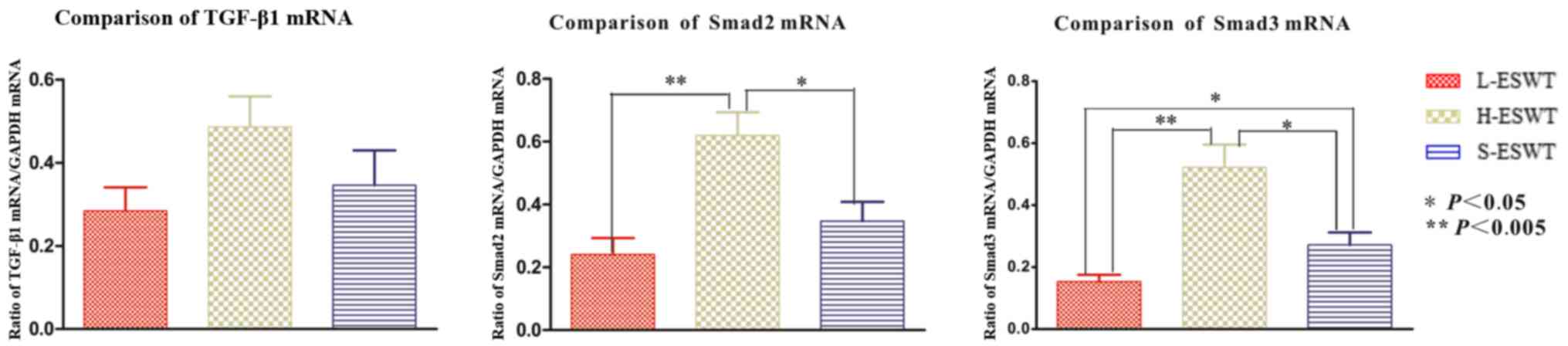
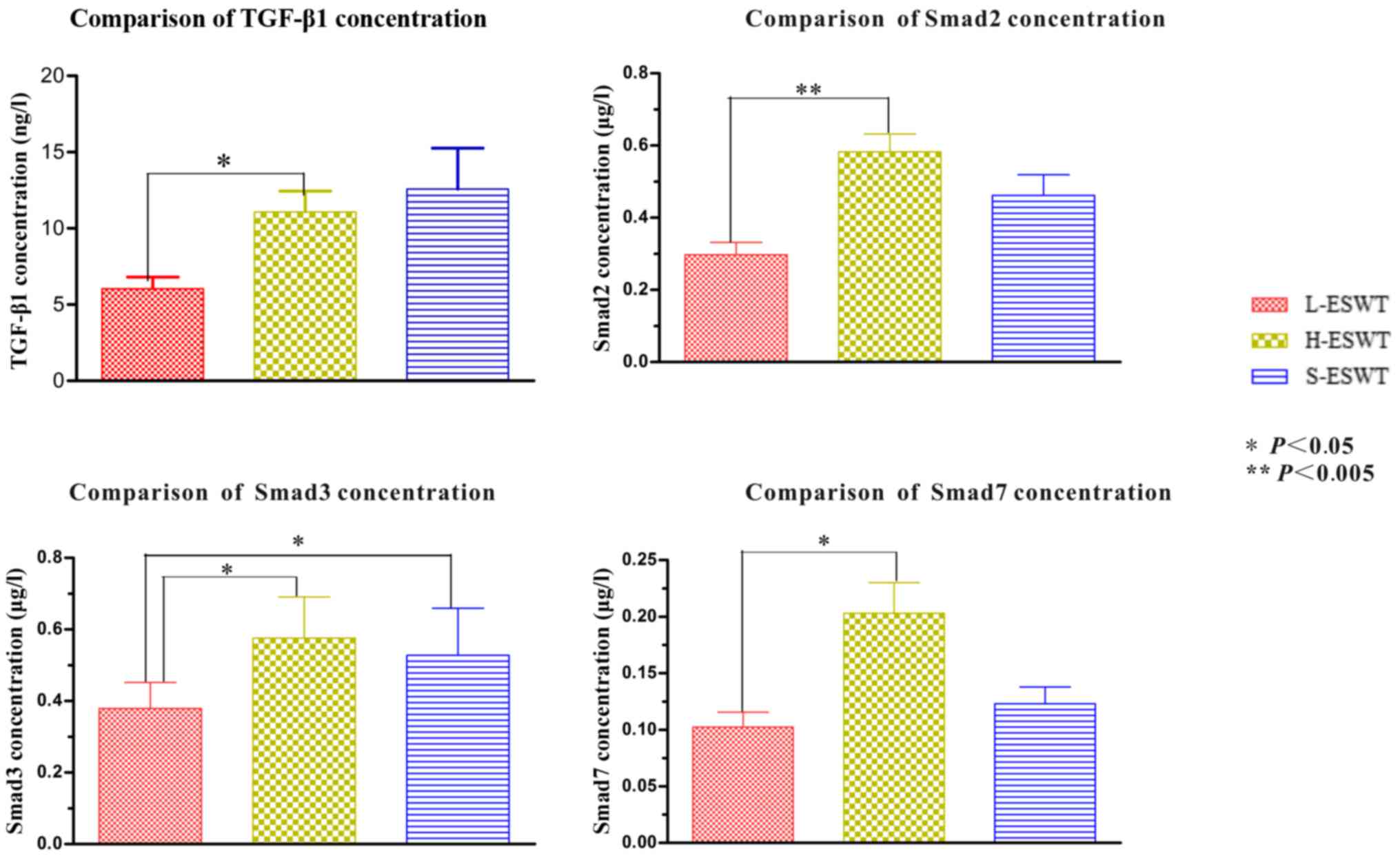
|
1
|
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T,
Ruzicka T and Jeschke MG: Hypertrophic scarring and keloids:
Pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol
Med. 17:113–125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Niessen FB, Spauwen PH, Schalkwijk J and
Kon M: On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: A review.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 104:1435–1458. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hardy MA: The biology of scar formation.
Phys Ther. 69:1014–1024. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayashida T, Decaestecker M and Schnaper
HW: Cross-talk between ERK MAP kinase and Smad signaling pathways
enhances TGF-beta-dependent responses in human mesangial cells.
FASEB J. 17:1576–1578. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asano Y, Ihn H, Yamane K, Jinnin M, Mimura
Y and Tamaki K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is involved in
alpha2(I) collagen gene expression in normal and scleroderma
fibroblasts. J Immunol. 172:7123–7135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu Z, Ding J, Shankowsky HA and Tredget
EE: The molecular mechanism of hypertrophic scar. J Cell Commun
Signal. 7:239–252. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klass BR, Grobbelaar AO and Rolfe KJ:
Transforming growth factor beta1 signalling, wound healing and
repair: A multifunctional cytokine with clinical implications for
wound repair, a delicate balance. Postgrad Med J. 85:9–14. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trisliana Perdanasari A, Torresetti M,
Grassetti L, Nicoli F, Zhang YX, Dashti T, Di Benedetto G and
Lazzeri D: Intralesional injection treatment of hypertrophic scars
and keloids: A systematic review regarding outcomes. Burns Trauma.
3:142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Steinstraesser L, Flak E, Witte B, Ring A,
Tilkorn D, Hauser J, Langer S, Steinau HU and Al-Benna S: Pressure
garment therapy alone and in combination with silicone for the
prevention of hypertrophic scarring: Randomized controlled trial
with intraindividual comparison. Plast Reconstr Surg.
