|
1
|
Iwata K, Doi A, Ohji G, Oka H, Oba Y,
Takimoto K, Igarashi W, Gremillion DH and Shimada T: Effect of
neutrophil elastase inhibitor (sivelestat sodium) in the treatment
of acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern Med.
49:2423–2432. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schmickl CN, Mastrobuoni S, Filippidis FT,
Shah S, Radic J, Murad MH, Toy P and Gajic O: Male-predominant
plasma transfusion strategy for preventing transfusion-related
acute lung injury: A systematic review. Crit Care Med. 43:205–225.
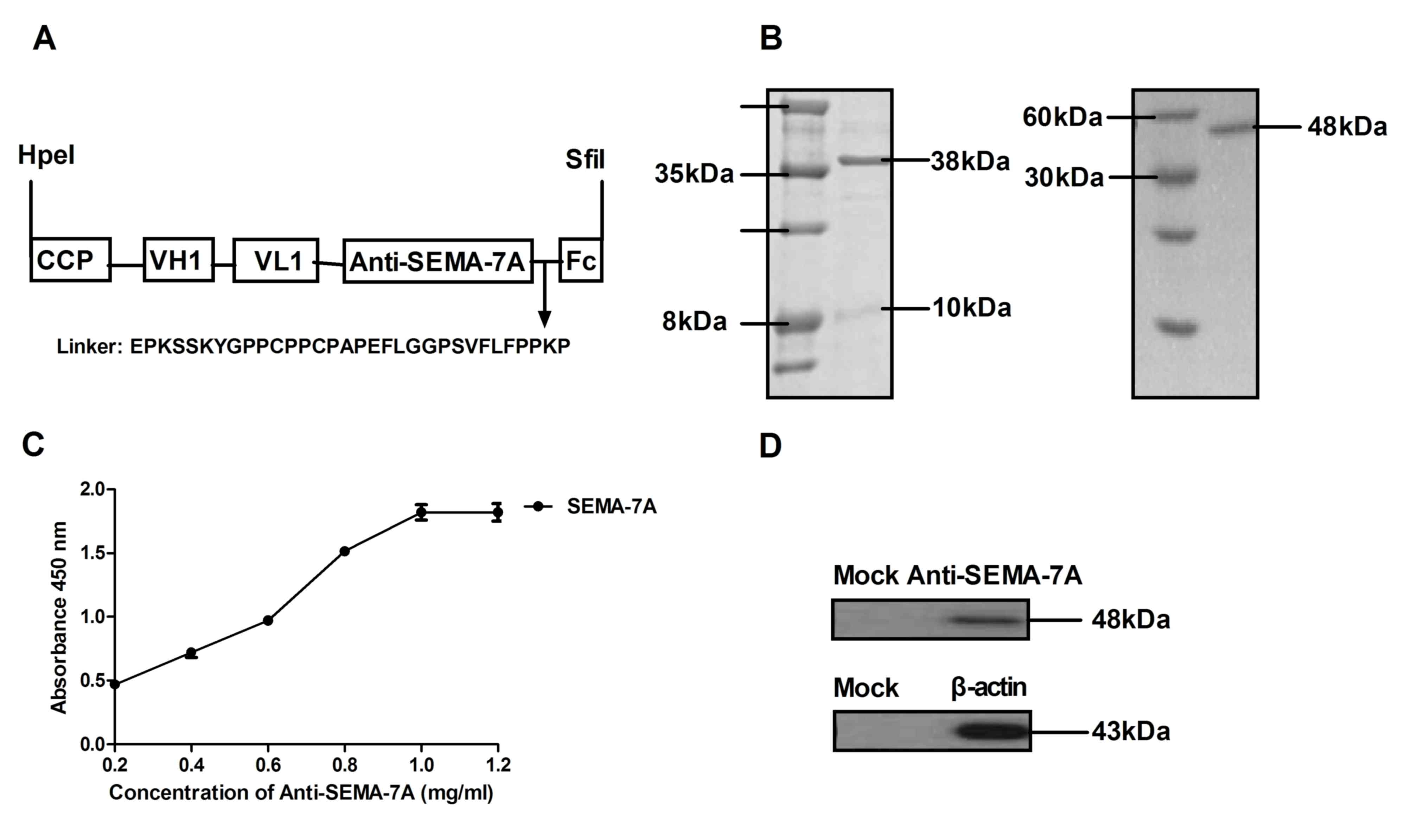
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim J, Song J and Lee M: Combinational
delivery of HMGB1 A box and heparin for acute lung injury. J
Control Release. 213:e572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Butt Y, Kurdowska A and Allen TC: Acute
lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
140:345–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hirano Y, Aziz M, Yang WL, Ochani M and
Wang P: Neutralization of osteopontin ameliorates acute lung injury
induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Shock. 46:431–438.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Braun RK, Koch JM, Hacker TA, Pegelow D,
Kim J, Raval AN, Schmuck EG, Schwahn DJ, Hei DJ, Centanni JM, et
al: Cardiopulmonary and histological characterization of an acute
rat lung injury model demonstrating safety of mesenchymal stromal
cell infusion. Cytotherapy. 18:536–545. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McIntyre LA, Moher D, Fergusson DA,
Sullivan KJ, Mei SH, Lalu M, Marshall J, Mcleod M, Griffin G,
Grimshaw J, et al: Efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for
acute lung injury in preclinical animal models: A Systematic
review. PLoS One. 11:e01471702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eves ND, Song Y, Piper A and Maher TM:
Year in review 2012: Acute lung injury, interstitial lung diseases,
sleep and physiology. Respirology. 18:555–564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cermáková Z, Simetka O and Kořístka M:
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)-review. Ceska
Gynekol. 78:211–215. 2013.(In Czech). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dzierba AL, Abel EE, Buckley MS and Lat I:
A review of inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolized epoprostenol in
acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Pharmacotherapy. 34:279–290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vlaar AP and Juffermans NP:
Transfusion-related acute lung injury: A clinical review. Lancet.
382:984–994. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sud S, Sud M, Friedrich JO, Meade MO,
Ferguson ND, Wunsch H and Adhikari NK: High frequency oscillation
in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress
syndrome (ARDS): Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ.
340:c23272010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaswal DS, Leung JM, Sun J, Cui X, Li Y,
Kern S, Welsh J, Natanson C and Eichacker PQ: Tidal volume and
plateau pressure use for acute lung injury from 2000 to present: A
systematic literature review. Crit Care Med. 42:2278–2289. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
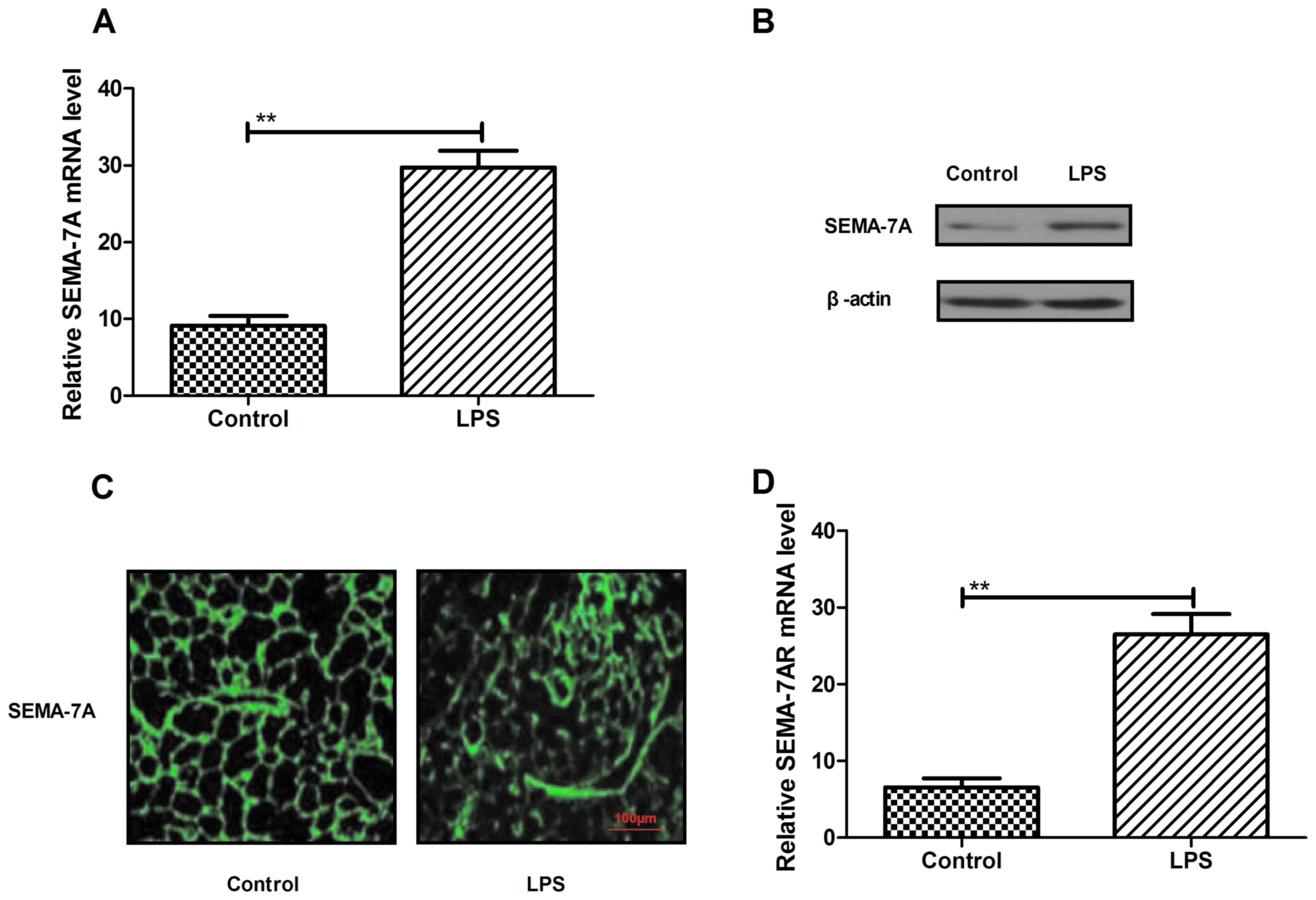
Zhang M, Wang L, Dong M, Li Z and Jin F:
