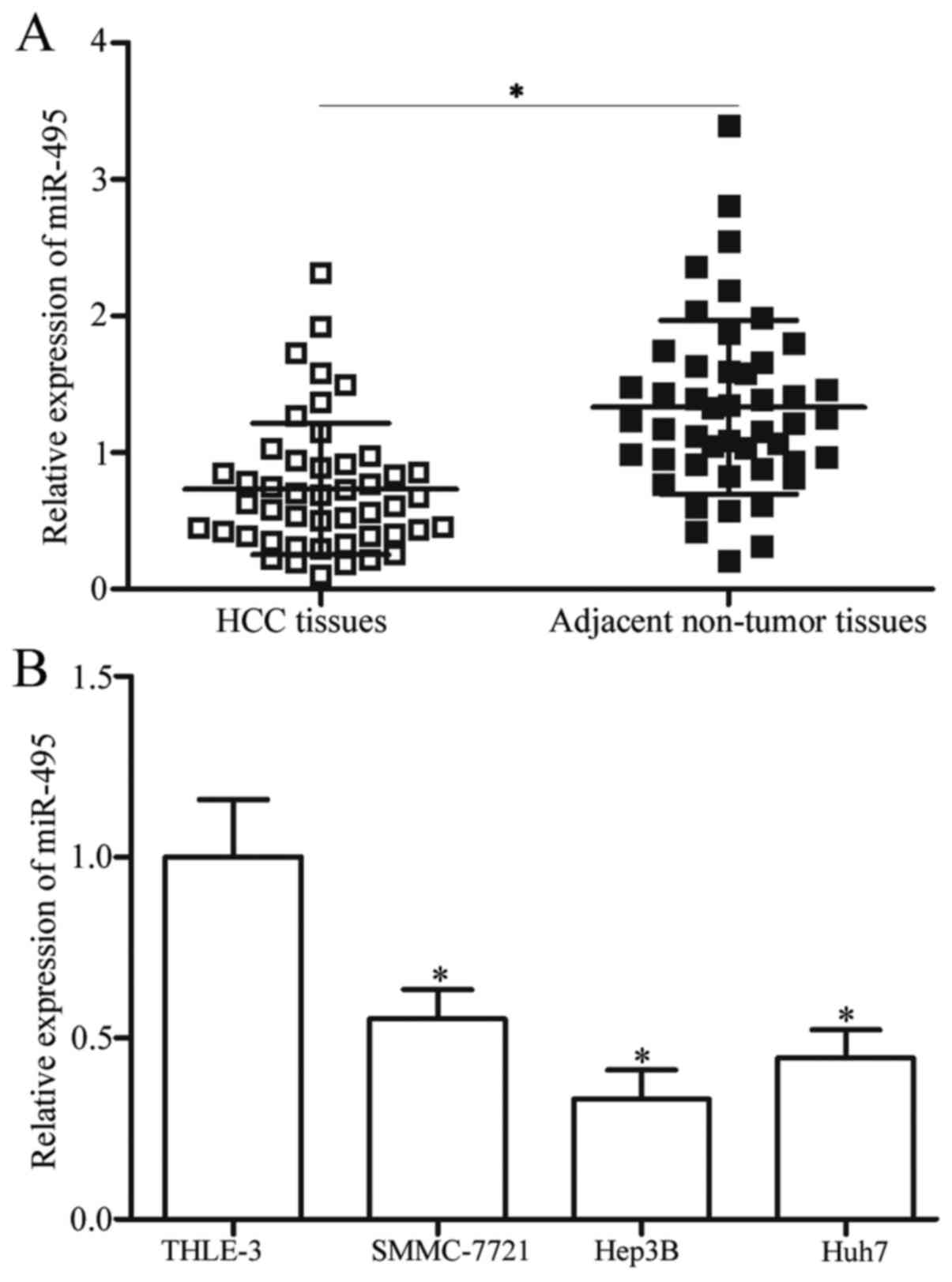
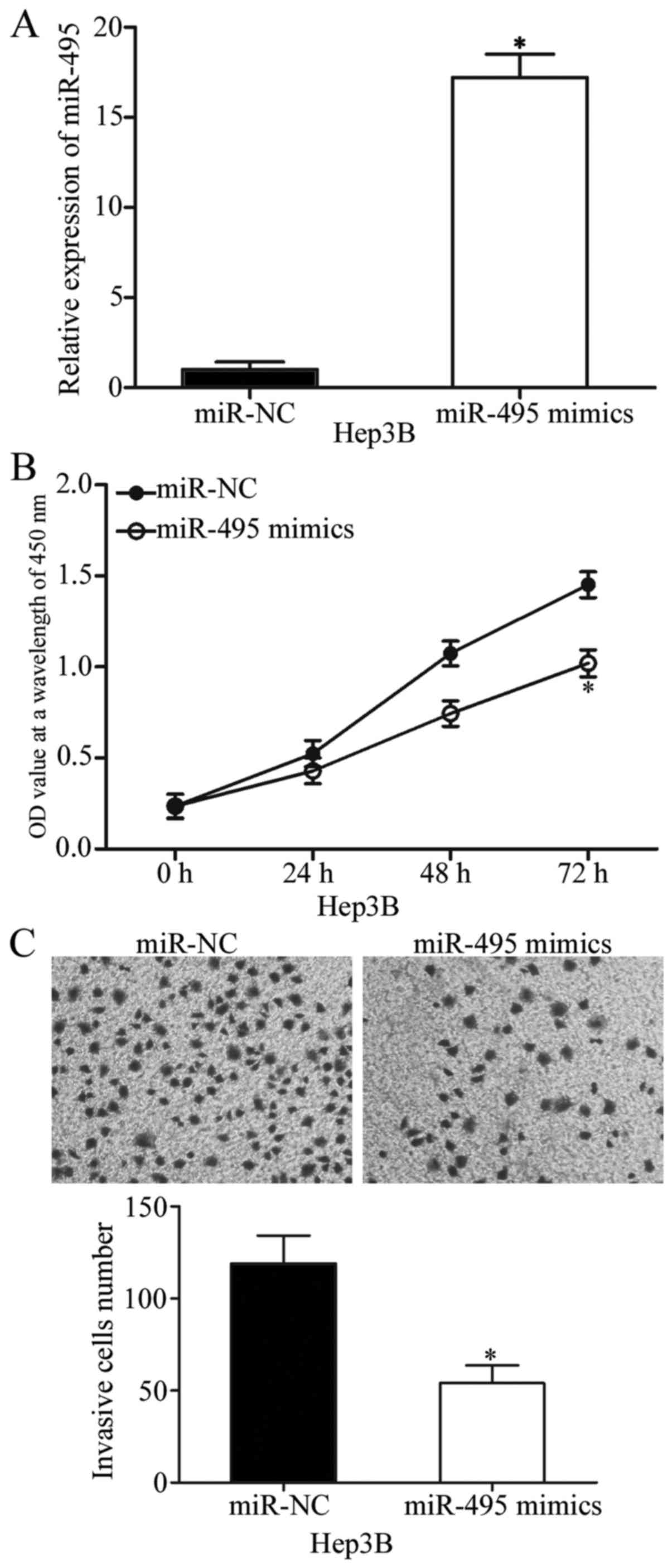
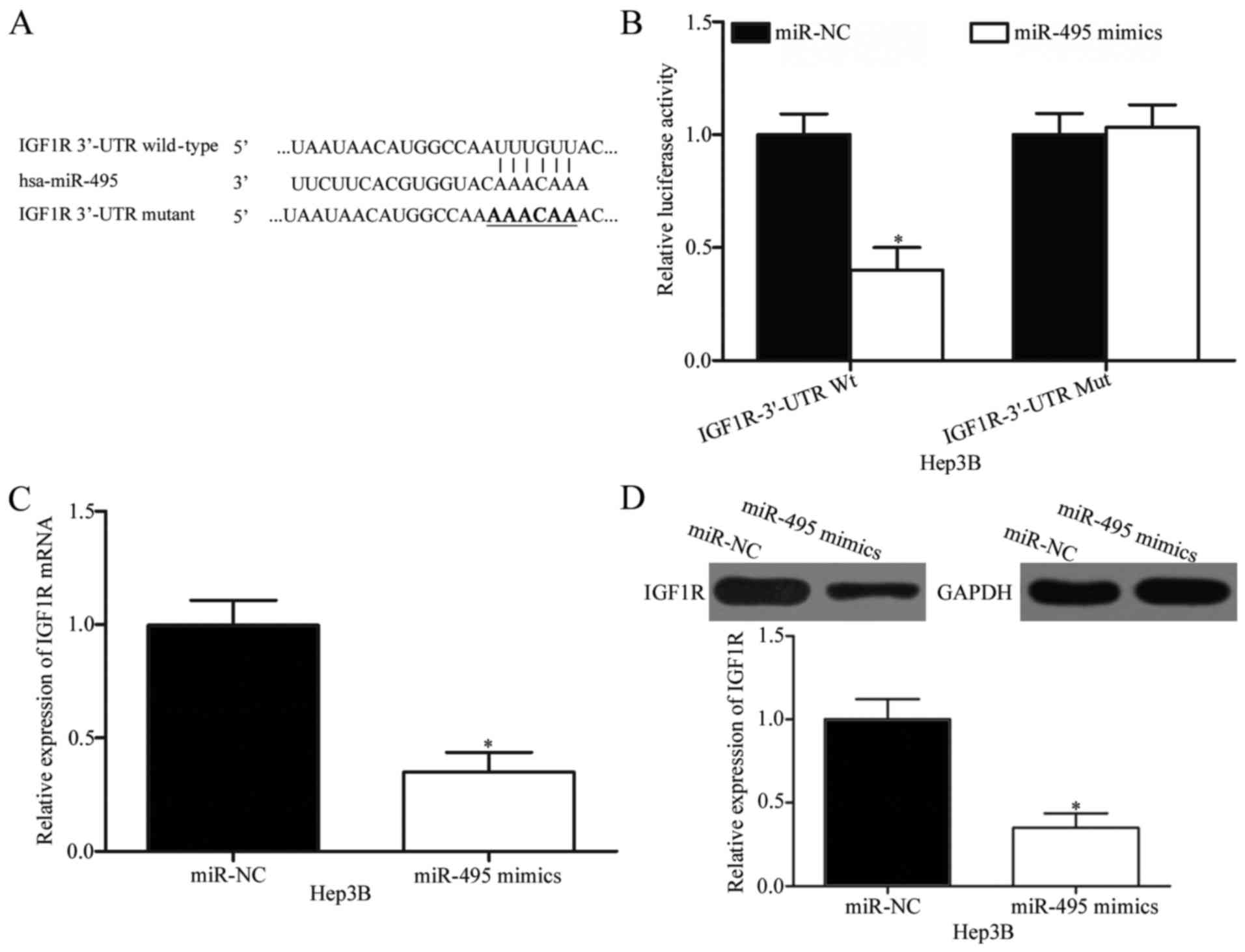
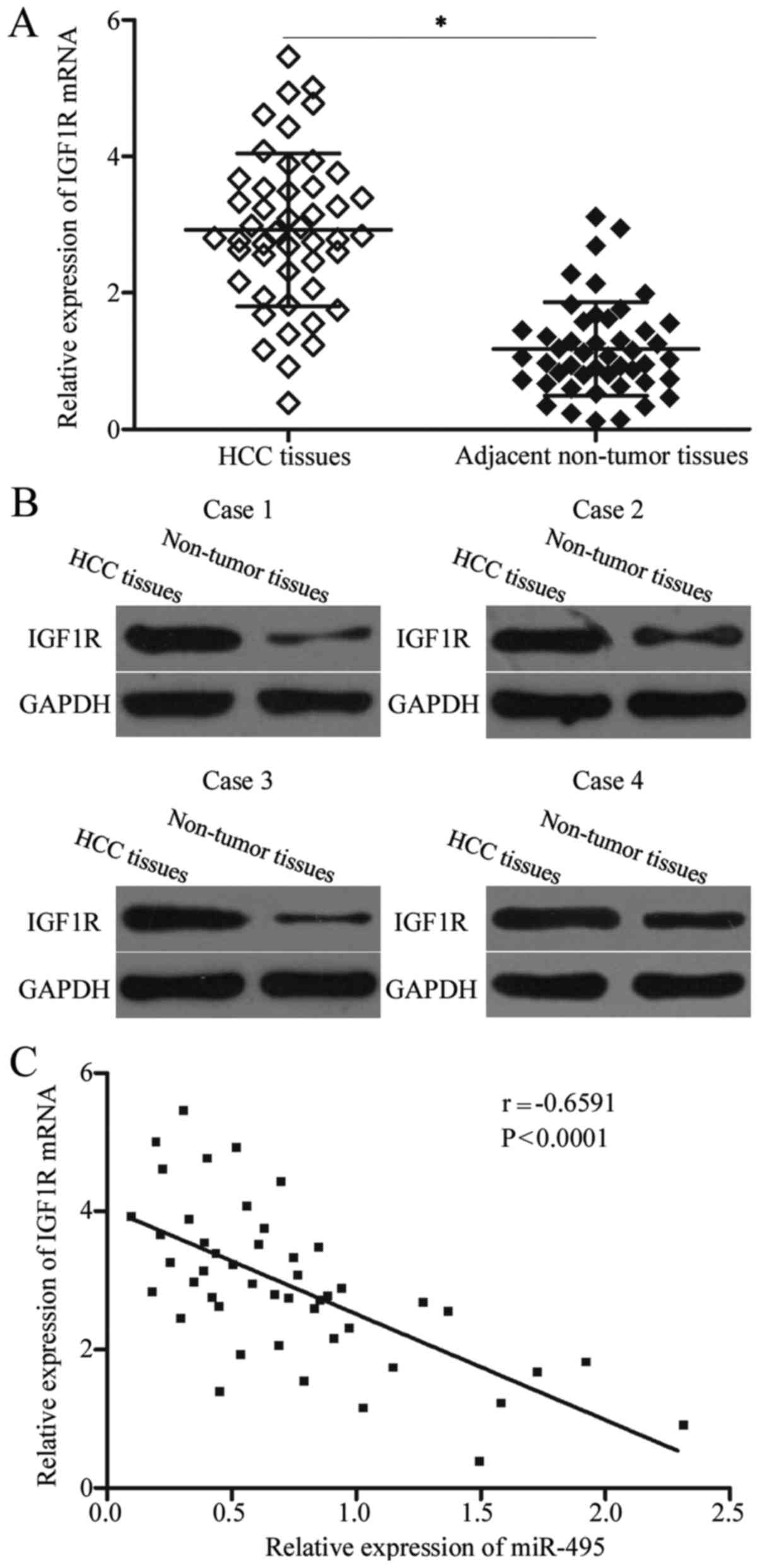
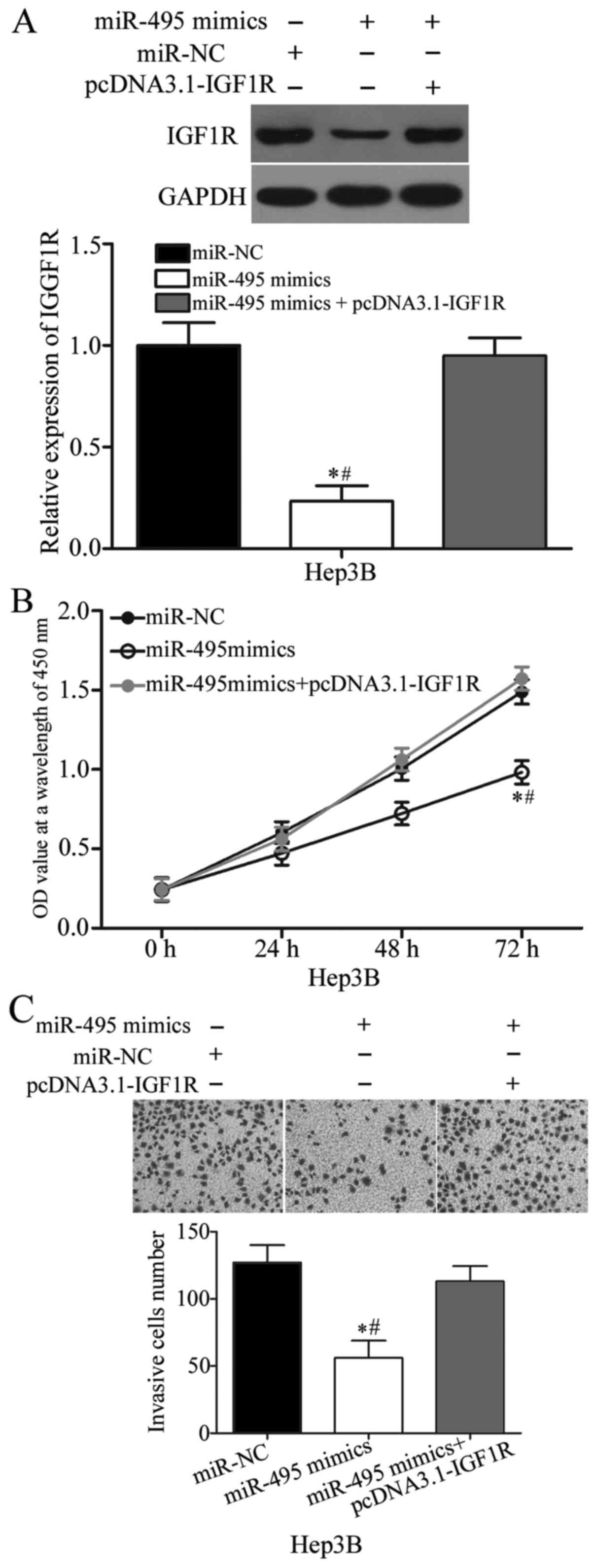
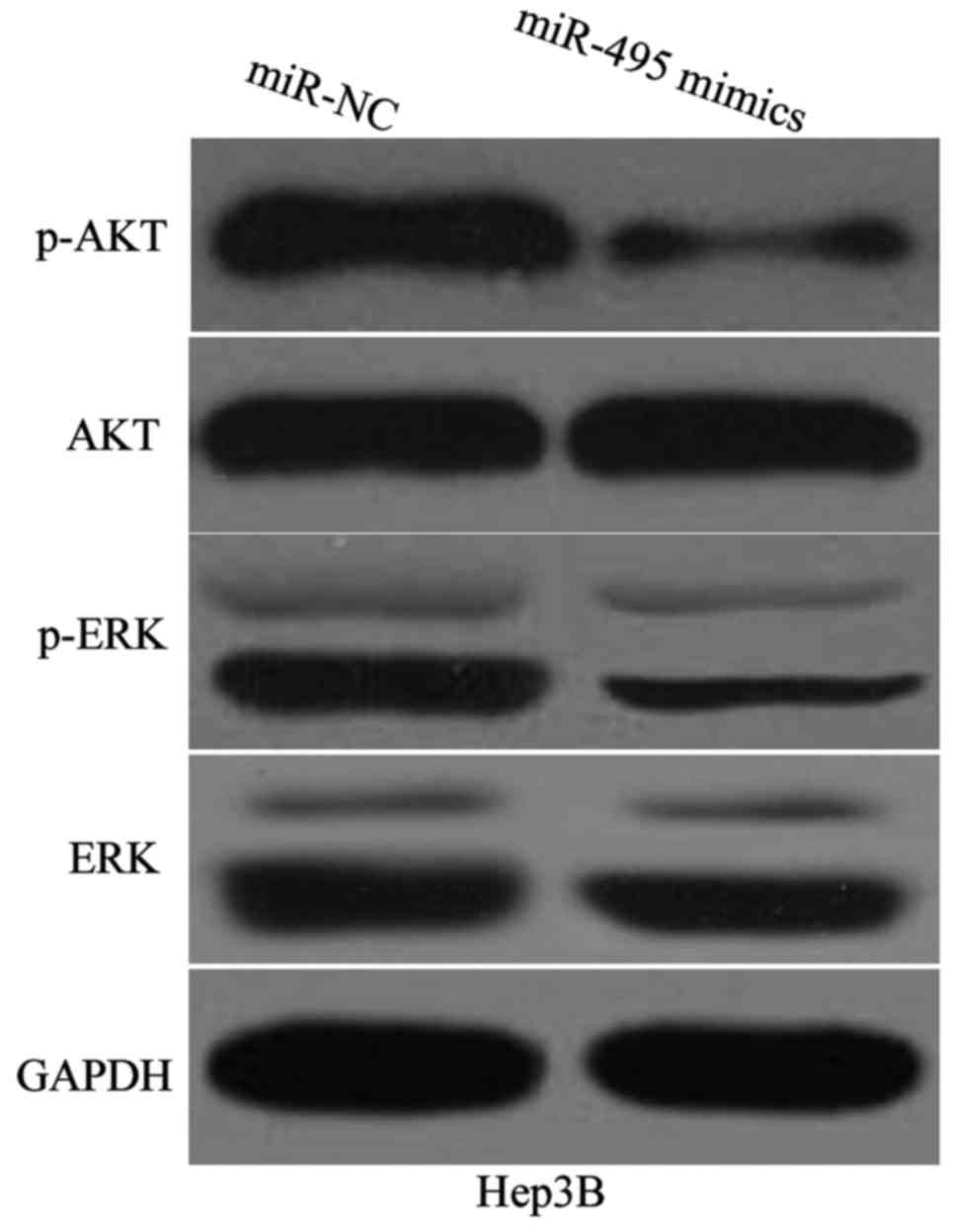
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Environmental factors
and risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 127 5
Suppl 1:S72–S78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng Z: Human genes involved in hepatitis
B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 20:7696–7706. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dhanasekaran R, Limaye A and Cabrera R:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends in worldwide epidemiology,
risk factors, diagnosis, and therapeutics. Hepat Med. 4:19–37.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ and Cressman EN:
Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
48:2047–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gu S, Jin L, Zhang F, Sarnow P and Kay MA:
