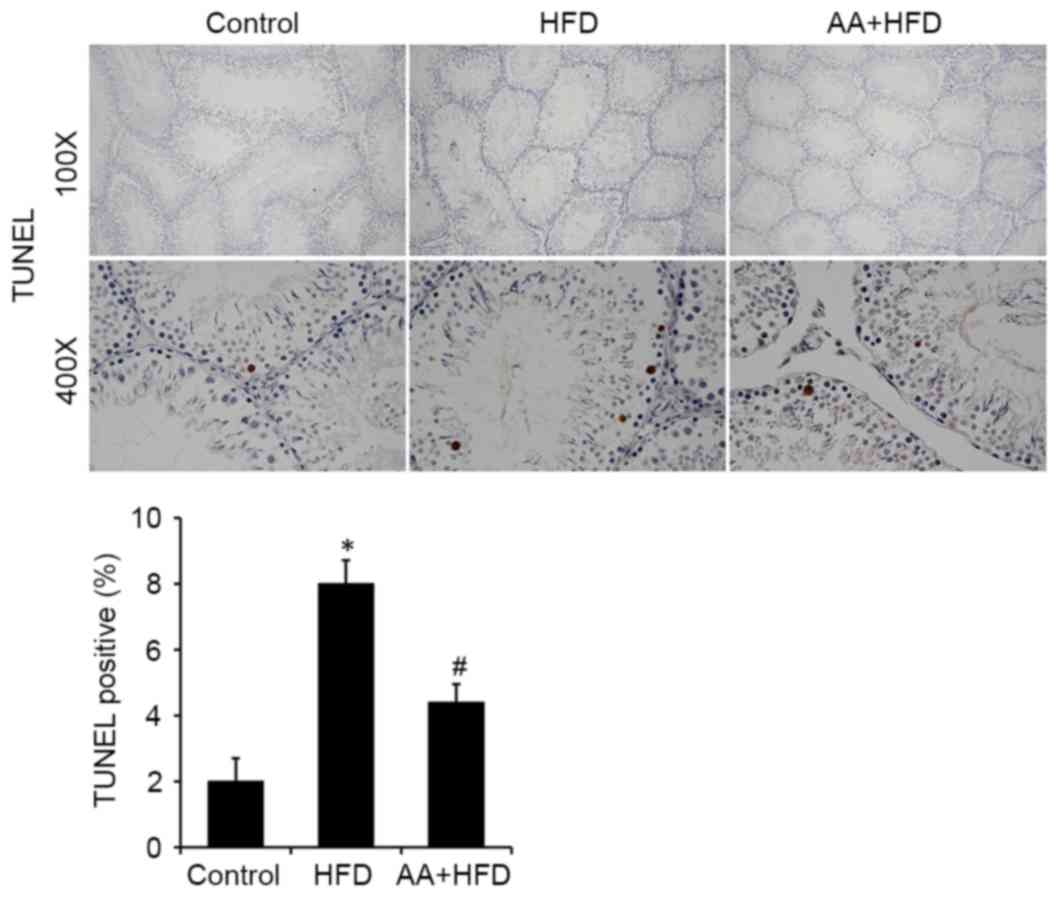
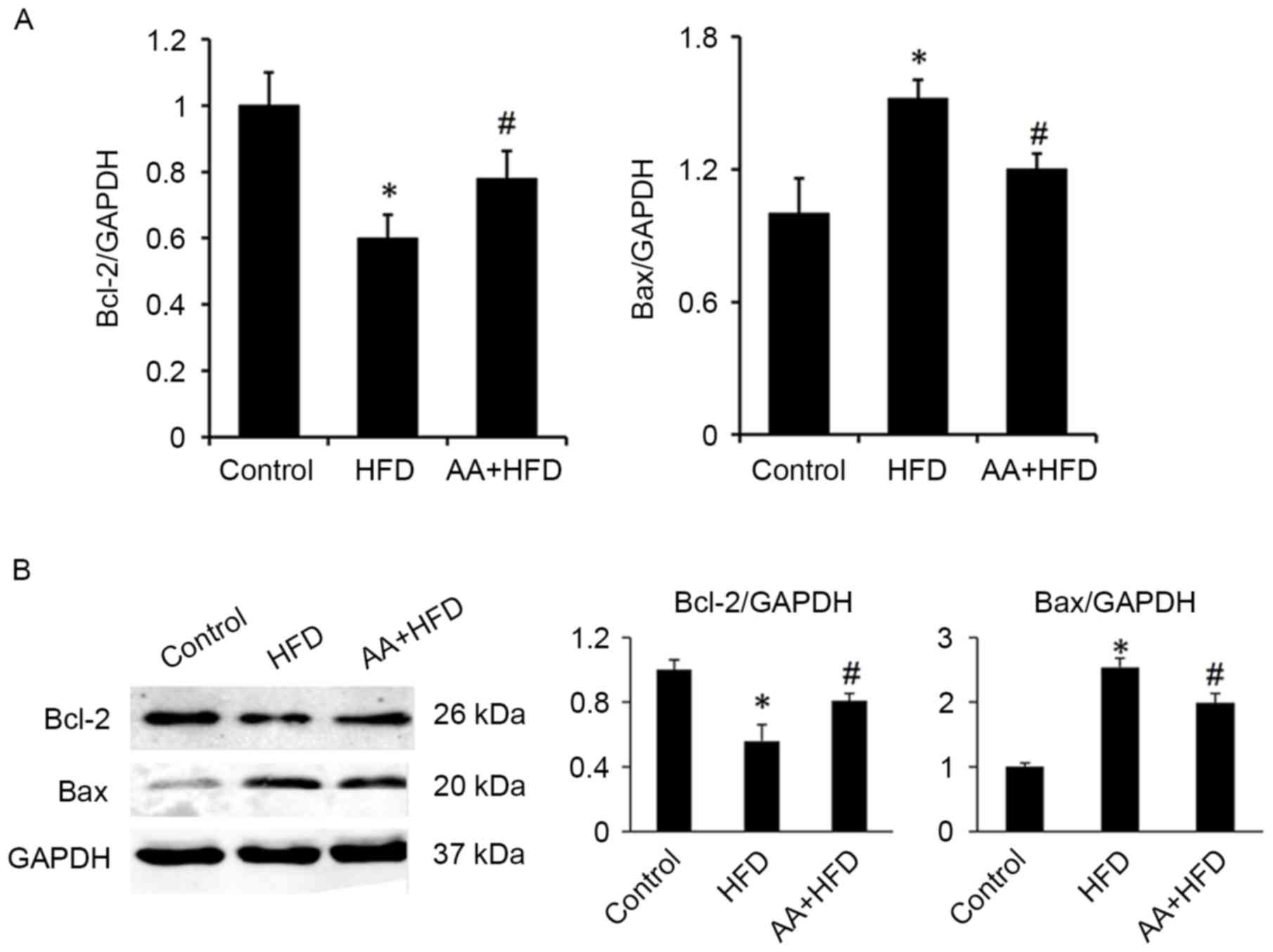
|
1
|
Botelho F, Figueiredo L, Leite R, Carvalho
A, Tomada N and Vendeira P: Predictive factors of a successful
testicular biopsy and subsequent clinical pregnancy. Andrologia.
44:237–242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlin A, Arredi B and Foresta C: Genetic
causes of male infertility. Reprod Toxicol. 22:133–141. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Adamson GD and Baker VL: Subfertility:
Causes, treatment and outcome. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol.
17:169–185. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barnett R: Obesity. Lancet. 366:9842005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Katib A: Mechanisms linking obesity to
male infertility. Cent European J Urol. 68:79–85. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hammoud AO, Meikle AW, Reis LO, Gibson M,
Peterson CM and Carrell DT: Obesity and male infertility: A
practical approach. Semin Reprod Med. 30:486–495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bellver J, Melo MA, Bosch E, Serra V,
Remohi J and Pellicer A: Obesity and poor reproductive outcome: The
potential role of the endometrium. Fertil Steril. 88:446–451. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hammoud AO, Wilde N, Gibson M, Parks A,
Carrell DT and Meikle AW: Male obesity and alteration in sperm
