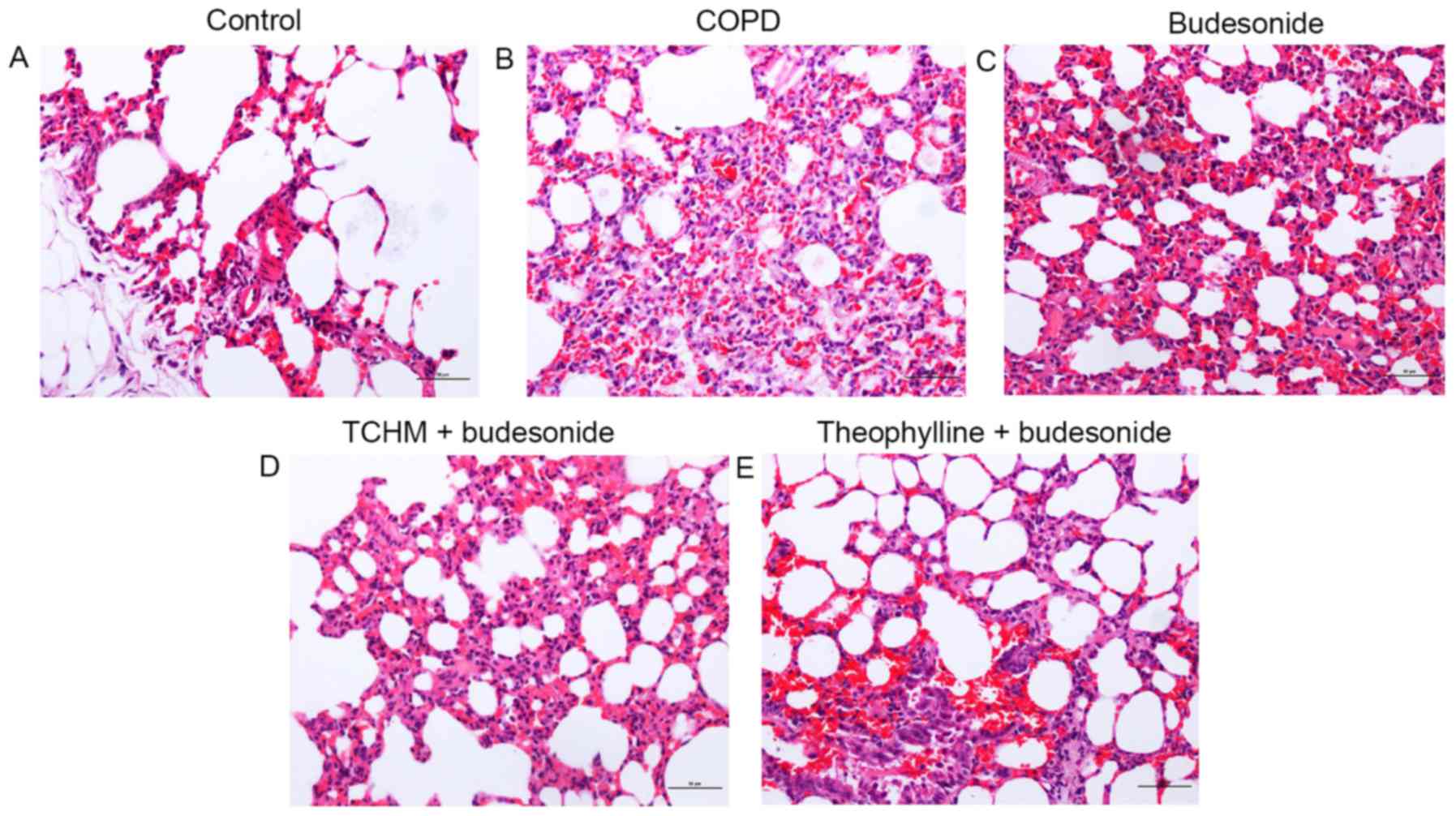
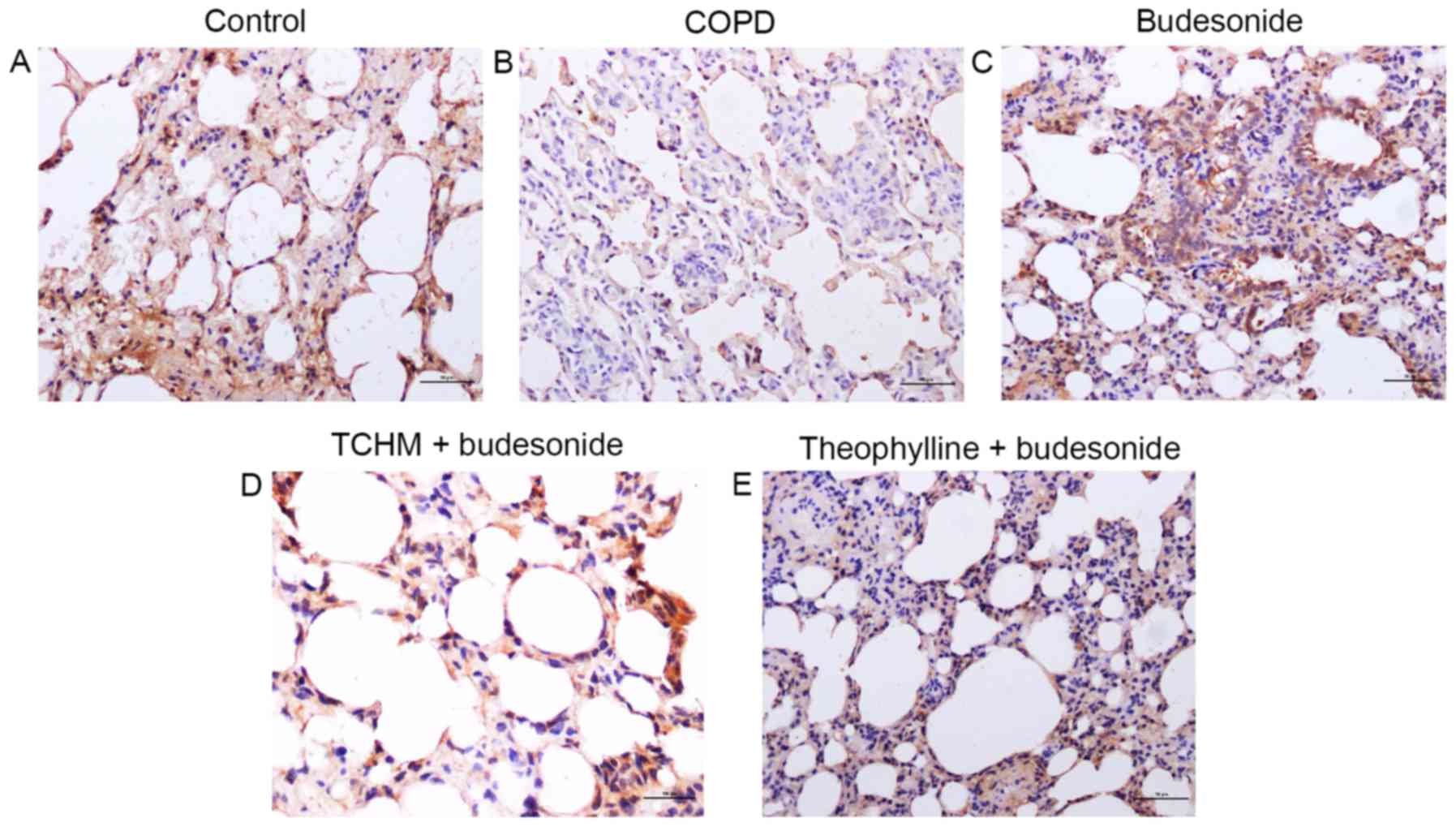
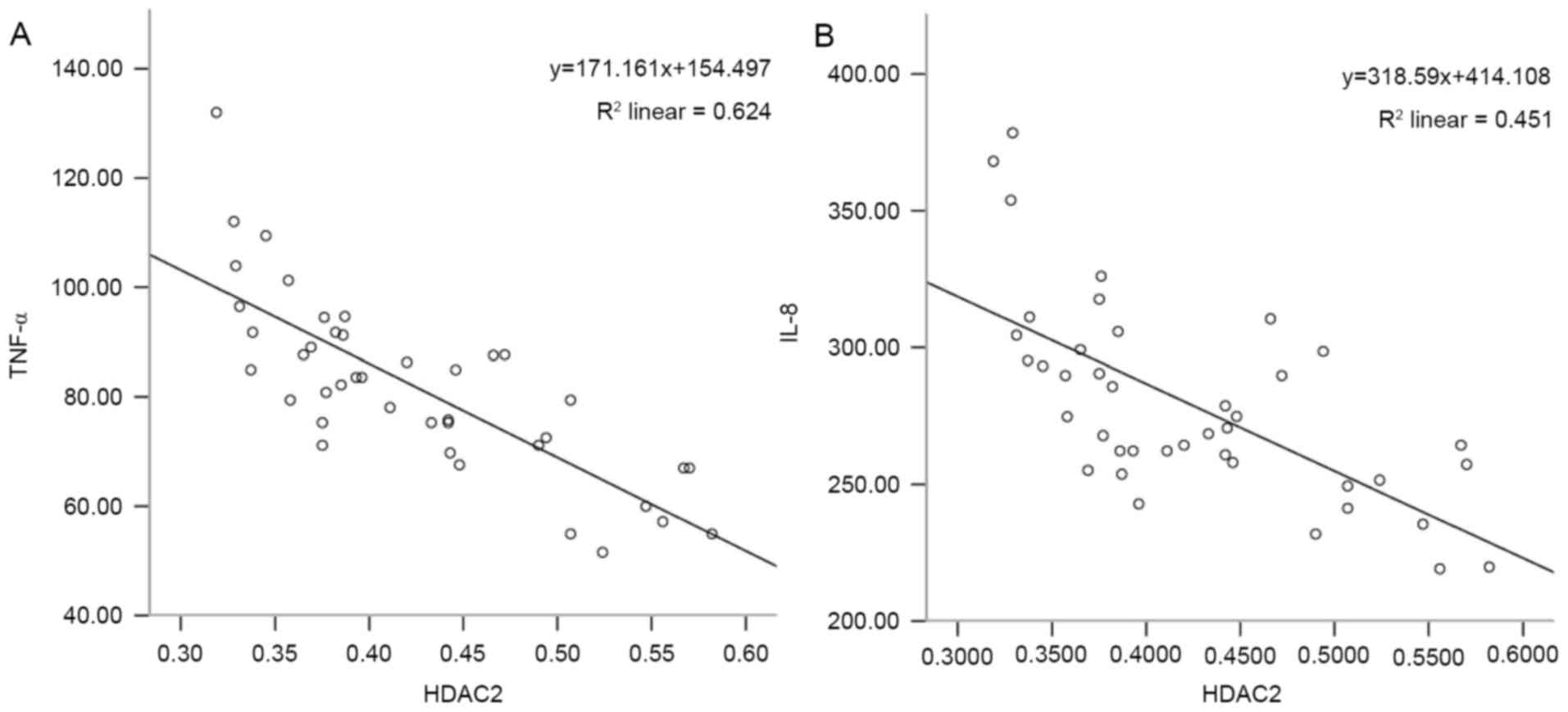
|
1
|
Han MK, Quibrera PM, Carretta EE, Barr RG,
Bleecker ER, Bowler RP, Cooper CB, Comellas A, Couper DJ, Curtis
JL, et al: Frequency of exacerbations in patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: An analysis of the SPIROMICS cohort.
Lancet Respir Med. 5:619–626. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Donnell R, Breen D, Wilson S and
Djukanovic R: Inflammatory cells in the airways in COPD. Thorax.
61:448–454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Papi A, Luppi F, Franco F and Fabbri LM:
Pathophysiology of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3:pp. 245–251. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
MacNee W: Pathogenesis of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2:pp. 258–266.
2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Crotty Alexander LE, Shin S and Hwang JH:
Inflammatory diseases of the lung induced by conventional cigarette
smoke: A review. Chest. 148:1307–1322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Newton R: Anti-inflammatory
glucocorticoids: Changing concepts. Eur J Pharmacol. 724:231–236.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ammit AJ: Glucocorticoid insensitivity as
