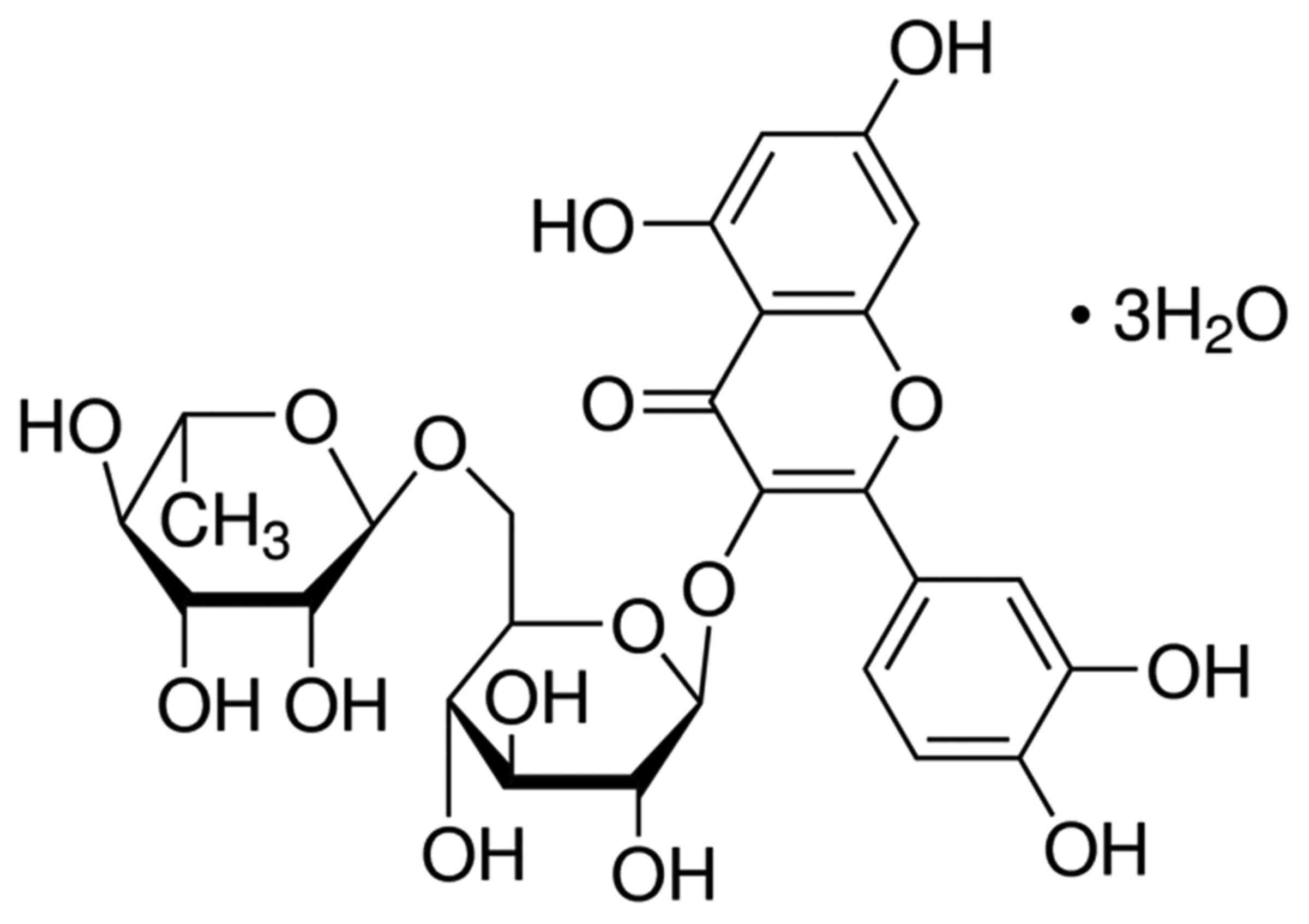
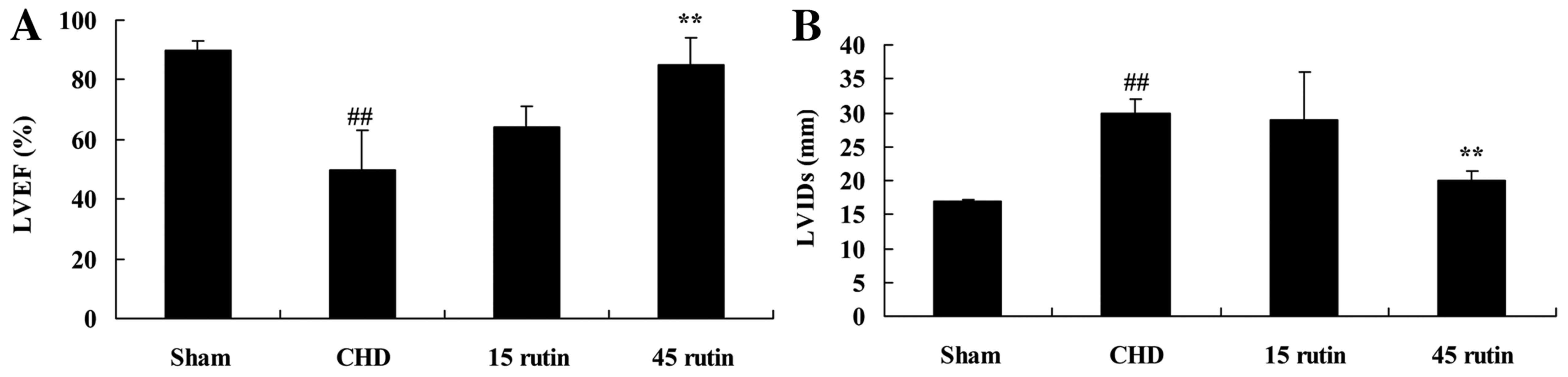
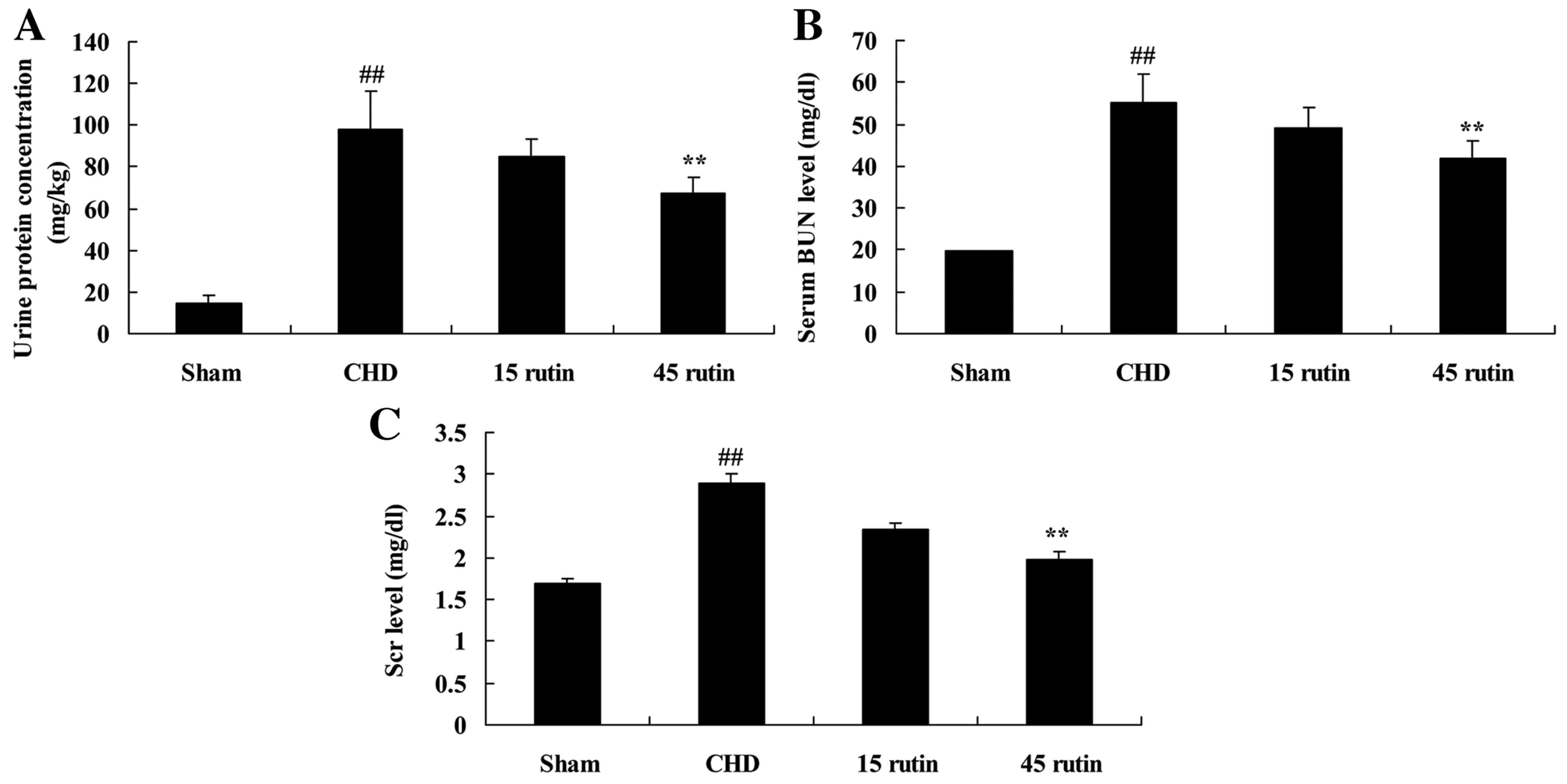
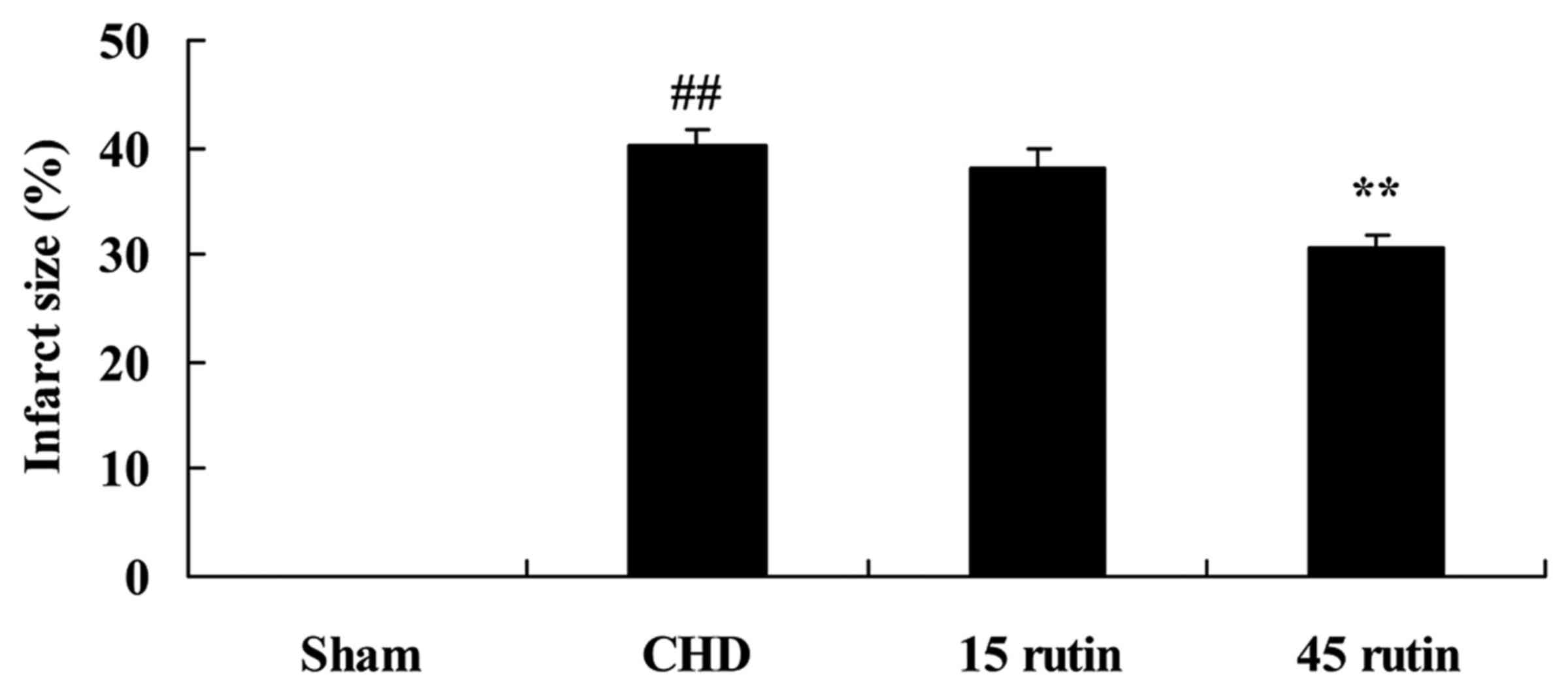
|
1
|
Ueno T, Chow LW and Toi M: Increases in
circulating VEGF levels during COX-2 inhibitor treatment in breast
cancer patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 60:277–279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chuah BY, Putti T, Salto-Tellez M,
Charlton A, Iau P, Buhari SA, Wong CI, Tan SH, Wong AL, Chan CW, et
al: Serial changes in the expression of breast cancer-related
proteins in response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol.
22:1748–1754. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kullo IJ, Jouni H, Olson JE, Montori VM
and Bailey KR: Design of a randomized controlled trial of
