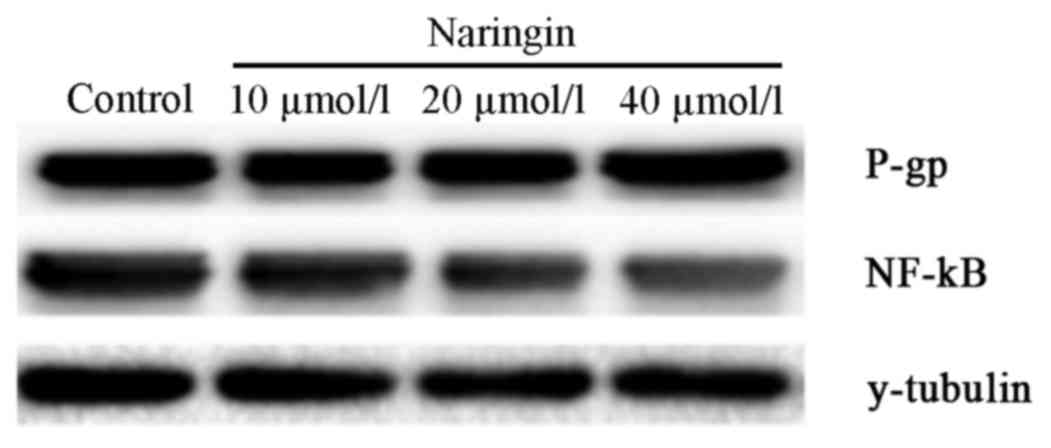
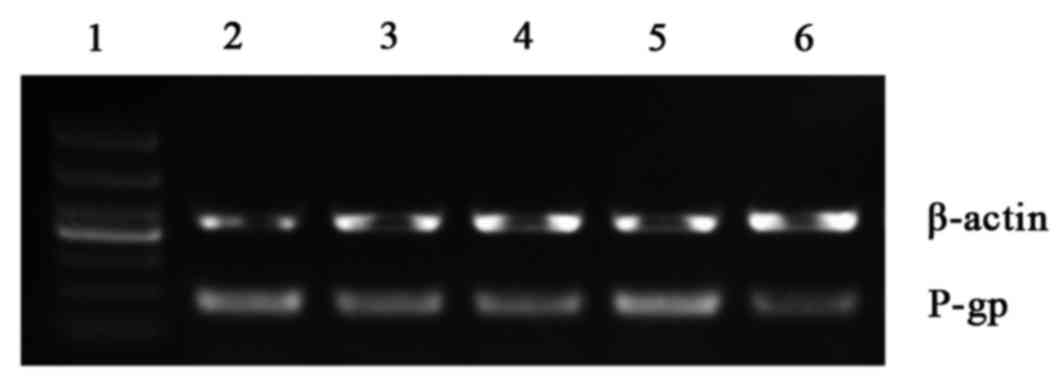
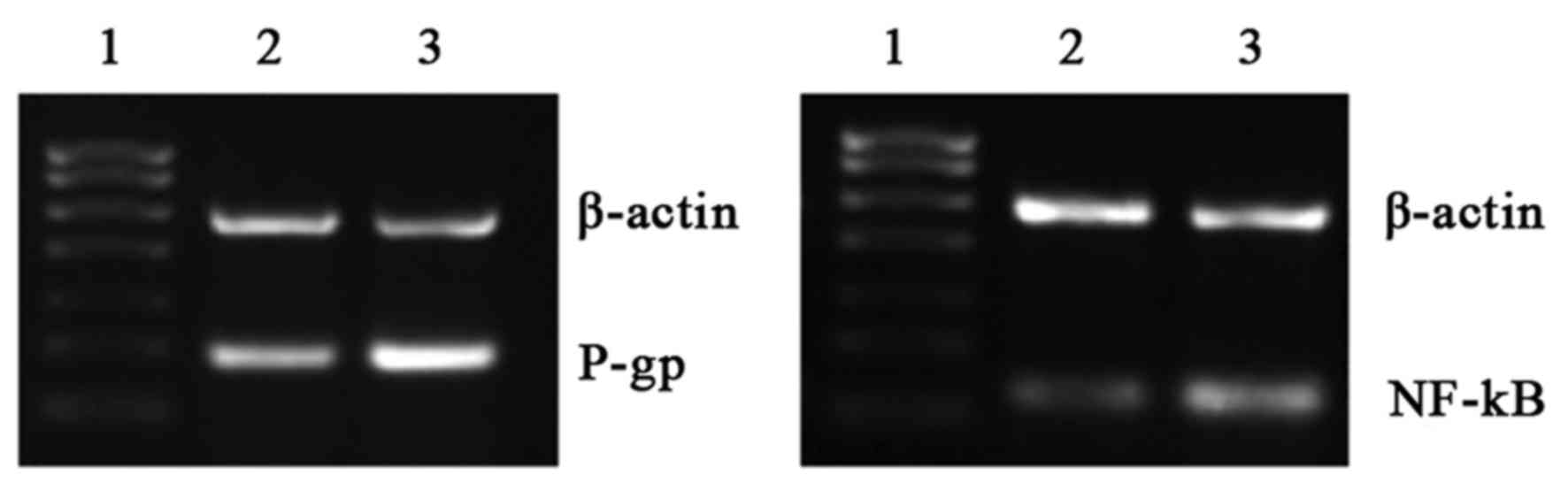
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eoh KJ, Lee JY, Yoon JW, Nam EJ, Kim S,
Kim SW and Kim YT: Role of systematic lymphadenectomy as part of
primary debulking surgery for optimally cytoreduced advanced
ovarian cancer: Reappraisal in the era of radical surgery.
Oncotarget. 8:37807–37816. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jessmon P, Boulanger T, Zhou W and
Patwardhan P: Epidemiology and treatment patterns of epithelial
ovarian cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 17:427–437. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Poveda Velasco A, Casado Herráez A,
Cervantes Ruipérez A, Gallardo Rincón D, García García E, González
Martín A, López García G, Mendiola Fernández C and Ojeda González
B; GEICO Group, : Treatment guidelines in ovarian cancer. Clin
Transl Oncol. 9:308–316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi M, Fuller CD, Thomas CR Jr and Wang
SJ: Conditional survival in ovarian cancer: Results from the SEER
dataset 1988–2001. Gynecol Oncol. 109:203–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Birt DF, Hendrieh S and Wang W: Dietary
agents in cancer prevention: Flavonoids and isoflavonoids.
Pharmacol Thera. 90:157–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Song SH, Hu X, Xiong YQ and Cai LP:
Effects of Naringin on expression of COX-2 mRNA and protein in
human ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther.
18:271–276. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Godwin P, Baird AM, Heavey S, Barr MP,
O'Byrne KJ and Gately K: Targeting nuclear factor kappaB to
overcome resistance to chemotherapy. Front Oncol. 3:1202013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goff B: Symptoms associated with ovarian
cancer. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 55:36–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mucciolk M and Benencia F: Toll-like
receptors in ovarian cancer as targets for immunotherapies. Front
Immunol. 5:3412014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bookman MA: First 1ine chemotherapy in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 55:96–113. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raja FA, Counsell N, Colombo N, Pfisterer
J, du Bois A, Parmar MK, Vergote IB, Gonzalez-Martin A, Alberts DS,
Plante M, et al: Platinum versus platinum, Combination chemotherapy
in platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis
using individual patient data. Ann Onco1. 24:3028–3034. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Schwab CL, English DP, Roque DM and Santin
AD: Taxanes: Their impact on gynecologic malignancy. Anticancer
Drugs. 25:522–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pellicciotta I, Yang CP, Venditti CA,
Goldberg GL and Shahabi S: Response to microtubμle-interacting
agents in primary epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int.
