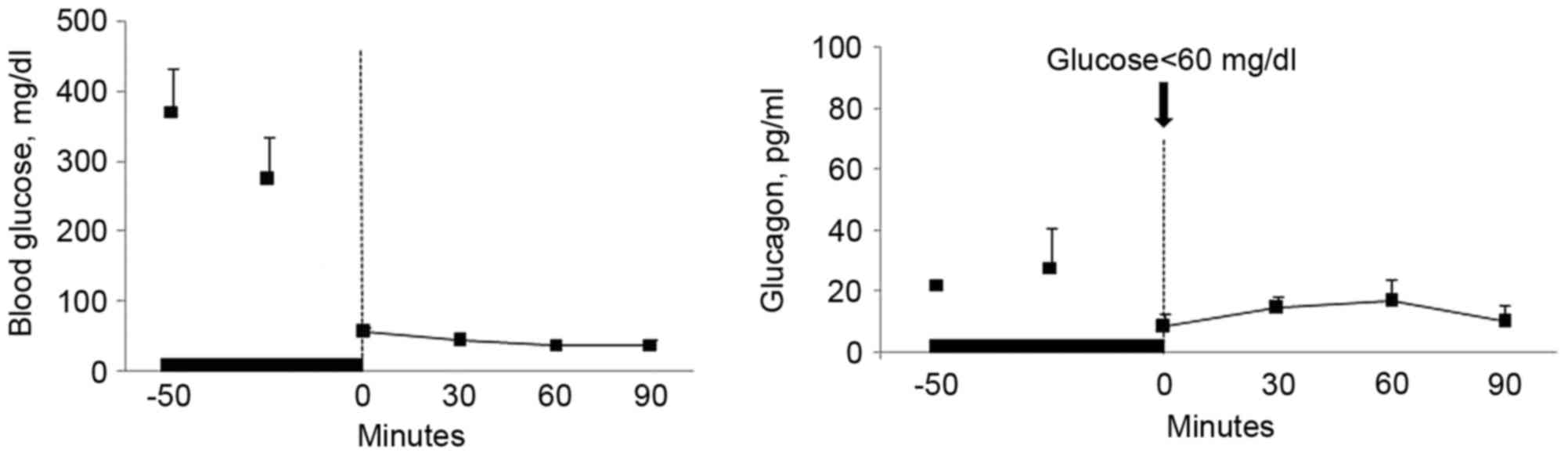
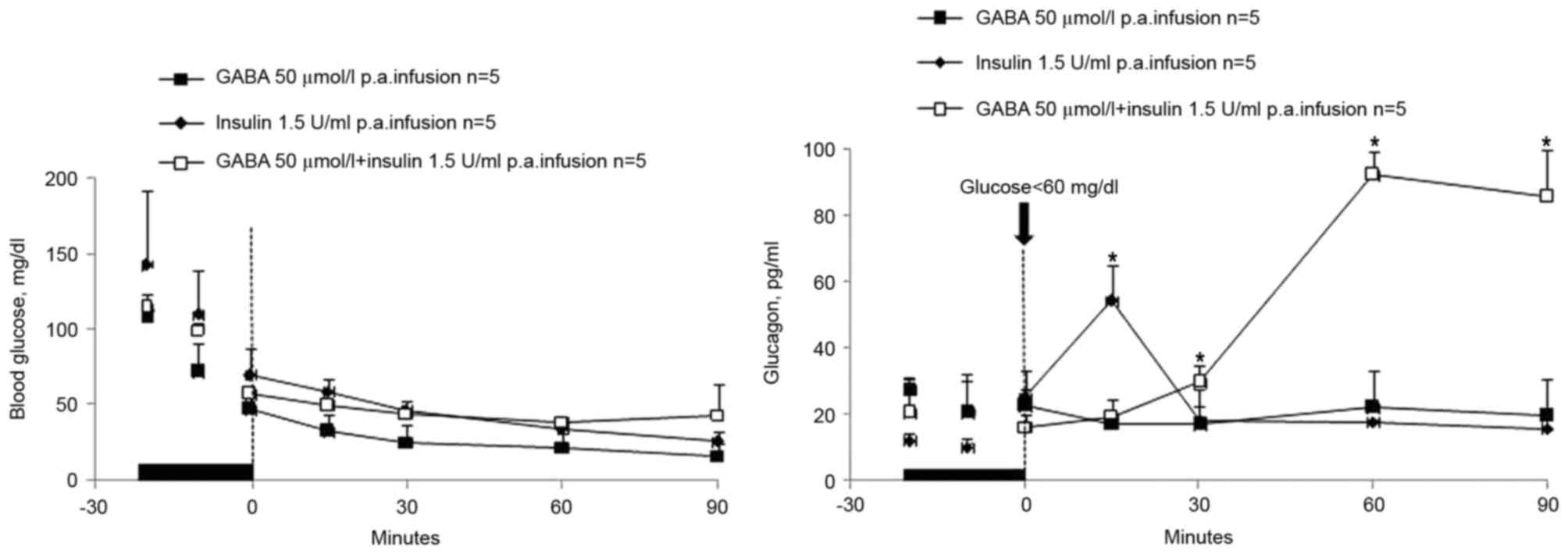
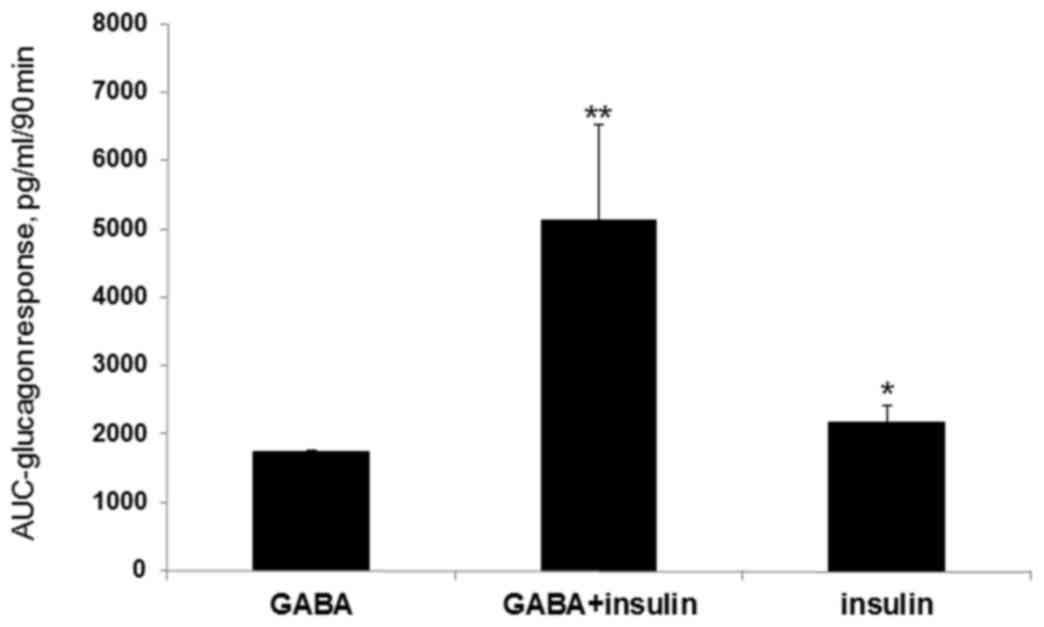
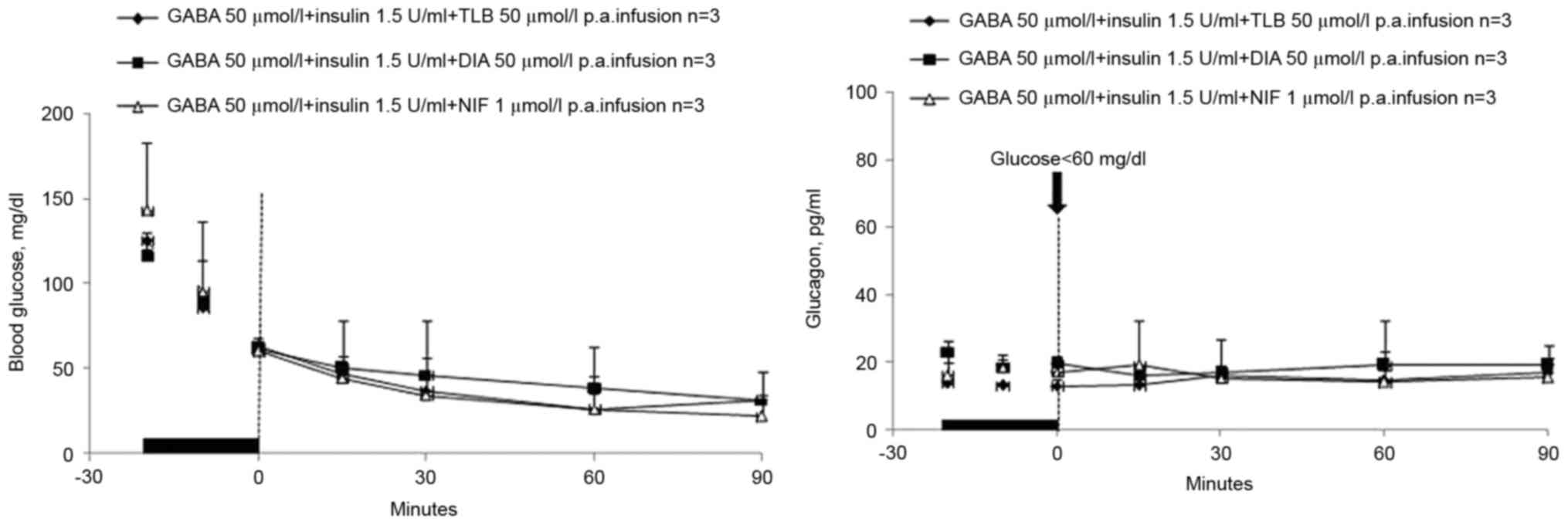
|
1
|
MacDonald PE, De Marinis YZ, Ramracheya R,
Salehi A, Ma X, Johnson PR, Cox R, Eliasson L and Rorsman P: A
K+ATP channel-dependent pathway within alpha cells regulates
glucagon release from both rodent and human islets of Langerhans.
PLoS Biol. 5:e1432007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vieira E, Salehi A and Gylfe E: Glucose
inhibits glucagon secretion by a direct effect on mouse pancreatic
alpha cells. Diabetologia. 50:370–379. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Q, Liang X and Wang S: Intra-isle
tglucagon secretion and action in the regulation of glucose
homeostasis. Front Physiol. 3:4852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou H, Zhang T, Harmon JS, Bryan J and
Robertson RP: Zinc, not insulin, regulates the rat alpha-cell
response to hypoglycemia in vivo. Diabetes. 56:1107–1112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou H, Tran PO, Yang S, Zhang T, LeRoy E,
Oseid E and Robertson RP: Regulation of alpha-cell function by the
beta-cell during hypoglycemia in Wistar rats: The ‘switch-off’
hypothesis. Diabetes. 53:1482–1487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hope KM, Tran PO, Zhou H, Oseid E, Leroy E
and Robertson RP: Regulation of alpha-cell function by the β-cell
in isolated human and rat islets deprived of glucose: The
‘switch-off’ hypothesis. Diabetes. 53:1488–1495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okada Y, Taniguchi H and Schimada C: High
concentration of GABA and high glutamate decarboxylase activity in
rat pancreatic islets and human insulinoma. Science. 194:620–622.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Briel G, Gylfe E, Hellman B and Neuhoff V:
Microdetermination of free amino acids in pancreatic islets
isolated from obese-hyperglycemic mice. Acta Physiol Scand.
