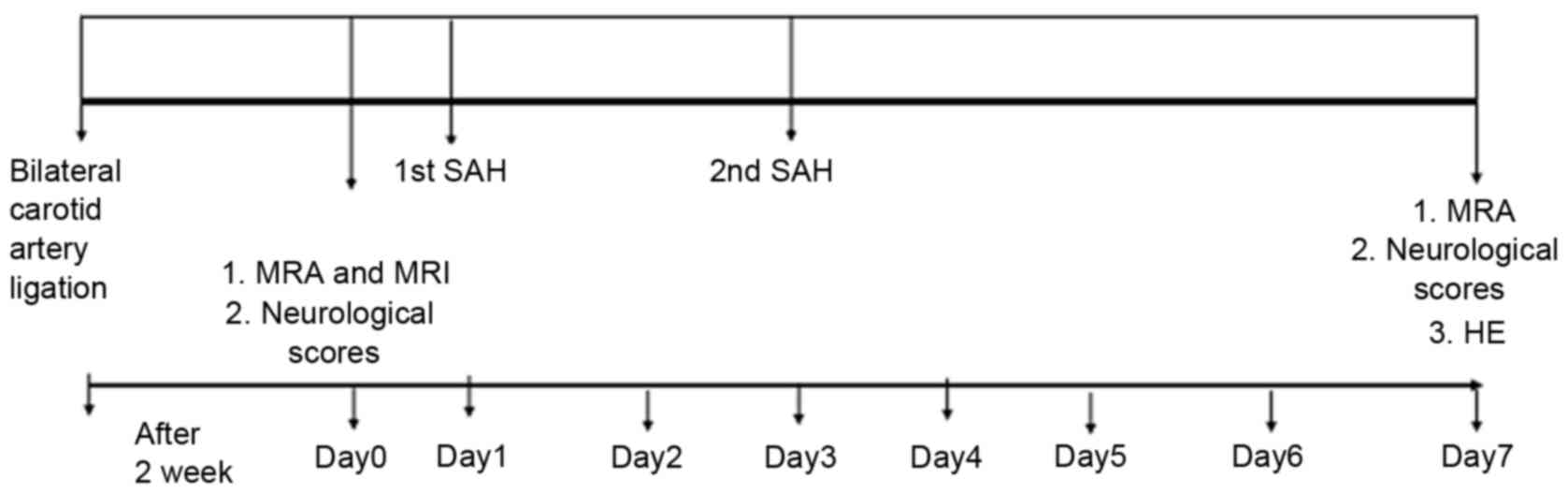
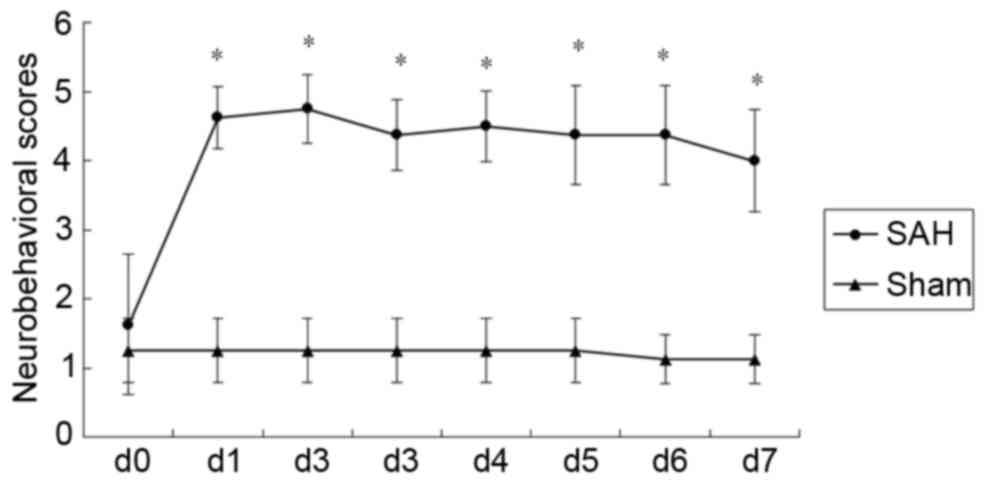
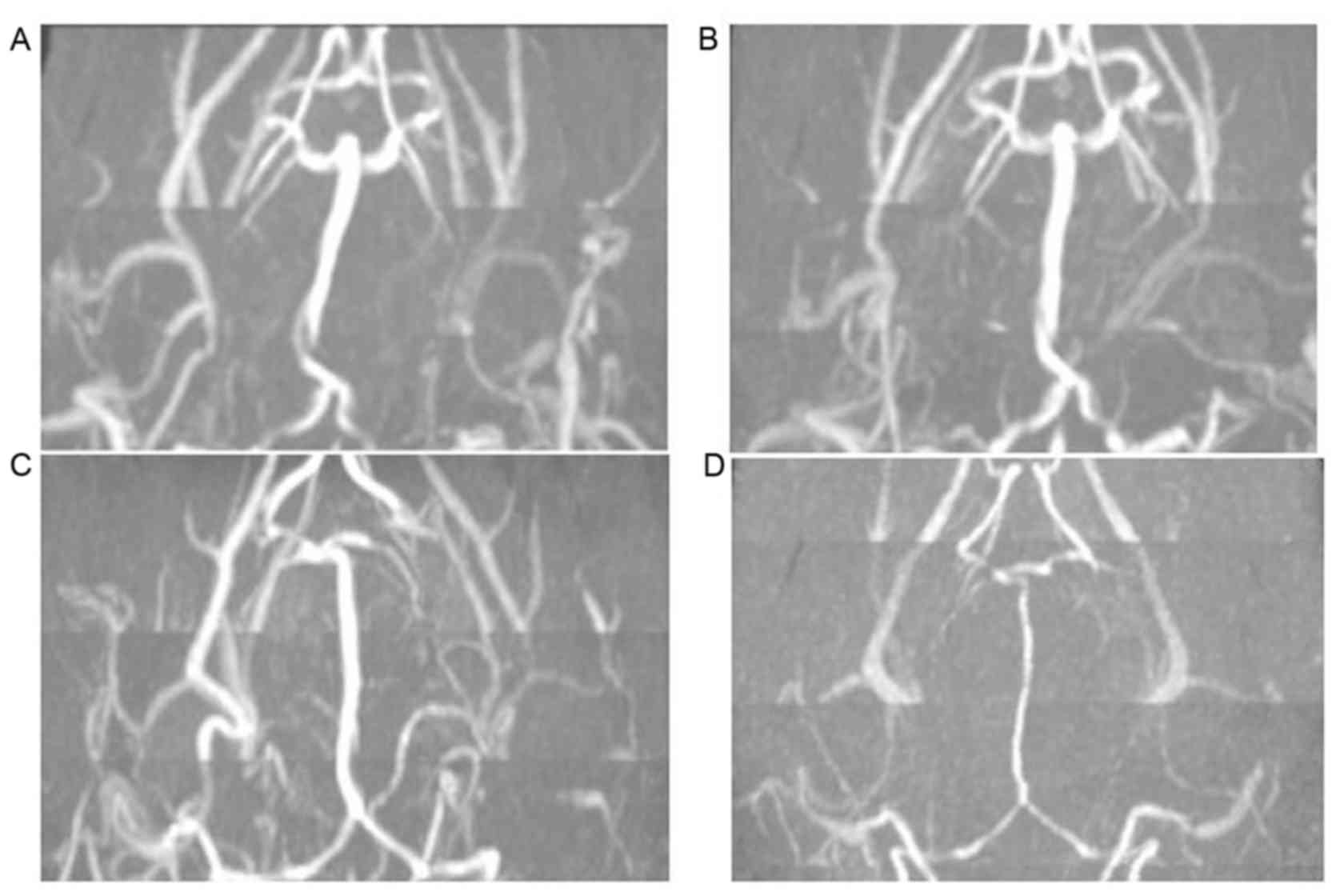
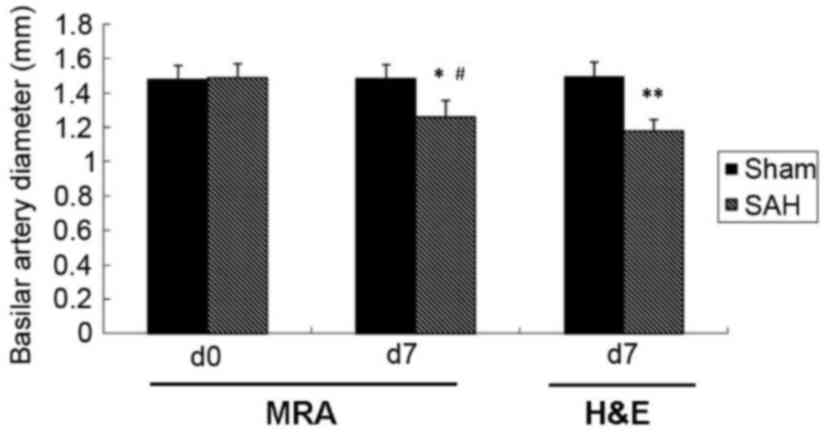
|
1
|
van Gijn J, Kerr RS and Rinkel GJ:
Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 369:306–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma
JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, Hoh BL, Kirkness CJ, Naidech
AM, Ogilvy CS, et al: Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals
from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association.