128:306e–313e. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cho YS, Jeon JH, Hong A, Yang HT, Yim H,
Cho YS, Kim DH, Hur J, Kim JH, Chun W, et al: The effect of burn
rehabilitation massage therapy on hypertrophic scar after burn: A
randomized controlled trial. Burns. 40:1513–1520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Azzam OA, Bassiouny DA, El-Hawary MS, El
Maadawi ZM, Sobhi RM and El-Mesidy MS: Treatment of hypertrophic
scars and keloids by fractional carbon dioxide laser: A clinical,
histological, and immunohistochemical study. Laser Med Sci.
31:9–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
O'Brien L and Jones DJ: Silicone gel
sheeting for preventing and treating hypertrophic and keloid scars.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 9:CD0038262013.
|
|
13
|
Ogawa R, Miyashita T, Hyakusoku H, Akaishi
S, Kuribayashi S and Tateno A: Postoperative radiation protocol for
keloids and hypertrophic scars: Statistical analysis of 370 sites
followed for over 18 months. Ann Plast Surg. 59:688–691. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zouboulis CC: Cryosurgery in dermatology.
Hautarzt. 66:834–848. 2015.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Liu LN, Yong Q, Deng JC and Cao
WG: Intralesional injection of adipose-derived stem cells reduces
hypertrophic scarring in a rabbit ear model. Stem Cell Res Ther.
6:1452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Williams CC and De Groote S: Clinical
inquiry: What treatment is best for hypertrophic scars and keloids?
J Fam Pract. 60:757–758. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ledon JA, Savas J, Franca K, Chacon A and
Nouri K: Intralesional treatment for keloids and hypertrophic
scars: A review. Dermatol Surg. 39:1745–1757. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Macintyre L and Baird M: Pressure garments
for use in the treatment of hypertrophic scars-a review of the
problems associated with their use. Burns. 32:10–15. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mustoe TA, Cooter RD, Gold MH, Hobbs FD,
Ramelet AA, Shakespeare PG, Stella M, Téot L, Wood FM and Ziegler
UE; International Advisory Panel on Scar Management, :
International clinical recommendations on scar management. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 110:560–571. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meaume S, Le Pillouer-Prost A, Richert B,
Roseeuw D and Vadoud J: Management of scars: Updated practical
guidelines and use of silicones. Eur J Dermatol. 24:435–443.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chaussy C, Brendel W and Schmiedt E:
Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock
waves. Lancet. 2:1265–1268. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rassweiler J, Rassweiler MC, Frede T and
Alken P: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: An opinion on its
future. Indian J Urol. 30:73–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Valchanou VD and Michailov P: High energy
shock waves in the treatment of delayed and nonunion of fractures.
Int Orthop. 15:181–184. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maffulli G, Hemmings S and Maffulli N:
Assessment of the effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave
therapy (ESWT) for soft tissue injuries (ASSERT): An online
database protocol. Transl Med UniSa. 10:46–51. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Speed C: A systematic review of shockwave
therapies in soft tissue conditions: Focusing on the evidence. Br J
Sports Med. 48:1538–1542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goertz O, Lauer H, Hirsch T, Ring A,
Lehnhardt M, Langer S, Steinau HU and Hauser J: Extracorporeal
shock waves improve angiogenesis after full thickness burn. Burns.
38:1010–1018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dymarek R, Halski T, Ptaszkowski K,
Slupska L, Rosinczuk J and Taradaj J: Extracorporeal shock wave
therapy as an adjunct wound treatment: A systematic review of the
literature. Ostomy Wound Manage. 60:26–39. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao JC, Xian CJ, Yu JA and Shi K:
Advancement in the research of effect of extracorporeal shock wave
therapy on wound angiogenesis. Chin J Injury Repair Wound Healing.
