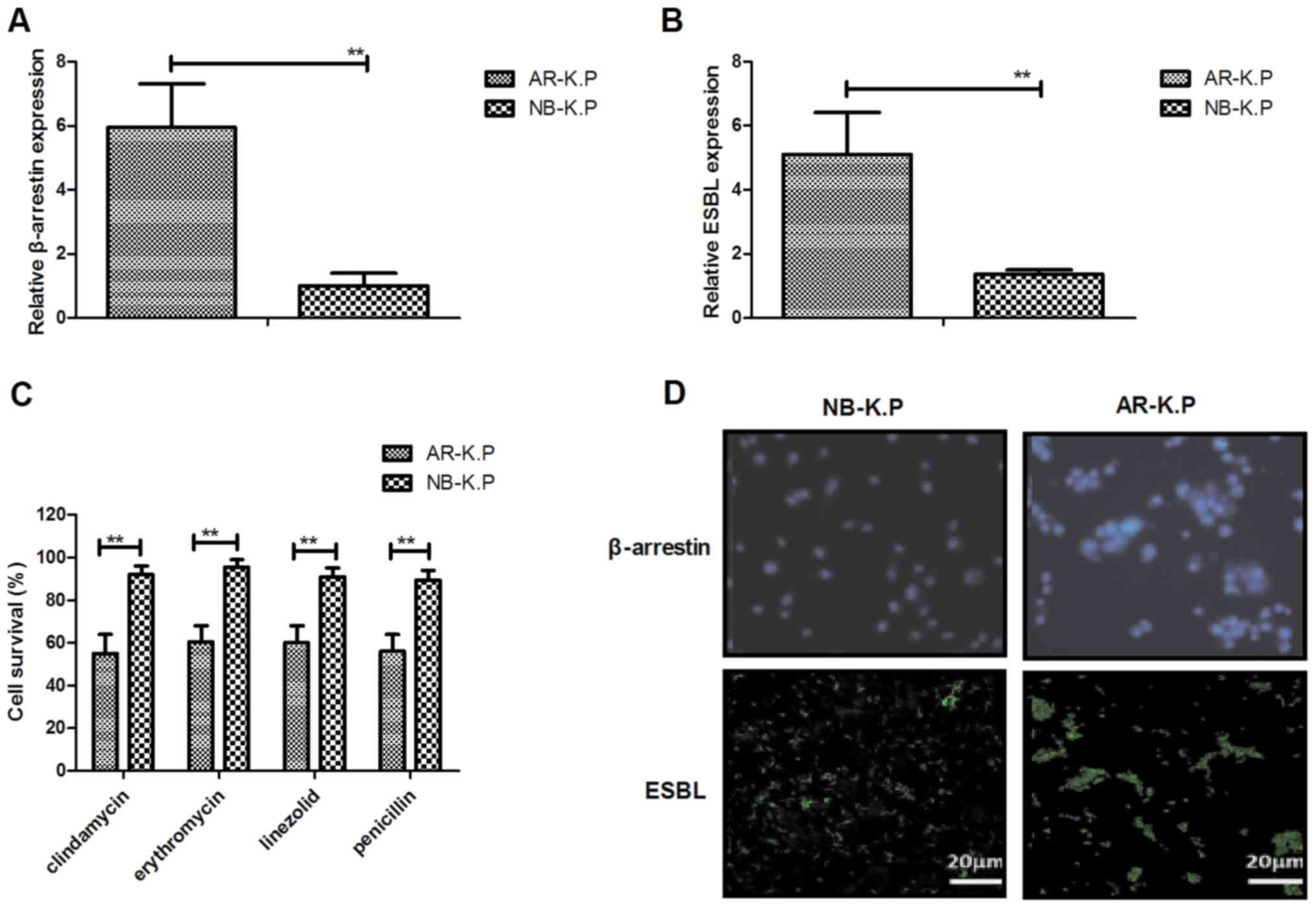
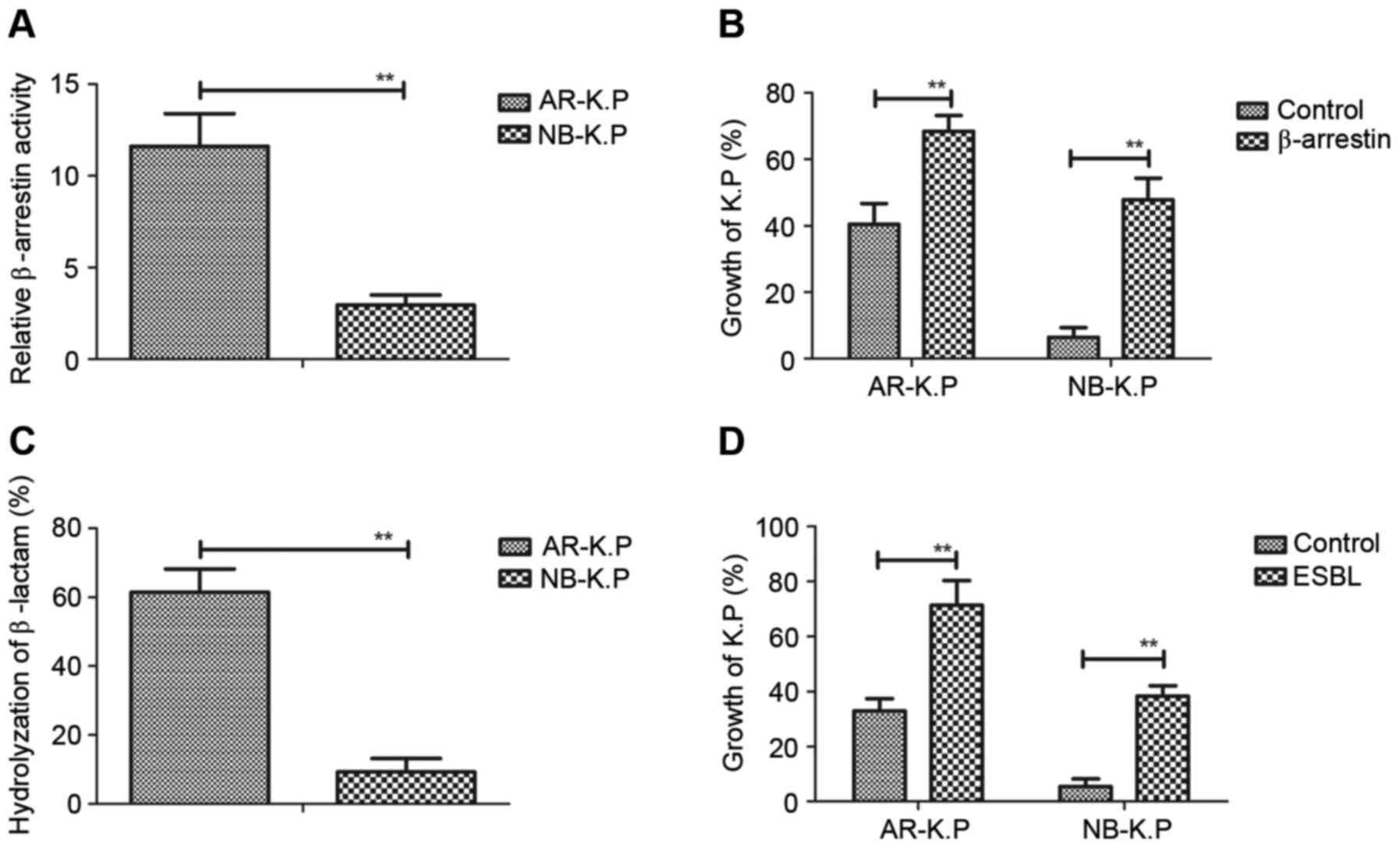
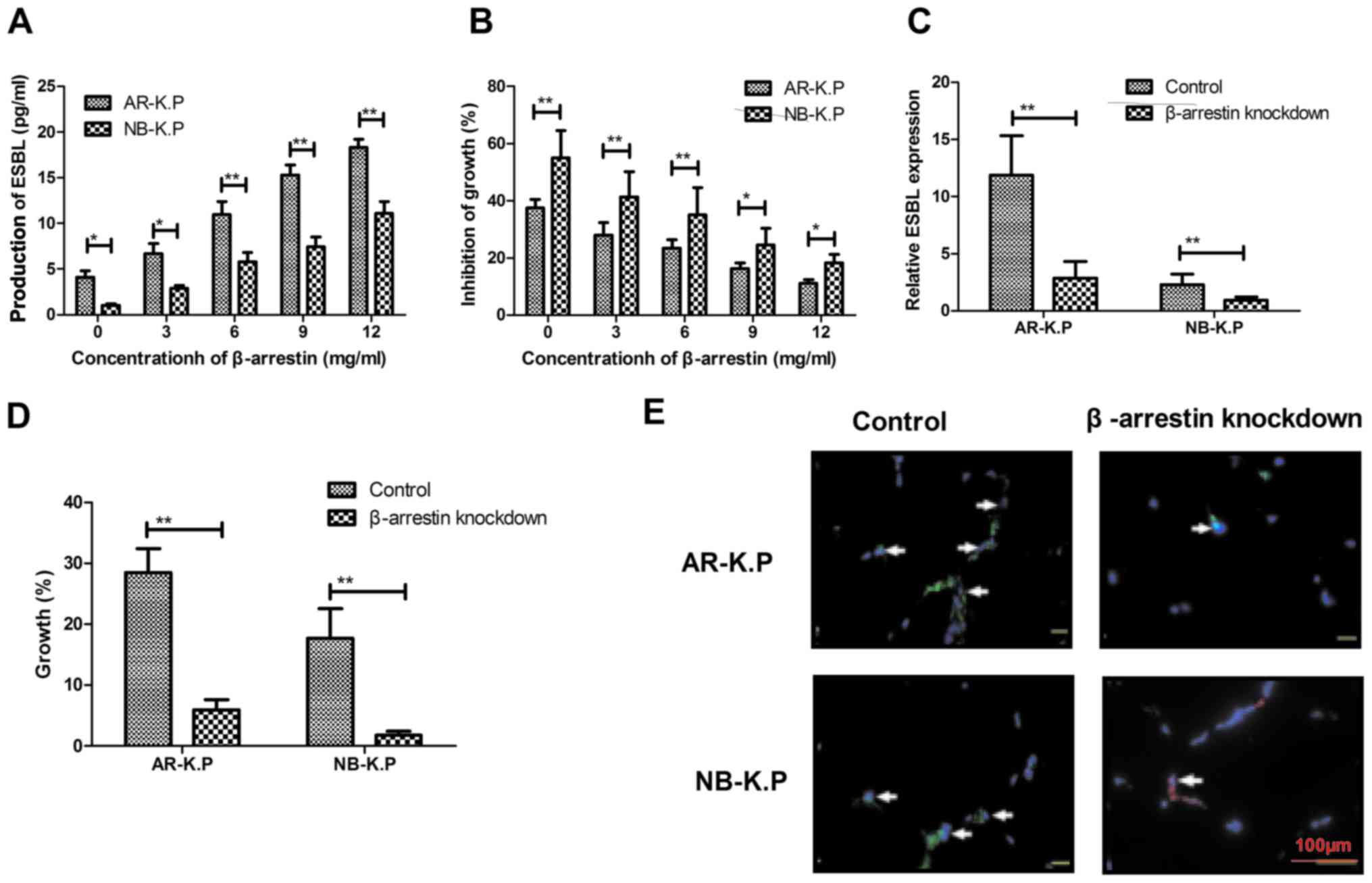
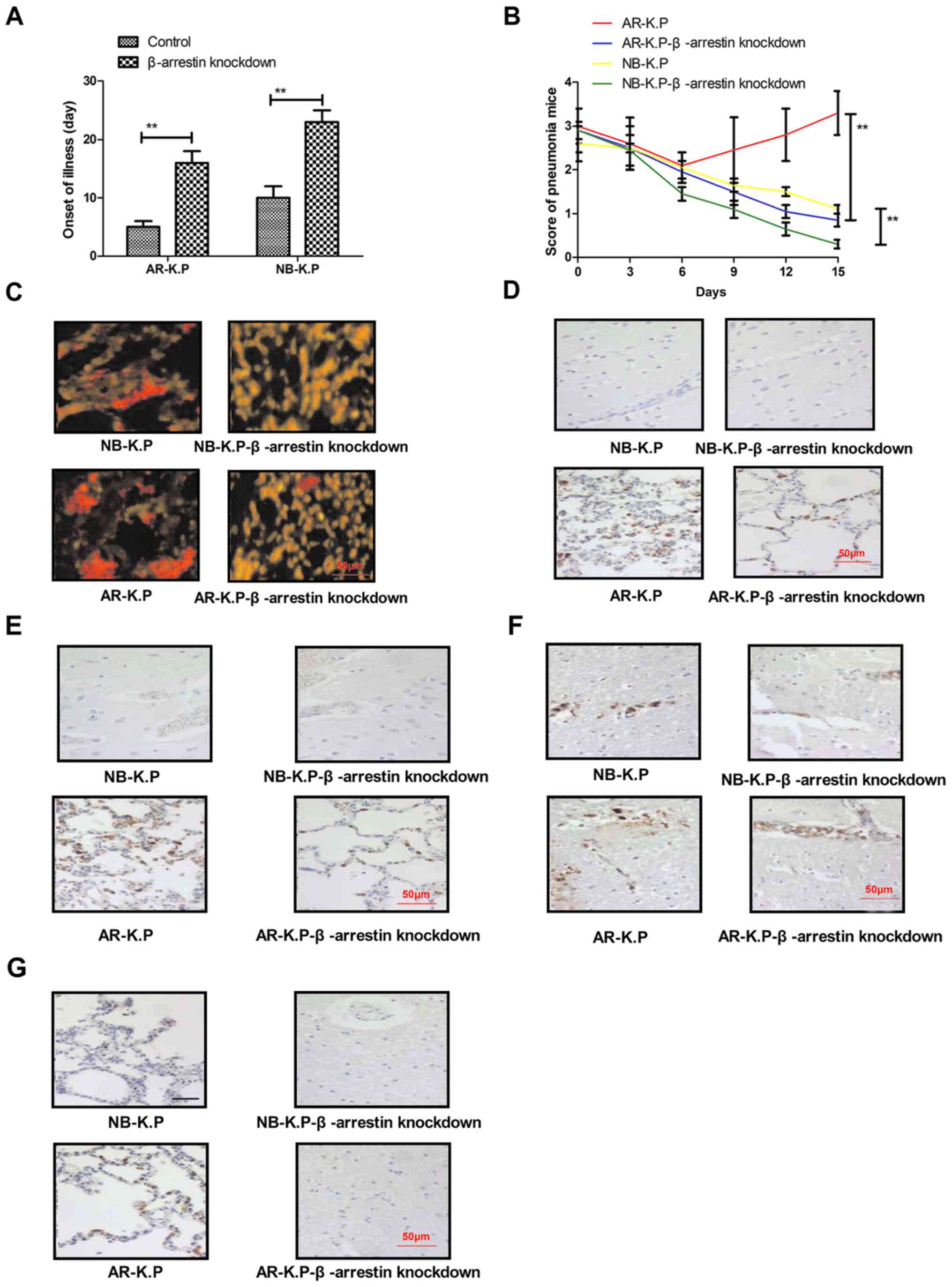
|
1
|
Li W, Dong K, Ren J and Qu X: A
β-Lactamase-imprinted responsive hydrogel for the treatment of
antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
55:8049–8053. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yosef I, Manor M and Qimron U:
Counteracting selection for antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Bacteriophage. 6:e10969962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh N, Sit MT, Chung DM, Lopez AA,
Weerackoon R and Yeh PJ: How often are antibiotic-resistant
bacteria said to ‘evolve’ in the news? PLoS One. 11:e01503962016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sharma VK, Johnson N, Cizmas L, McDonald
TJ and Kim H: A review of the influence of treatment strategies on
antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes.
