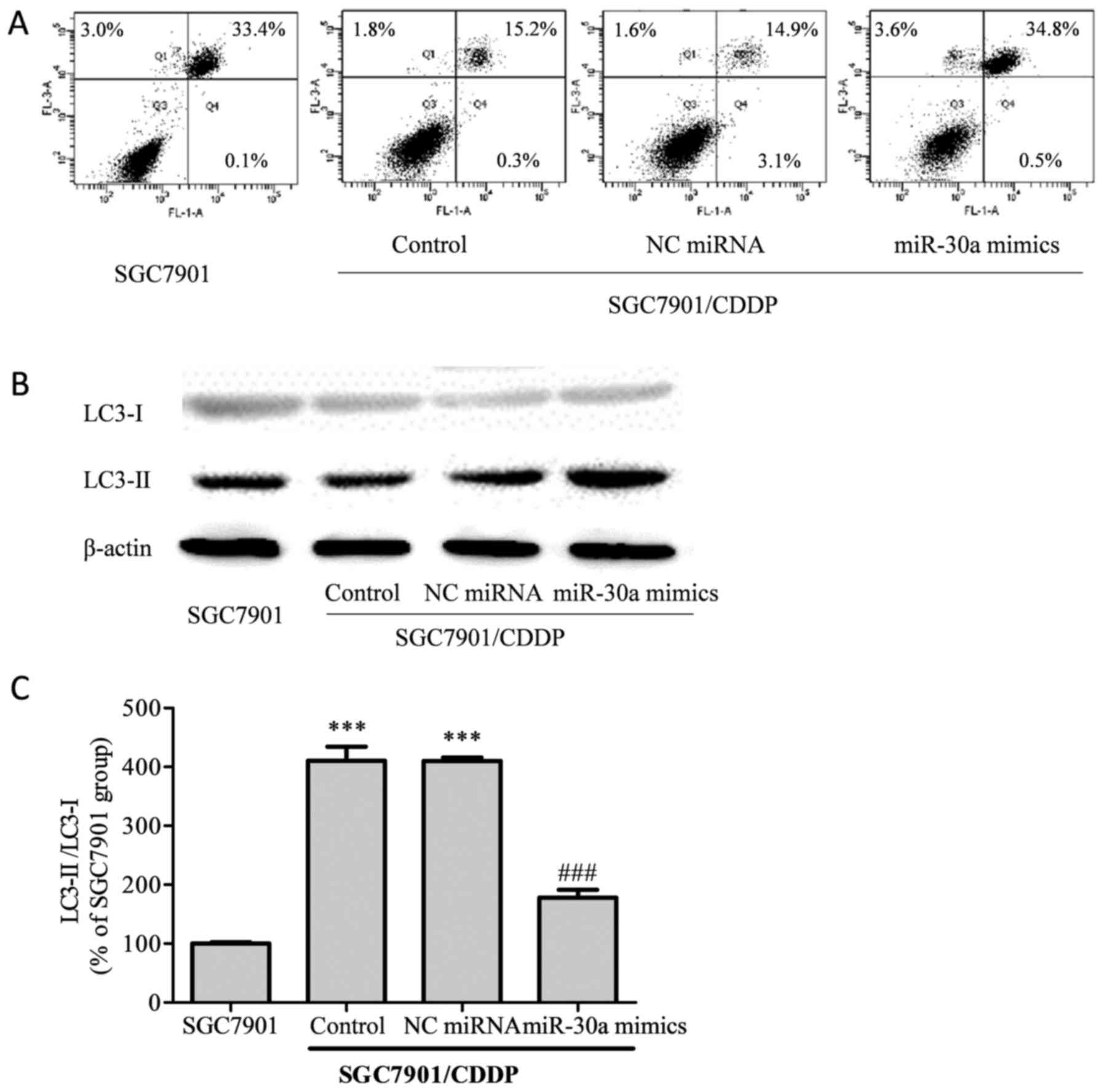
|
1
|
Xu W, Yang Z and Lu N: Molecular targeted
therapy for the treatment of gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:12016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu Y, Ying M, Huang C, Wei H, Jiang Z,
Peng X, Hu J, Du X, Wang B, Lin F, et al: Oncologic outcomes of
laparoscopy-assisted gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: A
large-scale multicenter retrospective cohort study from China. Surg
Endosc. 28:2048–2056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Connor R: The pharmacology of cancer
resistance. Anticancer Res. 27:1267–1272. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi JH, Lim HY, Joo HJ, Kim HS, Yi JW,
Kim HC, Cho YK, Kim MW and Lee KB: Expression of multidrug
resistance-associated protein1, P-glycoprotein and thymidylate
synthase in gastric cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil and
doxorubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy after curative resection.
