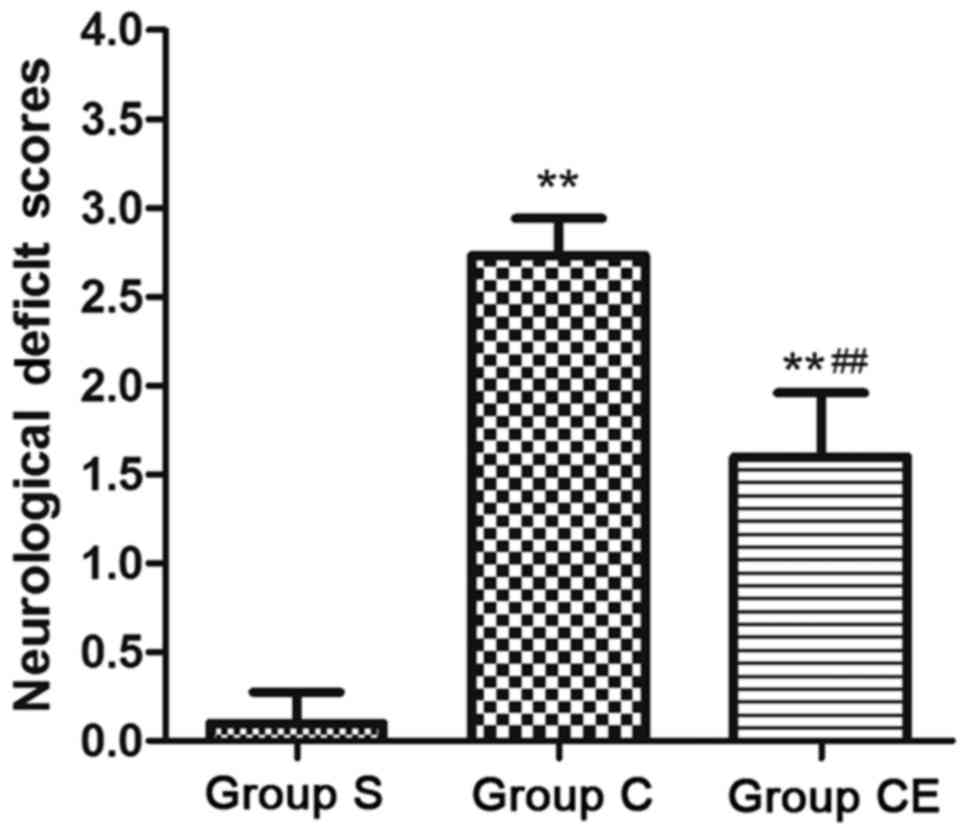
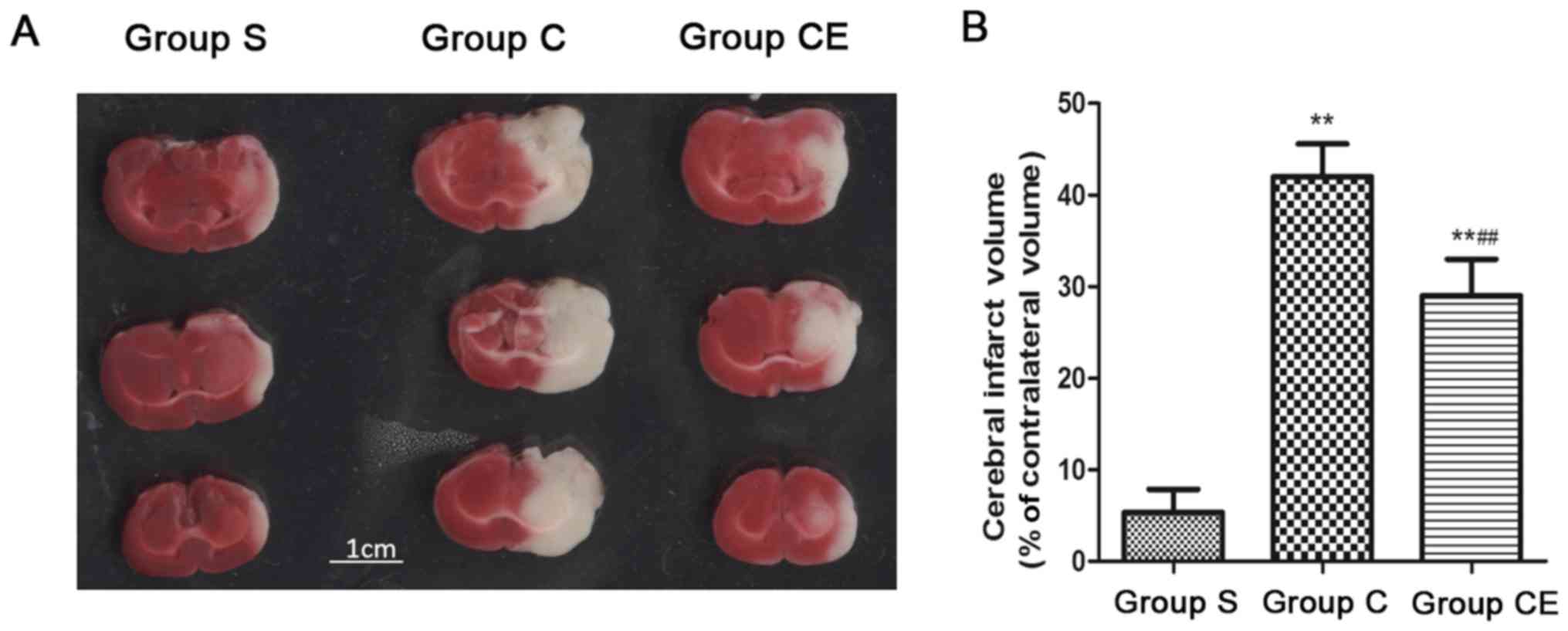
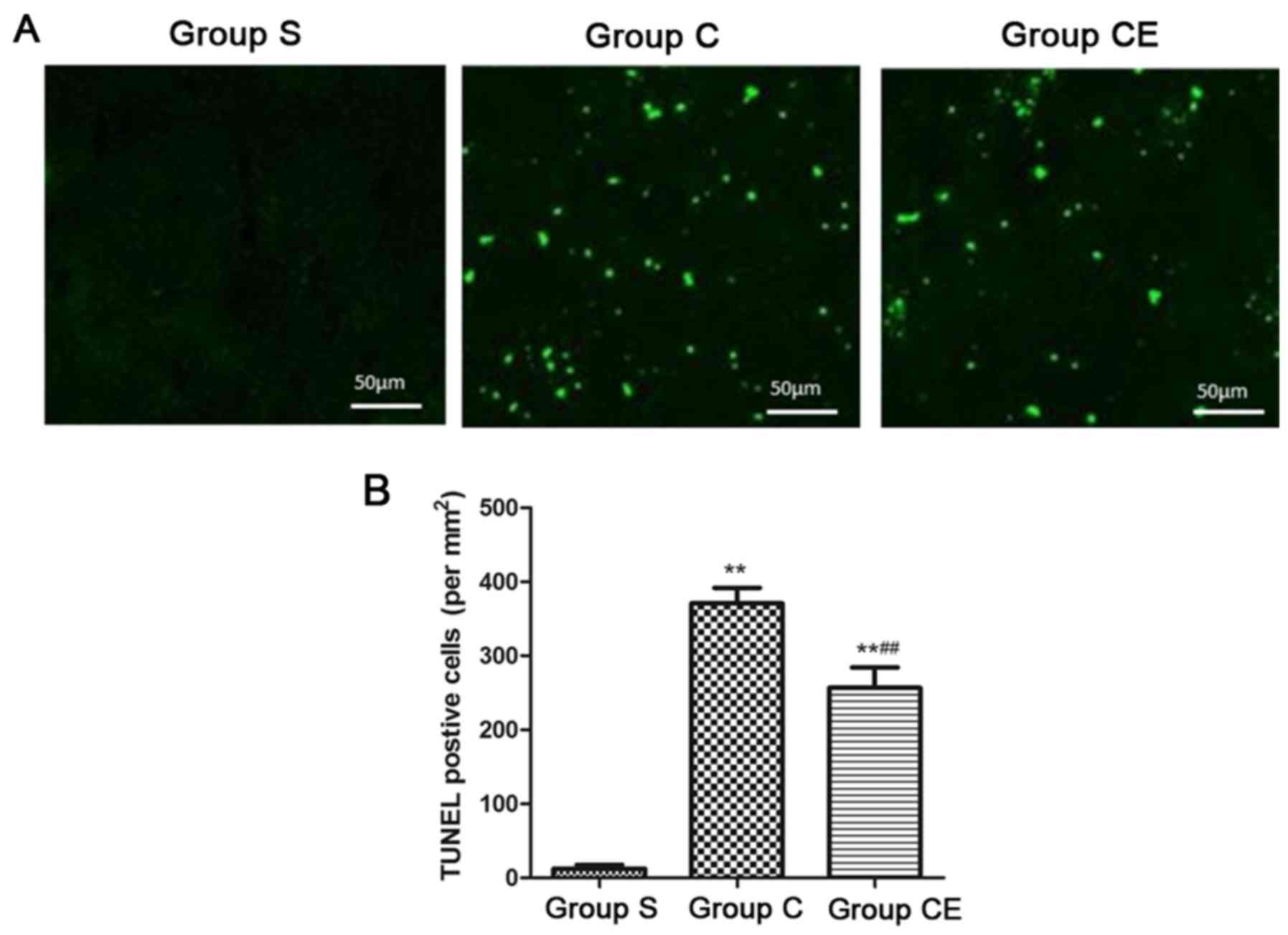
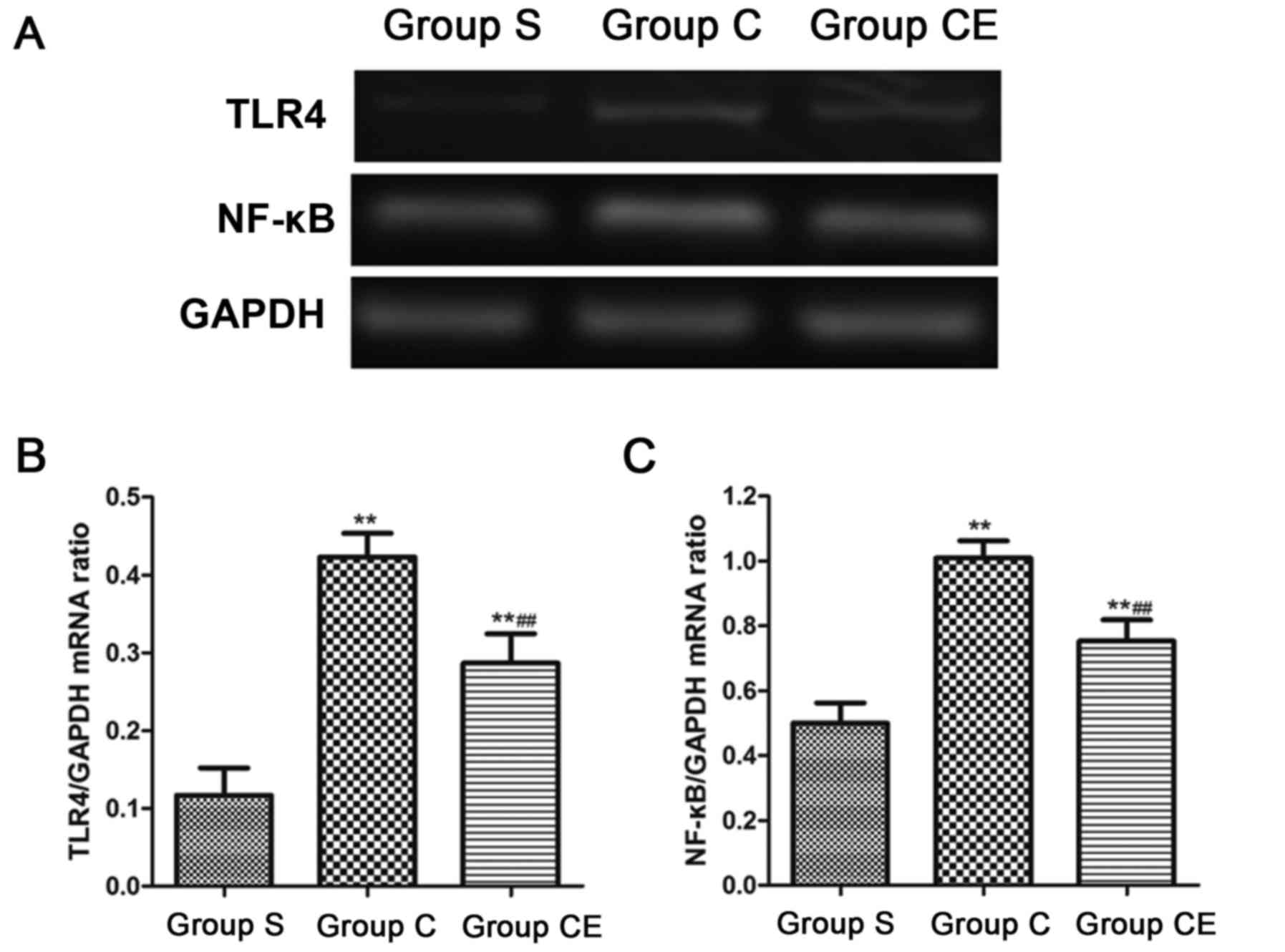
|
1
|
Park JS, Hwang NK, Oh DH and Chang MY:
Effect of head lift exercise on kinematic motion of the
hyolaryngeal complex and aspiration in patients with dysphagic
stroke. J Oral Rehabil. 17:554–559. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Keppel HJM: A novel selective AMPA
antagonist for stroke, neuropathic pain or epilepsy? Drug
Development Lessons Learned. Drug Dev Res. 95:126–132. 2016.