Chemosphere. 150:702–714. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lim MK, Lai PS, Ponnampalavanar SS, Syed
Omar SF, Taib NA, Yusof MY, Italiano CM, Kong DC and Kamarulzaman
A: Antibiotics in surgical wards: Use or misuse? A newly
industrialized country's perspective. J Infect Dev Ctries.
9:1264–1271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zimmer BL: Combating antibiotic-resistant
bacteria: The Microbiology lab answers the challenge. MLO Med Lab
Obs. 47:30–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Çöl A, Dedeić-Ljubović A, Salimović-Bešić
I and Hukic M: Antibiotic resistance profiles and genetic
similarities within a new generation of carbapenem-resistant
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-A. Baumannii complex resistotypes in
bosnia and herzegovina. Microb Drug Resist. 22:655–661. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tahrani L, Soufi L, Mehri I, Najjari A,
Hassan A, Van Loco J, Reyns T, Cherif A and Ben Mansour H:
Isolation and characterization of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
from pharmaceutical industrial wastewaters. Microb Pathog.
89:54–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Conen A, Frei R, Adler H, Dangel M, Fux CA
and Widmer AF: Microbiological screening is necessary to
distinguish carriers of plasmid-mediated AmpC
beta-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae and extended-spectrum
beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae because of
clinical similarity. PLoS One. 10:e01206882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schauss T, Glaeser SP, Gütschow A, Dott W
and Kämpfer P: Improved detection of extended spectrum
beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli in input and
output samples of German biogas plants by a selective
pre-enrichment procedure. PLoS One. 10:e01197912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bonnedahl J, Stedt J, Waldenström J,
Svensson L, Drobni M and Olsen B: Comparison of extended-spectrum
β-lactamase (ESBL) CTX-M genotypes in franklin gulls from Canada
and Chile. PLoS One. 10:e01413152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valenza G, Nickel S, Pfeifer Y, Pietsch M,
Voigtländer E, Lehner-Reindl V and Höller C: Prevalence and genetic
diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing
Escherichia coli in nursing homes in Bavaria, Germany. Vet
Microbiol. 200:138–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gajul SV, Mohite ST, Mangalgi SS, Wavare
SM and Kakade SV: Klebsiella pneumoniae in septicemic neonates with
special reference to extended spectrum β-lactamase, AmpC, metallo
β-lactamase production and multiple drug resistance in tertiary
care hospital. J Lab Physicians. 7:32–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sudarwanto M, Akineden Ö, Odenthal S,
Gross M and Usleber E: Extended-spectrum β-lactamase
(ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in bulk tank milk from dairy
farms in Indonesia. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 12:585–590. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rastogi V, Nirwan PS, Jain S and Kapil A:
Nosocomial outbreak of septicaemia in neonatal intensive care unit
due to extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella
pneumoniae showing multiple mechanisms of drug resistance. Indian J
Med Microbiol. 28:380–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bae D, Cheng CM and Khan AA:
Characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing
non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) from imported food products. Int J
Food Microbiol. 214:12–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Walther B, Lübke-Becker A, Stamm I, Gehlen
H, Barton AK, Janssen T, Wieler LH and Guenther S: Suspected
nosocomial infections with multi-drug resistant E. coli, including
extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing strains, in an
equine clinic. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 127:421–427.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schaufler K, Bethe A, Lübke-Becker A,
Ewers C, Kohn B, Wieler LH and Guenther S: Putative connection
between zoonotic multiresistant extended-spectrum beta-lactamase
(ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli in dog feces from a veterinary
campus and clinical isolates from dogs. Infect Ecol Epidemiol.
5:253342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ibrahim DR, Dodd CE, Stekel DJ, Ramsden SJ
and Hobman JL: Multidrug resistant, extended spectrum β-lactamase
(ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli isolated from a dairy farm. FEMS
Microbiol Ecol. 92:fiw0132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sanchez GV, Master RN, Clark RB, Fyyaz M,
Duvvuri P, Ekta G and Bordon J: Klebsiella pneumoniae antimicrobial
drug resistance, United States, 1998–2010. Emerg Infect Dis.