Stroke. 43:1711–1737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Przybycien-Szymanska MM and Ashley WW Jr:
Biomarker discovery in cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 24:1453–1464.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Steiner T, Juvela S, Unterberg A, Jung C,
Forsting M and Rinkel G; European Stroke Organization, : European
stroke organization guidelines for the management of intracranial
aneurysms and subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis. 35:93–112.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sen J, Belli A, Albon H, Morgan L, Petzold
A and Kitchen N: Triple-H therapy in the management of aneurysmal
subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2:614–621. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choudhari K: Prophylactic hyperdynamic
postoperative fluid therapy after aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage: A clinical, prospective, randomized, controlled study.
Neurosurgery. 50:1170–1172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muroi C, Seule M, Mishima K and Keller E:
Novel treatments for vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Curr
Opin Crit Care. 18:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shimoda M, Takeuchi M, Tominaga J, Oda S,
Kumasaka A and Tsugane R: Asymptomatic versus symptomatic infarcts
from vasospasm in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: Serial
magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery. 49:1341–1350. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Udoetuk JD, Stiefel MF, Hurst RW, Weigele
JB and LeRoux PD: Admission angiographic cerebral circulation time
may predict subsequent angiographic vasospasm after aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 61:1152–1161. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lougheed WM and Tom M: A method of
introducing blood into the subarachnoid space in the region of the
circle of Willis in dogs. Can J Surg. 4:329–337. 1961.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prunell GF, Mathiesen T and Svendgaard NA:
A new experimental model in rats for study of the pathophysiology
of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroreport. 13:2553–2556. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen S, Klebe KD, Vakhmyanin A, Fujii M
and Zhang JH: SAH models: Review, new modification, and
prospective. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 255–267. 2014
|
|
13
|
Otsuji T, Endo S, Hirashima Y, Nishijima M
and Takaku A: An experimental model of symptomatic vasospasm
induced by oxyhemoglobin in rabbits. Stroke. 25:657–662. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Titova E, Ostrowski RP, Zhang JH and Tang
J: Experimental models of subarachnoid hemorrhage for studies of
cerebral vasospasm. Neurol Res. 31:568–581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yunchang M, Qinxue D, Binbin J, Xin H,
Lili Y, Linbi C, Wujun G, Pengbo Z and Junlu W: Human tissue
kallikrein ameliorates cerebral vasospasm in a rabbit model of
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 37:1082–1095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stacul F, van der Molen AJ, Reimer P, Webb
JA, Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, Almén T, Aspelin P, Bellin MF, Clement
O, et al: Contrast induced nephropathy: Updated ESUR contrast media
safety committee guidelines. Eur Radiol. 21:2527–2541. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seeliger E, Sendeski M, Rihal CS and
Persson PB: Contrast-induced kidney injury: Mechanisms, risk
factors, and prevention. Eur Heart J. 33:2007–2015. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kruk M: Measuring behaviour into the
twenty-first century. Trends Neurosci. 20:187–189. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Taufique Z, May T, Meyers E, Falo C, Mayer
SA, Agarwal S, Park S, Connolly ES, Claassen J and Schmidt JM:
Predictors of poor quality of life 1 year after subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 78:256–264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang JP, Liu HJ and Liu RC: A modified
rabbit model of stroke: Evaluation using clinical MRI scanner.