|
|
3
|
Seto SW, Chang D, Jenkins A, Bensoussan A
and Kiat H: Angiogenesis in ischemic stroke and angiogenic effects
of Chinese herbal medicine. J Clin Med. 5:630–645. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vasileva D, Lubenova D, Mihova M,
Grigorova-Petrova K and Dimitrova A: Orthostatic reactivity in
patients with ischemic stroke in the chronic period. Open Access
Maced J Med Sci. 3:851–855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Boisserand LS, Kodama T, Papassin J,
Auzely R, Moisan A, Rome C and Detante O: Biomaterial applications
in cell-based therapy in experimental stroke. Stem Cells Int.
2016:68105622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang Y, Huang J, Tian J, Cao Y, Zhang G,
Wang C, Cao Y and Li J: The prevalence and risk factors of stroke
in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
12:1131–1134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Crivera C, Nelson WW, Schein JR and Witt
EA: Attitudes toward anticoagulant treatment among nonvalvular
atrial fibrillation patients at high risk of stroke and low risk of
bleed. Patient Prefer Adherence. 10:795–805. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y and Bajorek B: Clinical pre-test of
a computerised antithrombotic risk assessment tool for stroke
prevention in atrial fibrillation patients: Giving consideration to
NOACs. J Eval Clin Pract. 22:892–898. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hastrup S, Damgaard D, Johnsen SP and
Andersen G: Prehospital acute stroke severity scale to predict
large artery occlusion: Design and comparison with other scales.