13:332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sorbe B, Graflund M, Nygren L and Horvath
G: A study of docetaxel weekly or every three weeks in combination
with carboplatin as first line chemotherapy in epithelial ovarian
cancer: Hematological and non-hematological toxicity proftes. Oncol
Lett. 5:1140–1148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Colombo PE, Fabbro M, Theillet C, Bibeau
F, Rouanet P and Ray-Coquard I: Sensitivity and resistance to
treatment in the primary management of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 89:207–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Han A, Chen E, Singh RK,
Chichester CO, Moore RG, Singh AP and Vorsa N: The cranberry
flavonoids PAC DP-9 and quercetin aglycone induce cytotoxicity and
cell cycle arrest and increase cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:1924–1934. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Wang Y, Lei JC, Hao Y, Yang Y, Yang
CX and Yu JQ: Sensitisation of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by
flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata. Nat Prod Res. 28:683–689.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Salmah Y, Hasanah MG and Gan SK: Naringin
content in local citrus fruits. Food Chem. 37:113–121. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
You Q and Wu K: Naringin cardiovascular
pharmacological effects. Guangdong Med J. 31:3006–3008. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Meiyanto E, Hermawan A and Anindyajati:
Natural products for cancer-targeted therapy: Citrus flavonoids as
potent chemopreventive agents. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:427–436.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L and Cai LP: Reversal of drug
resistance and reversal mechanism of human ovarian cancer resistant
SKOV3/DDP cells by naringin. J Clin Oncol. 21:598–602. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Dharmapuri G, Doneti R, Philip GH and
Kalle AM: Celecoxib sensitize simatinib-resistant K562 cell
stoimatinib by inhibiting MRP1-5, ABCA2 and ABCG2 transporters via
Wnt and Ras signaling pathways. Leuk Res. 39:696–701. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Januchowski R, Wojtowicz K,
Sujka-Kordowska P, Andrzejewska M and Zabel M: MDR gene expression
analysis of six drug-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Biomed
Res Int. 2013:2417632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Januchowski R, Sterzyńska K, Zaorska K,
Sosińska P, Klejewski A, Brązert M, Nowicki M and Zabel M: Analysis
of MDR genes expression and cross-resistance in eight drug
resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. J Ovarian Res. 9:652016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abraham J, Salama NN and Azab AK: The role
of P-glycoprotein in drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Leuk
Lymphoma. 156:26–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tomiyasu H, Watanabe M, Sugita K,
Goto-Koshino Y, Fujino Y, Ohno K, Sugano S and Tsujimoto H:
Regμlations of ABCB1 and ABCG2 expression through MAPK pathways in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Anticancer Res.
33:5317–5323. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vasconcelos FC, Silva KL, Souza PS, Silva
LF, Moellmann-Coelho A, Klumb CE and Maia RC: Variation of MDR
proteins expression and activity levels according to clinical
status and evolution of CML patients. Cytometry B Clin Cytom.
80:158–166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Allen CT, Ricker JL, Chen Z and Van Waes
C: Role of activated nuclear factor-kappaB in the pathogenesis and
therapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck.
29:959–971. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Weichert W, Boehm M, Gekeler V, Bahra M,
Langrehr J, Neuhaus P, Denkert C, Imre G, Weller C, Hofmann HP, et
al: High expression of Rel A/P65is associated with activation of
nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent signaling in pancreatic cancer and
marks a patient population with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer.
97:523–530. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bivona TG, Hieronymus H, Parker J, Chang
K, Taron M, Rosell R, Moonsamy P, Dahlman K, Miller VA, Costa C, et
al: FAS and NF-κB signaling modulate dependence of lung cancers on
mutant EGFR. Nature. 471:523–526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Napetschnig J and Wu H: Molecular basis of
NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys. 42:443–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho HH, Song JS, Yu JM, Yu SS, Choi SJ,
Kim DH and Jung JS: Differential effect of NF-kappaB activity on
beta-catenin/Tcf pathway in various cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
582:616–622. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|