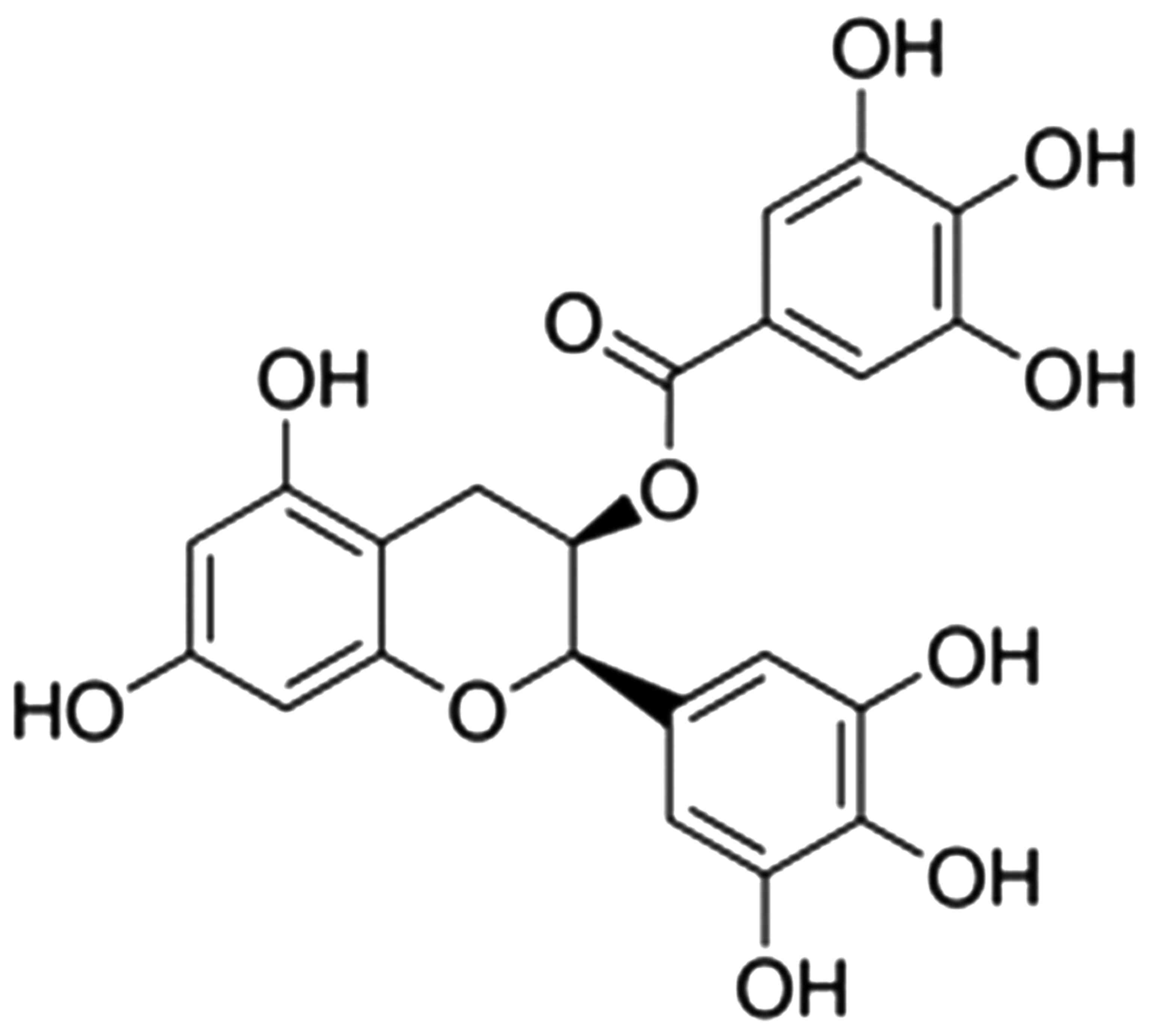
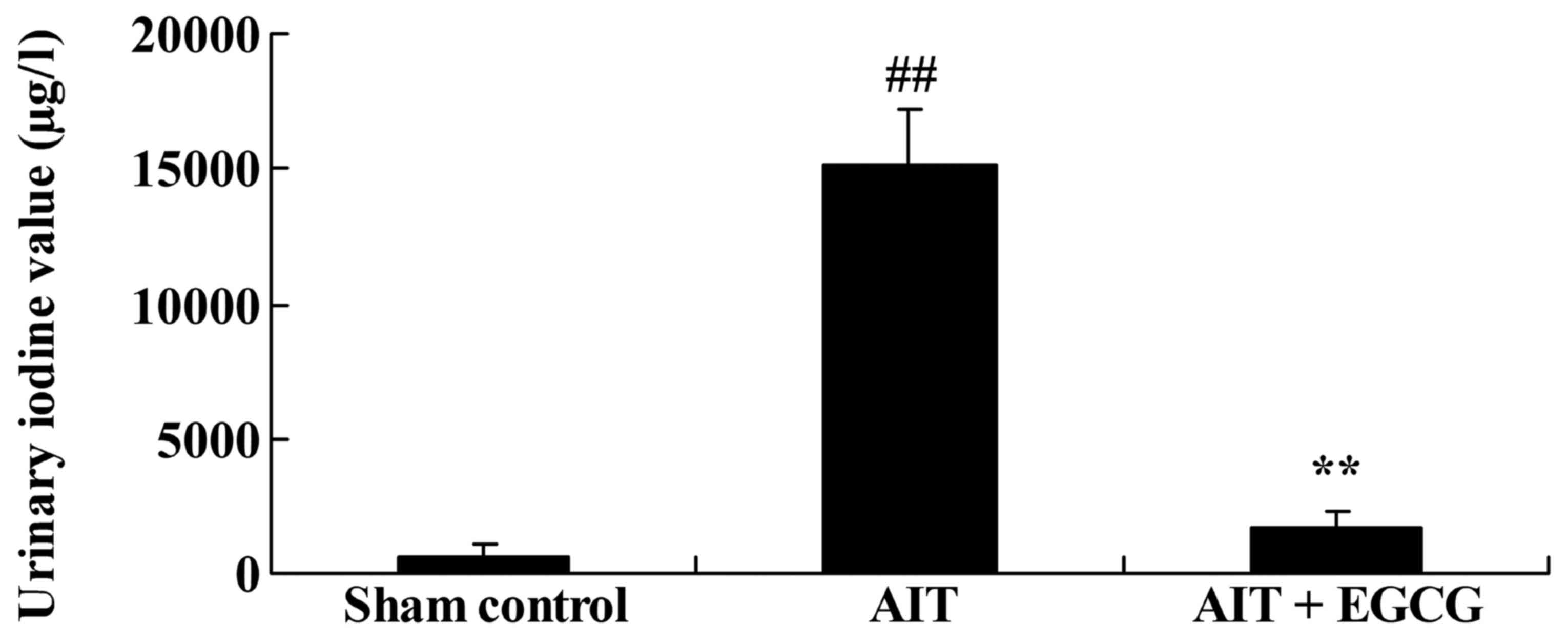
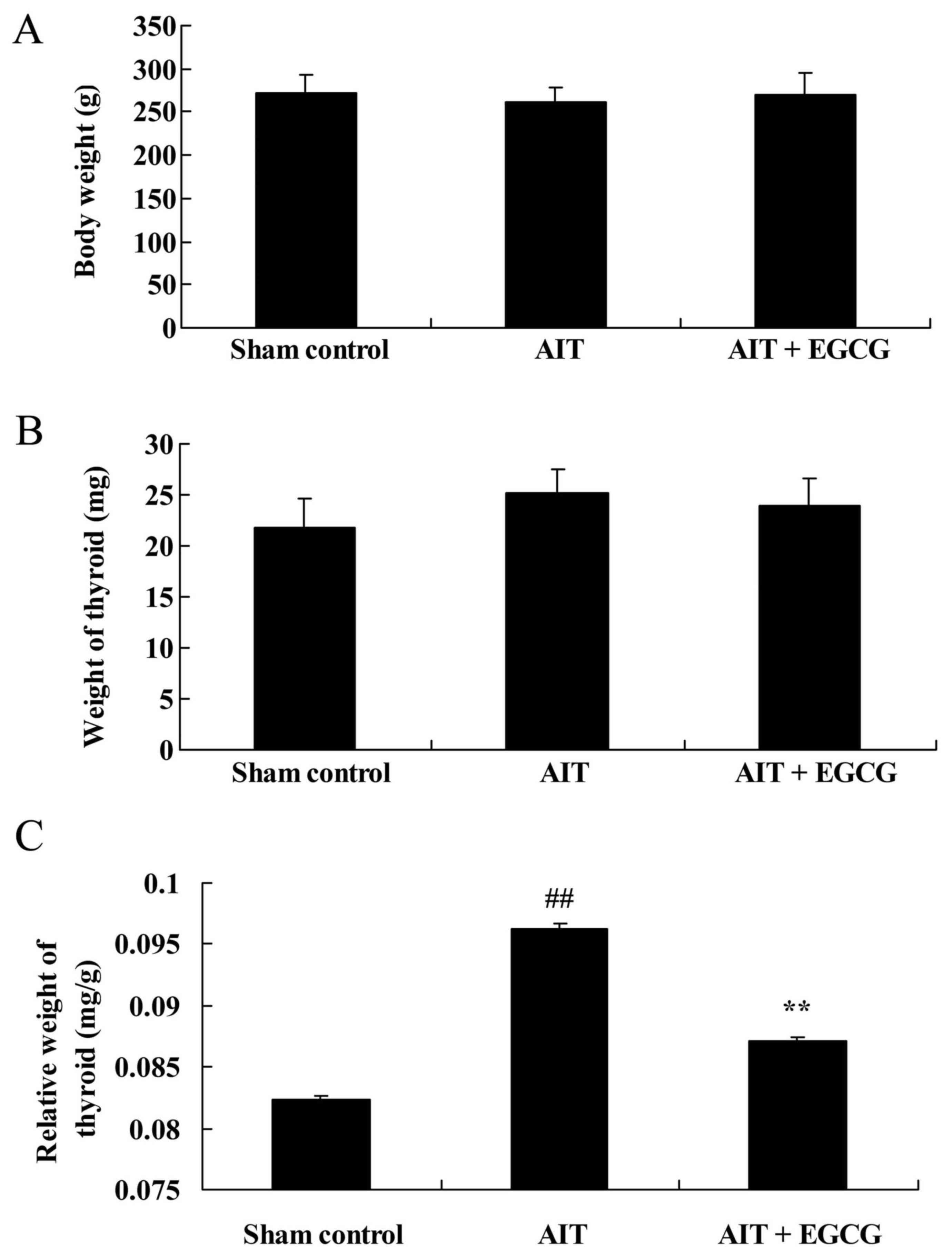
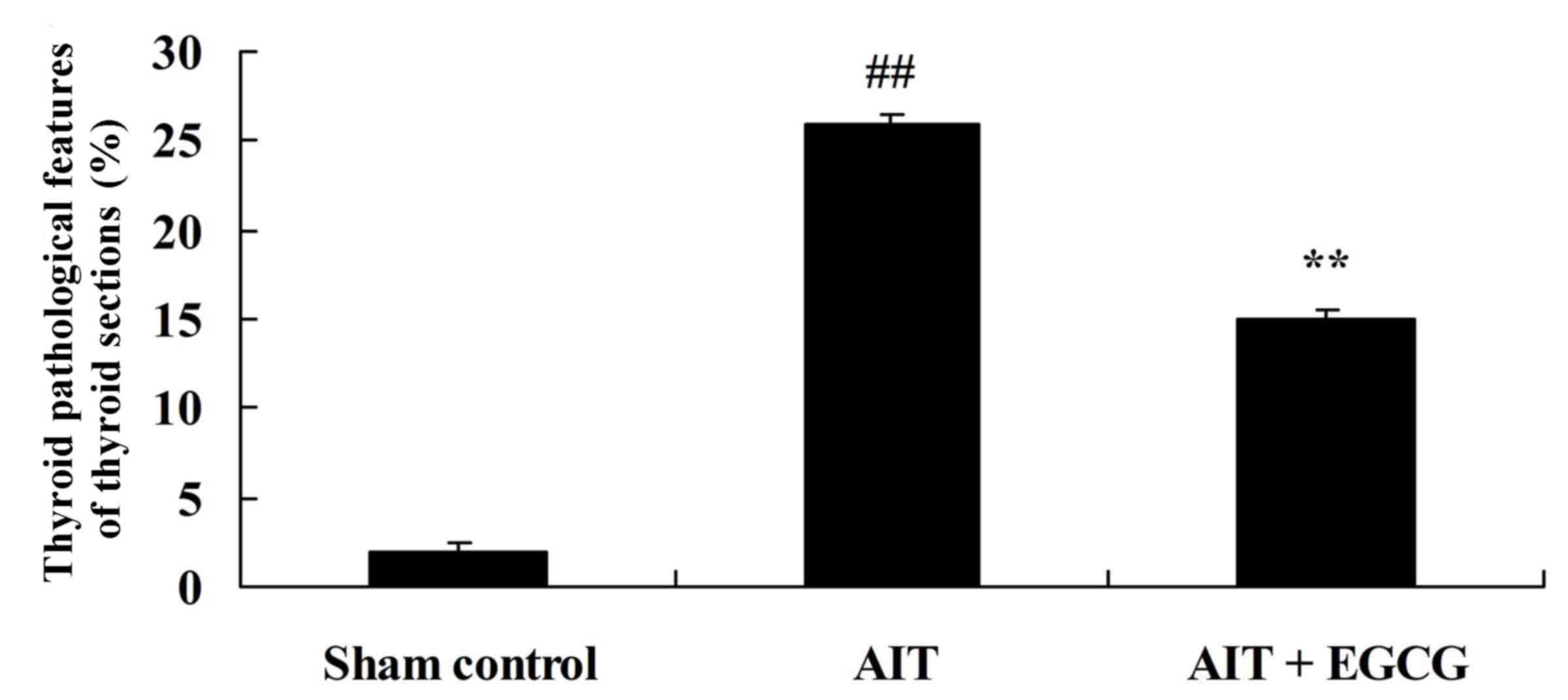
|
1
|
Nordio M and Basciani S: Efficacy of a
food supplement in patients with hashimoto thyroiditis. J Biol
Regul Homeost Agents. 29:93–102. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Krysiak R and Okopien B: The effect of
levothyroxine and selenomethionine on lymphocyte and monocyte
cytokine release in women with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 96:2206–2215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hofling DB, Chavantes MC, Juliano AG,
Cerri GG, Romão R, Yoshimura EM and Chammas MC: Low-level laser
therapy in chronic autoimmune thyroiditis: A pilot study. Lasers
Surg Med. 42:589–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sugiyama A, Zhu BM, Takahara A, Satoh Y
and Hashimoto K: Cardiac effects of salvia miltiorrhiza/dalbergia
odorifera mixture, an intravenously applicable Chinese medicine