19:133–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barger A, Schaade L, Krause G and Kramer
M: Strategies for recognition, prevention and control of
antimicrobial resistances in Germany-a draft from the Federal
German Ministry of Health. Gesundheitswesen. 70:631–635. 2008.(In
German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barthet G, Framery B, Gaven F, Pellissier
L, Reiter E, Claeysen S, Bockaert J and Dumuis A:
5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor activation of the extracellular
signal-regulated kinase pathway depends on Src activation but not
on G protein or beta-arrestin signaling. Mol Biol Cell.
18:1979–1991. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lipsky R, Potts EM, Tarzami ST, Puckerin
AA, Stocks J, Schecter AD, Sobie EA, Akar FG and Diversé-Pierluissi
MA: beta-Adrenergic receptor activation induces internalization of
cardiac Cav1.2 channel complexes through a beta-arrestin 1-mediated
pathway. J Biol Chem. 283:17221–17226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mittal N, Roberts K, Pal K, Bentolila LA,
Fultz E, Minasyan A, Cahill C, Pradhan A, Conner D, DeFea K, et al:
Select G-protein-coupled receptors modulate agonist-induced
signaling via a ROCK, LIMK, and β-arrestin 1 pathway. Cell Rep.
5:1010–1021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Borroni EM, Cancellieri C, Vacchini A,
Benureau Y, Lagane B, Bachelerie F, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Mizuno K,
Mantovani A, Bonecchi R and Locati M: β-arrestin-dependent
activation of the cofilin pathway is required for the scavenging
activity of the atypical chemokine receptor D6. Sci Signal.
6:ra30.1–11, S1-S3. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zoudilova M, Kumar P, Ge L, Wang P, Bokoch
GM and DeFea KA: Beta-arrestin-dependent regulation of the cofilin
pathway downstream of protease-activated receptor-2. J Biol Chem.
282:20634–20646. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zscheppang K, Kurth I, Wachtel N,
Dubrovska A, Kunz-Schughart LA and Cordes N: Efficacy of beta1
integrin and EGFR targeting in sphere-forming human head and neck
cancer cells. J Cancer. 7:736–745. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsueh PR, Ko WC, Wu JJ, Lu JJ, Wang FD, Wu
HY, Wu TL and Teng LJ: Consensus statement on the adherence to
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) Antimicrobial
Susceptibility Testing Guidelines (CLSI-2010 and CLSI-2010-update)
for Enterobacteriaceae in clinical microbiology laboratories in
Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 43:452–455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aguileta MA, Rojas-Rivera D, Goossens V,
Estornes Y, Van Isterdael G, Vandenabeele P and Bertrand MJ: A
siRNA screen reveals the prosurvival effect of protein kinase A
activation in conditions of unresolved endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Cell Death Differ. 23:1670–1680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wirries A, Breyer S, Quint K, Schobert R
and Ocker M: Thymoquinone hydrazone derivatives cause cell cycle
arrest in p53-competent colorectal cancer cells. Exp Ther Med.
1:369–375. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
George TP and Thomas T: Discrete wavelet
transform de-noising in eukaryotic gene splicing. BMC
Bioinformatics. 11 Suppl 1:S502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weigel RM, Qiao B, Barber DA, Teferedegne
B, Kocherginskaya S, White BA and Isaacson RE: Identification of
patterns of transmission of Salmonella within swine production
systems using pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and
repetitive sequence polymerase chain reaction (REP-PCR): A
quantitative analysis. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr.
114:397–400. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiao S, Wang J and Xiao N: MicroRNAs as
noninvasive biomarkers in bladder cancer detection: A diagnostic
meta-analysis based on qRT-PCR data. Int J Biol Markers.
31:e276–e285. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kishimoto M, Yamana H, Inoue S, Noda T,
Myojin T, Matsui H, Yasunaga H, Kawaguchi M and Imamura T:
Sivelestat sodium and mortality in pneumonia patients requiring
mechanical ventilation: Propensity score analysis of a Japanese
nationwide database. J Anesth. 31:405–412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ceccarelli G, Falcone M, Giordano A,
Mezzatesta ML, Caio C, Stefani S and Venditti M: Successful
ertapenem-doripenem combination treatment of bacteremic
ventilator-associated pneumonia due to colistin-resistant
KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
57:2900–2901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McCullough AR, Parekh S, Rathbone J, Del
Mar CB and Hoffmann TC: A systematic review of the public's
knowledge and beliefs about antibiotic resistance-authors'
response. J Antimicrob Chemother. 71:23662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bryce A, Hay AD, Lane IF, Thornton HV,
Wootton M and Costelloe C: Global prevalence of antibiotic
resistance in paediatric urinary tract infections caused by
Escherichia coli and association with routine use of antibiotics in
primary care: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ.
