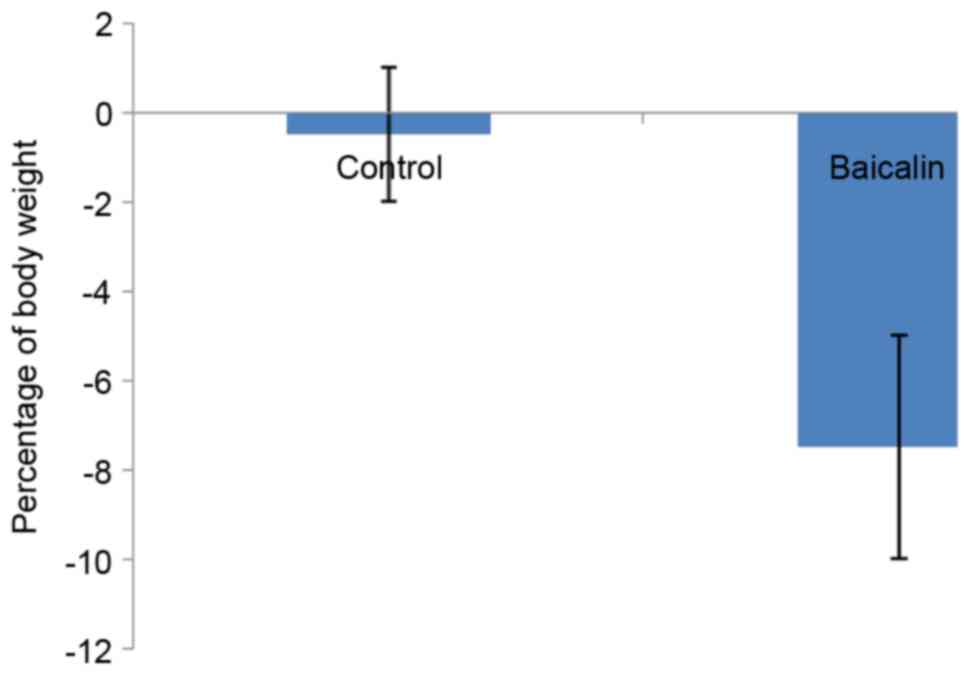
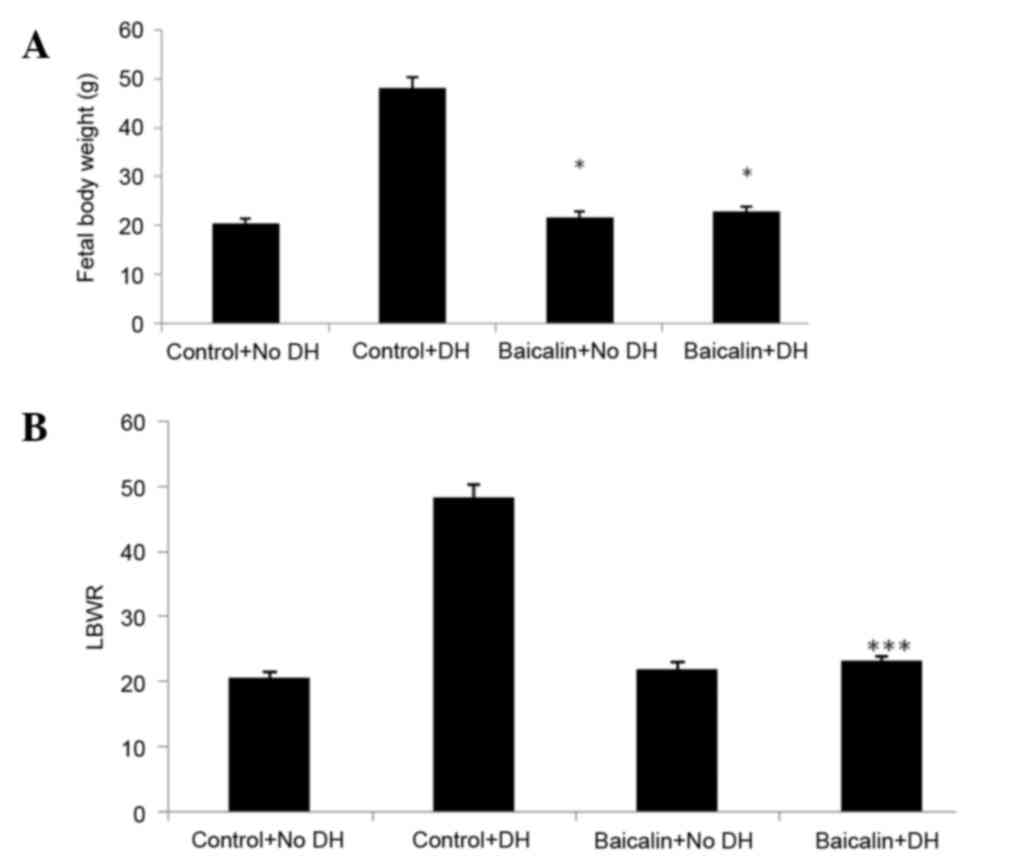
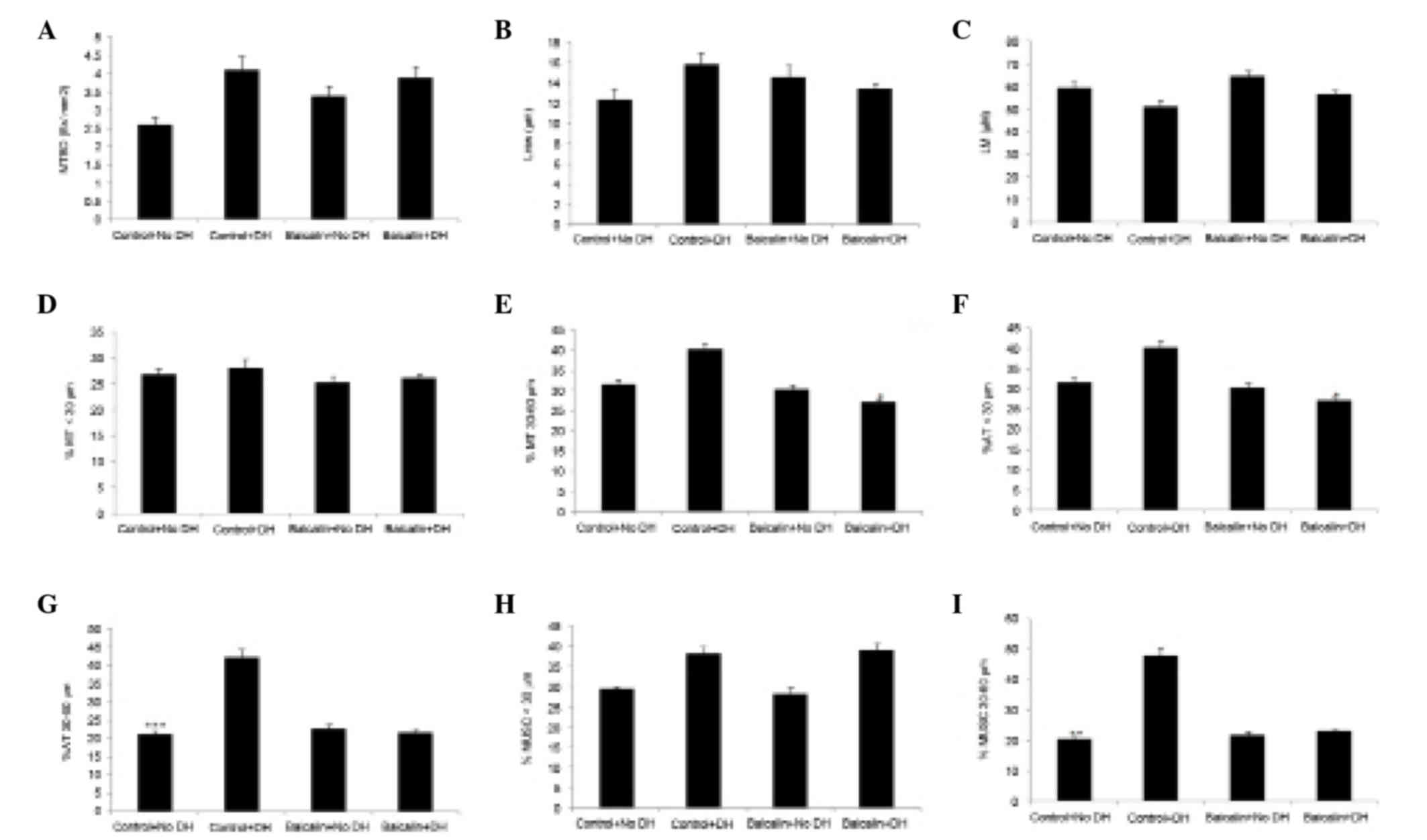
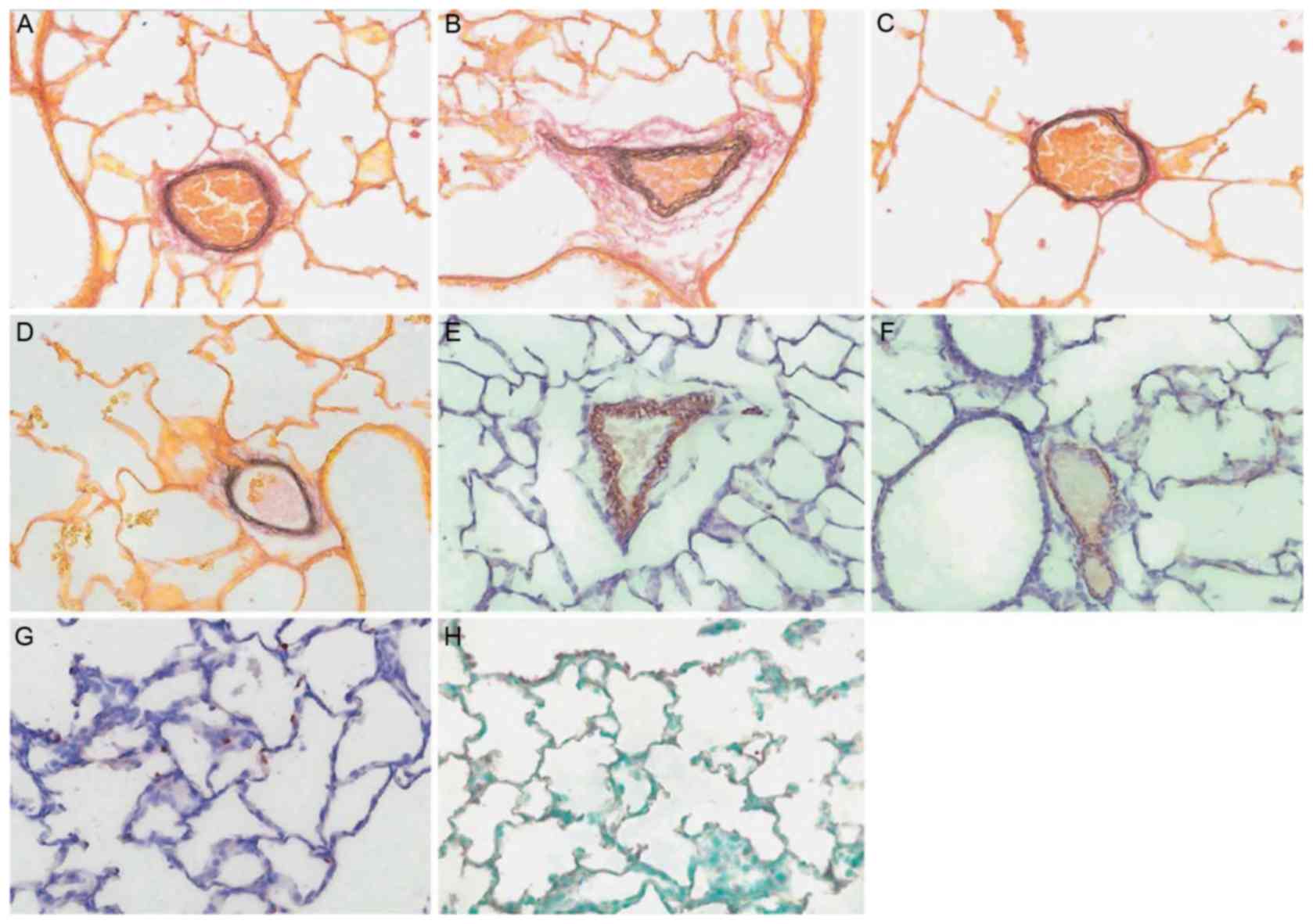
|
1
|
Clark RH, Hardin WD Jr, Hirschl RB, Jaksic
T, Lally KP, Langham MR Jr and Wilson JM: Current surgical
management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: A report from the
congenital diaphragmatic hernia study group. J Pediatr Surg.
33:1004–1009. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stoll C, Alembik Y, Dott B and Roth MP:
Associated malformations in cases with congenital diaphragmatic
hernia. Genet Couns. 19:331–339. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsao K and Lally KP: The congenital
diaphragmatic hernia study group: A voluntary international
registry. Semin Pediatr Surg. 17:90–97. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verbelen T, Lerut T, Coosemans W, De Leyn
P, Nafteux P, Van Raemdonck D, Deprest J and Decaluwé H: Antireflux
surgery after congenital diaphragmatic hernia repair: A plea for a
tailored approach. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 44:263–268. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dekoninck P, Gratacos E, Van Mieghem T,
Richter J, Lewi P, Ancel AM, Allegaert K, Nicolaides K and Deprest
J: Results of fetal endoscopic tracheal occlusion for congenital
diaphragmatic hernia and the set up of the randomized controlled
TOTAL trial. Early Hum Dev. 87:619–624. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trudinger BJ and Knight PC: Fetal age and
patterns of human fetal breathing movements. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
137:724–728. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Davey MG, Danzer E, Schwarz U, Robinson L,
Shegu S, Adzick NS, Flake AW and Hedrick HL: Prenatal
glucocorticoids improve lung morphology and partially restores
surfactant mRNA expression in lambs with diaphragmatic hernia
undergoing fetal tracheal occlusion. Pediatr Pulmonol.