disclosing genomic risk of coronary heart disease: The myocardial
infarction genes (MI-GENES) study. BMC Med Genomics. 8:512015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pradeepa R, Surendar J, Indulekha K,
Chella S, Anjana RM and Mohan V: Prevalence of metabolic syndrome
and its association with coronary artery disease among an urban
elderly south indian population (CURES- 145). J Assoc Physicians
India. 64:20–25. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nissen SE, Yeomans ND, Solomon DH, Lüscher
TF, Libby P, Husni ME, Graham DY, Borer JS, Wisniewski LM, Wolski
KE, et al: Cardiovascular safety of celecoxib, naproxen, or
ibuprofen for arthritis. N Engl J Med. 375:2519–2529. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shirai T, Nazarewicz RR, Wallis BB, Yanes
RE, Watanabe R, Hilhorst M, Tian L, Harrison DG, Giacomini JC,
Assimes TL, et al: The glycolytic enzyme PKM2 bridges metabolic and
inflammatory dysfunction in coronary artery disease. J Exp Med.
213:337–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li H, Sun K, Zhao R, Hu J, Hao Z, Wang F,
Lu Y, Liu F and Zhang Y: Inflammatory biomarkers of coronary heart
disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 22:504–515. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li S, Fan Q, He S, Tang T, Liao Y and Xie
J: MicroRNA-21 negatively regulates treg cells through a
TGF-β1/Smad-independent pathway in patients with coronary heart
disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:866–878. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thakur A, Schalk D, Tomaszewski E,
Kondadasula SV, Yano H, Sarkar FH and Lum LG: Microenvironment
generated during EGFR targeted killing of pancreatic tumor cells by
ATC inhibits myeloid-derived suppressor cells through COX2 and PGE2
dependent pathway. J Transl Med. 11:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schaan BD, Quadros AS, Sarmento-Leite R,
De Lucca G Jr, Bender A and Bertoluci M: ‘Correction:’ Serum
transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-beta-1) levels in diabetic
patients are not associated with pre-existent coronary artery
disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 6:192007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Zeini M, Lin CY, Lin CJ, Xiong Y,
Shang C, Han P, Li W, Quertermous T, Zhou B and Chang CP:
Epicardial calcineurin-NFAT signals through Smad2 to direct
coronary smooth muscle cell and arterial wall development.