Biological basis for restriction of microRNA targets to the 3′
untranslated region in mammalian mRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
16:144–150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan JJ, Chang Y, Zhang YN, Lin JS, He XX
and Huang HJ: miR-195 inhibits cell proliferation via targeting
AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 13:3118–3126.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pengcheng S, Ziqi W, Luyao Y, Xiangwei Z,
Liang L, Yuwei L, Lechen L and Wanhai X: MicroRNA-497 suppresses
renal cell carcinoma by targeting VEGFR-2 in ACHN cells. Biosci
Rep. 37:pii: BSR201702702017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li F, Guo Y, Liu J and Zhang R: The
significance of elevated plasma expression of microRNA 106b~25
clusters in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 12:e01784272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fateh A, Feizi MAH, Safaralizadeh R and
Azarbarzin S: Importance of miR-299-5p in colorectal cancer. Ann
Gastroenterol. 30:322–326. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lujambio A and Lowe SW: The microcosmos of
cancer. Nature. 482:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: microRNA
involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1126–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tan M, Mu X, Liu Z, Tao L, Wang J, Ge J
and Qiu J: microRNA-495 promotes bladder cancer cell growth and
invasion by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 483:867–873. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang W, Zheng J, Yu T and Wang J:
Overexpression of microRNA-495 suppresses the proliferation and
invasion and induces the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by
targeting high-mobility group nucleosome-binding domain 5. Oncol
Rep. 38:1099–1107. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu P, Hu Y, Ma L, Du M, Xia L and Hu Z:
miR-425 inhibits melanoma metastasis through repression of PI3K-Akt