widely used for patients with ischemic heart disease in China. Circ
J. 66:182–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iwasaki K, Kosaka K, Mori H, Okitsu R,
Furukawa K, Manabe Y, Yoshita M, Kanamori A, Ito N, Wada K, et al:
Open label trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Yokukansan,
a traditional Asian medicine, in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Am
Geriatr Soc. 59:936–938. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kristensen B, Hegedüs L, Madsen HO, Smith
TJ and Nielsen CH: Altered balance between self-reactive T helper
(Th)17 cells and Th10 cells and between full-length forkhead box
protein 3 (FoxP3) and FoxP3 splice variants in Hashimoto's
thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 180:58–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scarpa V, Kousta E, Tertipi A, Vakaki M,
Fotinou A, Petrou V, Hadjiathanasiou C and Papathanasiou A:
Treatment with thyroxine reduces thyroid volume in euthyroid
children and adolescents with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Horm
Res Paediatr. 73:61–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vecchiatti SM, Lin CJ, Capelozzi VL,
Longatto-Filho A and Bisi H: Prevalence of thyroiditis and
immunohistochemistry study searching for a morphologic consensus in
morphology of autoimmune thyroiditis in a 4613 autopsies series.
Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 23:402–408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang SH, Cao Z, Wolf JM, Van Antwerp M and
Baker JR Jr: Death ligand tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits experimental autoimmune
thyroiditis. Endocrinology. 146:4721–4726. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Zheng T, Mao Y, Xu C, Wu F, Bu L,
Mou X, Zhou Y, Yuan G, Wang S, et al: γδ T cells enhance B cells
for antibody production in Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and retinoic
acid induces apoptosis of the γδ T cell. Endocrine. 51:113–122.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee JY, Paik JS, Yun M, Lee SB and Yang
SW: The effect of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on IL-1β induced
IL-8 expression in orbital fibroblast from patients with
thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. PLoS One. 11:e01486452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu D, Perkins JT and Hennig B: EGCG
prevents PCB-126- induced endothelial cell inflammation via
epigenetic modifications of NF-κB target genes in human endothelial
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 28:164–170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Q, Qian Y, Chen F, Chen X, Chen Z and
Zheng M: EGCG attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines
production in LPS-stimulated L02 hepatocyte. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 46:31–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cui SL, Yu J and Shoujun L: Iodine intake
increases IP-10 expression in the serum and thyroids of rats with
experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. Int J Endocrinol.