Stroke. 21:487–491. 2016.
|
|
10
|
Zhang H, Li L, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xu
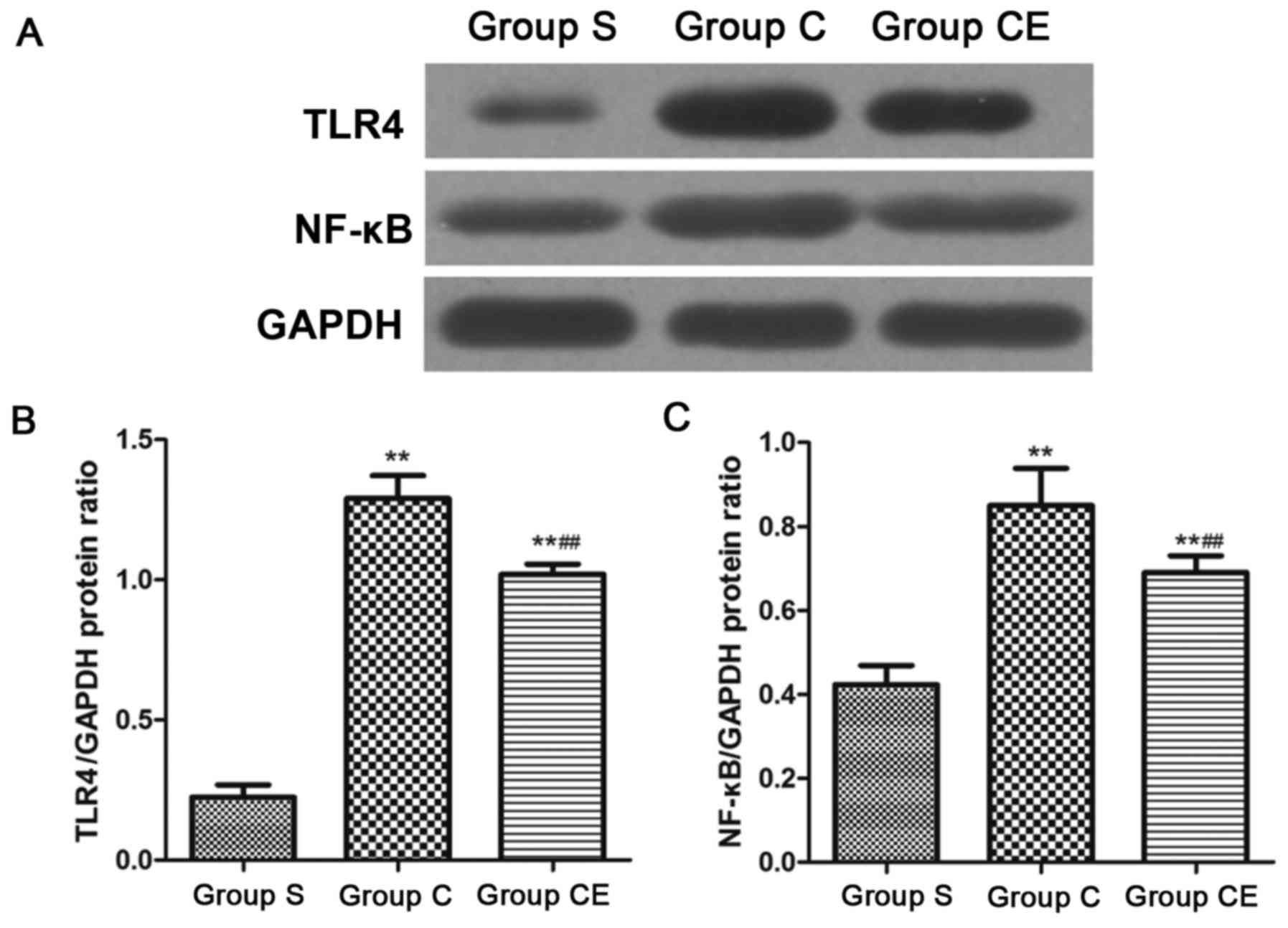
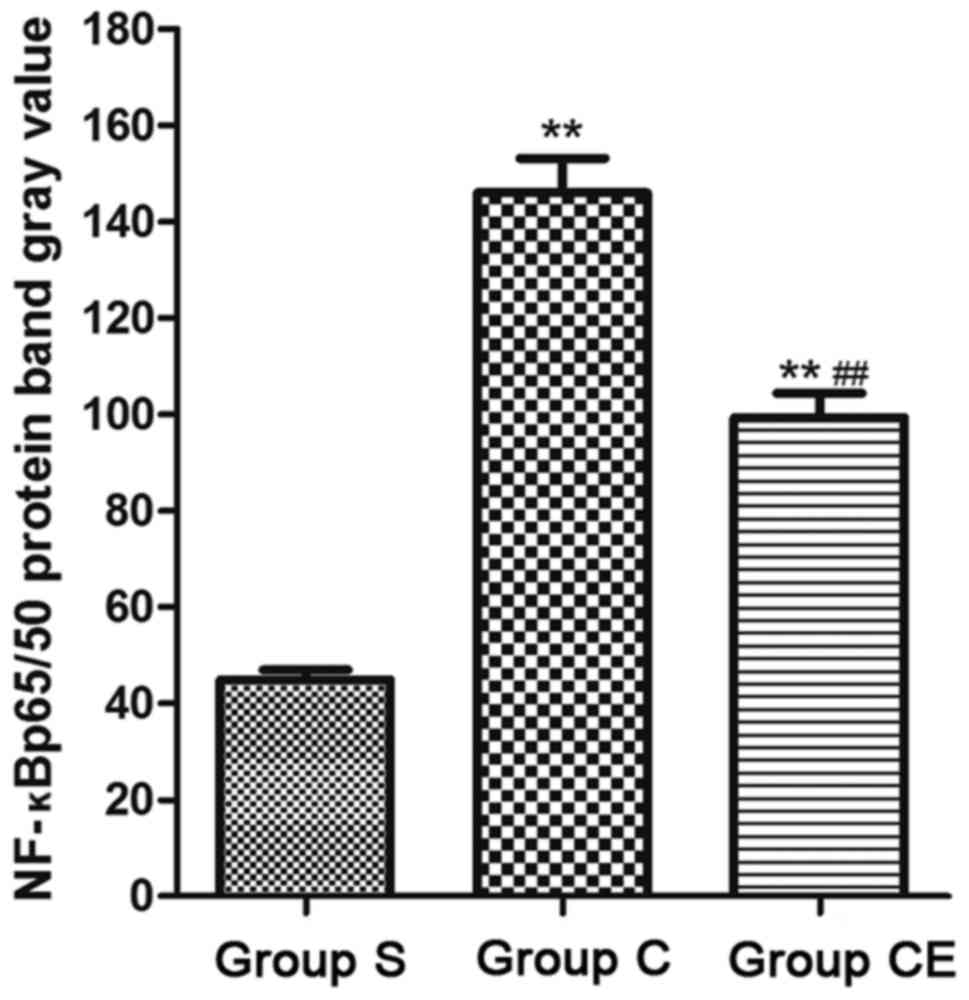
S, Zhao P and Liu T: Electroacupuncture could regulate the NF-κB
signaling pathway to ameliorate theinflammatory injury in focal
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion model rats. J Neurochem. 137:713–725.
2016.
|
|
11
|
Oshiro AH, Otsuki DA, Hamaji MW, Rosa KT,
Ida KK, Fantoni DT and Auler JO Jr: Differential Roles of TLR2 and
TLR4 in acute focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.
Brain Res. 70:577–590. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Gauberti M, Obiang P, Guedin P, Balossier
A, Gakuba C, Diependaele AS, Chazalviel L, Vivien D, Young AR, Agin
V, et al: Thrombotic stroke in the anesthetized monkey (Macaca
mulatta): Characterization by MRI - a pilot study. Cerebrovasc Dis.
33:329–339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hinohara H, Kadoi Y, Takahashi K, Saito S,
Kawauchi C and Mizutani A: Time course of changes in cerebral blood
flow velocity after tourniquet deflation in patients with diabetes
mellitus or previous stroke under sevoflurane anesthesia. J Anesth.
25:409–414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ying W, Pengfei G and Yuhong Z: TLR2 and
TLR4 in the brain injury caused by cerebral ischemia and
reperfusion. Mediators Inflamm. 9:2–9. 2016.
|
|
15
|
Lu L, Zhang G, Song C, Wang X, Qian W,
Wang Z, Liu Y, Gong S and Zhou S: Protection of ischemic post