352:i9392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Neupane S, Pant ND, Khatiwada S, Chaudhary
R and Banjara MR: Correlation between biofilm formation and
resistance toward different commonly used antibiotics along with
extended spectrum beta lactamase production in uropathogenic
Escherichia coli isolated from the patients suspected of urinary
tract infections visiting Shree Birendra Hospital, Chhauni,
Kathmandu, Nepal. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 5:52016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moradi J, Hashemi FB and Bahador A:
Antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii in Iran: A
systemic review of the published literature. Osong Public Health
Res Perspect. 6:79–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Khademi F, Poursina F, Hosseini E, Akbari
M and Safaei HG: Helicobacter pylori in Iran: A systematic review
on the antibiotic resistance. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 18:2–7.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee CY, Tsai HC, Lee SS and Chen YS:
Concomitant emphysematous prostatic and periurethral abscesses due
to Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report and review of the
literature. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 45:1099–1106.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Oliva A, Gizzi F, Mascellino MT, Cipolla
A, D'Abramo A, D'Agostino C, Trinchieri V, Russo G, Tierno F,
Iannetta M, et al: Bactericidal and synergistic activity of
double-carbapenem regimen for infections caused by
carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 22:147–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rosen DA, Hilliard JK, Tiemann KM, Todd
EM, Morley SC and Hunstad DA: Klebsiella pneumoniae FimK promotes
virulence in murine pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 213:649–658. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Netikul T and Kiratisin P: Genetic
Characterization of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and the
spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia ST340 at a
university hospital in Thailand. PLoS One. 10:e01391162015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Walker CD and Shankaran S: Extended
antibiotic resistance in carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella
pneumoniae: A case series. Am J Infect Control. 44:1050–1052. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sekowska A, Janicka G, Kłyszejko C, Wojda
M, Wróblewski M and Szymankiewicz M: Resistance of Klebsiella
pneumoniae strains producing and not producing ESBL
(extended-spectrum beta-lactamase) type enzymes to selected
non-beta-lactam antibiotics. Med Sci Monit. 8:BR100–BR104.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sanguinetti CM, De Benedetto F and
Miragliotta G: Bacterial agents of lower respiratory tract
infections (LRTIs), beta-lactamase production, and resistance to
antibiotics in elderly people. DEDALO Study Group. Int J Antimicrob
Agents. 16:467–471. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Boggio SB and Roveri OA: Catalytic
properties of an endogenous beta-lactamase responsible for the
resistance of Azospirillum lipoferum to beta-lactam antibiotics.
Microbiology. 149:445–450. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Uraz G, Simsek H and Celik B:
beta-Lactamase activities and resistance to antibiotics of
Haemophilus influenzae, H. parainfluenzae and H. aphrophilus
strains identified in throat cultures from children. Drug Metabol
Drug Interact. 16:217–228. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Soge OO, Adeniyi BA and Roberts MC: New
antibiotic resistance genes associated with CTX-M plasmids from
uropathogenic Nigerian Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 58:1048–1053. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ikeda Y, Kumagai H, Okazaki H, Fujishiro
M, Motozawa Y, Nomura S, Takeda N, Toko H, Takimoto E, Akazawa H,
et al: Monitoring β-arrestin recruitment via β-lactamase enzyme
fragment complementation: Purification of peptide E as a
low-affinity ligand for mammalian bombesin receptors. PLoS One.
10:e01274452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ramirez MS, Traglia GM, Lin DL, Tran T and
Tolmasky ME: Plasmid-Mediated antibiotic resistance and virulence
in Gram-begatives: The Klebsiella pneumoniae paradigm. Microbiol
Spectr. 2:2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|