a source of drug targets for respiratory disease. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 13:370–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malhotra D, Thimmulappa RK, Mercado N, Ito
K, Kombairaju P, Kumar S, Ma J, Feller-Kopman D, Wise R, Barnes P
and Biswal S: Denitrosylation of HDAC2 by targeting Nrf2 restores
glucocorticosteroid sensitivity in macrophages from COPD patients.
J Clin Invest. 121:4289–4302. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barnes PJ: Corticosteroid resistance in
patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:636–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hakim A, Adcock IM and Usmani OS:
Corticosteroid resistance and novel anti-inflammatory therapies in
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Current evidence and future
direction. Drugs. 72:1299–1312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koenderman L and Chilvers ER: Future
treatment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:
To reverse or not to reverse steroid resistance - that is the
question. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 134:323–324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun X, Li Q, Gong Y, Ren L, Wan H and Deng
W: Low-dose theophylline restores corticosteroid responsiveness in
rats with smoke-induced airway inflammation. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 90:895–902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barnes PJ: Development of new drugs for
COPD. Curr Med Chem. 20:1531–1540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsieh HY, Chiu PH and Wang SC: Histone
modifications and traditional Chinese medicinals. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 13:1152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Haifeng W, Hailong Z, Jiansheng L, Xueqing
Y, Suyun L, Bin L, Yang X and Yunping B: Effectiveness and safety
of traditional Chinese medicine on stable chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Complement Ther Med. 23:603–611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coyle M, Shergis JL, Liu S, Wu L, Zhang
AL, Guo X, Lu C and Xue CC: Safety of chinese herbal medicine for
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:3806782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong Y, Li Y, Sun Y, Mao J, Yao F, Tian Y,
Wang L, Li L, Li S and Li J: Bufei Jianpi granules improve skeletal
muscle and mitochondrial dysfunction in rats with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Complement Altern Med.