41:1188–1196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lewis NA, Holm BA, Rossman J, Swartz D and
Glick PL: Late administration of antenatal vitamin A promotes
pulmonary structural maturation and improves ventilation in the
lamb model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int.
27:119–124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li BQ, Fu T, Gong WH, Dunlop N, Kung H,
Yan Y, Kang J and Wang JM: The flavonoid baicalin exhibits
anti-inflammatory activity by binding to chemokines.
Immunopharmacology. 49:295–306. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tarragó T, Kichik N, Claasen B, Prades R,
Teixidó M and Giralt E: Baicalin, a prodrug able to reach the CNS,
is a prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem.
16:7516–7524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shieh DE, Cheng HY, Yen MH, Chiang LC and
Lin CC: Baicalin-induced apoptosis is mediated by Bcl-2-dependent,
but not p53-dependent, pathway in human leukemia cell lines. Am J
Chin Med. 34:245–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen CM, Wang LF and Cheng KT: Maternal
baicalin treatment increases fetal lung surfactant phospholipids in
rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:4087142011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu J, Yamamoto H, Gratacos E, Ge X,
Verbeken E, Sueishi K, Hashimoto S, Vanamo K, Lerut T and Deprest
J: Lung development following diaphragmatic hernia in the fetal
rabbit. Human Reprod. 15:2483–2488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hattori Y, Jojima T, Tomizawa A, Satoh H,
Hattori S, Kasai K and Hayashi T: A glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
analogue, liraglutide, upregulates nitric oxide production and
exerts anti-inflammatory action in endothelial cells. Diabetologia.
53:2256–2263. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Middleton E Jr, Kandaswami C and
Theoharides TC: The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells:
Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol
Rev. 52:673–751. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bonham M, Posakony J, Coleman I,
Montgomery B, Simon J and Nelson PS: Characterization of chemical
constituents in Scutellaria baicalensis with antiandrogenic and
growth-inhibitory activities toward prostate carcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:3905–3914. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang KL, Chen CS, Hsu CW, Li MH, Chang H,
Tsai SH and Chu SJ: Therapeutic effects of baicalin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Am J Chin
Med. 36:301–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eastwood MP, Kampmeijer A, Jimenez J, Zia
S, Vanbree R, Verbist G, Toelen J and Deprest JA: The effect of
transplacental administration of glucagon-like peptide-1 on fetal
lung development in the rabbit model of congenital diaphragmatic
hernia. Fetal Diagn Ther. 39:125–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Santos M, Bastos P, Gonzaga S, Roriz JM,
Baptista MJ, Nogueira-Silva C, Melo-Rocha G, Henriques-Coelho T,
Roncon-Albuquerque R Jr, Leite-Moreira AF, et al: Ghrelin
expression in human and rat fetal lungs and the effect of ghrelin
administration in nitrofen-induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
Pediatr Res. 59:531–537. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Keijzer R, Liu J, Deimling J, Tibboel D
and Post M: Dual-hit hypothesis explains pulmonary hypoplasia in
the nitrofen model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Pathol.
156:1299–1306. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Garne E, Haeusler M, Barisic I, Gjergja R,
Stoll C and Clementi M; Euroscan Study Group, : Congenital
diaphragmatic hernia: Evaluation of prenatal diagnosis in 20
European regions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 19:329–333. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Romaní-Pérez M, Outeiriño-Iglesias V,
Gil-Lozano M, González-Matías LC, Mallo F and Vigo E: Pulmonary
GLP-1 receptor increases at birth and exogenous GLP-1 receptor
agonists augmented surfactant-protein levels in litters from normal
and nitrofen-treated pregnant rats. Endocrinology. 154:1144–1155.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mendelson CR and Boggaram V: Hormonal and
developmental regulation of pulmonary surfactant synthesis in fetal
lung. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 4:351–378. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kamaruzaman NA, Kardia E, Kamaldin N',
Latahir AZ and Yahaya BH: The rabbit as a model for studying lung
disease and stem cell therapy. Biomed Res Int. 2013:6918302013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|