Cardiovasc Res. 101:120–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hosseinzadeh H and Nassiri-Asl M: Review
of the protective effects of rutin on the metabolic function as an
important dietary flavonoid. J Endocrinol Invest. 37:783–788. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chuffa LG, Fioruci-Fontanelli BA, Bordon
JG, Pires RB, Braga CP, Seiva FR and Fernandes AA: Rutin
ameliorates glycemic index, lipid profile and enzymatic activities
in serum, heart and liver tissues of rats fed with a combination of
hypercaloric diet and chronic ethanol consumption. Indian J Biochem
Biophys. 51:215–222. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu XL, Li YN, Zhang H, Su YJ, Zhou WW,
Zhang ZP, Wang SW, Xu PX, Wang YJ and Liu RT: Rutin inhibits
amylin-induced neurocytotoxicity and oxidative stress. Food Funct.
6:3296–3306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benavente-Garcia O and Castillo J: Update
on uses and properties of citrus flavonoids: New findings in
anticancer, cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory activity. J Agric
Food Chem. 56:6185–6205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han Y, Lu JS, Xu Y, Zhang L and Hong BF:
Rutin ameliorates renal fibrosis and proteinuria in
5/6-nephrectomized rats by anti-oxidation and inhibiting activation
of TGFβ1-smad signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4725–4734.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ammenwerth E, Woess S, Baumgartner C, Fetz
B, van der Heidt A, Kastner P, Modre-Osprian R, Welte S and Poelzl
G: Evaluation of an integrated telemonitoring surveillance system
in patients with coronary heart disease. Methods Inf Med.
54:388–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Salfati E, Nandkeolyar S, Fortmann SP,
Sidney S, Hlatky MA, Quertermous T, Go AS, Iribarren C, Herrington
DM, Goldstein BA and Assimes TL: Susceptibility loci for clinical
coronary artery disease and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis
throughout the life-course. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 8:803–811. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Jiang Y, Nguyen HD, Poo DC and
Wang W: The effect of a smartphone-based coronary heart disease
prevention (SBCHDP) programme on awareness and knowledge of CHD,
stress and cardiac-related lifestyle behaviours among the working
population in Singapore: A pilot randomised controlled trial.
Health Qual Life Outcomes. 15:492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Riegersperger M, Covic A and Goldsmith D:
Allopurinol, uric acid and oxidative stress in cardiorenal disease.
Int Urol Nephrol. 43:441–449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prasad K and Dhar I: Oxidative stress as a
mechanism of added sugar-induced cardiovascular disease. Int J
Angiol. 23:217–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Turan T, Menteşe Ü, Ağaç MT, Akyüz AR, Kul
S, Aykan AÇ, Bektaş H, Korkmaz L, Öztaş Menteşe S, Dursun İ and
Çelik Ş: The relation between intensity and complexity of coronary
artery lesion and oxidative stress in patients with acute coronary
syndrome. Anatol J Cardiol. 15:795–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang J, Wang M, Li Z, Bi X, Song J, Weng
S and Fu G: NADPH oxidase activation played a critical role in the
oxidative stress process in stable coronary artery disease. Am J
Transl Res. 8:5199–5210. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zurgil N, Solodeev I, Gilburd B, Shafran
Y, Afrimzon E, Avtalion R, Shoenfeld Y and Deutsch M: Monitoring
the apoptotic process induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein
in Jurkat T-lymphoblast and U937 monocytic human cell lines. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 40:97–113. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pintér Ö, Hardi P, Nagy T, Gasz B, Kovács
V, Arató E, Sínay L, Lénárd L and Jancsó G: The role of GST
polymorphism in reperfusion induced oxidative stress, inflammatory
responses and clinical complications after surgical and
percutaneous coronary intervention. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc.