Br J Cancer. 86:1578–1585. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morin PJ: Drug resistance and the
microenvironment: Nature and nurture. Drug Resist Updat. 6:169–172.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lippert TH, Ruoff HJ and Volm M: Intrinsic
and acquired drug resistance in malignant tumors. The main reason
for therapeutic failure. Arzneimittelforschung. 58:261–264.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang M and Du X: Noncoding RNAs in
gastric cancer: Research progress and prospects. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:6610–6618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tan P and Yeoh KG: Genetics and molecular
pathogenesis of gastric adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology.
149:1153–1162.e3. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song JH and Meltzer SJ: MicroRNAs in
pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of gastroesophageal cancers.
Gastroenterology. 143:35–47.e2. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang M and Du X: Noncoding RNAs in
gastric cancer: Research progress and prospects. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:6610–6618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Z, Chen L, Zhang X, Xu X, Xing H,
Zhang Y, Li W, Yu H, Zeng J, Jia J, et al: RUNX3 regulates vimentin
expression via miR-30a during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:610–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li C, Zou J, Zheng G and Chu J: miR-30a
decreases multidrug resistance (MDR) of gastric cancer cells. Med
Sci Monit. 0:02016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lai YC, Chuang YC, Chang CP and Yeh TM:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor has a permissive role in
concanavalin A-induced cell death of human hepatoma cells through
autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 6:e20082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi WJ and Gao JB: Molecular mechanisms of
chemoresistance in gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
8:673–681. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
An Y, Zhang Z, Shang Y, Jiang X, Dong J,
Yu P, Nie Y and Zhao Q: miR-23b-3p regulates the chemoresistance of
gastric cancer cells by targeting ATG12 and HMGB2. Cell Death Dis.
6:e17662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao L, Wang Y, Jiang L, He M, Bai X, Yu L
and Wei M: MiR-302a/b/c/d cooperatively sensitizes breast cancer
cells to adriamycin via suppressing P-glycoprotein(P-gp) by
targeting MAP/ERK kinase kinase 1 (MEKK1). J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abraham I, Jain S, Wu CP, Khanfar MA,
Kuang Y, Dai CL, Shi Z, Chen X, Fu L, Ambudkar SV, et al: Marine
sponge-derived sipholane triterpenoids reverse P-glycoprotein
(ABCB1)-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 80:1497–1506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fayad W, Fryknäs M, Brnjic S, Olofsson MH,
Larsson R and Linder S: Identification of a novel topoisomerase
inhibitor effective in cells overexpressing drug efflux
transporters. PLoS One. 4:e72382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu G, Pei F, Yang F, Li L, Amin AD, Liu
S, Buchan JR and Cho WC: Role of autophagy and apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18:pii: E3672017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qian HR and Yang Y: Functional role of
autophagy in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:17641–17651. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Talaiezadeh A, Jalali F, Galehdari H and
Khodadadi A: Time depended Bcl-2 inhibition might be useful for a
targeted drug therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 15:1052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cai Y, Xu P, Yang L, Xu K, Zhu J, Wu X,
Jiang C, Yuan Q, Wang B, Li Y and Qiu Y: HMGB1-mediated autophagy
decreases sensitivity to oxymatrine in SW982 human synovial sarcoma
cells. Sci Rep. 6:378452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An X, Sarmiento C, Tan T and Zhu H:
Regulation of multidrug resistance by microRNAs in anti-cancer
therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 7:38–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Donovan TR, O'Sullivan GC and McKenna
SL: Induction of autophagy by drug-resistant esophageal cancer
cells promotes their survival and recovery following treatment with
chemotherapeutics. Autophagy. 7:509–524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kumar A, Singh UK and Chaudhary A:
Targeting autophagy to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy.
Future Med Chem. 7:1535–1542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li LQ, Xie WJ, Pan D, Chen H and Zhang L:
Inhibition of autophagy by bafilomycin A1 promotes chemosensitivity
of gastric cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37:653–659. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bhattacharya B, Low SH, Soh C, Mustapa N
Kamal, Beloueche-Babari M, Koh KX, Loh J and Soong R: Increased
drug resistance is associated with reduced glucose levels and an
enhanced glycolysis phenotype. Br J Pharmacol. 171:3255–3267. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang C and Pan Y: Fluorouracil induces
autophagy-related gastric carcinoma cell death through Beclin-1
upregulation by miR-30 suppression. Tumour Biol. Jul 25–2015.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
30
|
Liu J, Zhang Y, Qu J, Xu L, Hou K, Zhang
J, Qu X and Liu Y: β-Elemene-induced autophagy protects human
gastric cancer cells from undergoing apoptosis. BMC Cancer.
11:1832011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee J, Giordano S and Zhang J: Autophagy,
mitochondria and oxidative stress: Cross-talk and redox signalling.
Biochem J. 441:523–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, Li B, Chen Y, Ren X,
Liu CG and Yang JM: Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted
microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells. Autophagy. 5:816–823. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|