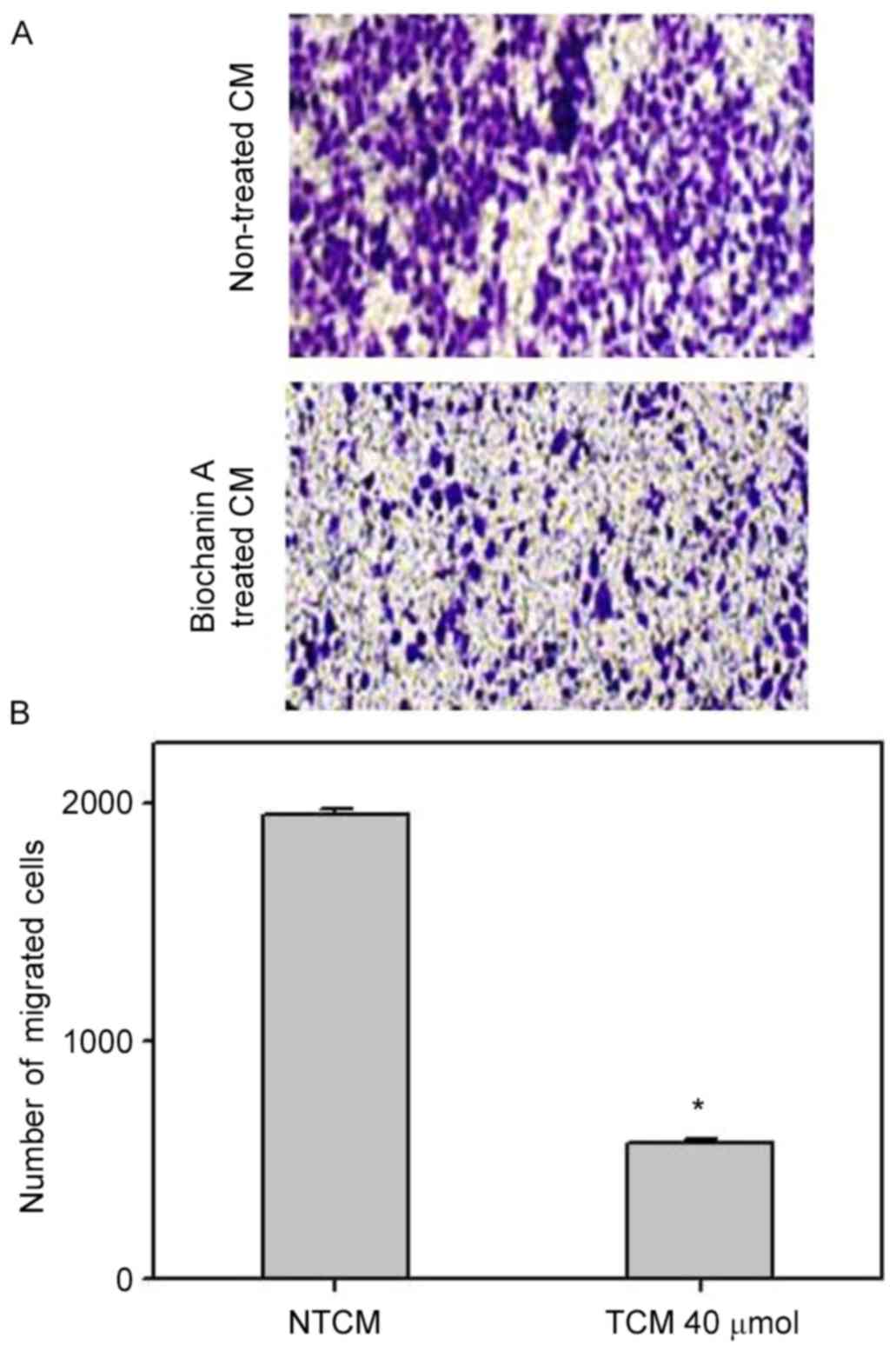
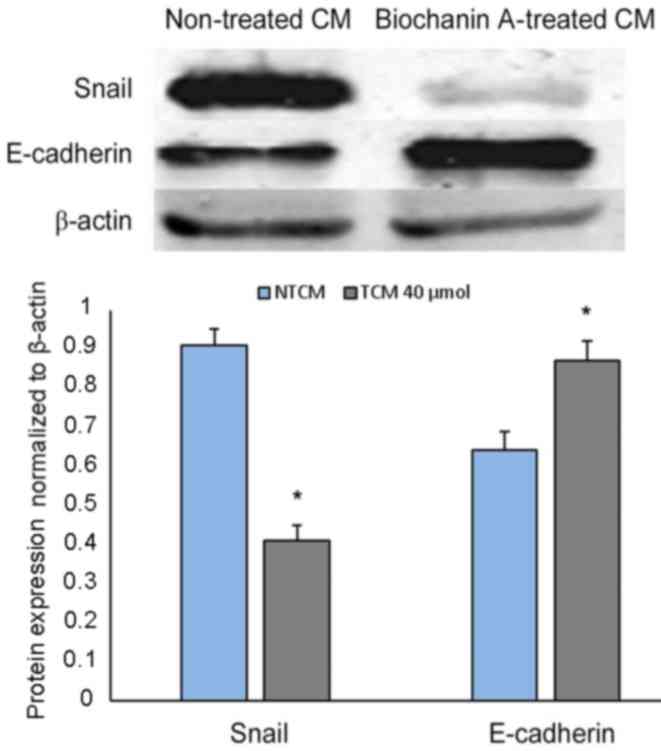
|
1
|
Xu J, Liu X, Zhou S and Wei M: Combination
of immunotherapy with anaerobic bacteria for immune gene therapy of
solid tumours. Gene Ther Mol Biol. 13:36–52. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Bender E: Epidemiology: The dominant
malignancy. Nature. 513:S2–S3. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shibuya K, Mathers CD, Boschi-Pinto C,
Lopez AD and Murray CJ: Global and regional estimates of cancer
mortality and incidence by site: II. Results for the global burden
of disease. BMC Cancer. 2:372002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, Harewood
R, Spika D, Wang XS, Bannon F, Ahn JV, Johnson CJ, Bonaventure A,
et al: Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis
of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279
population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet.
