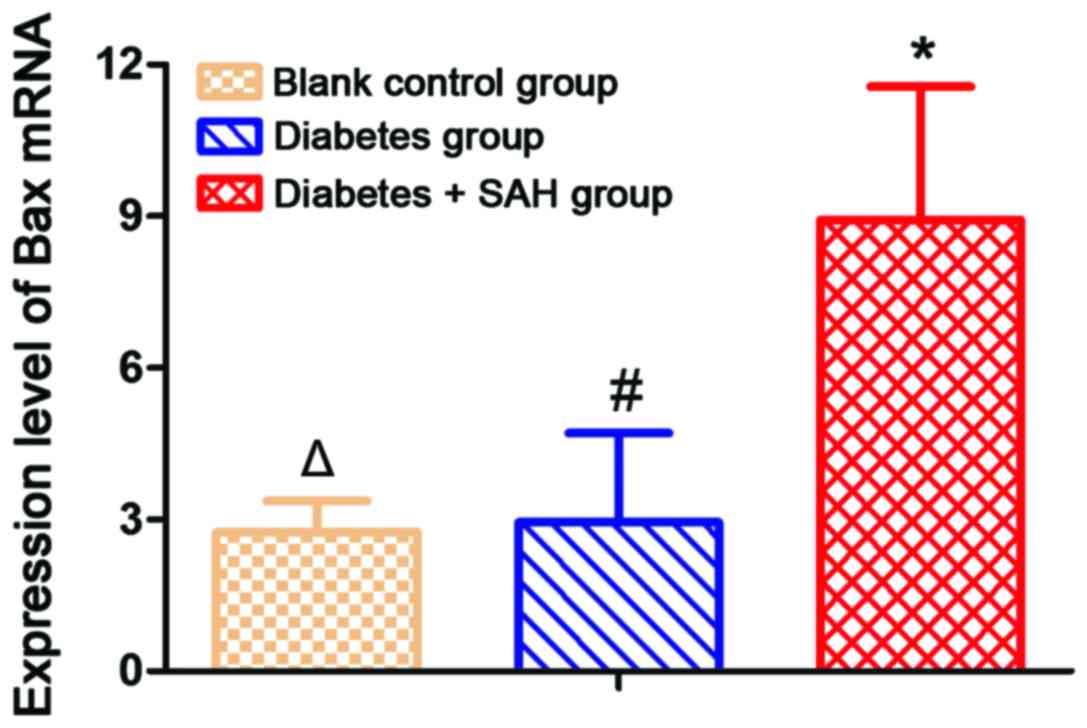
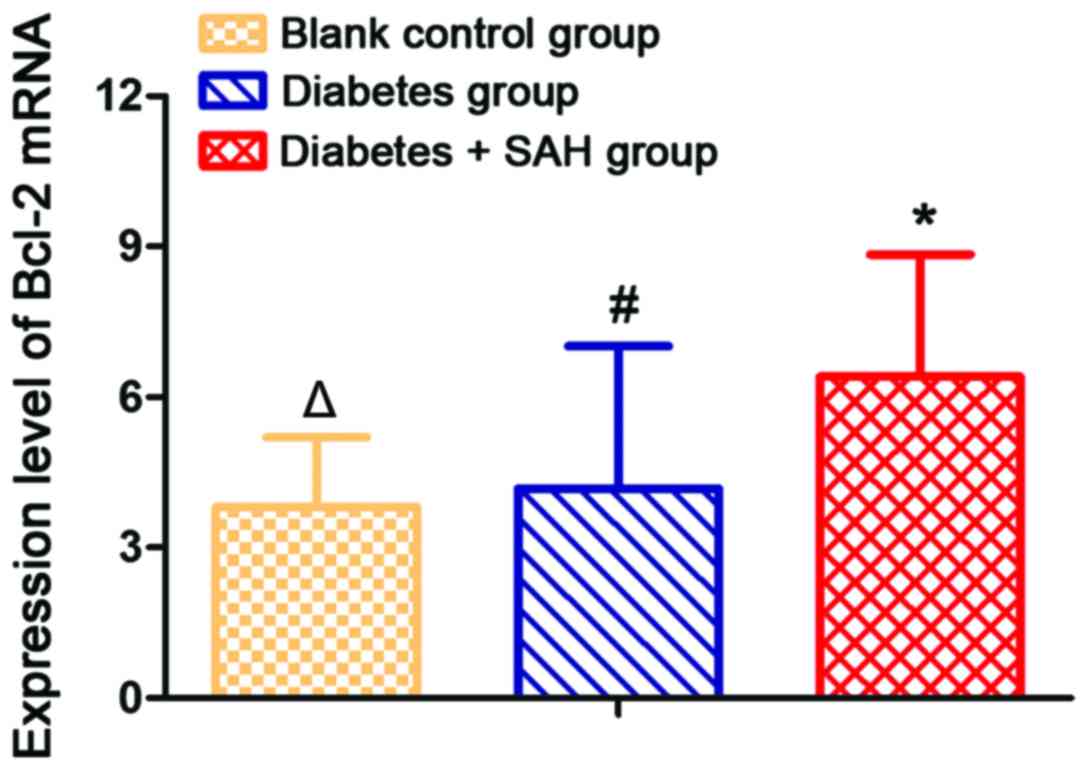
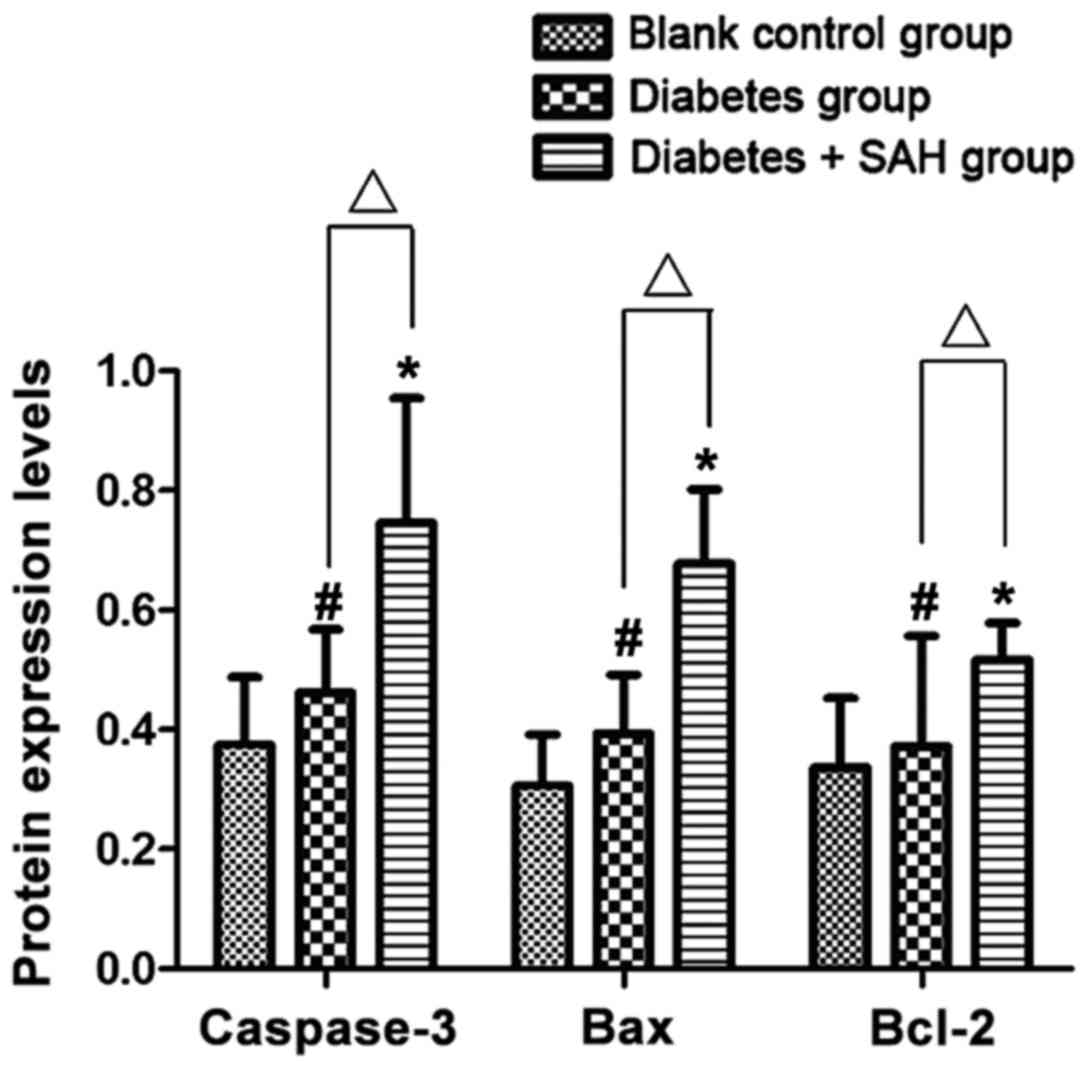
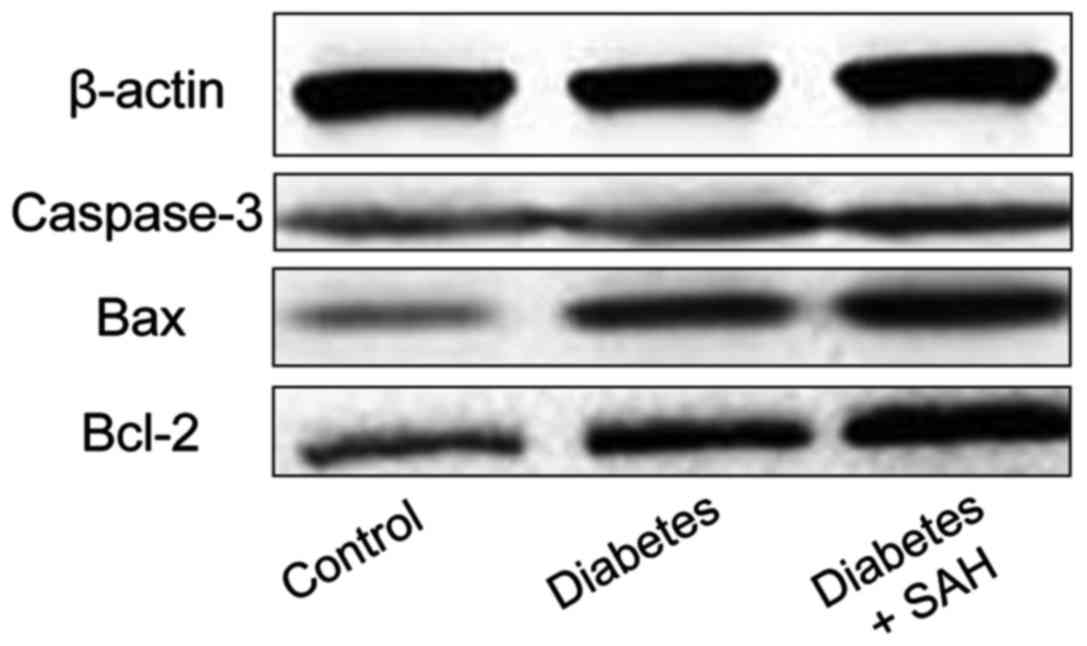
|
1
|
Li S, Xiao X, Ni X, Ye Z, Zhao J and Hang
C: Tetramethylpyrazine protects against early brain injury after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage by affecting
mitochondrial-dependent caspase-3 apoptotic pathway. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2017:35149142017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fujii M, Sherchan P, Soejima Y, Hasegawa
Y, Flores J, Doycheva D and Zhang JH: Cannabinoid receptor type 2
agonist attenuates apoptosis by activation of phosphorylated
CREB-Bcl-2 pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Exp
Neurol. 261:396–403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Wang JF and Hu XM: Caspase-3 in
serum predicts outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Clin Chim Acta. 460:196–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li H, Yu JS, Zhang HS, Yang YQ, Huang LT,
Zhang DD and Hang CH: Increased expression of caspase-12 after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurochem Res. 41:3407–3416.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Edebali N, Tekin IÖ, Açıkgöz B, Açıkgöz S,
Barut F, Sevinç N and Sümbüloğlu V: Apoptosis and necrosis in the
circumventricular organs after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
