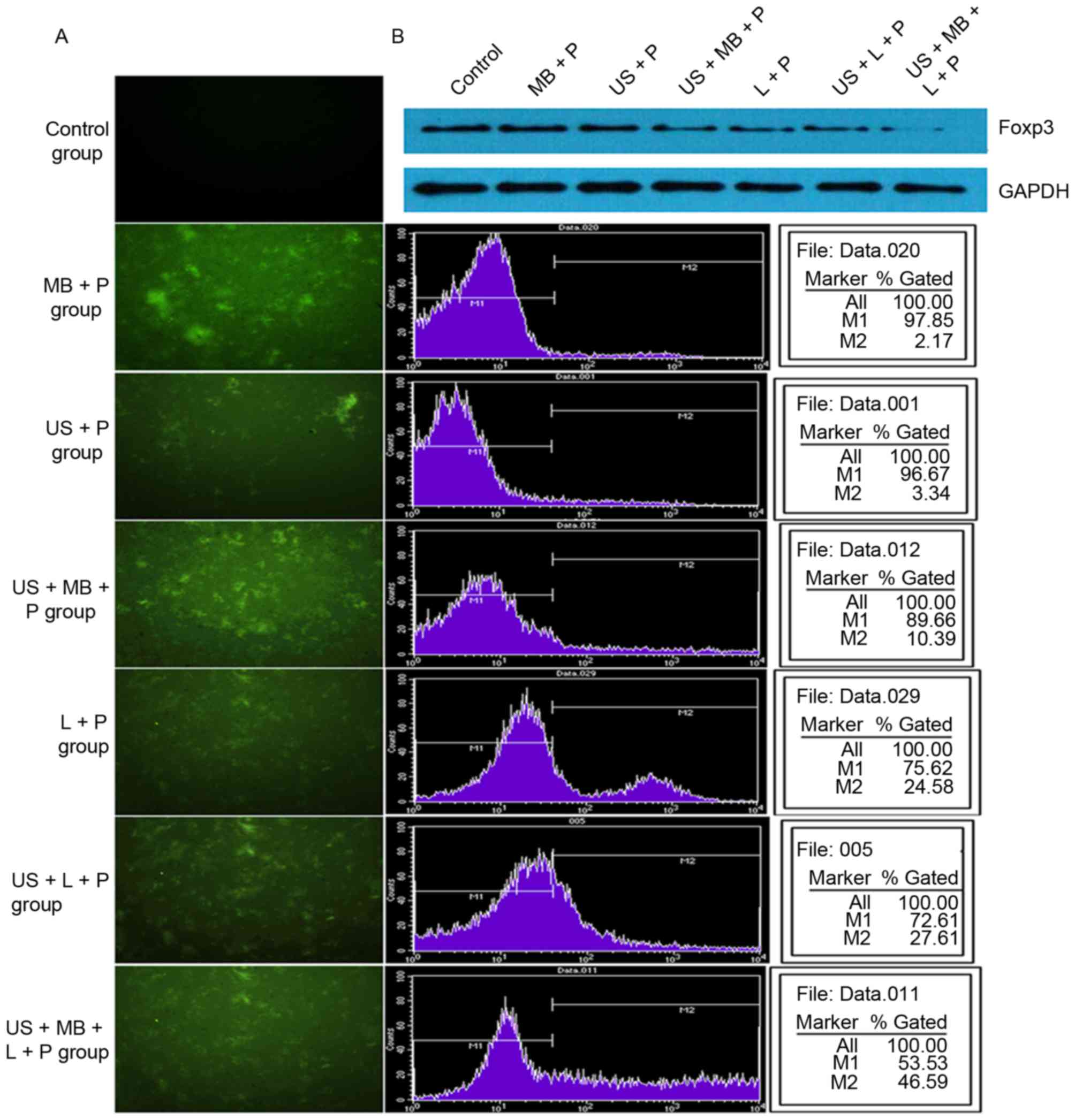
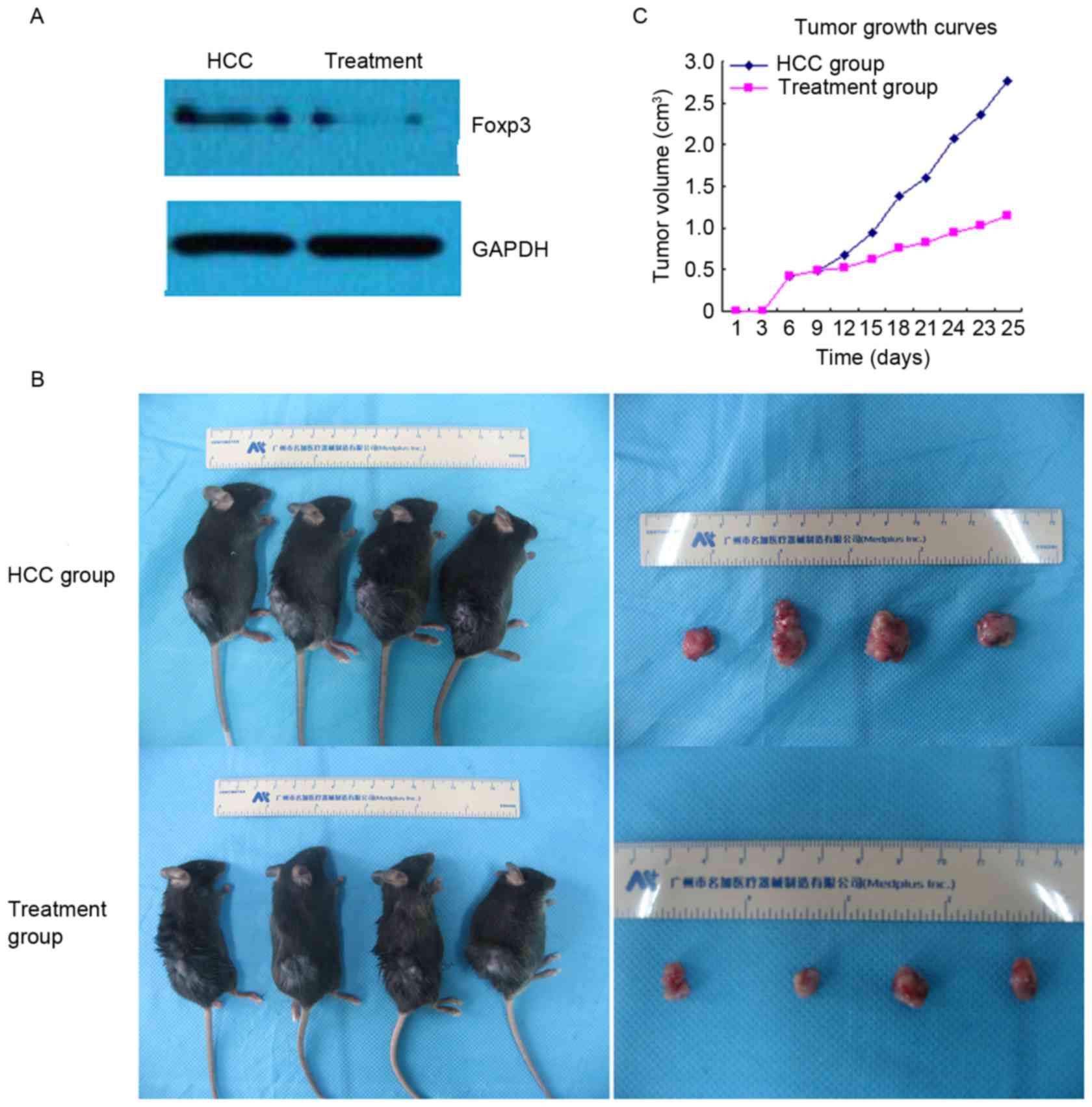
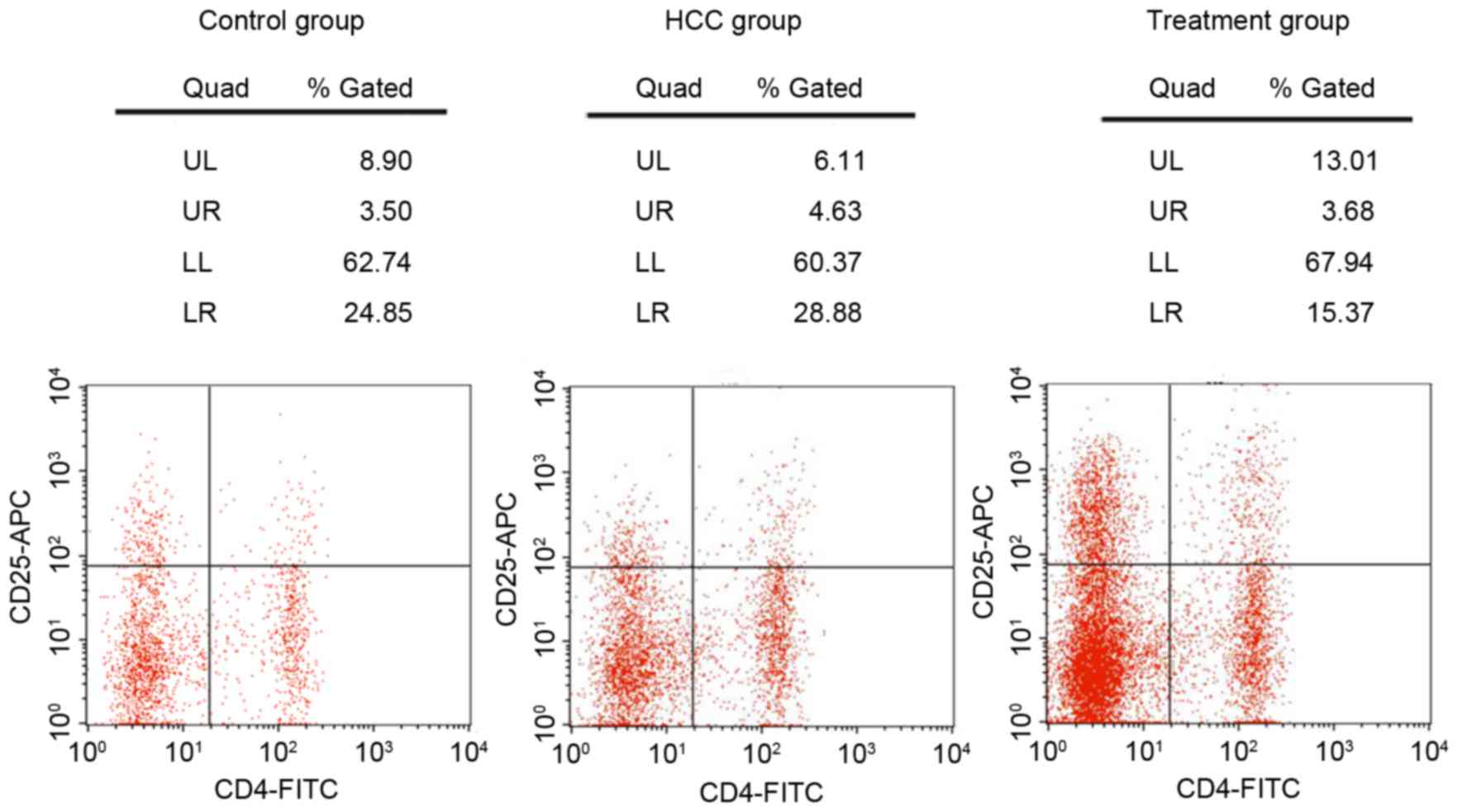
|
1
|
Han KH, Kudo M, Ye SL, Choi JY, Poon RP,
Seong J, Park JW, Ichida T, Chung JW, Chow P and Cheng AL: Asian
consensus workshop report: Expert consensus guideline for the
management of intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in
Asia. Oncology. 81 Suppl 1:S158–S164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pardee AD and Butterfield LH:
Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: Unique challenges and
clinical opportunities. Oncoimmunology. 1:48–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ganss R and Hanahan D: Tumor
microenvironment can restrict the effectiveness of activated
antitumor lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 58:4673–4681. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Linehan DC and Goedegebuure PS: CD25+ CD4+
regulatory T-cells in cancer. Immunol Res. 32:155–168. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
von Boehmer H: Mechanisms of suppression
by suppressor T cells. Nat Immunol. 6:338–344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fontenot JD and Rudensky AY: A well
adapted regulatory contrivance: Rregulatory T cell development and
the forkhead family transcription factor Foxp3. Nat Immunol.
6:331–337. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsai BY, Suen JL and Chiang BL:
Lentiviral-mediated Foxp3 RNAi suppresses tumor growth of
regulatory T cell-like leukemia in a murine tumor model. Gene Ther.
