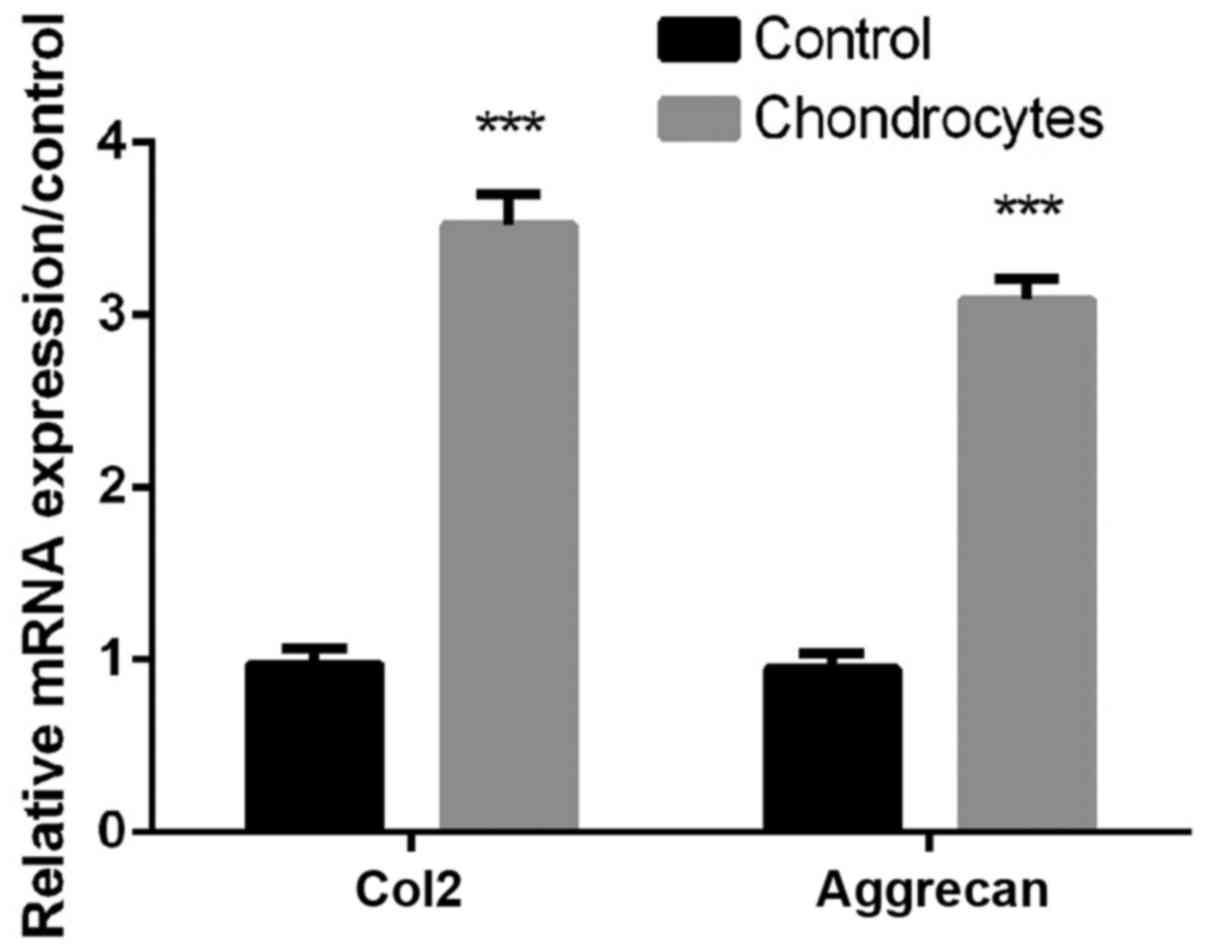
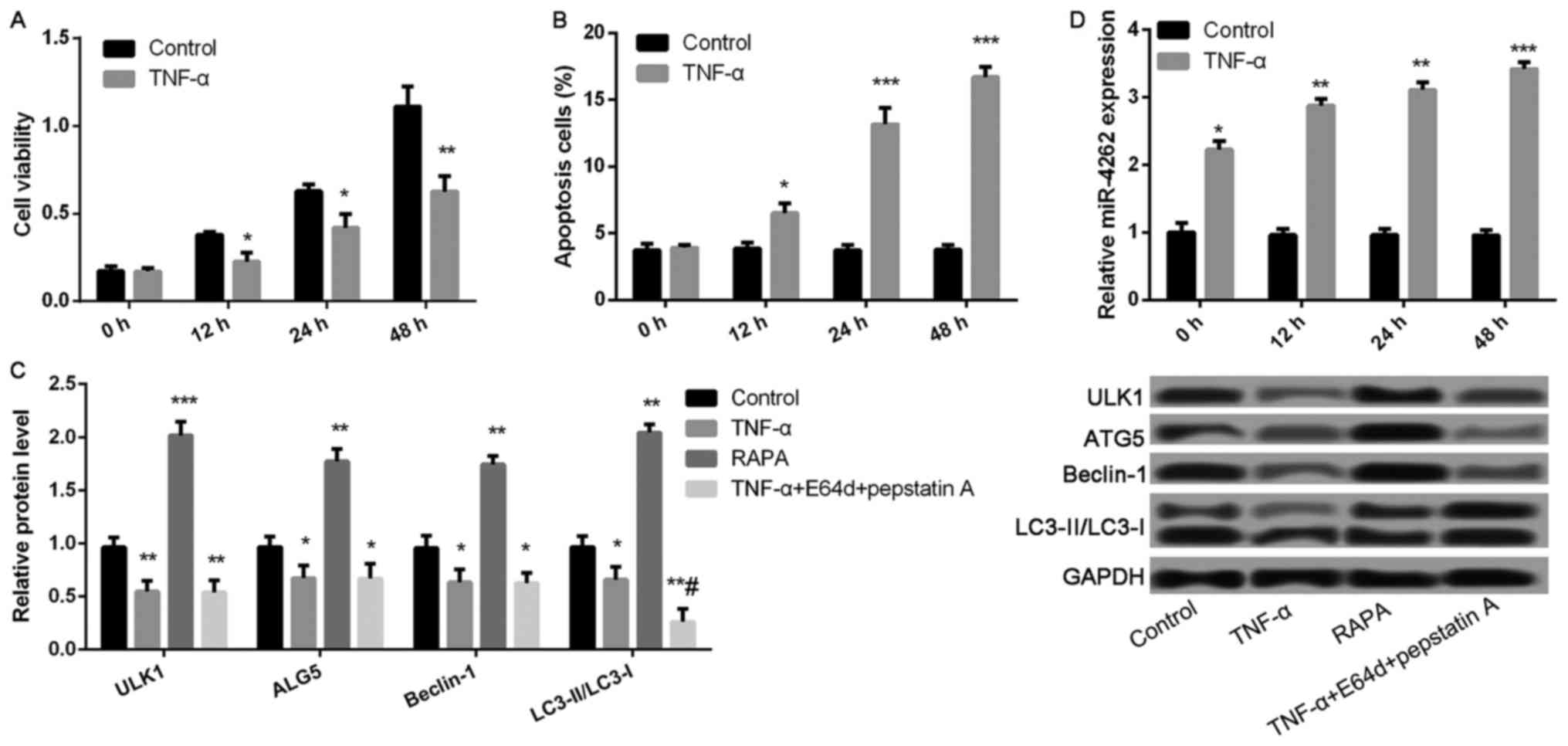
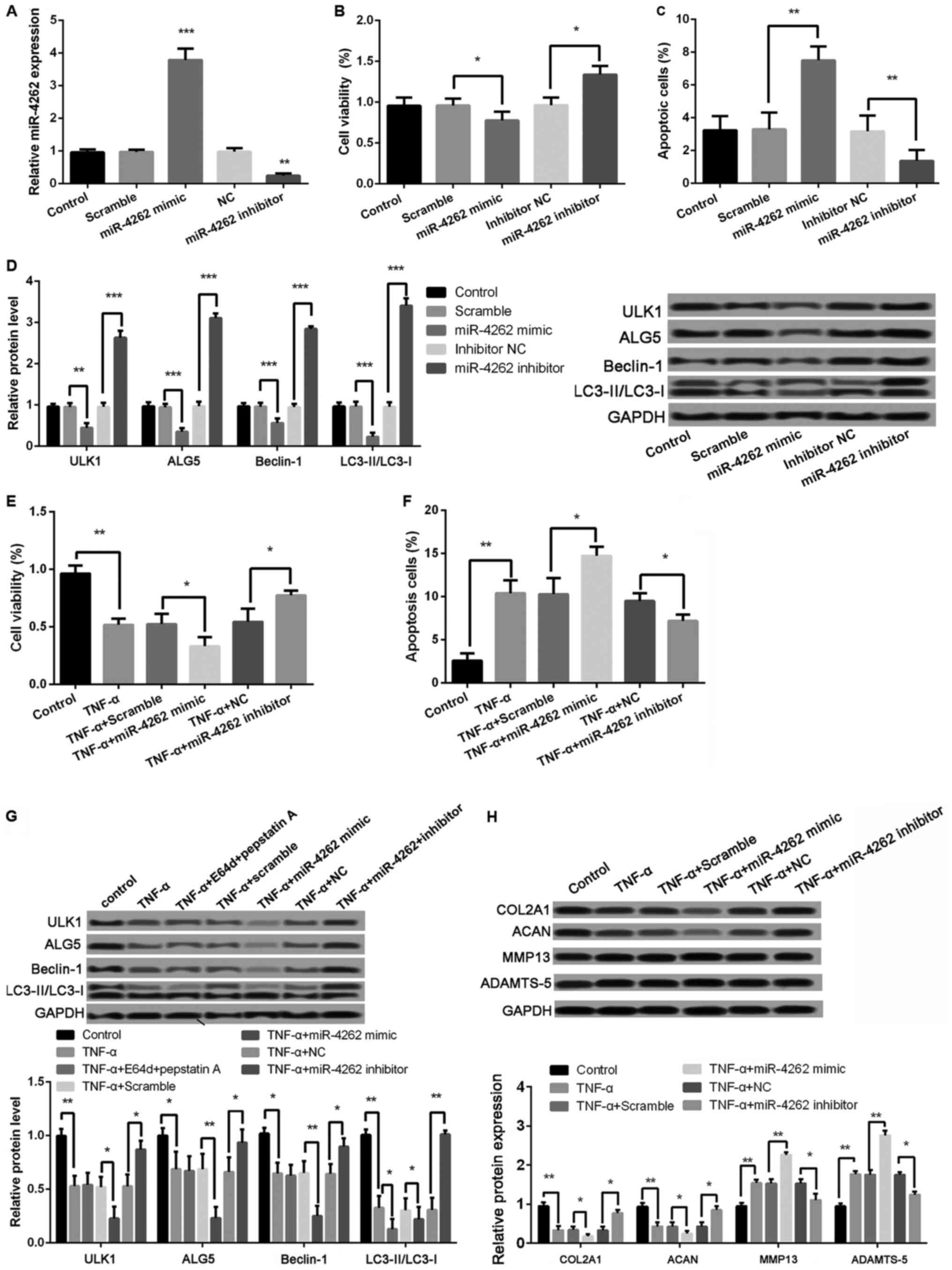
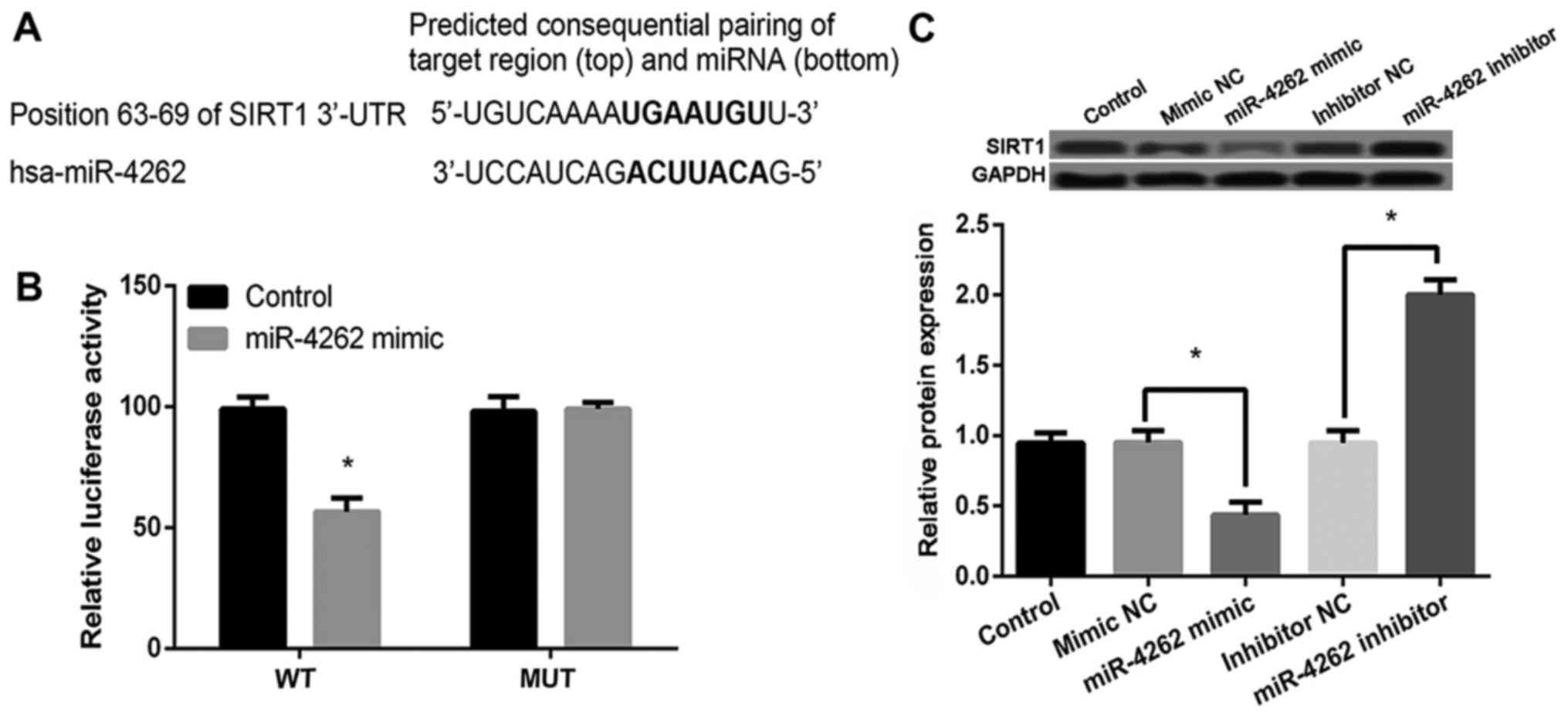
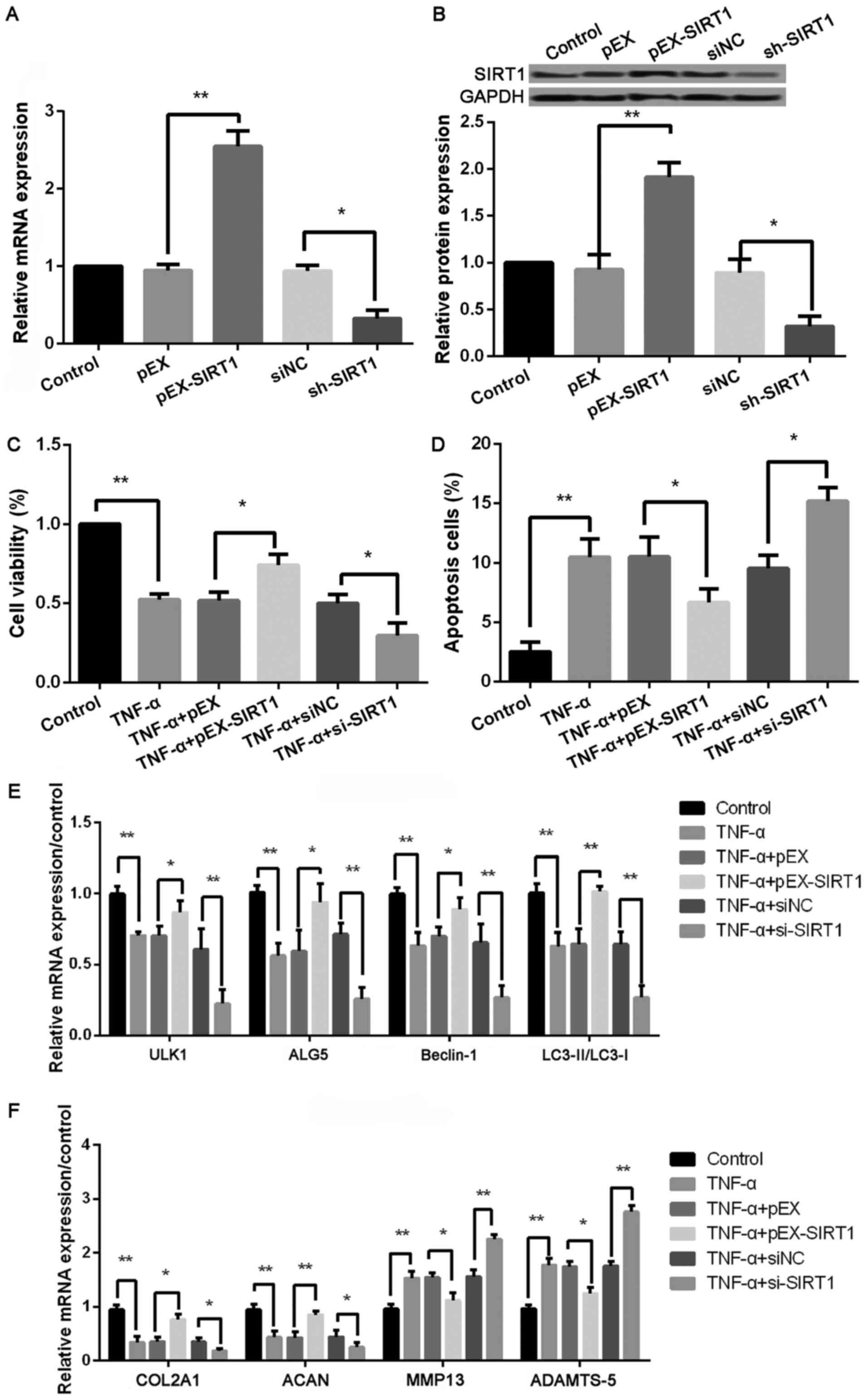
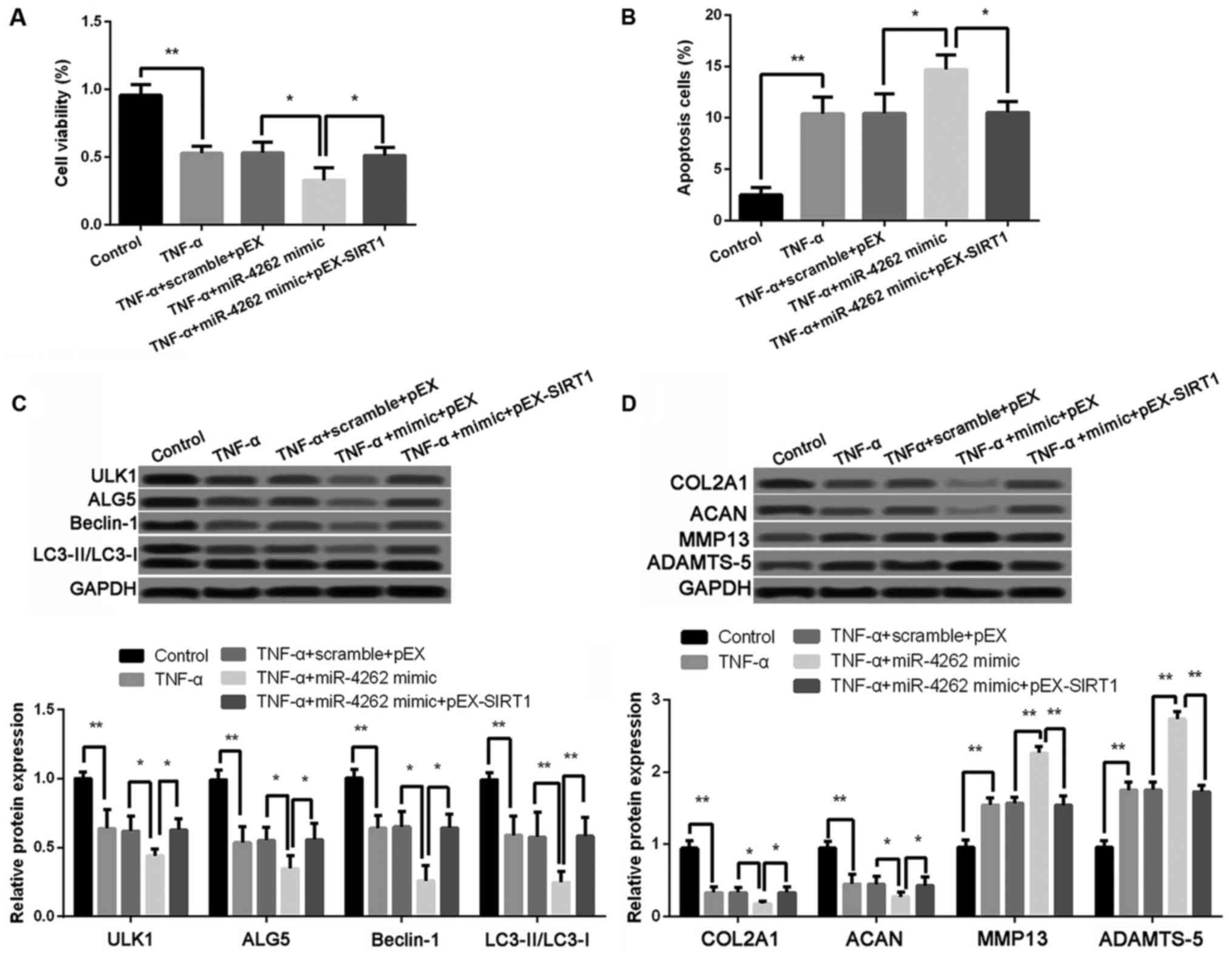
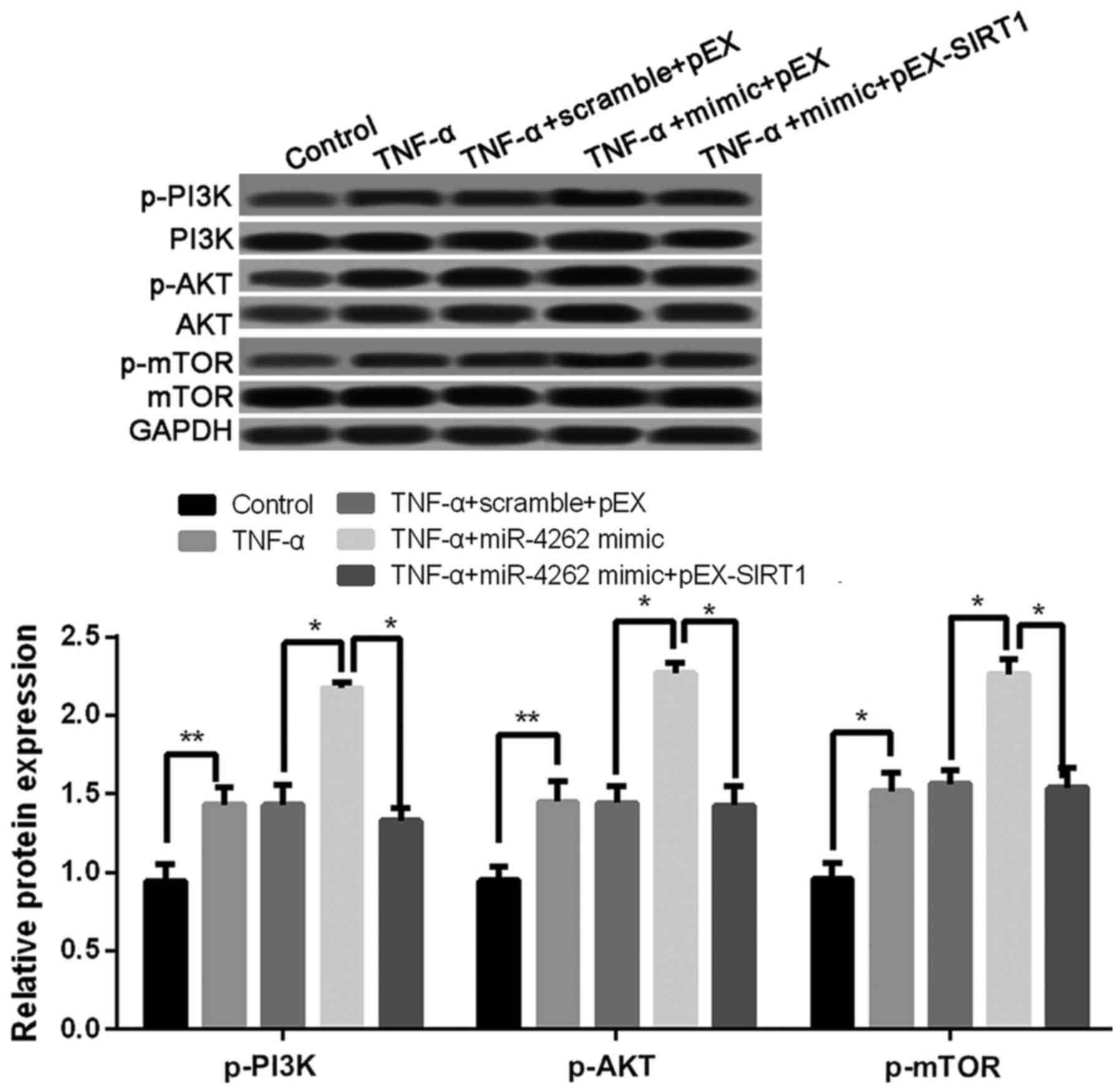
|
1
|
Glynjones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis. Lancet.
386:376–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Neogi T: The epidemiology and impact of
pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1145–1153.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wilkins JM, Loughlin J and Snelling SJ:
