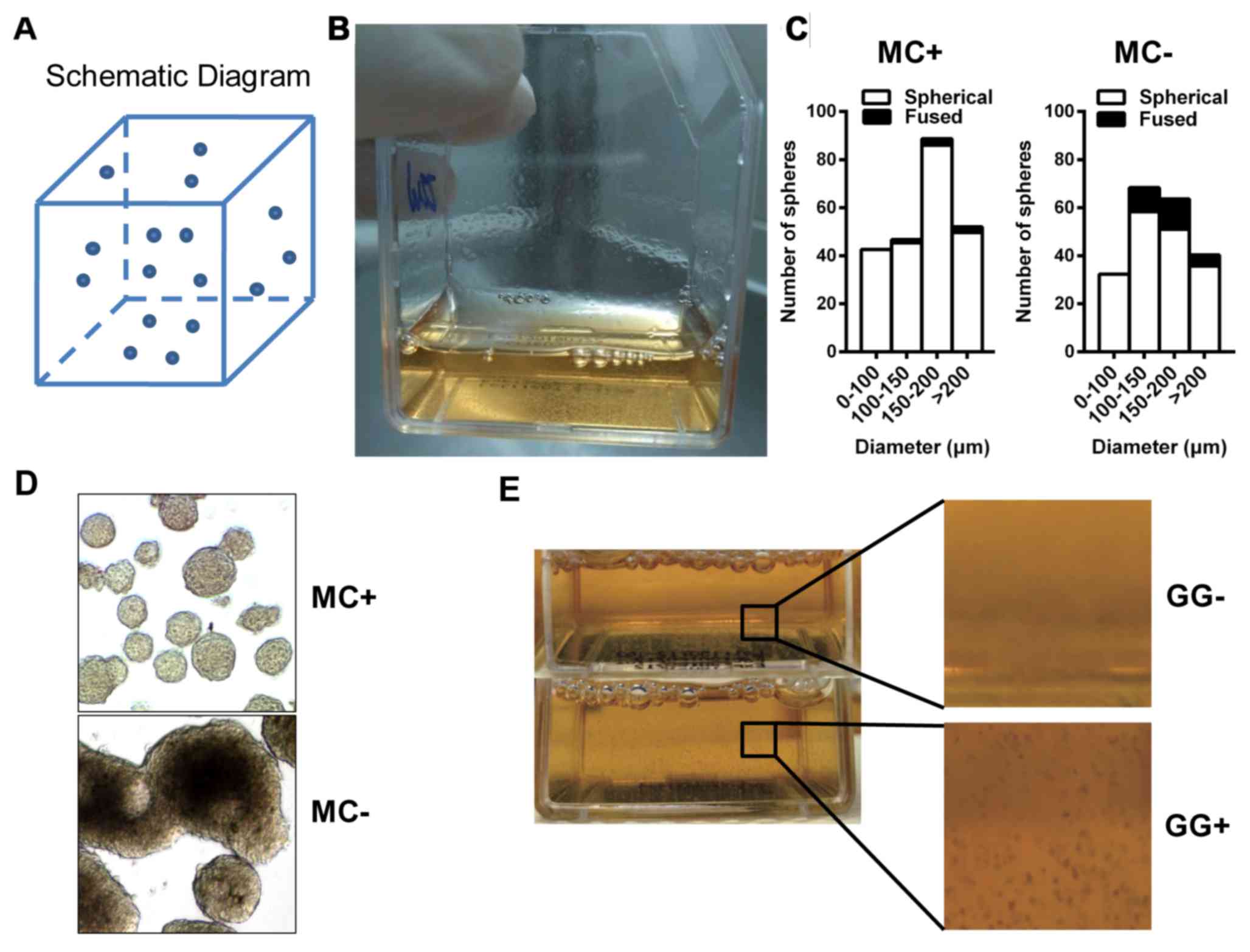
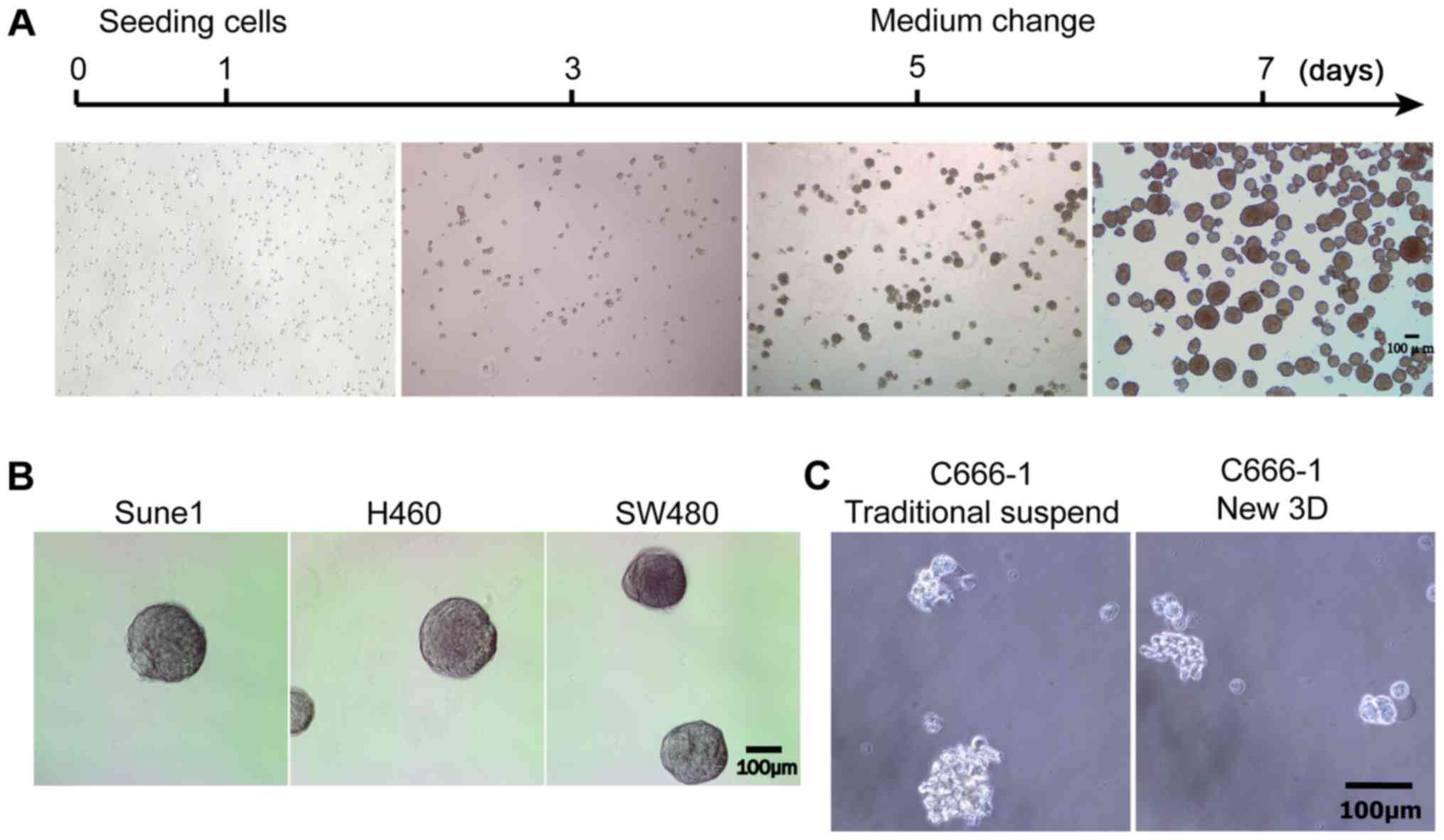
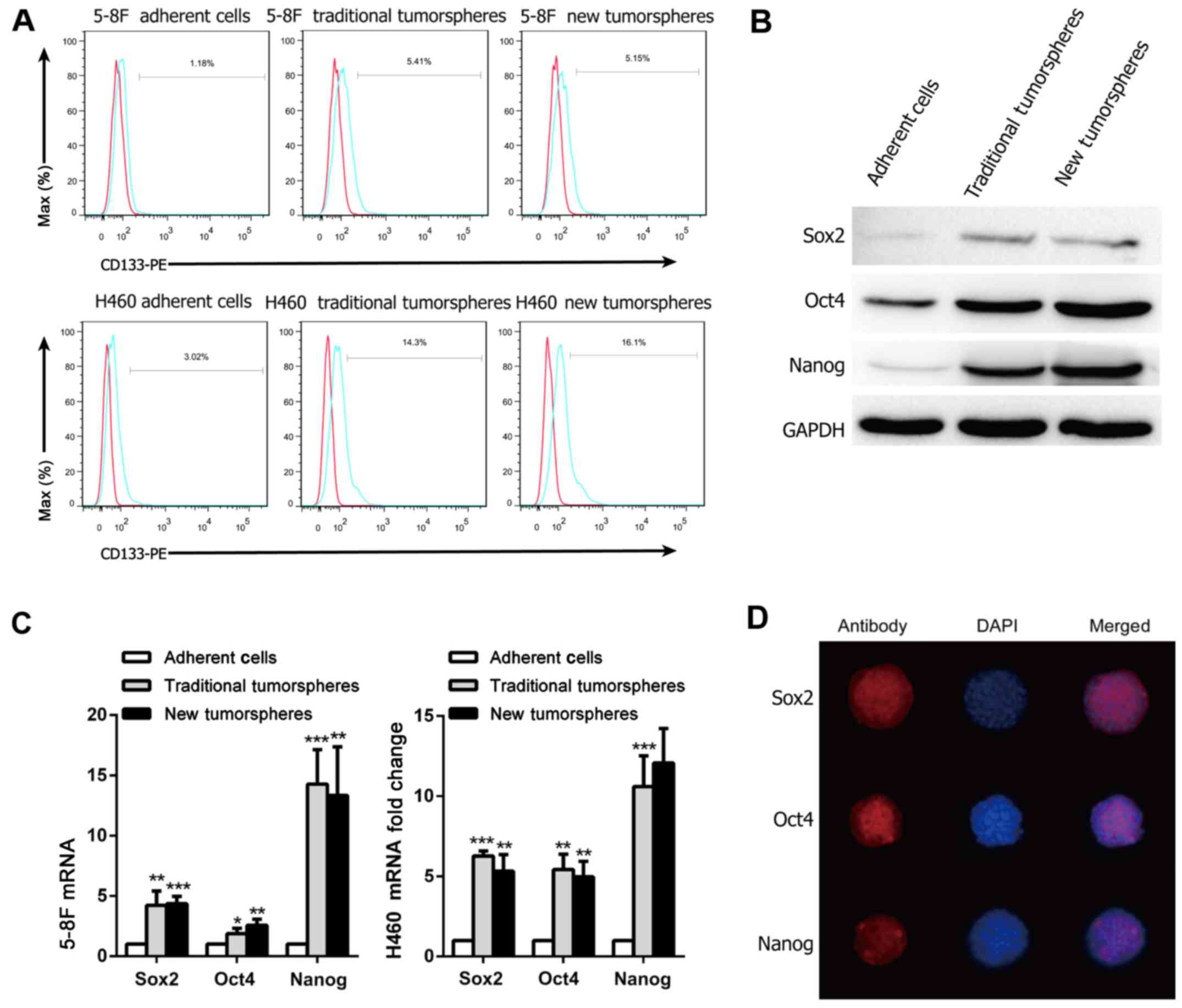
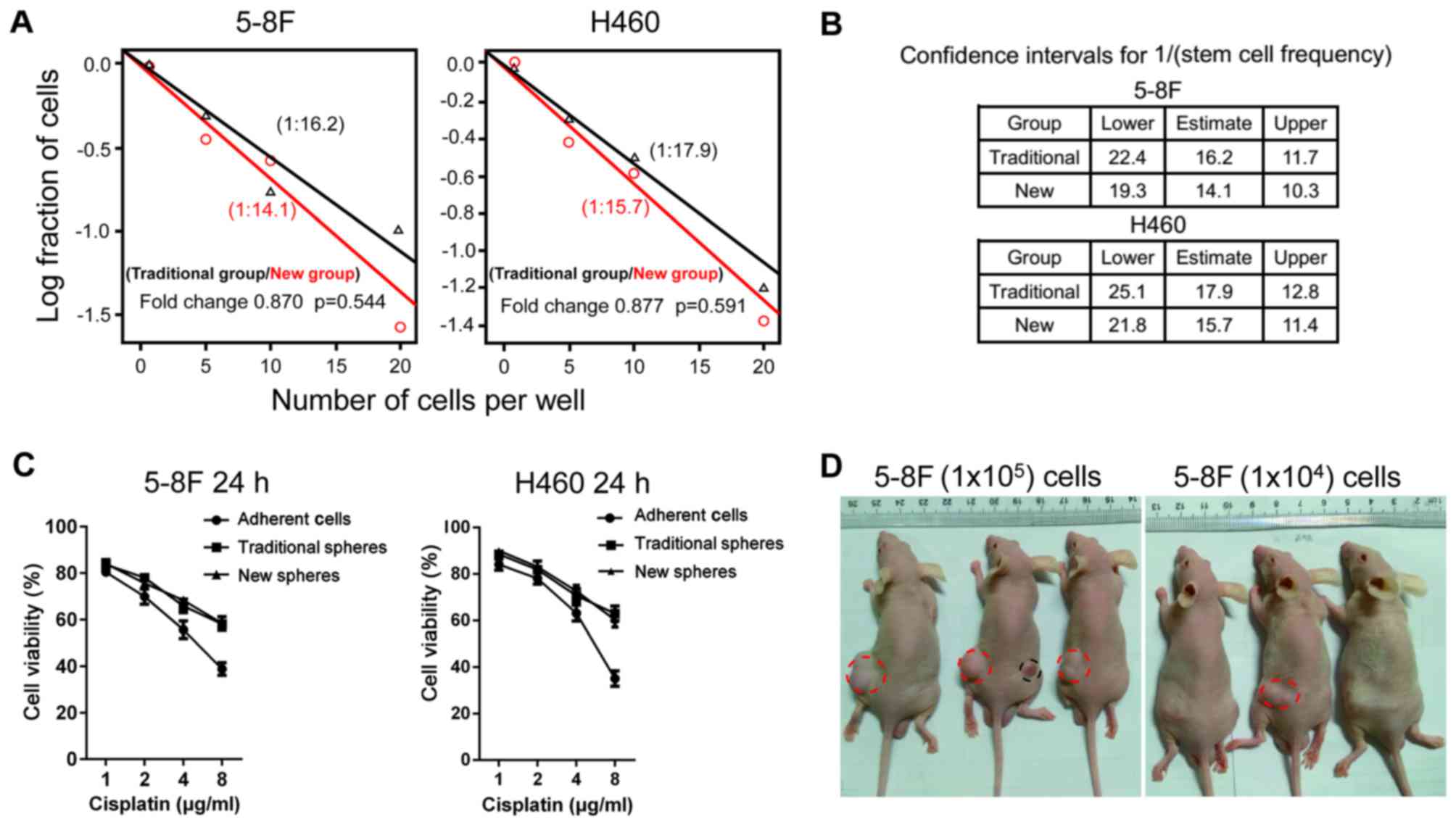
|
1
|
Flemming A: Cancer stem cells: Targeting
the root of cancer relapse. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:1652015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Adorno-Cruz V, Kibria G, Liu X, Doherty M,
Junk DJ, Guan D, Hubert C, Venere M, Mulkearns-Hubert E, Sinyuk M,
et al: Cancer stem cells: Targeting the roots of cancer, seeds of
metastasis, and sources of therapy resistance. Cancer Res.
75:924–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lim YC, Oh SY, Cha YY, Kim SH, Jin X and
Kim H: Cancer stem cell traits in squamospheres derived from
primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol.