17:972–979. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ormandy LA, Hillemann T, Wedemeyer H,
Manns MP, Greten TF and Korangy F: Increased populations of
regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 65:2457–2464. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang XH, Yamagiwa S, Ichida T, Matsuda Y,
Sugahara S, Watanabe H, Sato Y, Abo T, Horwitz DA and Aoyagi Y:
Increase of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T-cells in the liver of patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 45:254–262. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walton CB, Anderson CD, Boulay R and
Shohet RV: Introduction to the ultrasound targeted microbubble
destruction technique. J Vis Exp. 52:e29632011.
|
|
14
|
Geis NA, Katus HA and Bekeredjian R:
Microbubbles as a vehicle for gene and drug delivery: Current
clinical implications and future perspectives. Curr Pharm Design.
18:2166–2183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li YS, Davidson E, Reid CN and McHale AP:
Optimising ultrasound-mediated gene transfer (sonoporation) in
vitro and prolonged expression of a transgene in vivo: Potential
applications for gene therapy of cancer. Cancer Lett. 273:62–69.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujii H, Sun Z, Li SH, Wu J, Fazel S,
Weisel RD, Rakowski H, Lindner J and Li RK: Ultrasound-targeted
gene delivery induces angiogenesis after a myocardial infarction in
mice. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2:869–879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carson AR, McTiernan CF, Lavery L, Hodnick
A, Grata M, Leng X, Wang J, Chen X, Modzelewski RA and Villanueva
FS: Gene therapy of carcinoma using ultrasound-targeted microbubble
destruction. Ultrasound Med Biol. 37:393–402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kee KM, Wang JH, Lin CY, Wang CC, Cheng YF
and Lu SN: Validation of the 7th edition TNM staging system for
hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of 8,828 patients in a single
medical center. Dig Dis Sci. 58:2721–2728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saayman SM, Lazar DC, Scott TA, Hart JR,
Takahashi M, Burnett JC, Planelles V, Morris KV and Weinberg MS:
Potent and targeted activation of latent HIV-1 using the
CRISPR/dCas9 activator complex. Mol Ther. 24:488–498. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ewert KK, Ahmad A, Bouxsein NF, Evans HM
and Safinya CR: Non-viral gene delivery with cationic liposome-DNA
complexesGene Therapy Protocols. Springer; New York, NY: pp.
159–175. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Karmali PP and Chaudhuri A: Cationic
liposomes as non-viral carriers of gene medicines: Resolved issues,
open questions, and future promises. Med Res Rev. 27:696–722. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang HH, Mei MH, Fei R, Liao WJ, Wang XY,
Qin LL, Wang JH, Wei L and Chen HS: Regulatory T cell depletion
enhances tumor specific CD8 T-cell responses, elicited by tumor
antigen NY-ESO-1b in hepatocellular carcinoma patients, in vitro.
Int J Oncol. 36:841–848. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM,
Dooley JL, Farr AG and Rudensky AY: Regulatory T cell lineage
specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity.
22:329–341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dieckmann D, Plottner H, Berchtold S,
Berger T and Schuler G: Ex vivo isolation and characterization of
CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells with regulatory properties from human blood.
J Exp Med. 193:1303–1310. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shevach EM: CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells:
More questions than answers. Nature Rev Immunol. 2:389–400.
2002.
|
|
26
|
Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, Tanaka Y,
Herrmann V, Doherty G, Drebin JA, Strasberg SM, Eberlein TJ,
Goedegebuure PS and Linehan DC: Prevalence of regulatory T cells is
increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of
patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol.
169:2756–2761. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ono M, Yaguchi H, Ohkura N, Kitabayashi I,
Nagamura Y, Nomura T, Miyachi Y, Tsukada T and Sakaguchi S: Foxp3
controls regulatory T-cell function by interacting with AML1/Runx1.
Nature. 446:685–689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pandiyan P, Zheng L, Ishihara S, Reed J
and Lenardo MJ: CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce
cytokine deprivation-mediated apoptosis of effector CD4+ T cells.
Nat Immunol. 8:1353–1362. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nair S, Boczkowski D, Fassnacht M,
Pisetsky D and Gilboa E: Vaccination against the forkhead family
transcription factor Foxp3 enhances tumor immunity. Cancer Res.
67:371–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nishikawa H and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 127:759–767. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett
N, Phillips HS and Ferrara N: Inhibition of vascular endothelial
growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in
vivo. Nature. 362:841–844. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|