15:512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tian Y, Li Y, Li J, Xie Y, Wang M, Dong Y,
Li L, Mao J, Wang L and Luo S: Bufei Yishen granule combined with
acupoint sticking improves pulmonary function and morphormetry in
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats. BMC Complement Altern
Med. 15:2662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Yang L, Yao Q, Li Y, Tian Y, Li S,
Jiang S, Wang Y, Li X and Guo Z: Effects and mechanism of bufei
yishen formula in a rat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:3819762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Li JS, Li WW, Li SY, Tian YG, Lu XF,
Jiang SL and Wang Y: Long-term effects of three Tiao-Bu Fei-Shen
therapies on NF-κB/TGF-β1/smad2 signaling in rats with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14:1402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang C, Li Z, Liu X, Peng Q, Li F, Li D
and Wang C: Effect of Liuweibuqi capsule, a Chinese patent
medicine, on the JAK1/STAT3 pathway and MMP9/TIMP1 in a chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease rat model. J Tradit Chin Med.
35:54–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yange T, Ya L, Jiansheng L, Suyun L, Suli
J, Ying W, Xiaofan L and Weiwei L: Effects of therapies for
regulating and reinforcing lung and kidney on osteoporosis in rats
with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Tradit Chin Med.
35:175–183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng Y, Dai Y and Zhou LH: Clincal
Observation on TCM Combined with western medicine in treatment of
COPD with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome. J Emerg Traditi
Chin Med. 22:301–302. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Chen L, Zhang GL, Chen M, Ji JX and Wang
SG: The curative effect of Liujunzi decoction in the treatment of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in peroid with lung
sleep deficiency type. Zhong Yi Yao Dao Bao. 21:79–81. 2015.(In
Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Pei XJ, Lu YX, Zhang LD, Tan MC and Shi W:
Clinical observation of modified Liujunzi decoction for respiratory
muscle fatigue of stable phase patients with chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Xin Zhong Yi. 46:59–61. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Shan L: The intervention effect of
supplemeting qi, activating blood circulation, resolving phlegm and
its different combination regimens on COPD Rats. Guangzhou Univ
Chin Med. 70:12012.
|
|
27
|
Wang LD and Pan W: Treatment for 36 cases
of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at mild and remission
stages with salmeterol fluticasone and mixture of replenising Qi
and nourishing yin. West J Tradit Chin Med. 25:76–77. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Zhang HP, Fu JJ, Fan T, Zhang WB, Wang ZL,
Wang L and Wang G: Histone deacetylation of memory T lymphocytes by
You-Gui-Wan alleviates allergen-induced eosinophilic airway
inflammation in asthma. Chin Med. 10:92015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tazaki G, Kondo T, Tajiri S, Tsuji C,
Shioya S and Tanigaki T: Functional residual capacity and airway
resistance in rats of COPD model induced by systemic hyaluronidase.
Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 31:125–127. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
An ZP: BS: Lung function test in wistar
rats. Chin J Lab Anim Sci. 12:102–104. 2013.
|
|
31
|
Mercado N, To Y, Ito K and Barnes PJ:
Nortriptyline reverses corticosteroid insensitivity by inhibition
of phosphoinositide-3-kinase-δ. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 337:465–470.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou R, Luo F, Lei H, Zhang K, Liu J, He
H, Gao J, Chang X, He L, Ji H, et al: Liujunzi Tang, a famous
traditional Chinese medicine, ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced
mouse model of COPD. J Ethnopharmacol. 193:643–651. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Tian YG, Li JS, Dong YQ, Wang MH,
Feng SX, Li LL, Mao J, Wang LL and Luo S: Bufei Yishen granules
combined with acupoint sticking therapy suppress oxidative stress
in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats: Via regulating
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma signaling. J
Ethnopharmacol. 193:354–361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu J, Li X and Qin Y: Exploration of
regularity of treating AECOPD based on cluster analysis. J Emerg
Tradit Chin Med. 23:1436–1437. 2014.
|
|
35
|
Wang ZY and Gu C: Effect of BaiBuNong
decoction on rat COPD model histopathology and inflammatory
mediators. J Shandong Tradit Chin Med. 33:1010–1013. 2014.
|
|
36
|
Wang YX, XM and Zhao QP: Effect of rectal
delivery Pingchuan decoction on TNF-α, IL-8 and VEGF in rat COPD
model. J Guangming Tradit Chin Med. 29:705–707. 2014.
|
|
37
|
Lei ZL, GY and Zhong HW: Effect of
ShenHaYiFei capsule on TNF-α expression in rat COPD model. Henan
Tradit Chin Med. 34:822–825. 2014.
|
|
38
|
Shang LX, WY and Zhang LZ: Effect of
AiLuoKeChuanNing on inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress in
rat COPD model. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae. 24:168–171.
2014.
|