as detected with annexin V and caspase 3 immunostaining. Neurol
Res. 36:1114–1120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu ZQ, Jia Y and Chen G: Possible
involvement of cathepsin B/D and caspase-3 in deferoxamine-related
neuroprotection of early brain injury after subarachnoid
haemorrhage in rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 40:270–283. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maione AG, Brudno Y, Stojadinovic O, Park
LK, Smith A, Tellechea A, Leal EC, Kearney CJ, Veves A, Tomic-Canic
M, et al: Three-dimensional human tissue models that incorporate
diabetic foot ulcer-derived fibroblasts mimic in vivo features of
chronic wounds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 21:499–508. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu H, Shi JX, Chen HL, Hang CH, Wang HD
and Yin HX: Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the
cerebral artery after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain
Res. 1262:73–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simard JM, Tosun C, Ivanova S, Kurland DB,
Hong C, Radecki L, Gisriel C, Mehta R, Schreibman D and Gerzanich
V: Heparin reduces neuroinflammation and transsynaptic neuronal
apoptosis in a model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res.
3 Suppl 1:155–165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai J, Cao S, Chen J, Yan F, Chen G and
Dai Y: Progesterone alleviates acute brain injury via reducing
apoptosis and oxidative stress in a rat experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage model. Neurosci Lett. 600:238–243. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yunchang M, Qinxue D, Binbin J, Xin H,
Lili Y, Linbi C, Wujun G, Pengbo Z and Junlu W: Human tissue
kallikrein ameliorates cerebral vasospasm in a rabbit model of
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 37:1082–1089. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han Y, Zhang T, Su J, Zhao Y, Chenchen
Wang and Li X: Apigenin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal
apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage.
J Clin Neurosci. 40:157–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang H, Xu R, Xie F, Xu W, Zeng MF, Wang
X and Zhu J: Protective effects of perfluorooctyl-bromide
nanoparticles on early brain injuries following subarachnoid
hemorrhage in rats. Am J Transl Res. 7:1404–1416. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goksu E, Dogan O, Ulker P, Tanrıover G,
Konuk E, Dilmac S, Kirac E, Demır N and Aslan M: Pentoxifylline
alleviates early brain injury in a rat model of subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 158:1721–1730. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yin C, Huang GF, Sun XC, Guo Z and Zhang
JH: Tozasertib attenuates neuronal apoptosis via DLK/JIP3/MA2K7/JNK
pathway in early brain injury after SAH in rats. Neuropharmacology.
108:316–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujii M, Sherchan P, Soejima Y, Doycheva D
and Zhang JH: Subarachnoid hemorrhage-triggered acute hypotension
is associated with left ventricular cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a
rat model. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 121:145–150. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen J, Qian C, Duan H, Cao S, Yu X, Li J,
Gu C, Yan F, Wang L and Chen G: Melatonin attenuates neurogenic
pulmonary edema via the regulation of inflammation and apoptosis
after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Pineal Res. 59:469–477.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Erşahin M, Ozsavcı D, Sener A, Ozakpınar
OB, Toklu HZ, Akakin D, Sener G and Yeğen BÇ: Obestatin alleviates
subarachnoid haemorrhage-induced oxidative injury in rats via its
anti-apoptotic and antioxidant effects. Brain Inj. 27:1181–1189.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tso MK, Lass E, Ai J and Loch Macdonald R:
Valproic acid treatment after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Acta Neurochir (Suppl). 120:81–85. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Topkoru BC, Altay O, Duris K, Krafft PR,
Yan J and Zhang JH: Nasal administration of recombinant osteopontin
attenuates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Stroke. 44:3189–3194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|