2014:5810692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eguchi K: Apoptosis in autoimmune
diseases. Intern Med. 40:275–284. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arslan S, Korkmaz Ö, Özbilüm N and Berkan
Ö: Association between NF-κBI and NF-κBIA polymorphisms and
coronary artery disease. Biomed Rep. 3:736–740. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaczmarek E, Lacka K,
Jarmolowska-Jurczyszyn D, Sidor A and Majewski P: Changes of B and
T lymphocytes and selected apopotosis markers in Hashimoto's
thyroiditis. J Clin Pathol. 64:626–630. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Myśliwiec J, Okota M, Nikołajuk A and
Górska M: Soluble Fas, Fas ligand and Bcl-2 in autoimmune thyroid
diseases: Relation to humoral immune response markers. Adv Med Sci.
51:119–122. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Mysliwiec J, Okłota M, Nikołajuk A and
Górska M: Age related changes of soluble Fas, Fas ligand and Bcl-2
in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Endokrynol Pol. 58:492–495.
2007.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adikesavan G, Vinayagam MM, Abdulrahman LA
and Chinnasamy T: (−)-Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) stabilize the
mitochondrial enzymes and inhibits the apoptosis in cigarette
smoke-induced myocardial dysfunction in rats. Mol Biol Rep.
40:6533–6545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bossowski A, Czarnocka B, Bardadin K,
Stasiak-Barmuta A, Urban M, Dadan J, Ratomski K and Bossowska A:
Identification of apoptotic proteins in thyroid gland from patients
with Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Autoimmunity.
41:163–173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Minatoguchi S, Kariya T, Uno Y, Arai M,
Nishida Y, Hashimoto K, Wang N, Aoyama T, Takemura G, Fujiwara T
and Fujiwara H: Caspase-dependent and serine protease-dependent DNA
fragmentation of myocytes in the ischemia-reperfused rabbit heart:
These inhibitors do not reduce infarct size. Jpn Circ J.
65:907–911. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhitao J, Long L, Jia L, Yunchao B and
Anhua W: Temozolomide sensitizes stem-like cells of glioma spheres
to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via upregulation of casitas B-lineage
lymphoma (c-Cbl) protein. Tumour Biol. 36:9621–9630. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zauli G, Tisato V, Melloni E, Volpato S,
Cervellati C, Bonaccorsi G, Radillo O, Marci R and Secchiero P:
Inverse correlation between circulating levels of TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand and 17β-estradiol. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 99:E659–E664. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ge Y, Yan D, Deng H, Chen W and An G:
Novel molecular regulators of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in NSCLC cells.
Clin Lab. 61:1855–1863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
El-Karaksy SM, Kholoussi NM, Shahin RM,
El-Ghar MM and Gheith Rel-S: TRAIL mRNA expression in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells of Egyptian SLE patients. Gene.
527:211–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang N, Wang X, Huo Q, Li X, Wang H,
Schneider P, Hu G and Yang Q: The oncogene metadherin modulates the
apoptotic pathway based on the tumor necrosis factor superfamily
member TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand) in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 288:9396–9407. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ramamurthy V, Yamniuk AP, Lawrence EJ,
Yong W, Schneeweis LA, Cheng L, Murdock M, Corbett MJ, Doyle ML and
Sheriff S: The structure of the death receptor 4-TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (DR4-TRAIL) complex. Acta Crystallogr F
Struct Biol Commun. 71:1273–1281. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aktas O, Prozorovski T, Smorodchenko A,
Savaskan NE, Lauster R, Kloetzel PM, Infante-Duarte C, Brocke S and
Zipp F: Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate mediates T cellular
NF-kappa B inhibition and exerts neuroprotection in autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 173:5794–5800. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|