conditioning against transient focal ischemia-induced brain damage
is associated with inhibition of neuroinflammation via modulation
of TLR2 and TLR4 pathways. J Neuroinflammation. 16:686–691.
2016.
|
|
16
|
Tomuschat C, O'Donnell AM, Coyle D, Dreher
N, Kelly D and Puri P: Neuroprotective effect of kaempferol
flycosides against brain injury and neuroinflammation by inhibiting
the activation of NF-κB and STAT3 in transient focal stroke.
Pediatr Res. 80:1787–1799. 2016.
|
|
17
|
Zhang M, Yin HJ, Wang WP, Li J and Wang
XL: Over-expressed human TREK-1 inhibits CHO cell proliferation via
inhibiting PKA and p38 MAPK pathways and subsequently inducing G1
arrest. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:1190–1198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levitz J, Royal P, Comoglio Y, Wdziekonski
B, Schaub S, Clemens DM, Isacoff EY and Sandoz G: Long non-coding
RNA C2dat1 regulates CaMKIIδ expression to promote neuronal
survival through the NF-κB signaling pathway following cerebral
ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:pp. 266–271. 2016;
|
|
19
|
Zhu HT, Bian C, Yuan JC, Chu WH, Xiang X,
Chen F, Wang CS, Feng H and Lin JK: Curcumin attenuates acute
inflammatory injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling
pathway in experimental traumatic brain injury. J
Neuroinflammation. 62:97–110. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Vivier D, Bennis K, Lesage F and Ducki S:
Daphnetin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in
mice via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed Res.
59:328–335. 2016.
|