9:80–84. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Zhao J, Xue Y, Yu J, Shi K, Xian C and
Zhou X: Advances in the research of mechanism of enhancement of
wound healing with extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Zhonghua Shao
Shang Za Zhi. 31:315–317. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fioramonti P, Cigna E, Onesti MG, Fino P,
Fallico N and Scuderi N: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the
management of burn scars. Dermatol Surg. 38:778–782. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho YS, Joo SY, Cui H, Cho SR, Yim H and
Seo CH: Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on scar pain in
burn patients: A prospective, randomized, single-blind,
placebo-controlled study. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e45752016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saggini R, Saggini A, Spagnoli AM, Dodaj
I, Cigna E, Maruccia M, Soda G, Bellomo RG and Scuderi N:
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: An emerging treatment modality
for retracting scars of the hands. Ultrasound Med Biol. 42:185–195.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morris DE, Wu L, Zhao LL, Bolton L, Roth
SI, Ladin DA and Mustoe TA: Acute and chronic animal models for
excessive dermal scarring: Quantitative studies. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 100:674–681. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Köse O and Waseem A: Keloids and
hypertrophic scars: Are they two different sides of the same coin?
Dermatol Surg. 34:336–346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Scott PG, Dodd CM, Tredget EE, Ghahary A
and Rahemtulla F: Immunohistochemical localization of the
proteoglycans decorin, biglycan and versican and transforming
growth factor-beta in human post-burn hypertrophic and mature
scars. Histopathology. 26:423–431. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shah M, Foreman DM and Ferguson MW:
Neutralisation of TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 or exogenous addition
of TGF-beta 3 to cutaneous rat wounds reduces scarring. J Cell Sci.
108:985–1002. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Desmoulière A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F and
Gabbiani G: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth
muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in
quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol.
122:103–111. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moulin V, Larochelle S, Langlois C,
Thibault I, Lopez-Vallé CA and Roy M: Normal skin wound and
hypertrophic scar myofibroblasts have differential responses to
apoptotic inductors. J Cell Physiol. 198:350–358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kopp J, Preis E, Said H, Hafemann B,
Wickert L, Gressner AM, Pallua N and Dooley S: Abrogation of
transforming growth factor-beta signaling by SMAD7 inhibits
collagen gel contraction of human dermal fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
280:21570–21576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schmierer B and Hill CS: TGFbeta-SMAD
signal transduction: Molecular specificity and functional
flexibility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:970–982. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Massagué J: How cells read TGF-beta
signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:169–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arno AI, Gauglitz GG, Barret JP and
Jeschke MG: New molecular medicine-based scar management
strategies. Burns. 40:539–551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Annes JP, Munger JS and Rifkin DB: Making
sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci. 116:217–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen W, Fu X, Sun T, Sun X, Zhao Z and
Sheng Z: Change of gene expression of transforming growth
factor-beta1, Smad 2 and Smad 3 in hypertrophic scars skins.
Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 40:17–19. 2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu C, Jiang J, Boye A, Jiang Y and Yang Y:
Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extract suppresses
rabbits' hypertrophic scar by modulating the TGF-β/Smad signal.
Dermatology. 229:363–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bai X, He T, Liu J, Wang Y, Fan L, Tao K,
Shi J, Tang C, Su L and Hu D: Loureirin B inhibits fibroblast
proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition in hypertrophic
scar via TGF-β/Smad pathway. Exp Dermatol. 24:355–360. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Chu J, Wen CJ, Fu SB, Qian YL, Wo
Y, Wang C and Wang DR: Functional characterization of TRAP1-like
protein involved in modulating fibrotic processes mediated by
TGF-β/Smad signaling in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Exp Cell
Res. 332:202–211. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schultze-Mosgau S, Blaese MA, Grabenbauer
G, Wehrhan F, Kopp J, Amann K, Rodemann HP and Rödel F: Smad-3 and
Smad-7 expression following anti-transforming growth factor beta 1
(TGFbeta1)-treatment in irradiated rat tissue. Radiother Oncol.
70:249–259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ashcroft GS, Yang X, Glick AB, Weinstein
M, Letterio JL, Mizel DE, Anzano M, Greenwell-Wild T, Wahl SM, Deng
C and Roberts AB: Mice lacking Smad3 show accelerated wound healing
and an impaired local inflammatory response. Nat Cell Biol.
1:260–266. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|