Neurol Res. 31:1092–1096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Majoie CB, Sprengers ME, van Rooij WJ,
Lavini C, Sluzewski M, van Rijn JC and den Heeten GJ: MR
angiography at 3T versus digital subtraction angiography in the
follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 26:1349–1356. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Amerongen MJ, Boogaarts HD, de Vries
J, Verbeek AL, Meijer FJ, Prokop M and Bartels RH: MRA versus DSA
for follow-up of coiled intracranial aneurysms: A meta-analysis.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 35:1655–1661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Endo S, Branson PJ and Alksne JF:
Experimental model of symptomatic vasospasm in rabbits. Stroke.
19:1420–1425. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kertmen H, Gürer B, Yilmaz ER, Arikok AT,
Kanat MA, Ergüder BI and Sekerci Z: The comparative effects of
recombinant human erythropoietin and darbepoetin-alpha on cerebral
vasospasm following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in the
rabbit. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 156:951–962. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bederson JB, Connolly ES Jr, Batjer HH,
Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, Duldner JE Jr, Harbaugh RE, Patel
AB and Rosenwasser RH; American Heart Association, : Guidelines for
the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A statement
for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the
Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 40:994–1025.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Venti M: Subarachnoid and intraventricular
hemorrhage. Front Neurol Neurosci. 30:149–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harrod CG, Bendok BR and Batjer HH:
Prediction of cerebral vasospasm in patients presenting with
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A review. Neurosurgery.
56:633–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Crowley RW, Medel R, Dumont AS, Ilodigwe
D, Kassell NF, Mayer SA, Ruefenacht D, Schmiedek P, Weidauer S,
Pasqualin A and Macdonald RL: Angiographic vasospasm is strongly
correlated with cerebral infarction after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Stroke. 42:919–923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jadhav V, Sugawara T, Zhang J, Jacobson P
and Obenaus A: Magnetic resonance imaging detects and predicts
early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in a canine
experimental model. J Neurotrauma. 25:1099–1106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumar A, Kato Y, Hayakawa M, Junpei O,
Watabe T, Imizu S, Oguri D and Hirose Y: Recent advances in
diagnostic approaches for sub-arachnoid hemorrhage. Asian J
Neurosurg. 6:94–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pryor JC, Setton A, Nelson PK and
Berenstein A: Complications of diagnostic cerebral angiography and
tips on avoidance. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 6:751–758.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Laslo AM, Eastwood JD, Chen FX and Lee TY:
Dynamic CT perfusion imaging in subarachnoid hemorrhage-related
vasospasm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 27:624–631. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hotta K, Sorimachi T, Osada T, Baba T,
Inoue G, Atsumi H, Ishizaka H, Matsuda M, Hayashi N and Matsumae M:
Risks and benefits of CT angiography in spontaneous intracerebral
hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 156:911–917. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pierot L, Portefaix C, Rodriguez-Régent C,
Gallas S, Meder JF and Oppenheim C: Role of MRA in the detection of
intracranial aneurysm in the acute phase of subarachnoid
hemorrhage. J Neuroradiol. 40:204–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frontera JA, Ahmed W, Zach V, Jovine M,
Tanenbaum L, Sehba F, Patel A, Bederson JB and Gordon E: Acute
ischaemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage, relationship with early
brain injury and impact on outcome: A prospective quantitative MRI
study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 86:71–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Griffiths PD, Wilkinson ID, Mitchell P,
Patel MC, Paley MN, Romanowski CA, Powell T, Hodgson TJ, Hoggard N
and Jellinek D: Multimodality MR imaging depiction of hemodynamic
changes and cerebral ischemia in subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 22:1690–1677. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wani AA, Phadke R, Behari S, Sahu R,
Jaiswal A and Jain V: Role of diffusion-weighted MRG in predicting
outcome in subarachnoid hemorrhage due to anterior communicating
artery aneurysms. Turk Neurosurg. 18:10–16. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang CC, Lai CJ, Tsai MH, Wu YC, Chen KT,
Jou MJ, Fu PI, Wu CH and Wei IH: Effects of melatonin on the nitric
oxide system and protein nitration in the hypobaric hypoxic rat
hippocampus. BMC Neurosci. 16:612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|