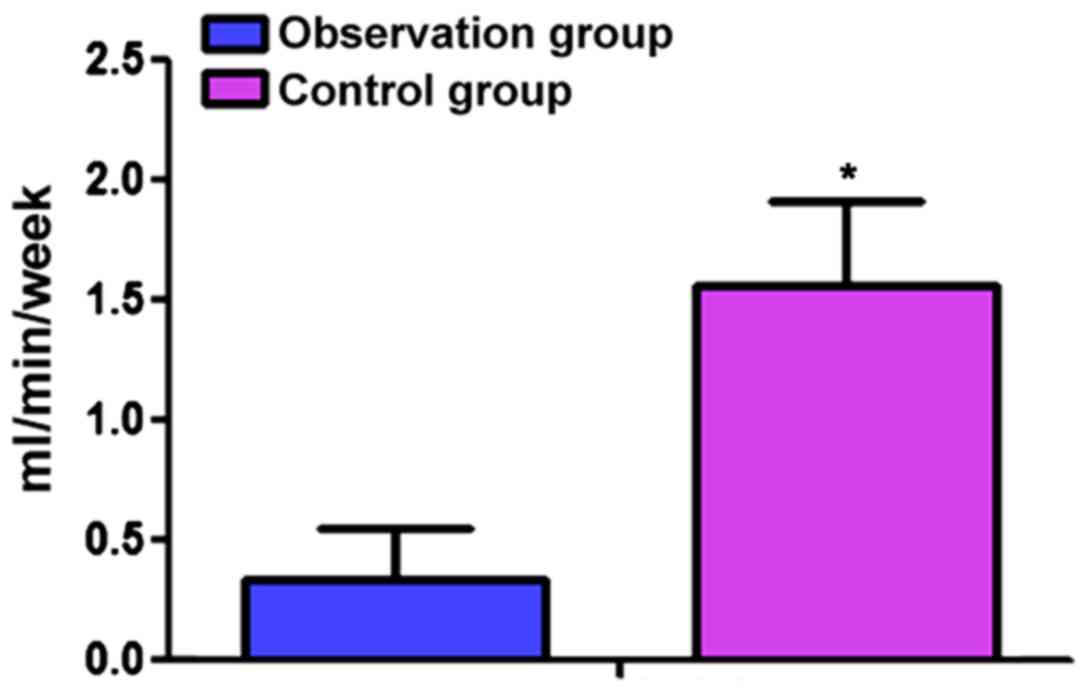
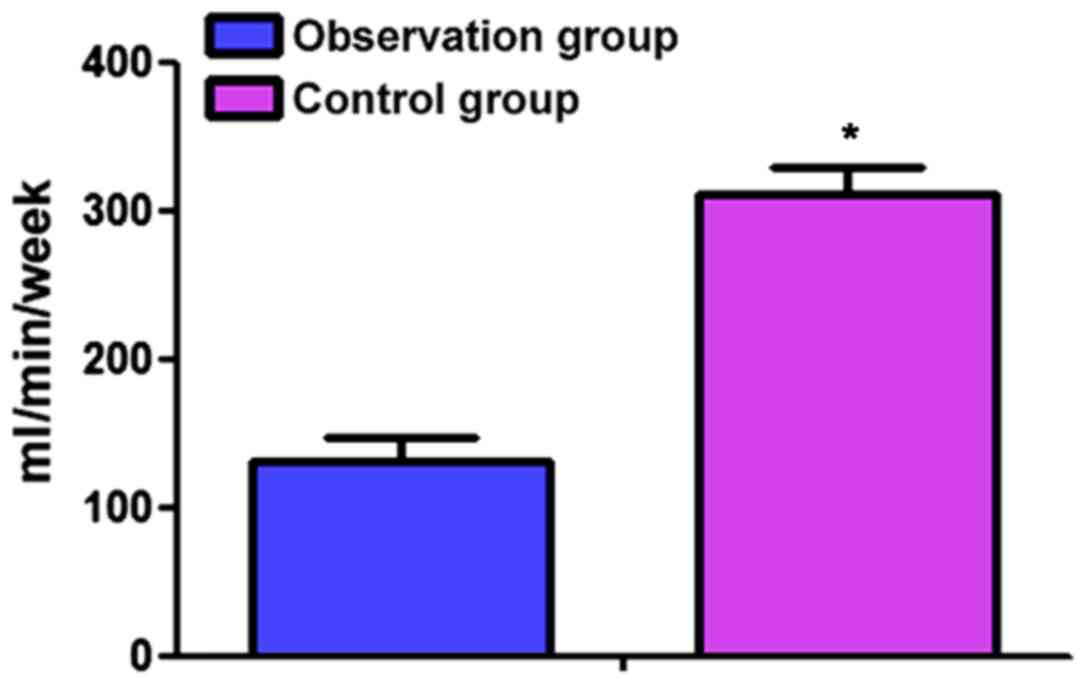
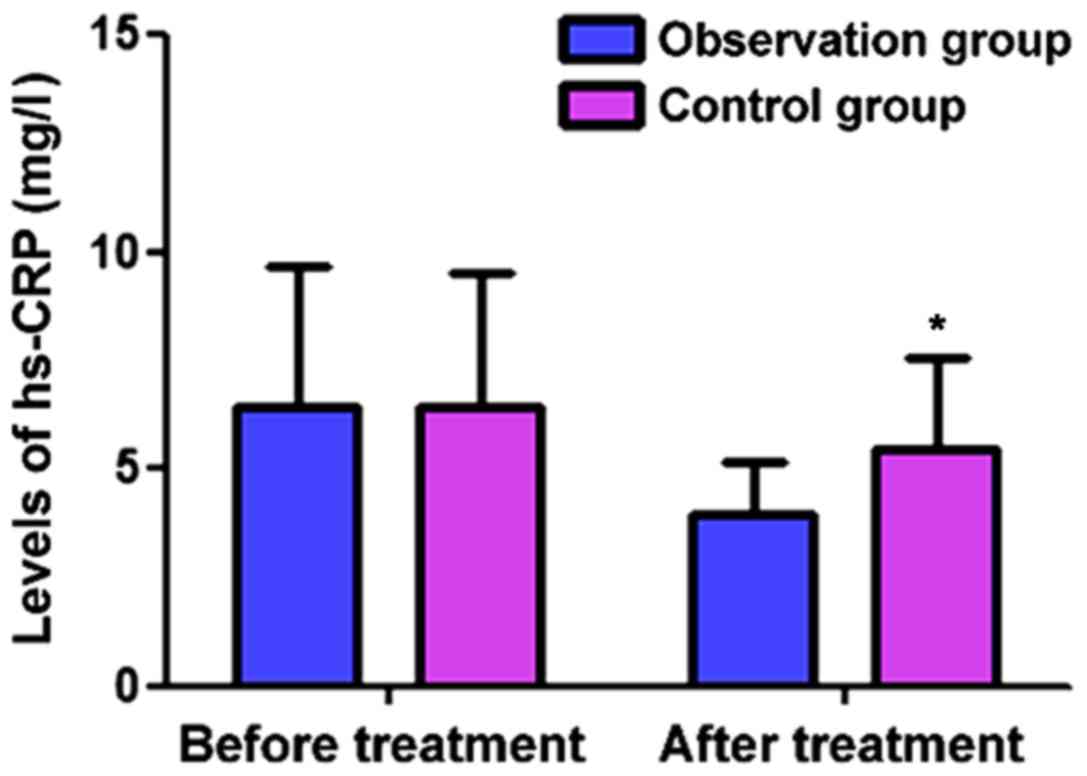
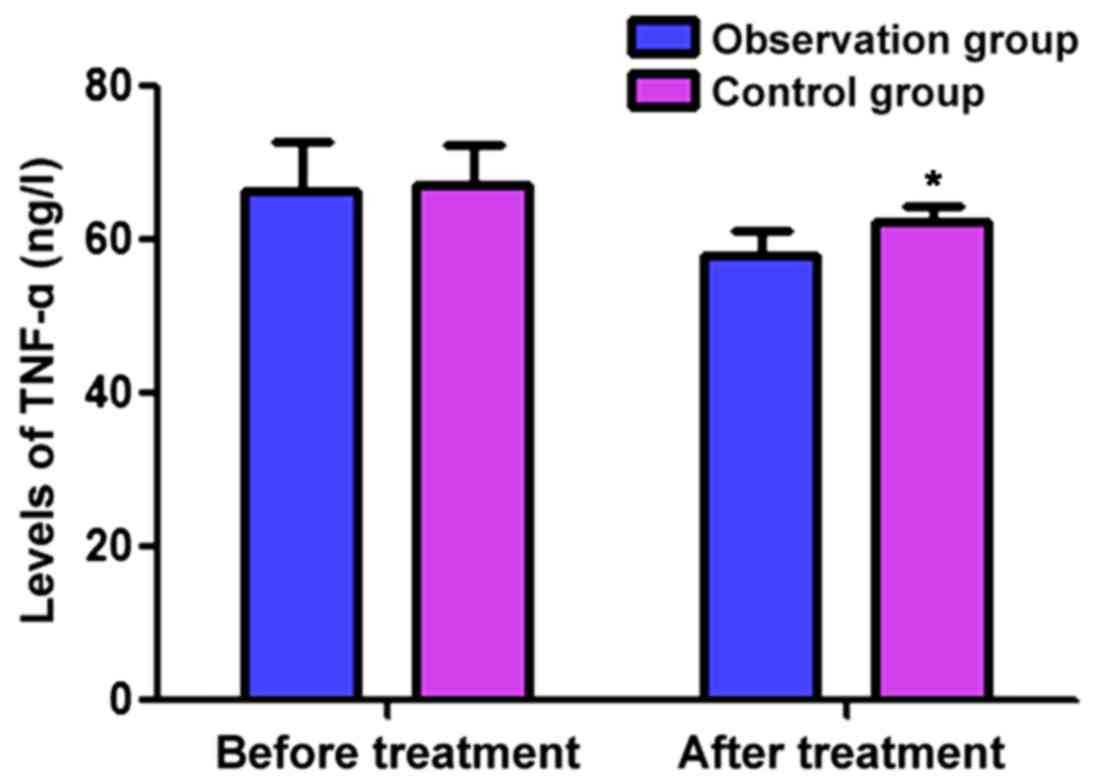
|
1
|
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, Wang W, Liu B,
Liu J, Chen M, He Q, Liao Y, Yu X, et al: Prevalence of chronic
kidney disease in China: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet.