Endothelial Semaphorin 7A promotes inflammation in seawater
aspiration-induced acute lung injury. Int J Mol Sci.
15:19650–19661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Holmes S, Downs AM, Fosberry A, Hayes PD,
Michalovich D, Murdoch P, Moores K, Fox J, Deen K, Pettman G, et
al: Sema7A is a potent monocyte stimulator. Scand J Immunol.
56:270–275. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
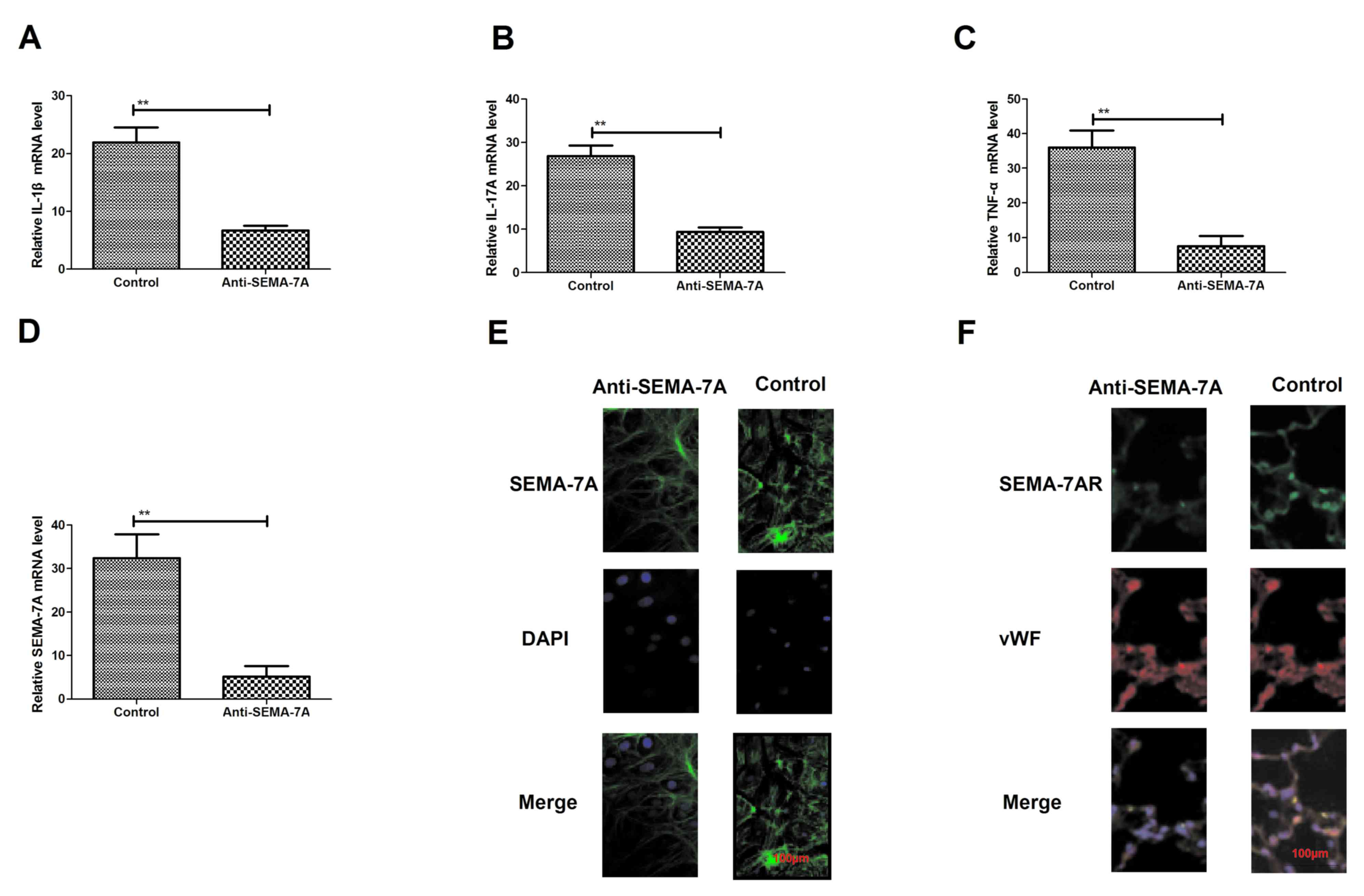
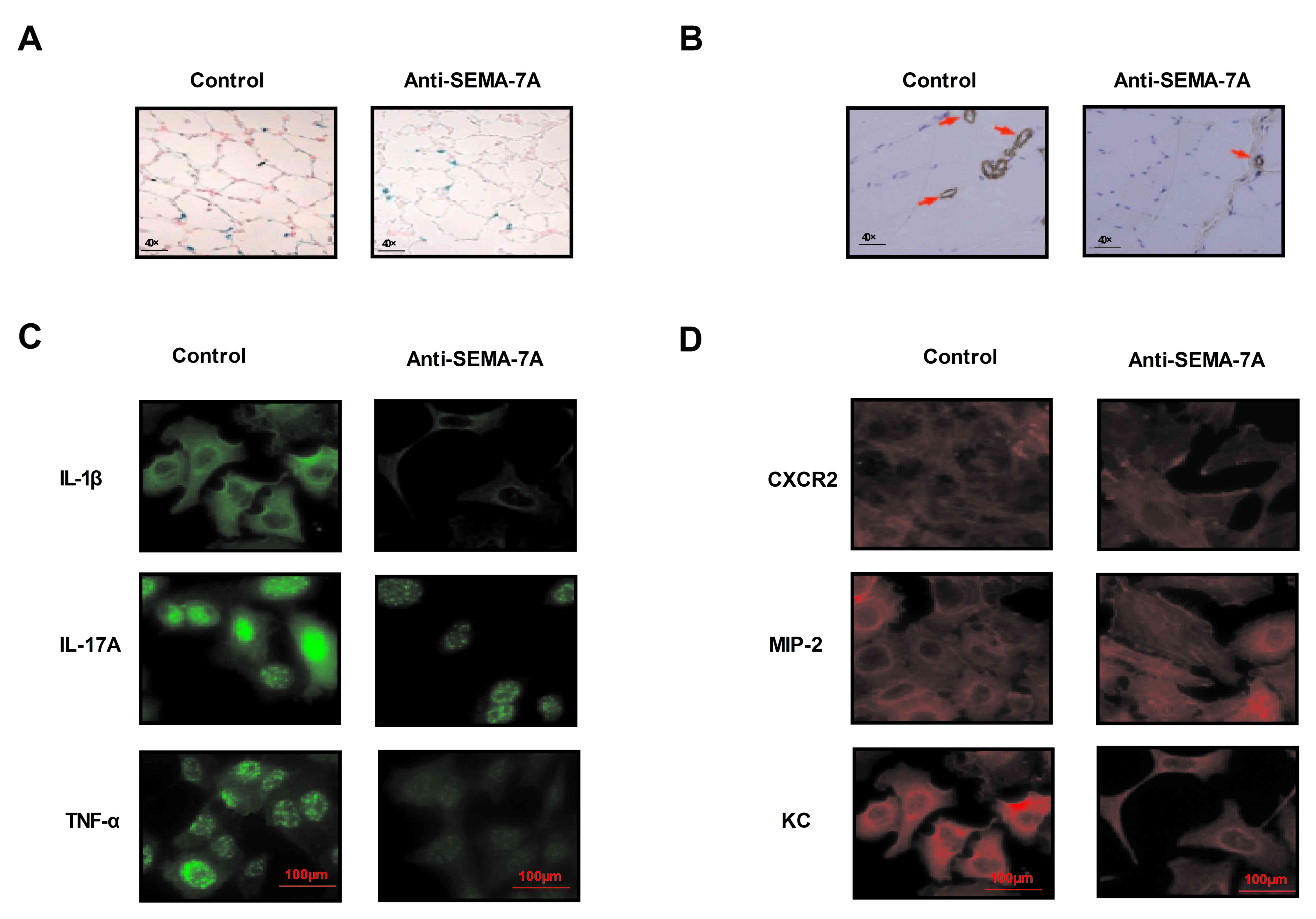
Roth JM, Köhler D, Schneider M, Granja TF
and Rosenberger P: Semaphorin 7A aggravates pulmonary inflammation
during lung injury. PLoS One. 11:e01469302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu H, Yao L, Chou L, Yang JH, Zhang YX, Li
XL and Shan BE: Construction and functional analysis of an
anti-human cervical carcinoma/anti-human CD3 single-chain
bispecific antibody. Mol Med Rep. 14:804–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh PK, Agrawal R, Kamboj DV and Singh
L: Construction of recombinant single chain variable fragment
(ScFv) antibody against superantigen for immunodetection using
antibody phage display technology. Methods Mol Biol. 1396:207–225.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pasello M, Zamboni S, Mallano A, Flego M,
Picci P, Cianfriglia M and Scotlandi K: Design and construction of
a new human naive single-chain fragment variable antibody library,
IORISS1. J Biotechnol. 224:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bjarnadottir SG and Flengsrud R: Affinity
chromatography, two-dimensional electrophoresis, adapted
immunodepletion and mass spectrometry used for detection of porcine
and piscine heparin-binding human plasma proteins. J Chromatogr B
Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 944:107–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
London AS, Mackay K, Lihon M, He Y and
Alabi BR: Gel filtration chromatography as a method for removing
bacterial endotoxin from antibody preparations. Biotechnol Prog.
30:1497–1501. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rauch S, Johannes A, Zollhofer B and
Muellenbach RM: Evaluating intra-abdominal pressures in a porcine
model of acute lung injury by using a wireless motility capsule.
