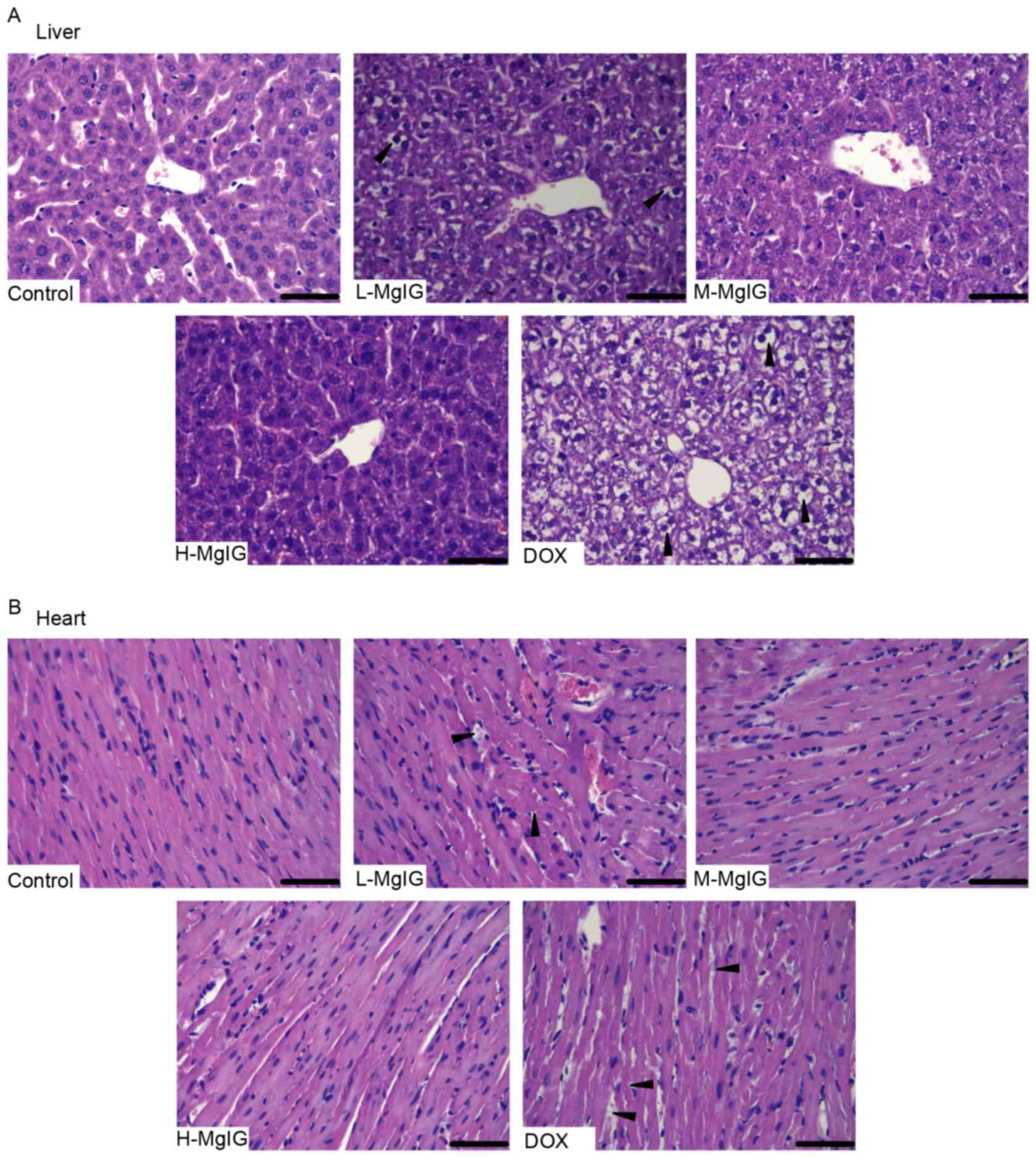
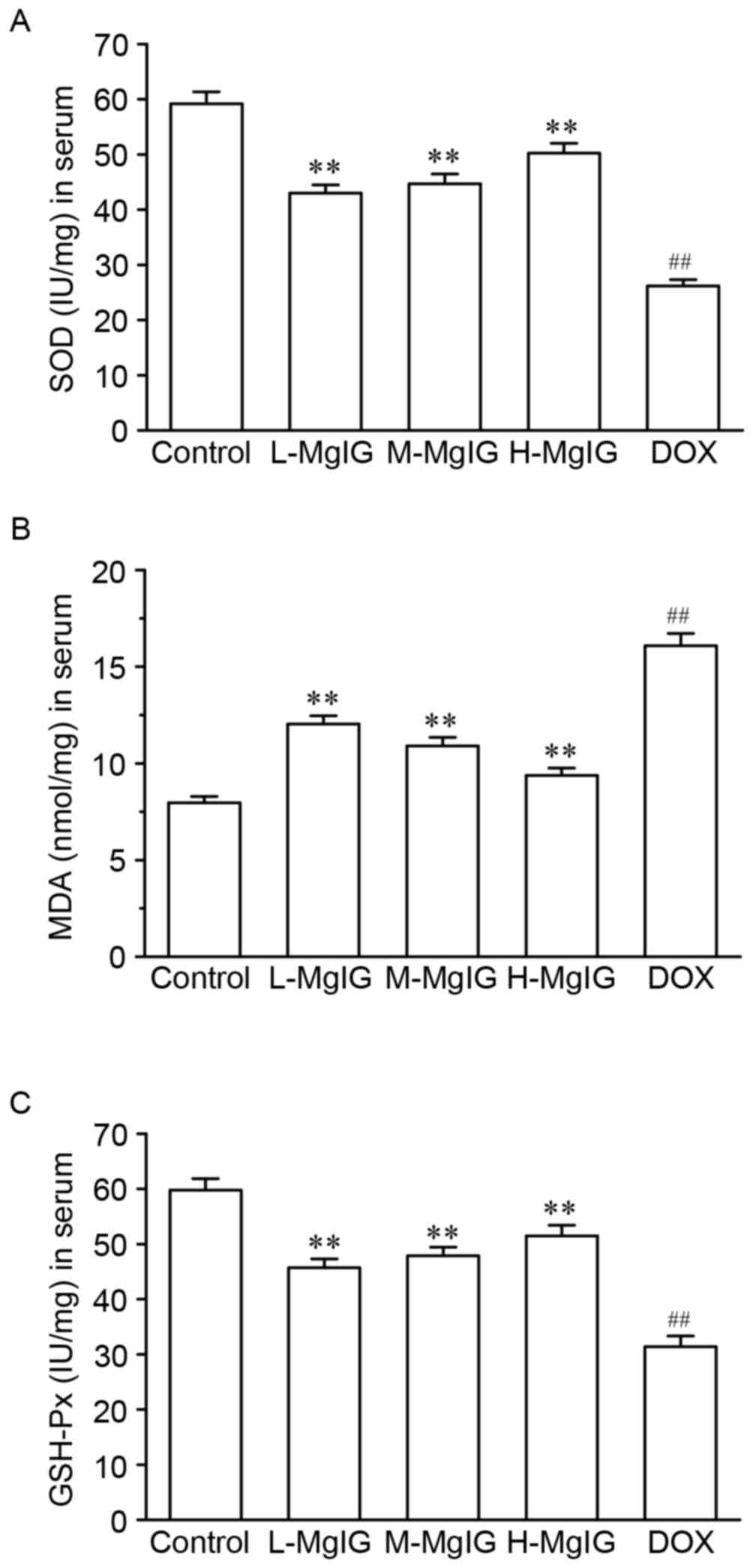
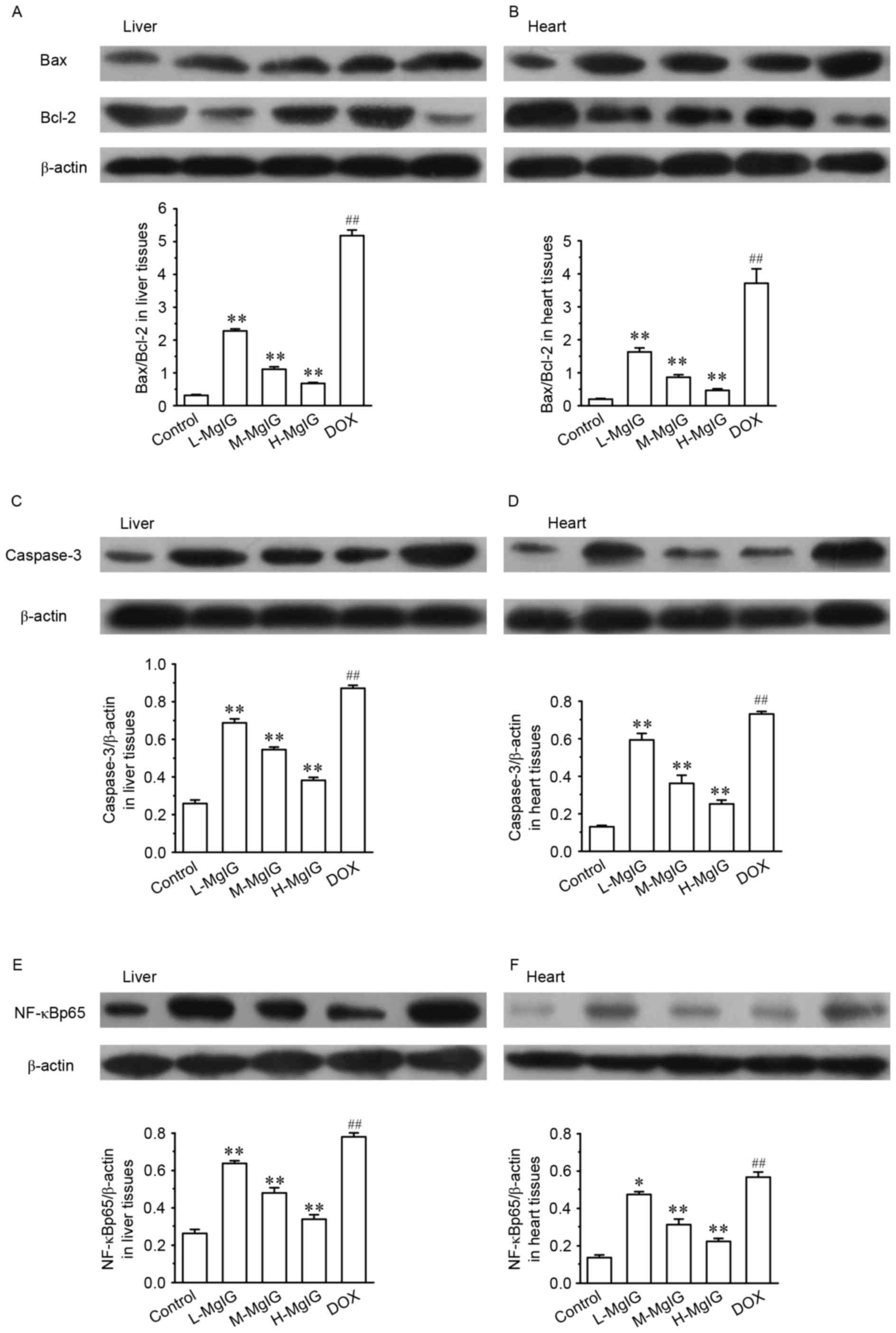
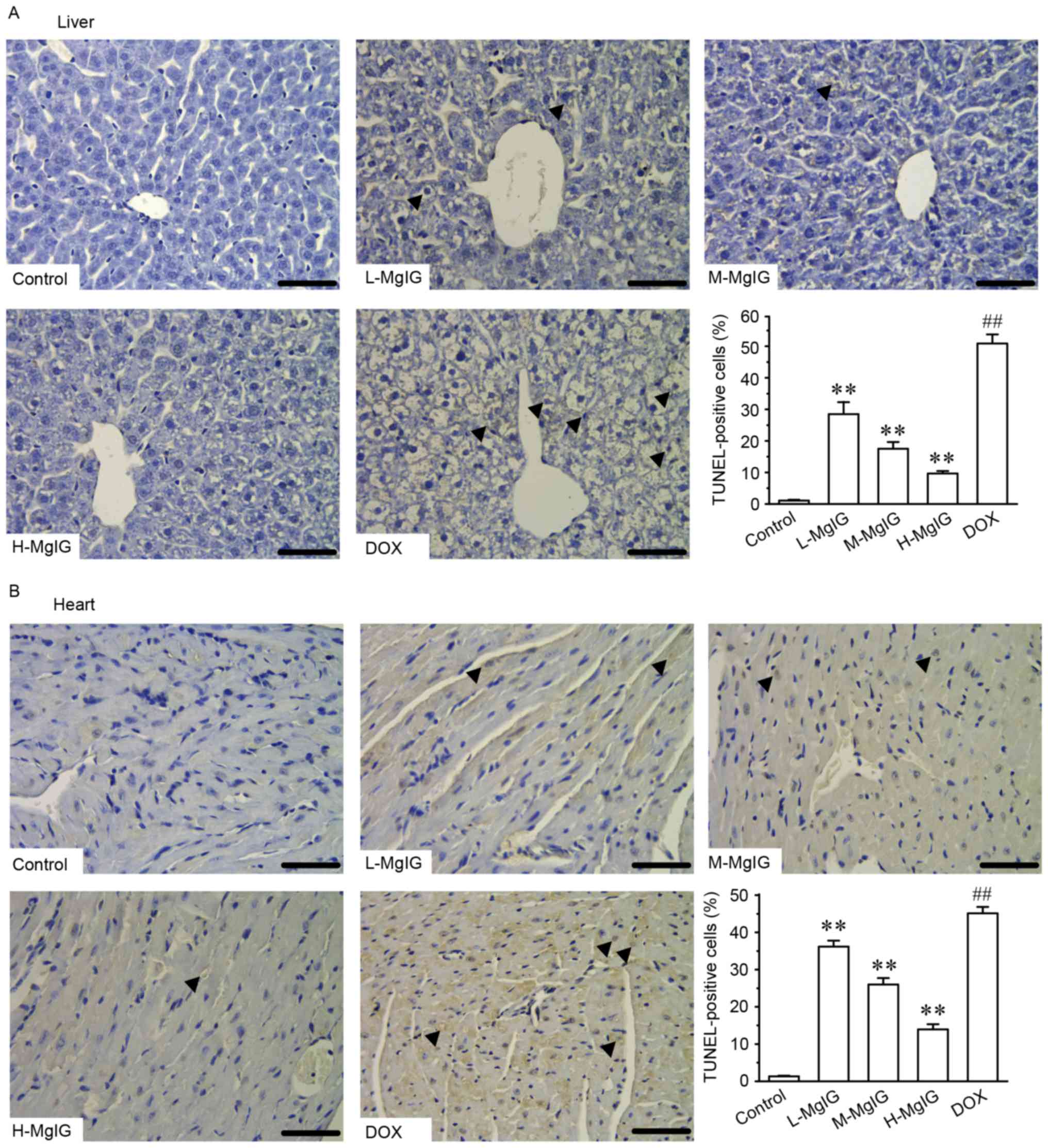
|
1
|
Andersen-Parrado P: Licorice: Not just
candy, but a tonic herb with myriad healing properties. Better
Nutrition. 59:33–34. 1997.
|
|
2
|
Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel, .
Final report on the safety assessment of glycyrrhetinic acid,
potassium glycyrrhetinate, disodium succinoyl glycyrrhetinate,
glyceryl glycyrrhetinate, glycyrrhetinyl stearate, stearyl
glycyrrhetinate, glycyrrhizic acid, ammonium glycyrrhizate,
dipotassium glycyrrhizate, disodium glycyrrhizate, trisodium
glycyrrhizate, methyl glycyrrhizate, and potassium glycyrrhizinate.