84:247–253. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gylfe E and Hellman B: Role of glucose as
a regulator and precursor of aminoacidsin the pancreatic
beta-cells. Endocrinology. 94:1150–1156. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hedrington MS, Farmerie S, Ertl AC, Wang
Z, Tate DB and Davis SN: Effects of antecedent GABAA activation
with alprazolam on counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in
healthy humans. Diabetes. 59:1074–1081. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawai K and Unger RH: Effects of
gamma-aminobutyric acid on insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin
release from isolated perfused dog pancreas. Endocrinology.
113:111–113. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Minuk GY and Sarjeant EJ: Insulin and
glucagon secretion by the dog pancreas during intravenous and oral
administration of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Horm Metab Res.
17:313–314. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cavagnini F, Pinto M, Dubini A, Invitti C,
Cappelletti G and Polli EE: Effects of gamma aminobutyric acid
(GABA) and muscimol on endocrine pancreatic function in man.
Metabolism. 31:73–77. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Passariello N, Giugliano D, Torella R,
Sgambato S, Coppola L and Frascolla N: A possible role of
gamma-aminobutyric acid in the control of the endocrine pancreas. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 54:1145–1149. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gilon P, Bertrand G, Loubatières-Mariani
MM, Remacle C and Henquin JC: The influence of gamma-aminobutyric
acid on hormone release by the mouse and rat endocrine pancreas.
Endocrinology. 129:2521–2529. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Franklin I, Gromada J, Gjinovci A,
Theander S and Wollheim CB: Beta cell secretory products activate
alpha cell ATP-dependent potassium channels to inhibit glucagon
release. Diabetes. 54:1808–1815. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mehanna AS: Insulin and oral antidiabetic
agents. Am J Pharmaceutical Ed. 69:1–11. 2005.
|
|
18
|
Samols E, Tyler J and Marks V:
Glucagon-insulin interrelationships. Pergamon Press; Elmsford, NY:
pp. 151–174. 1972
|
|
19
|
Maruyama H, Hisatomi A, Orci L, Orci L,
Grodsky GM and Unger RH: Insulin within islets is a physiologic
glucagon release inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 74:2296–2299. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raju B and Cryer PE: Loss of the decrement
in intraislet insulin plausibly explains loss of the glucagon
response to hypoglycemia in insulin-deficient diabetes:
Documentation of the intraislet insulin hypothesis in humans.
Diabetes. 54:757–764. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu E, Kumar M, Zhang Y, Ju W, Obata T,
Zhang N, Liu S, Wendt A, Deng S, Ebina Y, et al: Intra-islet
insulin suppresses glucagon release via GABA-GABAA receptor system.
Cell Metab. 3:47–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rorsman P, Berggren PO, Bokvist K, Ericson
H, Möhler H, Ostenson CG and Smith PA: Glucose-inhibition of
glucagon secretion involves activation of GABAA-receptor chloride
channels. Nature. 341:233–236. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Göpel S, Zhang Q, Eliasson L, Ma XS,
Galvanovskis J, Kanno T, Salehi A and Rorsman P: Capacitance
measurements of exocytosisin mouse pancreatic alpha-, beta- and
delta-cells within intact islets of Langerhans. J Physiol.
556:711–726. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Göpel SO, Kanno T, Barg S, Weng XG,
Gromada J and Rorsman P: Regulation of glucagon release in mouse
α-cells by KATP channels and inactivation of TTX-sensitive Na+
channels. J Physiol. 528:509–520. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Slucca M, Harmon JS, Oseid EA, Bryan J and
Robertson RP: ATP-sensitive K+ channel mediates the zinc switch-off
signal for glucagon response during glucose deprivation. Diabetes.
59:128–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|