Med Sci Monit. 18:BR163–BR166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang L, Wu X, Liu F, Duan Y and Li S:
Novel biodegradable polylactide/poly(ethylene glycol) mice lles
prepared by direct dissolution method for controlled delivery of
anticancer drugs. Pharm Res. 26:2332–2342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gutierrez-Franco A, Costa C, Eixarch H,
Castillo M, Medina-Rodríguez EM, Bribián A, de Castro F, Montalban
X and Espejo C: Differential expression of sema3A and sema7A in a
murine model of multiple sclerosis: Implications for a therapeutic
design. Clin Immunol. 163:22–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Allegra M, Zaragkoulias A, Vorgia E,
Ioannou M, Litos G, Beug H and Mavrothalassitis G: Semaphorin-7a
reverses the ERF-induced inhibition of EMT in Ras-dependent mouse
mammary epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 23:3873–3881. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jeon CM, Shin IS, Shin NR, Hong JM, Kwon
OK, Kim JH, Oh SR, Bach TT, Hai DV, Quang BH, et al: Clausena
anisata-mediated protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute lung injury in mice. Int J Mol Med. 37:1091–1098. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bianchi AM, Reboredo MM, Lucinda LM, Reis
FF, Silva MV, Rabelo MA, Holanda MA, Oliveira JC, Lorente JÁ and
Pinheiro Bdo V: The Effects of Prone position ventilation on
experimental mild acute lung injury induced by intraperitoneal
lipopolysaccharide injection in rats. Lung. 194:193–199. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ariza-Prota M, Pando-Sandoval A and
Garcia-Clemente M: Lung injury caused by all-trans-retinoic acid in
the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Arch Bronconeumol.
52:441–442. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Piper A, Song Y, Eves ND and Maher TM:
Year in review 2013: Acute lung injury, interstitial lung diseases,
sleep and physiology. Respirology. 19:428–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McMullen SM, Meade M, Rose L, Burns K,
Mehta S, Doyle R and Henzler D; Canadian Critical Care Trials Group
(CCCTG), : Partial ventilatory support modalities in acute lung
injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome-a systematic review.
PLoS One. 7:e401902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Osaka D, Shibata Y, Kanouchi K, Nishiwaki
M, Kimura T, Kishi H, Abe S, Inoue S, Tokairin Y, Igarashi A, et
al: Soluble endothelial selectin in acute lung injury complicated
by severe pneumonia. Int J Med Sci. 8:302–308. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seki H, Fukunaga K, Arita M, Arai H,
Nakanishi H, Taguchi R, Miyasho T, Takamiya R, Asano K, Ishizaka A,
et al: The anti-inflammatory and proresolving mediator resolvin E1
protects rat from bacterial pneumonia and acute lung injury. J
Immunol. 184:836–843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nieuwenhuizen L, de Groot PG, Grutters JC
and Biesma DH: A review of pulmonary coagulopathy in acute lung
injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome and pneumonia. Eur J
Haematol. 82:413–425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakamura S, Yanagihara K, Izumikawa K,
Seki M, Kakeya H, Yamamoto Y, Mukae H, Tashiro T and Kohno S:
Efficacy of sivelestat for acute lung injury due to severe
bacterial pneumonia with systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 46:793–797. 2008.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Czopik AK, Bynoe MS, Palm N, Raine CS and
Medzhitov R: Semaphorin 7A is a negative regulator of T cell
responses. Immunity. 24:591–600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Garcia-Gonzalez MJ, Dominguez-Rodriguez A
and Ferrer-Hita JJ: Unusual etiology of acute lung injury in a
patient with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol.
117:e95–e97. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Delorme G, Saltel F, Bonnelye E, Jurdic P
and Machuca-Gayet I: Expression and function of semaphorin 7A in
bone cells. Biol Cell. 97:589–597. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morote-Garcia JC, Napiwotzky D, Köhler D
and Rosenberger P: Endothelial Semaphorin 7A promotes neutrophil
migration during hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp.
14146–14151. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zarbock A, Bishop J, Muller H, Schmolke M,
Buschmann K, Van Aken H and Singbartl K: Chemokine homeostasis vs.
chemokine presentation during severe acute lung injury: the other
side of the Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 298:L462–L471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bhatia M, Zemans RL and Jeyaseelan S: Role
of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 46:566–572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Allegra M, Zaragkoulias A, Vorgia E,
Ioannou M, Litos G, Beug H and Mavrothalassitis G: Semaphorin-7a
reverses the ERF-induced inhibition of EMT in Ras-dependent mouse
mammary epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 23:3873–3881. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kojicic M, Li G, Hanson AC, Lee KM, Thakur
L, Vedre J, Ahmed A, Baddour LM, Ryu JH and Gajic O: Risk factors
for the development of acute lung injury in patients with
infectious pneumonia. Crit Care. 16:R462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|