parameters. Fertil Steril. 90:2222–2225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee J, Richburg JH, Younkin SC and
Boekelheide K: The Fas system is a key regulator of germ cell
apoptosis in the testis. Endocrinology. 138:2081–2088. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sinha HA and Swerdloff RS: Hormonal and
genetic control of germ cell apoptosis in the testis. Rev Reprod.
4:38–47. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tapanainen JS, Tilly JL, Vihko KK and
Hsueh AJ: Hormonal control of apoptotic cell death in the testis:
Gonadotropins and androgens as testicular cell survival factors.
Mol Endocrinol. 7:643–650. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aitken RJ and Baker MA: Causes and
consequences of apoptosis in spermatozoa; contributions to
infertility and impacts on development. Int J Dev Biol. 57:265–272.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
MacFarlane M and Williams AC: Apoptosis
and disease: A life or death decision. EMBO Rep. 5:674–678. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barroso G, Morshedi M and Oehninger S:
Analysis of DNA fragmentation, plasma membrane translocation of
phosphatidylserine and oxidative stress in human spermatozoa. Hum
Reprod. 15:1338–1344. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Zhao R, Guo C, Jiang S, Yang J, Xu
Y, Liu Y, Fan L, Xiong W, Ma J, et al: Knockout of BRD7 results in
impaired spermatogenesis and male infertility. Sci Rep.