Int J Toxicol. 26 Suppl 2:S79–S112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ming LJ and Yin AC: Therapeutic effects of
glycyrrhizic acid. Nat Prod Commun. 8:415–418. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Rossum TG, Vulto AG, de Man RA,
Brouwer JT and Schalm SW: Review article: Glycyrrhizin as a
potential treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol
Ther. 12:199–205. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie C, Li X, Wu J, Liang Z, Deng F, Xie W,
Zhu M, Zhu J, Zhu W, Geng S, et al: Anti-inflammatory activity of
magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate through inhibition of phospholipase
a2/arachidonic acid pathway. Inflammation. 38:1639–1648. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tang GH, Yang HY, Zhang JC, Ren JJ, Sang
XT, Lu X, Zhong SX and Mao YL: Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate
inhibits inflammatory response through STAT3 pathway to protect
remnant liver function. World J Gastroenterol. 21:12370–12380.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng J, Wu G, Hu GX, Peng YZ and Xiong
XJ: Protective effects against and potential mechanisms underlying
the effect of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate in hypoxia-reoxygenation
injury in rat liver cells. Genet Mol Res. 14:15453–15461. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang X, Qin J and Lu S: Magnesium
isoglycyrrhizinate protects hepatic L02 cells from
ischemia/reperfusion induced injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4755–4764. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng Y, Zhang J, Shang J and Zhang L:
Prevention of free fatty acid-induced hepatic lipotoxicity in HepG2
cells by magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate in vitro. Pharmacology.
84:183–190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vincenzi B, Armento G, Spalato Ceruso M,
Catania G, Leakos M, Santini D, Minotti G and Tonini G:
Drug-induced hepatotoxicity in cancer patients-implication for
treatment. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 15:1219–1238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kalyanaraman B: Teaching the basics of
redox biology to medical and graduate students: Oxidants,
antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biol. 1:244–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS, Bakheet SA,
Al-Bekari AM, Al-Shabanah OA, Al-Majed A, Al-Yahya AA and Qureshi
S: Effect of metformin on clastogenic and biochemical changes
induced by adriamycin in Swiss albino mice. Mutat Res. 634:93–100.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Panda S and Kar A:
Periplogenin-3-O-D-glucopyranosyl
-(1->6)-D-glucopyaranosyl-(1->4) -D-cymaropyranoside,
isolated from Aegle marmelos protects doxorubicin induced
cardiovascular problems and hepatotoxicity in rats. Cardiovasc
Ther. 27:108–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zordoky BN, Anwar-Mohamed A, Aboutabl ME
and El-Kadi AO: Acute doxorubicin toxicity differentially alters
cytochrome P450 expression and arachidonic acid metabolism in rat
kidney and liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 39:1440–1450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Mei X, Yuan J, Lu W, Li B and Xu
D: Taurine zinc solid dispersions attenuate doxorubicin-induced
hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
289:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong Q, Chen L, Lu Q, Sharma S, Li L,
Morimoto S and Wang G: Quercetin attenuates doxorubicin
cardiotoxicity by modulating Bmi-1 expression. Br J Pharmacol.
171:4440–4454. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Indu R, Azhar TS, Nair A and Nair CK:
Amelioration of doxorubicin induced cardio-and hepato-toxicity by
carotenoids. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:62–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kalyanaraman B, Joseph J, Kalivendi S,
Wang S, Konorev E and Kotamraju S: Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis:
Implications in cardiotoxicity. Mol Cell Biochem 234–235. 1–124.
2002.
|
|
19
|
Tacar O, Sriamornsak P and Dass CR:
Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and
novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:157–170. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pieniazek A, Czepas J, Piasecka-Zelga J,
Gwoździński K and Koceva-Chyła A: Oxidative stress induced in rat
liver by anticancer drugs doxorubicin, paclitaxel and docetaxel.
Adv Med Sci. 58:104–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
National Institute of Health, . Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National Academies
Press; Washington, DC: 1996
|
|
22
|
Arola OJ, Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki
M, Parvinen M and Voipio-Pulkki LM: Acute doxorubicin
cardiotoxicity involves cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cancer Res.