Osteoarthritis genetics: Current status and future prospects.
Future Rheumatol. 2:607–620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schachar R and Ogilvie-Harris D:
Osteoarthritis: Joint conservation strategiesOsteoarthritis. Kapoor
M and Mahomed N: Springer International Publishing; Switzerland:
2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Litwic A, Edwards MH, Dennison EM and
Cooper C: Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull.
105:185–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jovanovic M and Hengartner M: miRNAs and
apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 25:6176–6187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saito Y, Saito H, Liang G and Friedman JM:
Epigenetic alterations and MicroRNA misexpression in cancer and
autoimmune diseases: A critical review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.
47:128–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Condorelli G, Latronico MV and Cavarretta
E: microRNAs in cardiovascular diseases: Current knowledge and the
road ahead. J Am Coll Cardiol. 63:2177–2187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tan L, Yu JT and Tan L: Causes and
consequences of MicroRNA dysregulation in neurodegenerative
diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 51:1249–1262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin S and Gregory RI: MicroRNA biogenesis
pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:321–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ji Y, Gao F, Sun B, Hao J and Liu Z:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibits apoptosis of pulmonary
endothelial cells during acute lung injury through suppressing
SMAD2 phosphorylation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:2203–2212. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang D, Li Z, Zhang Y, Tu C, Huo J and
Liu Y: miR-4262 promotes the proliferation of human cutaneous
malignant melanoma cells through KLF6-mediated EGFR inactivation
and p21 upregulation. Oncol Rep. 36:3657–3663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu S, Wu J, Gao Y, Han G, Ding W and Huang
X: MicroRNA-4262 activates the NF-κB and enhances the proliferation
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 86:43–49.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song K, Liu N, Yang Y and Qiu X:
Regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasion through osteopontin
modification by miR-4262. Tumour Biol. 37:6493–6499. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujita N, Matsushita T, Ishida K, Kubo S,
Matsumoto T, Takayama K, Kurosaka M and Kuroda R: Potential
involvement of SIRT1 in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis through
the modulation of chondrocyte gene expressions. J Orthop Res.
29:511–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takayama K, Ishida K, Matsushita T, Fujita
N, Hayashi S, Sasaki K, Tei K, Kubo S, Matsumoto T, Fujioka H, et
al: SIRT1 regulation of apoptosis of human chondrocytes. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:2731–2740. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matsuzaki T, Matsushita T, Takayama K,
Matsumoto T, Nishida K, Kuroda R and Kurosaka M: Disruption of
Sirt1 in chondrocytes causes accelerated progression of
osteoarthritis under mechanical stress and during ageing in mice.
