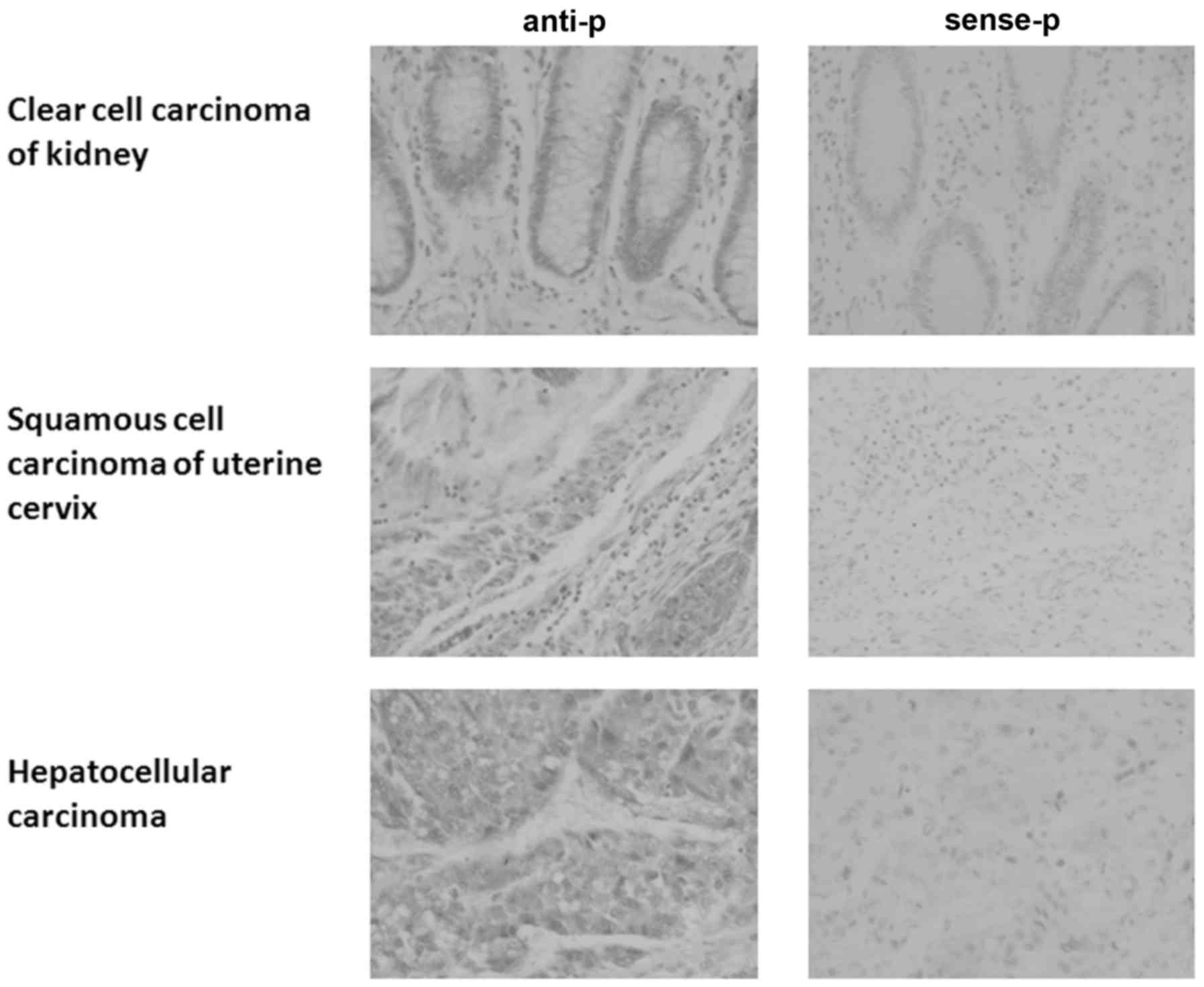
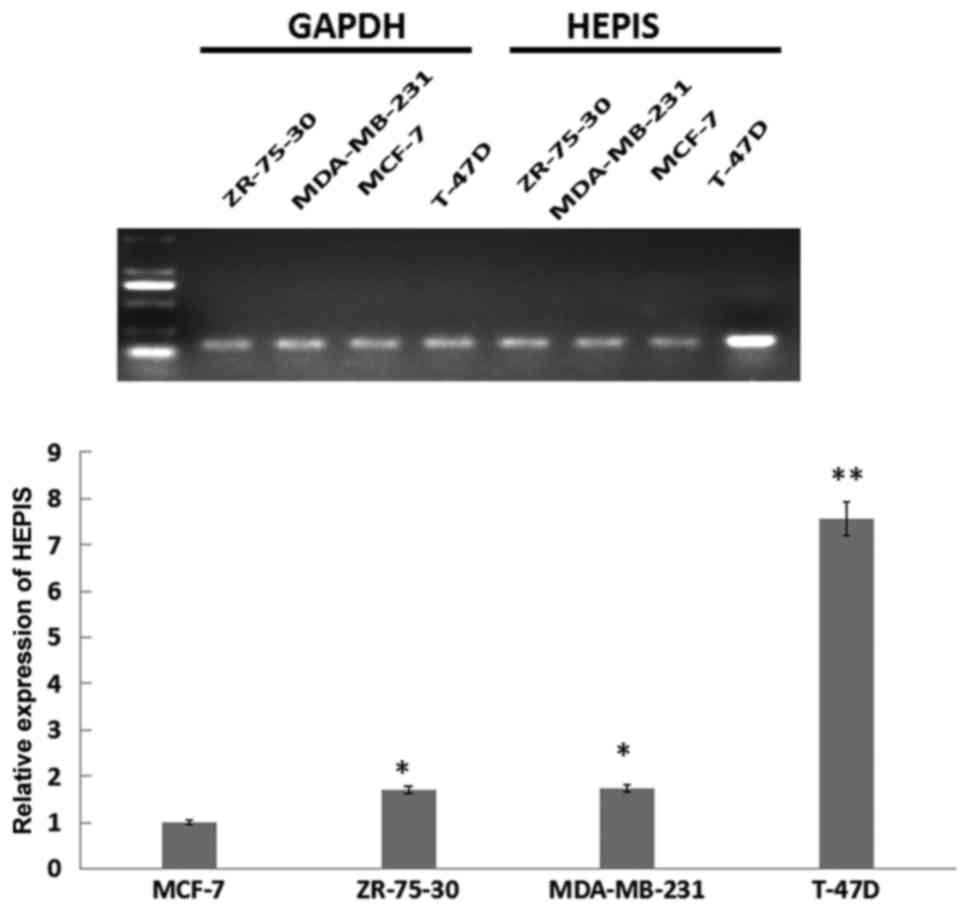
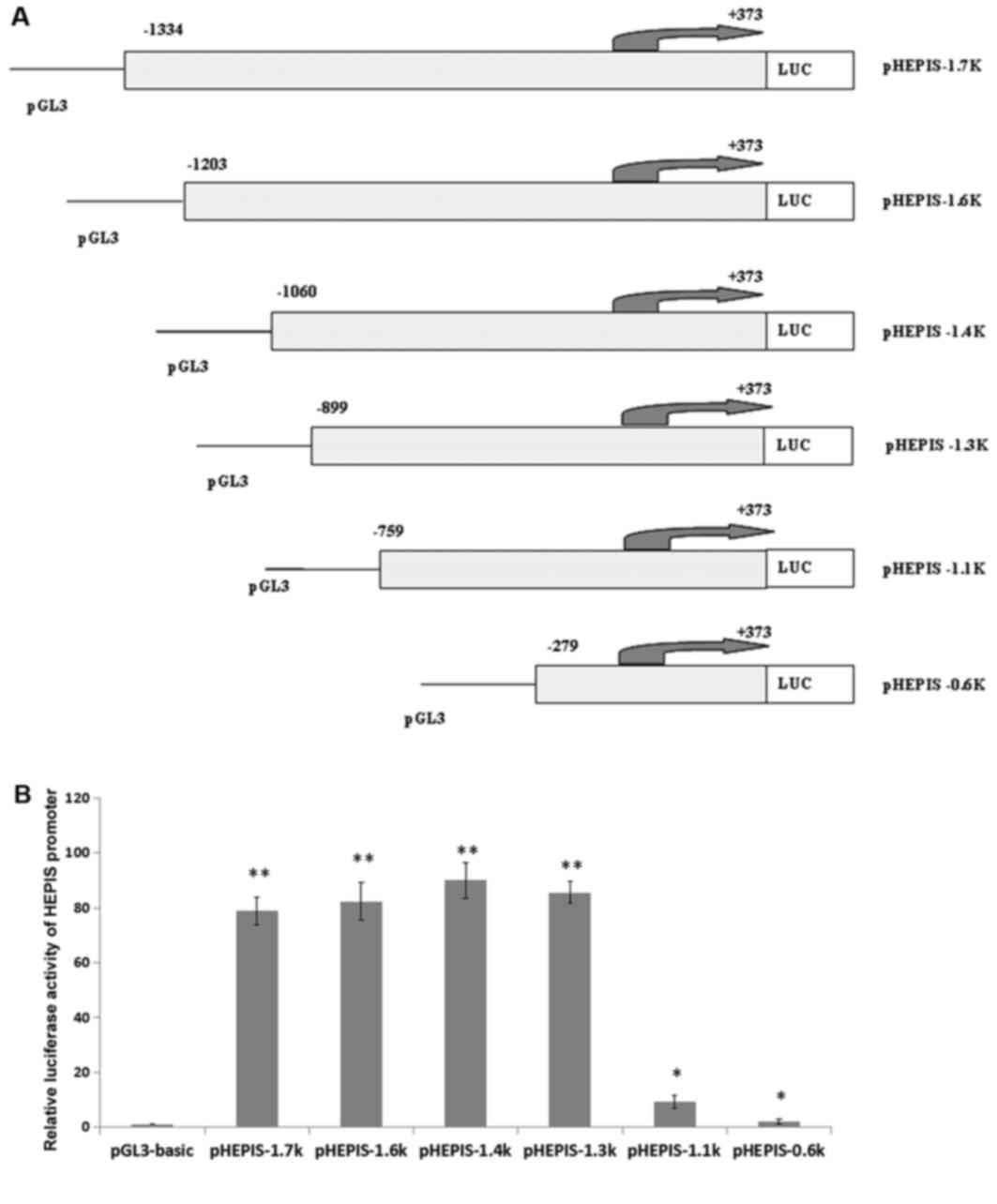
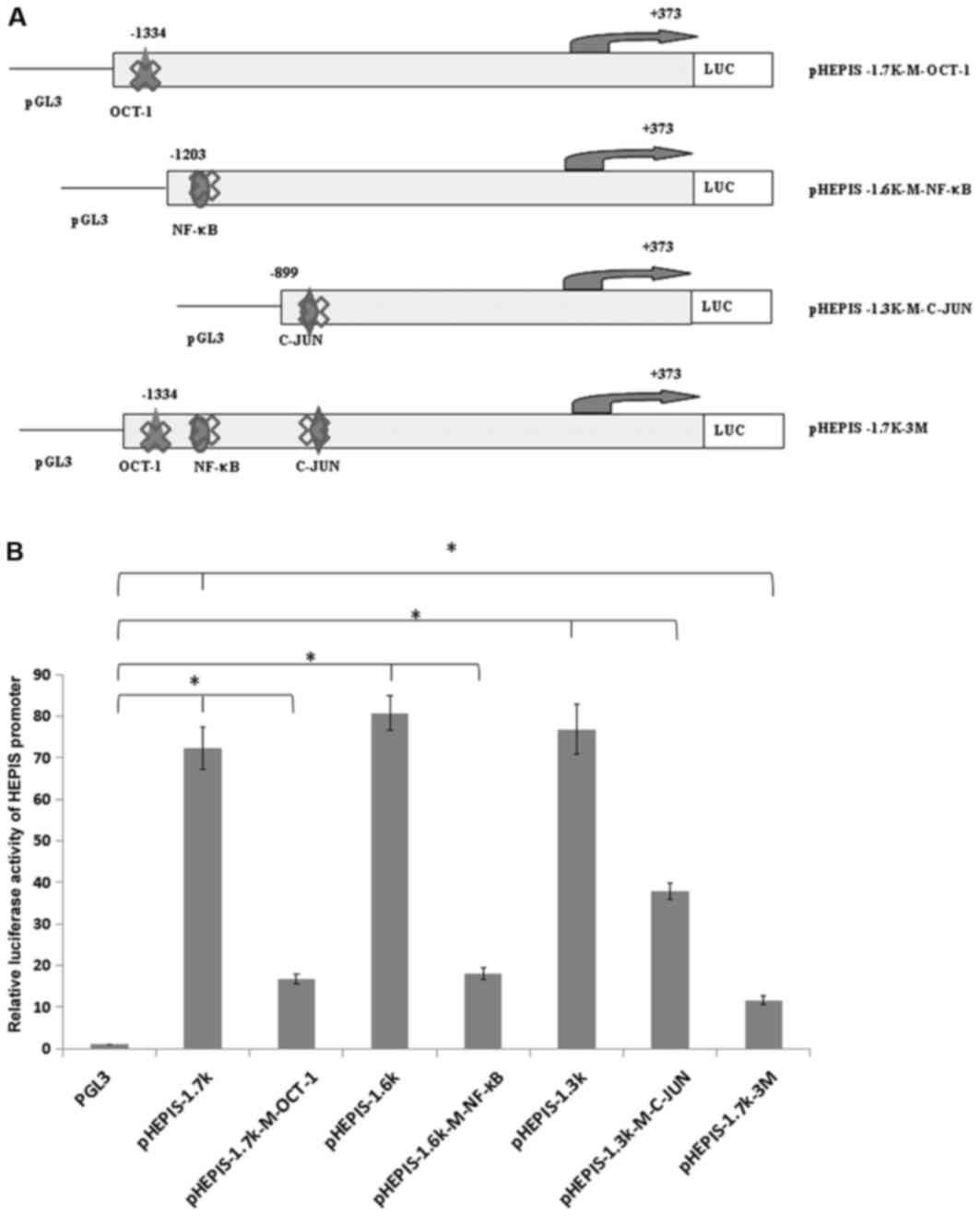
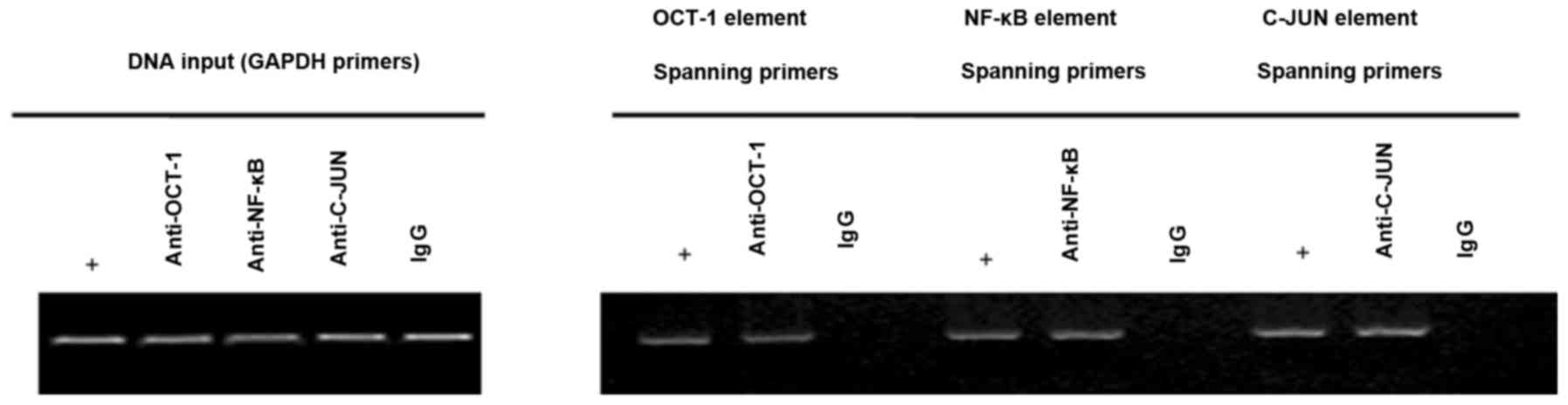
|
1
|
Hong M, Li W, Wang L, Jiang L, Liu L, Zhao
H and Li Q: Identification of a novel transcriptional repressor
(HEPIS) that interacts with nsp-10 of SARS coronavirus. Viral
immunol. 21:153–162. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sawicki SG, Sawicki DL, Younker D, Meyer
Y, Thiel V, Stokes H and Siddell SG: Functional and genetic
analysis of coronavirus replicase-transcriptase proteins. PLoS
Pathog. 1:e392005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edwards R, Machina A, McGregor G and van
den Driessche P: A modelling framework for gene regulatory networks
including transcription and translation. Bull Math Biol.