pathway by targeting IGF-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 75:51–57. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu YY, Tian J, Hao Q and Yin LR:
MicroRNA-495 downregulates FOXC1 expression to suppress cell growth
and migration in endometrial cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:239–251. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang X, Huang H, Li Z, He C, Li Y, Chen
P, Gurbuxani S, Arnovitz S, Hong GM, Price C, et al: MiR-495 is a
tumor-suppressor microRNA down-regulated in MLL-rearranged
leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp. 19397–19402. 2012;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin SB, Zhou L, Liang ZY, Zhou WX and Jin
Y: Expression of GRK2 and IGF1R in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance. J Clin Pathol.
70:754–759. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao WF, Liu JW, Sheng GL and Huang DS:
Blockade of IGF-IR exerts anticancer effects in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 4:719–722. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang W, Liu K, Liu S, Ji B, Wang Y and
Liu Y: MicroRNA-133a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting
IGF-1R in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:9779–9788.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo T, Feng Y, Liu Q, Yang X, Jiang T,
Chen Y and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-320a suppresses in GBM patients and
modulates glioma cell functions by targeting IGF-1R. Tumour Biol.
35:11269–11275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen G, Fang T, Huang Z, Qi Y, Du S, Di T,
Lei Z, Zhang X and Yan W: MicroRNA-133a inhibits osteosarcoma cells
proliferation and invasion via targeting IGF-1R. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 38:598–608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuan J, Ji H, Xiao F, Lin Z, Zhao X, Wang
Z, Zhao J and Lu J: MicroRNA-340 inhibits the proliferation and