Ann Rheum Dis. 73:1397–1404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moon MH, Jeong JK, Lee YJ, Seol JW,
Jackson CJ and Park SY: SIRT1, a class III histone deacetylase,
regulates TNF-α-induced inflammation in human chondrocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:470–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang D, Cao X, Li J and Zhao G: MiR-210
inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting DR6 in
osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 5:127752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li L, Jia J, Liu X, Yang S, Ye S, Yang W
and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-16-5p controls development of osteoarthritis
by targeting SMAD3 in chondrocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 21:5160–5167.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Jie J, Yang S, Liu X, Ye S and
Tian H: MicroRNA-21 controls the development of osteoarthritis by
targeting GDF-5 in chondrocytes. Exp Mol Med. 46:e792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Guo Y, Wang C and Yu H, Yu X and
Yu H: MicroRNA-142-3p inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and
inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting HMGB1. Inflammation.
39:1718–1728. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang K, Ren Y, Liu Y, Zhang J and He JJ:
miR-4262 promotes proliferation and invasion of human breast cancer
cells through directly targeting KLF6 and KLF15. Oncol Res.
25:277–283. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu W, Xiao L, Cao C, Hua S and Wu D: UBE2T
promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and
metastasis by activating the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:15161–15172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Almonte-Becerril M, Navarro-Garcia F,
Gonzalez-Robles A, Vega-Lopez MA, Lavalle C and Kouri JB: Cell
death of chondrocytes is a combination between apoptosis and
autophagy during the pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis within an
experimental model. Apoptosis. 15:631–638. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu LG, Xu C and Yilihamu T: Autophagy
genes associated with chondrocyte apoptosis: protection and
balancing effects. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 19:3231–3235. 2015.(In
Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Kapoor M, Martelpelletier J, Lajeunesse D,
Pelletier JP and Fahmi H: Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the
pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:33–42.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aizawa T, Kon T, Einhorn TA and
Gerstenfeld LC: Induction of apoptosis in chondrocytes by tumor
necrosis factor-alpha. J Orthop Res. 19:785–796. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stanic I, Facchini A, Borzì RM, Vitellozzi
R, Stefanelli C, Goldring MB, Guarnieri C, Facchini A and Flamigni
F: Polyamine depletion inhibits apoptosis following blocking of
survival pathways in human chondrocytes stimulated by tumor
necrosis factor-alpha. J Cell Physiol. 206:138–146. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee SW, Song YS, Lee SY, Yoon YG, Lee SH,
Park BS, Yun I, Choi H, Kim K, Chung WT and Yoo YH: Downregulation
of protein kinase CK2 activity facilitates tumor necrosis
factor-α-mediated chondrocyte death through apoptosis and
autophagy. PLoS One. 6:e191632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bohensky J, Shapiro IM, Leshinsky S,
Watanabe H and Srinivas V: PIM-2 is an independent regulator of
chondrocyte survival and autophagy in the epiphyseal growth plate.
J Cell Physiol. 213:246–251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bohensky J, Shapiro IM, Leshinsky S,
Terkhorn SP, Adams CS and Srinivas V: HIF-1 regulation of
chondrocyte apoptosis: Induction of the autophagic pathway.
Autophagy. 3:207–214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang ZM, Du SH, Huang LG, Li JH, Xiao L
and Tong P: Leptin promotes apoptosis and inhibits autophagy of
chondrocytes through upregulating lysyl oxidase-like 3 during
osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
24:1246–1253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goldring MB: Molecular regulation of the
chondrocyte phenotype. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.
2:517–520. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dvir-Ginzberg M, Gagarina V, Lee EJ and
Hall DJ: Regulation of cartilage-specific gene expression in human
chondrocytes by SirT1 and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase. J
Biol Chem. 283:36300–36310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gagarina V, Gabay O, Dvir-Ginzberg M, Lee
EJ, Brady JK, Quon MJ and Hall DJ: SirT1 enhances survival of human
osteoarthritic chondrocytes by repressing protein tyrosine
phosphatase 1B and activating the insulin-like growth factor
receptor pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1383–1392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu CQ, Liu BJ, Wu JF, Xu YC, Duan XH, Cao
YX and Dong JC: Icariin attenuates LPS-induced acute inflammatory
responses: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathway.
Eur J Pharmacol. 642:146–153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luo J, Manning BD and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:257–262. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen J, Crawford R and Xiao Y: Vertical
inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway for the treatment of
osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 114:245–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|