77:953–983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shanmugam MK, Nguyen AH, Kumar AP, Tan BK
and Sethi G: Targeted inhibition of tumor proliferation, survival,
and metastasis by pentacyclic triterpenoids: Potential role in
prevention and therapy of cancer. Cancer Lett. 320:158–170. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sterling K and Bresnick E: Oct-1
transcription factor is a negative regulator of rat CYP1A1
expression via an octamer sequence in its negative regulatory
element. Mol Pharmacol. 49:329–337. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee MC, Toh LL, Yaw LP and Luo Y:
Drosophila octamer elements and Pdm-1 dictate the coordinated
transcription of core histone genes. J Biol Chem. 285:9041–9053.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang P, Wang Q, Sun J, Wu J, Li H, Zhang
N, Huang Y, Su B, Li RK, Liu L, et al: POU homeodomain protein
Oct-1 functions as a sensor for cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem.
284:26456–26465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malin S, Linderson Y, Almqvist J, Ernberg
I, Tallone T and Pettersson S: DNA-dependent conversion of Oct-1
and Oct-2 into transcriptional repressors by Groucho/TLE. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:4618–4625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou C, Tong Y, Wawrowsky K, Bannykh S,
Donangelo I and Melmed S: Oct-1 induces pituitary tumor
transforming gene expression in endocrine tumors. Endocr-Relat
Cancer. 15:817–831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Obinata D, Takayama K, Urano T, Murata T,
Kumagai J, Fujimura T, Ikeda K, Horie-Inoue K, Homma Y, Ouchi Y, et
al: Oct1 regulates cell growth of LNCaP cells and is a prognostic
factor for prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:1021–1028. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Zhu S, Shen M, Liu J, Wang M, Li
C, Wang Y, Deng A and Mei Q: STAT3 is involved in esophageal
carcinogenesis through regulation of Oct-1. Carcinogenesis.
34:678–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang YP, Song GH, Chen J, Xiao C, Li C,
Zhong L, Sun X, Wang ZW, Deng GL, Yu FD, et al: Elevated OCT1
participates in colon tumorigenesis and independently predicts poor
prognoses of colorectal cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 37:3247–3255.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-[kappa] B activity. Annu
Rev Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gebel HM, Braun DP, Tambur A, Frame D,
Rana N and Dmowski WP: Spontaneous apoptosis of endometrial tissue
is impaired in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril.
69:1042–1047. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huxford T, Malek S and Ghosh G: Structure
and mechanism in NF-kappa B/I kappa B signaling. Cold Spring Harb
Symp Quant Biol. 64:533–540. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shaulian E and Karin M: AP-1 in cell
proliferation and survival. Oncogene. 20:2390–2400. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eferl R and Wagner EF: AP-1: A
double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:859–868.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li GC, Gustafson-Brown C, Hanks SK, Nason
K, Arbeit JM, Pogliano K, Wisdom RM and Johnson RS: c-Jun is
essential for organization of the epidermal leading edge. Dev Cell.
4:865–877. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen G, Jeong WS, Hu R and Kong AN:
Regulation of Nrf2, NF-kappaB, and AP-1 signaling pathways by
chemopreventive agents. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:1648–1663. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu F, Yang S, Lv S, Peng Y, Meng L, Gou L
and Zhang X: Analysis of AC3-33 gene expression in multiple organ
cancer and adjacent normal tissue by RNA in situ hybridization.
Oncol Lett. 9:2795–2798. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu F, Meng Y, Gou L and Zhang X: Analysis
of promoters and CREB/AP-1 binding sites of the human TMEM174 gene.
Exp Ther Med. 6:1290–1294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Denijn M, Schuurman HJ, Jacobse KC and De
Weger RA: In situ hybridization: A valuable tool in diagnostic
pathology. APMIS. 100:669–681. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vale G and Dell'Orto P: Non-radioactive
nucleic acid probes: Labeling and detection procedures. Liver.
12:243–251. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Farnham PJ: Insights from genomic
profiling of transcription factors. Nat Rev Genet. 10:605–616.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|