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting JAK1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:578–584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duan X, Bai J, Wei J, Li Z, Liu X and Xu
G: MicroRNA-508-5p suppresses metastasis in human gastric cancer by
targeting S-phase kinase-associated protein 2. Mol Med Rep.
16:2163–2171. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma F, Li W, Liu C, Li W, Yu H, Lei B, Ren
Y, Li Z, Pang D and Qian C: MiR-23a promotes TGF-beta1-induced EMT
and tumor metastasis in breast cancer cells by directly targeting
CDH1 and activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncotarget.
8:69538–69550. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han K, Li J, Zhao H, Liang P, Huang X,
Zheng L, Li Y, Yang T and Wang L: Identification of the typical
miRNAs and target genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
10:229–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Afonso MB, Rodrigues PM, Simão AL and
Castro RE: Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Clin Med. 5:pii: E302016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gandhi NS, Tekade RK and Chougule MB:
Nanocarrier mediated delivery of siRNA/miRNA in combination with
chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy: Current progress and
advances. J Control Release. 194:238–256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang C, Yun Z, Zhao T, Liu X and Ma X:
MiR-495 is a predictive biomarker that downregulates GFI1
expression in medulloblastoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1430–1439.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, Italiano
D, Finazzi-Agro' E, Levine AJ, Bernardini S, Garabadgiu AV, Melino
G and Candi E: MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c,
miR-377, miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p,
mapped to the 14q32.31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis,
migration and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells.