6:217762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bhat GK, Sea TL, Olatinwo MO, Simorangkir
D, Ford GD, Ford BD and Mann DR: Influence of a leptin deficiency
on testicular morphology, germ cell apoptosis and expression levels
of apoptosis-related genes in the mouse. J Androl. 27:302–310.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan WJ, Mu Y, Yu N, Yi TL, Zhang Y, Pang
XL, Cheng D and Yang J: Protective effects of metformin on
reproductive function in obese male rats induced by high-fat diet.
J Assist Reprod Genet. 32:1097–1104. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bonte F, Dumas M, Chaudagne C and Meybeck
A: Influence of asiatic acid, madecassic acid and asiaticoside on
human collagen I synthesis. Planta Med. 60:133–135. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma ZG, Dai J, Wei WY, Zhang WB, Xu SC,
Liao HH, Yang Z and Tang QZ: Asiatic acid protects against cardiac
hypertrophy through activating AMPKα signalling pathway. Int J Biol
Sci. 12:861–871. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Lu Q, Yu DS, Chen YP, Shang J,
Zhang LY, Sun HB and Liu J: Asiatic acid mitigates hyperglycemia
and reduces islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rat, a spontaneous type
2 diabetic animal model. Chin J Nat Med. 13:529–534.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan SL, Yang HT, Lee YJ, Lin CC, Chang MH
and Yin MC: Asiatic acid ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and
insulin resistance in mice consuming a high-fat diet. J Agric Food
Chem. 62:4625–4631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiong Y, Ding H, Xu M and Gao J:
Protective effects of asiatic acid on rotenone- or
H2O2-induced injury in SH-SY5Y cells.
Neurochem Res. 34:746–754. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chao PC, Lee HL and Yin MC: Asiatic acid
attenuated apoptotic and inflammatory stress in the striatum of
MPTP-treated mice. Food Funct. 7:1999–2005. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS,
Naylor BA, Treacher DF and Turner RC: Homeostasis model assessment:
Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma
glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia.
28:412–419. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghanayem BI, Bai R, Kissling GE, Travlos G
and Hoffler U: Diet-induced obesity in male mice is associated with
reduced fertility and potentiation of acrylamide-induced
reproductive toxicity. Biol Reprod. 82:96–104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kokilavani P, Suriyakalaa U, Elumalai P,
Abirami B, Ramachandran R, Sankarganesh A and Achiraman S:
Antioxidant mediated ameliorative steroidogenesis by Commelina
benghalensis L. and Cissus quadrangularis L. against quinalphos
induced male reproductive toxicity. Pestic Biochem Physiol.
109:18–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wei ZT, Lu XL, Zhang G, Yu J, Li H, Jia
GH, Li JT and Zhang JM: The long-term effects of superovulation on
fertility and sexual behavior of male offspring in mice. J Assist
Reprod Genet. 31:555–560. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-tie quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pasquali R, Patton L and Gambineri A:
Obesity and infertility. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes.
14:482–487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Plant TM and Marshall GR: The functional
significance of FSH in spermatogenesis and the control of its
secretion in male primates. Endocr Rev. 22:764–786. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang C, Chen YT, Yeh SD, Xu Q, Wang RS,
Guillou F, Lardy H and Yeh S: Infertility with defective
spermatogenesis and hypotestosteronemia in male mice lacking the
androgen receptor in sertoli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:pp.
6876–6881. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sakkas D, Seli E, Bizzaro D, Tarozzi N and
Manicardi GC: Abnormal spermatozoa in the ejaculate: Abortive
apoptosis and faulty nuclear remodelling during spermatogenesis.
Reprod Biomed Online. 7:428–432. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sukhotnik I and Nativ O, Roitburt A, Bejar
D, Coran AG, Mogilner JG and Nativ O: Methotrexate induces germ
cell apoptosis and impairs spermatogenesis in a rat. Pediatr Surg
Int. 29:179–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gurfinkel DM, Chow S, Hurren R, Gronda M,
Henderson C, Berube C, Hedley DW and Schimmer AD: Disruption of the
endoplasmic reticulum and increases in cytoplasmic calcium are
early events in cell death induced by the natural triterpenoid
Asiatic acid. Apoptosis. 11:1463–1471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kavitha CV, Jain AK, Agarwal C, Pierce A,
Keating A, Huber KM, Serkova NJ, Wempe MF, Agarwal R and Deep G:
Asiatic acid induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptotic
death in glioblastoma multiforme cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Mol Carcinog. 54:1417–1429. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qi D and Young LH: AMPK: Energy sensor and
survival mechanism in the ischemic heart. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
26:422–429. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma ZG, Yuan YP, Xu SC, Wei WY, Xu CR,
Zhang X, Wu QQ, Liao HH, Ni J and Tang QZ: CTRP3 attenuates cardiac
dysfunction, inflammation, oxidative stress and cell death in
diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Diabetologia. 60:1126–1137. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tsao SM and Yin MC: Antioxidative and
antiinflammatory activities of asiatic acid, glycyrrhizic acid and
oleanolic acid in human bronchial epithelial cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 63:3196–3204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|