60:1789–1792. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Yang R, Yuan B, Liu Y and Liu C:
The antiviral and antimicrobial activities of licorice, a
widely-used Chinese herb. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:310–315. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Q, Wang J, Liu R, Wang Z, Li Y, Zhang
Y, Hao X, Huang Y, Xie W and Wei H: Amelioration of concanavalin
A-induced autoimmune hepatitis by magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate
through inhibition of CD4(+)CD25(−)CD69(+) subset proliferation.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:443–453. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Navarro VJ and Senior JR: Drug-related
hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med. 354:731–739. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang JP, Zhang YY, Zhang Y, Gao YG, Ma
JJ, Wang N, Wang JY, Xie Y, Zhang FH and Chu L: Salvia miltiorrhiza
(Danshen) injection ameliorates iron overload-induced cardiac
damage in mice. Planta Med. 79:744–752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dawson EA, Shave R, George K, Whyte G,
Ball D, Gaze D and Collinson P: Cardiac drift during prolonged
exercise with echocardiographic evidence of reduced diastolic
function of the heart. Eur J Appl Physiol. 94:305–309. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chan EM, Thomas MJ, Bandy B and Tibbits
GF: Effects of doxorubicin, 4-epirubicin, and antioxidant enzymes
on the contractility of isolated cardiomyocytes. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 74:904–910. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shirakami Y, Sakai H and Shimizu M:
Retinoid roles in blocking hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary
Surg Nutr. 4:222–228. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shrum B, Costello P, McDonald W, Howlett
C, Donnelly M and McAlister VC: In vitro three dimensional culture
of hepatocellular carcinoma to measure prognosis and responsiveness
to chemotherapeutic agents. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 5:204–208.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
González-Vallinas M and Breuhahn K:
MicroRNAs are key regulators of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell
dissemination-what we learned from microRNA-494. Hepatobiliary Surg
Nutr. 5:372–376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ozben T: Oxidative stress and apoptosis:
Impact on cancer therapy. J Pharm Sci. 96:2181–2196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Conklin KA: Chemotherapy-associated
oxidative stress: Impact on chemotherapeutic effectiveness. Integr
Cancer Ther. 3:294–300. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Wang H, Cui L, Zhang Y, Liu Y,
Chu X, Liu Z, Zhang J and Chu L: Continuing treatment with Salvia
miltiorrhiza injection attenuates myocardial fibrosis in chronic
iron-overloaded mice. PLoS One. 10:e01240612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fridovich I: Oxygen radicals from
acetaldehyde. Free Radic Biol Med. 7:557–558. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Forman HJ and Dickinson DA: Introduction
to serial reviews on 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal as a signaling molecule.
Free Radic Biol Med. 37:594–596. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gutteridge JM: Lipid peroxidation and
antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage. Clin Chem.
41:1819–1828. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou S, Palmeira CM and Wallace KB:
Doxorubicin-induced persistent oxidative stress to cardiac
myocytes. Toxicol Lett. 121:151–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kalender Y, Yel M and Kalender S:
Doxorubicin hepatotoxicity and hepatic free radical metabolism in
rats. The effects of vitamin E and catechin. Toxicology. 209:39–45.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Robinson P, Kasembeli M, Bharadwaj U,
Engineer N, Eckols KT and Tweardy DJ: Substance P receptor
signaling mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and
triple-negative breast cancer chemoresistance. Biomed Res Int.
2016:19592702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Krishnamurthy B, Rani N, Bharti S,
Golechha M, Bhatia J, Nag TC, Ray R, Arava S and Arya DS:
Febuxostat ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.
Chem Biol Interact. 237:96–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang YW, Shi J, Li YJ and Wei L:
Cardiomyocyte death in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Arch
Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 57:435–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR:
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment
of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng B, Wu L, Ma L, Liu S, Li L, Xie W
and Li X: Telekin induces apoptosis associated with the
mitochondria-mediated pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1118–1125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nagai K, Oda A and Konishi H: Theanine
prevents doxorubicin-induced acute hepatotoxicity by reducing
intrinsic apoptotic response. Food Chem Toxicol. 78:147–152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Muller I, Niethammer D and Bruchelt G:
Anthracycline-derived chemotherapeutics in apoptosis and free
radical cytotoxicity (Review). Int J Mol Med. 1:491–494.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|