379:815–822. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chawla LS, Eggers PW, Star RA and Kimmel
PL: Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as
interconnected syndromes. N Engl J Med. 371:58–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carville S, Wonderling D and Stevens P;
Guideline Development Group, : Early identification and management
of chronic kidney disease in adults: Summary of updated NICE
guidance. BMJ. 349:g45072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guan Y, Wu XX, Duan JL, Yin Y, Guo C, Wei
G, Wang YH, Zhu YR, Weng Y, Xi MM, et al: Effects and mechanism of
combination of Rhein and Danshensu in the treatment of chronic
kidney disease. Am J Chin Med. 43:1381–1400. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teschke R, Zhang L, Long H, Schwarzenboeck
A, Schmidt-Taenzer W, Genthner A, Wolff A, Frenzel C, Schulze J and
Eickhoff A: Traditional Chinese medicine and herbal hepatotoxicity:
A tabular compilation of reported cases. Ann Hepatol. 14:7–19.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
KDOQI, . KDOQI Clinical Practice
Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and
Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 49:12–154. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gámez-Méndez AM, Vargas-Robles H,
Arellano-Mendoza M, Cruz-Laguna E, Rios A and Escalante B: Early
stage of obesity potentiates nitric oxide reduction during the
development of renal failure. J Nephrol. 27:281–287. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, Turnbull F, Neal
B, Barzi F, Cass A, Baigent C, Chalmers J, Li N, Woodward M, et al
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration, : Blood
pressure lowering and major cardiovascular events in people with
and without chronic kidney disease: Meta-analysis of randomised
controlled trials. BMJ. 347:f56802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang SH, Filler G and Lindsay RM:
Residual renal function calculated from serum cystatin C
measurements and knowledge of the weekly standard Kt/V urea. Perit
Dial Int. 32:102–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li JY, Yu JS, Hu WH, Du YJ and Liu XY:
Study on the characteristics of syndrome distribution of
malnutrition in chronic renal failure in traditional Chinese
medicine. World J Integr Trad West Med. 724–726. 2009.
|
|
11
|
Coresh J and Jafar TH: Disparities in
worldwide treatment of kidney failure. Lancet. 385:1926–1928. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nistor I, Palmer SC, Craig JC, Saglimbene
V, Vecchio M, Covic A and Strippoli GF: Convective versus diffusive
dialysis therapies for chronic kidney failure: An updated
systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Am J Kidney Dis.
63:954–967. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pihlstrøm H, Mjøen G, Dahle DO, Pilz S,
Midtvedt K, März W, Abedini S, Holme I, Fellström B, Jardine A, et
al: Symmetric dimethylarginine as predictor of graft loss and
all-cause mortality in renal transplant recipients.
Transplantation. 98:1219–1225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao H, Wang T and Yu RH: A cohort study on
delaying the progress of chronic renal failure mainly with Modified
Shenqi Dihuang Decoction. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
32:39–42. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lv L, Wu SY, Wang GF, Zhang JJ, Pang JX,
Liu ZQ, Xu W, Wu SG and Rao JJ: Effect of astragaloside IV on
hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes in diabetic mice induced by a
high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Phytother Res. 24:219–224.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gui D, Guo Y, Wang F, Liu W, Chen J, Chen
Y, Huang J and Wang N: Astragaloside IV, a novel antioxidant,
prevents glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
PLoS One. 7:e398242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qi W, Niu J, Qin Q, Qiao Z and Gu Y:
Astragaloside IV attenuates glycated albumin-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting oxidative stress
in renal proximal tubular cells. Cell Stress Chaperones.
19:105–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Norouzi J, Yadollahpour A, Mirbagheri SA,
Mazdeh MM and Hosseini SA: Predicting renal failure progression in
chronic kidney disease using integrated intelligent fuzzy expert
system. Comput Math Methods Med. 2016:60808142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moutaftsi M, Tscharke DC, Vaughan K,
Koelle DM, Stern L, Calvo-Calle M, Ennis F, Terajima M, Sutter G,
Crotty S, et al: Uncovering the interplay between CD8, CD4 and
antibody responses to complex pathogens. Future Microbiol.
5:221–239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Noack M and Miossec P: Th17 and regulatory
T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun
Rev. 13:668–677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|