Oncogene. 33:5173–5182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lv C, Bai Z, Liu Z, Luo P and Zhang J:
MicroRNA-495 suppresses human renal cell carcinoma malignancy by
targeting SATB1. Am J Transl Res. 7:1992–1999. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Y, Luo D, Tian W, Li Z and Zhang X:
Demethylation of miR-495 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
promotes apoptosis by targeting STAT-3 in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
37:3581–3589. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang L, Liu JL, Yu L, Liu XX, Wu HM, Lei
FY, Wu S and Wang X: Downregulated miR-495 [Corrected] inhibits the
G1-S phase transition by targeting Bmi-1 in breast cancer.
Medicine. 94:e7182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei T, Zhu W, Fang S, Zeng X, Huang J,
Yang J, Zhang J and Guo L: miR-495 promotes the chemoresistance of
SCLC through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Etk/BMX. Am
J Cancer Res. 7:628–646. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chu H, Chen X, Wang H, Du Y, Wang Y, Zang
W, Li P, Li J, Chang J, Zhao G and Zhang G: MiR-495 regulates
proliferation and migration in NSCLC by targeting MTA3. Tumour
Biol. 35:3487–3494. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nie S, Li K, Huang Y, Hu Q, Gao X and Jie
S: miR-495 mediates metabolic shift in glioma cells via targeting
Glut1. J Craniofac Surg. 26:e155–e158. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang B, Yuan F, Liu J, Li Y, Zhou F, Liu
X, Hao Z, Li Q, Zheng Y and Wang W: Hsa-miR-495 acts as a tumor
suppressor gene in glioma via the negative regulation of MYB. Mol
Med Rep. 14:977–982. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen SM, Chen HC, Chen SJ, Huang CY, Chen
PY, Wu TW, Feng LY, Tsai HC, Lui TN, Hsueh C and Wei KC:
MicroRNA-495 inhibits proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme
cells by downregulating cyclin-dependent kinase 6. World J Surg
Oncol. 11:872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li JZ, Wang ZL, Xu WH, Li Q, Gao L and
Wang ZM: MicroRNA-495 regulates migration and invasion in prostate
cancer cells via targeting Akt and mTOR signaling. Cancer Invest.
34:181–188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song L, Li Y, Li W, Wu S and Li Z: miR-495
enhances the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to
platinum by modulation of copper-transporting P-type adenosine
triphosphatase A (ATP7A). J Cell Biochem. 115:1234–1242. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang YH, Han XD, Qiu Y, Xiong J, Yu Y,
Wang B, Zhu ZZ, Qian BP, Chen YX, Wang SF, et al: Increased
expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is correlated
with tumor metastasis and prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma.
J Surg Oncol. 105:235–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shiratsuchi I, Akagi Y, Kawahara A,
Kinugasa T, Romeo K, Yoshida T, Ryu Y, Gotanda Y, Kage M and
Shirouzu K: Expression of IGF-1 and IGF-1R and their relation to
clinicopathological factors in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:2541–2545. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma Y, Cheng Q, Ren Z, Xu L, Zhao Y, Sun J,
Hu S and Xiao W: Induction of IGF-1R expression by EGR-1
facilitates the growth of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
317:150–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gryko M, Kiśluk J, Cepowicz D, Zińczuk J,
Kamocki Z, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Pryczynicz A, Czyżewska J, Kemona
A and Kędra B: Expression of insulin-like growth factor receptor
type 1 correlate with lymphatic metastases in human gastric cancer.
Pol J Pathol. 65:135–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pengchong H and Tao H: Expression of
IGF-1R, VEGF-C and D2-40 and their correlation with lymph node
metastasis in endometrial adenocarcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
32:660–664. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xie QX, Lin XC, Zhang MF, Han CX and Guo
YH: Expression of IGF-I and IGF-IR in bladder cancer. Ai Zheng.
23:707–709. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|