66:261–272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Crobu F, Palumbo L, Franco E, Bergerone S,
Carturan S, Guarrera S, Frea S, Trevi G, Piazza A and Matullo G:
Role of TGF-beta1 haplotypes in the occurrence of myocardial
infarction in young Italian patients. BMC Med Genet. 9:132008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Purnomo Y, Piccart Y, Coenen T, Prihadi JS
and Lijnen PJ: Oxidative stress and transforming growth
factor-beta1-induced cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord
Drug Targets. 13:165–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Huang F, Li J and
Wang S: MicroRNAs, TGF-β signaling and the inflammatory
microenvironment in cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:115–125. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen Y, Zhang C and Chen Y: TGF-β in
inflammatory bowel diseases: A tale of the janus-like cytokine.
Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 25:335–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Valls N, Gormaz JG, Aguayo R, González J,
Brito R, Hasson D, Libuy M, Ramos C, Carrasco R, Prieto JC, et al:
Amelioration of persistent left ventricular function impairment
through increased plasma ascorbate levels following myocardial
infarction. Redox Rep. 21:75–83. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Forbes K, Souquet B, Garside R, Aplin JD
and Westwood M: Transforming growth factor-{beta} (TGF{beta})
receptors I/II differentially regulate TGF{beta}1 and IGF-binding
protein-3 mitogenic effects in the human placenta. Endocrinology.
151:1723–1731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thu VT, Kim HK, le T Long, Thuy TT, Huy
NQ, Kim SH, Kim N, Ko KS, Rhee BD and Han J: NecroX-5 exerts
anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects via modulation of the
TNFα/Dcn/TGFβ1/Smad2 pathway in hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated rat
hearts. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 20:305–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhong Y, Cheng CF, Luo YZ, Tian CW, Yang
H, Liu BR, Chen MS, Chen YF and Liu SM: C-reactive protein
stimulates RAGE expression in human coronary artery endothelial
cells in vitro via ROS generation and ERK/NF-κB activation. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 36:440–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tarone G, Sbroggiò M and Brancaccio M: Key
role of ERK1/2 molecular scaffolds in heart pathology. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 70:4047–4054. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu J, Wang L, Akinyi M, Li Y, Duan Z, Zhu
Y and Fan G: Danshensu protects isolated heart against ischemia
reperfusion injury through activation of Akt/ERK1/2/Nrf2 signaling.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:14793–14804. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee YH, Lee SJ, Jung JE, Kim JS, Lee NH
and Yi HK: Terrein reduces age-related inflammation induced by
oxidative stress through Nrf2/ERK1/2/HO-1 signalling in aged HDF
cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 33:479–486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hao Q, Chen X, Wang X, Dong B and Yang C:
Curcumin attenuates angiotensin ii-induced abdominal aortic
aneurysm by inhibition of inflammatory response and ERK signaling
pathways. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:2709302014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pang X, Liu J, Li Y, Zhao J and Zhang X:
Emodin inhibits homocysteine-induced c-reactive protein generation
in vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating ppargamma expression
and ROS-ERK1/2/p38 signal pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01312952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jeong JJ, Ha YM, Jin YC, Lee EJ, Kim JS,
Kim HJ, Seo HG, Lee JH, Kang SS, Kim YS and Chang KC: Rutin from
Lonicera japonica inhibits myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced
apoptosis in vivo and protects H9c2 cells against hydrogen
peroxide-mediated injury via ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signals in vitro.
Food Chem Toxicol. 47:1569–1576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hamamdzic D, Fenning RS, Patel D, Mohler
ER III, Orlova KA, Wright AC, Llano R, Keane MG, Shannon RP,
Birnbaum MJ and Wilensky RL: Akt pathway is hypoactivated by
synergistic actions of diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia
resulting in advanced coronary artery disease. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 299:H699–H706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moghbelinejad S, Nassiri-Asl M, Farivar
TN, Abbasi E, Sheikhi M, Taghiloo M, Farsad F, Samimi A and Hajiali
F: Rutin activates the MAPK pathway and BDNF gene expression on
beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Lett.
224:108–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|