47:83–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fan X, Liu S, Su F, Pan Q and Lin T:
Effective enrichment of prostate cancer stem cells from spheres in
a suspension culture system. Urol Oncol. 30:314–318. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weiswald LB, Bellet D and Dangles-Marie V:
Spherical cancer models in tumor biology. Neoplasia. 17:1–15. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zweigerdt R, Olmer R, Singh H, Haverich A
and Martin U: Scalable expansion of human pluripotent stem cells in
suspension culture. Nat Protoc. 6:689–700. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen L, Xiao Z, Meng Y, Zhao Y, Han J, Su
G, Chen B and Dai J: The enhancement of cancer stem cell properties
of MCF-7 cells in 3D collagen scaffolds for modeling of cancer and
anti-cancer drugs. Biomaterials. 33:1437–1444. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su G, Zhao Y, Wei J, Han J, Chen L, Xiao
Z, Chen B and Dai J: The effect of forced growth of cells into 3D
spheres using low attachment surfaces on the acquisition of
stemness properties. Biomaterials. 34:3215–3222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rao W, Zhao S, Yu J, Lu X, Zynger DL and
He X: Enhanced enrichment of prostate cancer stem-like cells with
miniaturized 3D culture in liquid core-hydrogel shell
microcapsules. Biomaterials. 35:7762–7773. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Palomeras S, Rabionet M, Ferrer I, Sarrats
A, Garcia-Romeu ML, Puig T and Ciurana J: Breast cancer stem cell
culture and enrichment using poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffolds.
Molecules. 21:5372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moxon SR and Smith AM: Controlling the
rheology of gellan gum hydrogels in cell culture conditions. Int J
Biol Macromol. 84:79–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pijper A: Methylcellulose and bacterial
motility. J Bacteriol. 53:257–269. 1947.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
García MC, Alfaro MC and Muñoz J: Rheology
of sheared gels based on low acyl-gellan gum. Food Sci Technol Int.
22:325–332. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vilela JA and da Cunha RL: High acyl
gellan as an emulsion stabilizer. Carbohydr Polym. 139:115–124.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gilbert CA and Ross AH: Cancer stem cells:
Cell culture, markers, and targets for new therapies. J Cell
Biochem. 108:1031–1038. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Silginer M, Weller M, Ziegler U and Roth
P: Integrin inhibition promotes atypical anoikis in glioma cells.
Cell Death Dis. 5:e10122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Debnath J and Brugge JS: Modelling
glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev
Cancer. 5:675–688. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martinez-Cruzado L, Tornin J, Santos L,
Rodriguez A, García-Castro J, Morís F and Rodriguez R: Aldh1
expression and activity increase during tumor evolution in sarcoma
cancer stem cell populations. Sci Rep. 6:278782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carmody LC, Germain AR, VerPlank L, Nag
PP, Muñoz B, Perez JR and Palmer MA: Phenotypic high-throughput
screening elucidates target pathway in breast cancer stem cell-like
cells. J Biomol Screen. 17:1204–1210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prajapati VD, Jani GK, Zala BS and
Khutliwala TA: An insight into the emerging exopolysaccharide
gellan gum as a novel polymer. Carbohydr Polym. 93:670–678. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sutherland IW: Novel and established
applications of microbial polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol.
16:41–46. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramburrun P, Kumar P, Choonara YE, du Toit
LC and Pillay V: Design and characterization of neurodurable
gellan-xanthan pH-responsive hydrogels for controlled drug
delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 14:291–306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoshida Y, Takahashi K, Okita K, Ichisaka
T and Yamanaka S: Hypoxia enhances the generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 5:237–241. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carnero A and Lleonart M: The hypoxic
microenvironment: A determinant of cancer stem cell evolution.
Bioessays. 38 Suppl 1:S65–S74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hongisto V, Jernström S, Fey V, Mpindi JP,
Sahlberg K Kleivi, Kallioniemi O and Perälä M: High-throughput 3D
screening reveals differences in drug sensitivities between culture
models of JIMT1 breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e772322013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wong GS and Rustgi AK: Matricellular
proteins: Priming the tumour microenvironment for cancer
development and metastasis. Br J Cancer. 108:755–761. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Plaks V, Kong N and Werb Z: The cancer
stem cell niche: How essential is the niche in regulating stemness
of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell. 16:225–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|