385:977–1010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Denlinger CE, Ikonomidis JS, Reed CE and
Spinale FG: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition: The doorway to
metastasis in human lung cancers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
140:505–513. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and García De Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Casas E, Kim J, Bendesky A, Ohno-Machado
L, Wolfe CJ and Yang J: Snail2 is an essential mediator of
Twist1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and metastasis.
Cancer Res. 71:245–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Graham RE, Gandhi TK, Borus J, Seger AC,
Burdick E, Bates DW, Phillips RS and Weingart SN: Risk of
concurrent use of prescription drugs with herbal and dietary
supplements in ambulatory careAdvances in Patient Safety: New
Directions and Alternative Approaches. 4. Henriksen K, Battles JB,
Keyes MA and Grady ML: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
(US); Rockville, MD: pp. 1–22. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peng CC, Glassman PA, Trilli LE,
Hayes-Hunter J and Good CB: Incidence and severity of potential
drug-dietary supplement interactions in primary care patients: An
exploratory study of 2 outpatient practices. Arch Intern Med.
164:630–636. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rhee SM, Garg VK and Hershey CO: Use of
complementary and alternative medicines by ambulatory patients.
Arch Intern Med. 164:1004–1009. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dergal JM, Gold JL, Laxer DA, Lee MS,
Binns MA, Lanctôt KL, Freedman M and Rochon PA: Potential
interactions between herbal medicines and conventional drug
therapies used by older adults attending a memory clinic. Drugs
Aging. 19:879–886. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Breinholt V, Hossaini A, Svendsen GW,
Brouwer C and Nielsen E: Estrogenic activity of flavonoids in mice.
The importance of estrogen receptor distribution, metabolism and
bioavailability. Food Chem Toxicol. 38:555–564. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang QY, Meng QH, Zhang ZT, Tian ZJ and
Liu H: Synthesis solubility lipids-lowering and liver-protection
activities of sulfonated formononetin. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 44:386–389.
2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kole L, Giri B, Manna SK, Pal B and Ghosh
S: Biochanin-A, an isoflavon, showed antiproliferative and
anti-inflammatory activities through the inhibition of iNOS
expression, p38-MAPK and ATF-2 phosphorylation and blocking NF κB
nuclear translocation. Eur J Pharmacol. 653:8–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Michaelis M, Sithisarn P and Cinatl J Jr:
Effects of flavonoid-induced oxidative stress on anti-H5N1
influenza a virus activity exerted by baicalein and biochanin A.
BMC Res Notes. 7:3842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qiu L, Lin B, Lin Z, Lin YP, Lin M and
Yang X: Biochanin A ameliorates the cytokine secretion profile of
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages by a PPARγ-dependent
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 5:217–222. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen HQ, Jin ZY and Li GH: Biochanin A
protects dopaminergic neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced
damage through inhibition of microglia activation and
proinflammatory factors generation. Neurosci Lett. 417:112–117.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Biradar SM, Joshi H and Chheda TK:
Biochanin-A ameliorates behavioural and neurochemical derangements
in cognitive-deficit mice for the betterment of Alzheimer's
disease. Hum Exp Toxicol. 33:369–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mishra P, Kale RK and Kar A:
Chemoprevention of mammary tumorigenesis and chemomodulation of the
antioxidative enzymes and peroxidative damage in prepubertal
Sprague Dawley rats by Biochanin A. Mol Cell Biochem. 312:1–9.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang S and Morris ME: Effect of the
flavonoids biochanin A and silymarin on the P-glycoprotein-mediated
transport of digoxin and vinblastine in human intestinal Caco-2
cells. Pharm Res. 20:1184–1191. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harini R, Ezhumalai M and Pugalendi KV:
Antihyperglycemic effect of biochanin A, a soy isoflavone, on
streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 676:89–94. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ko WC, Lin LH, Shen HY, Lai CY, Chen CM
and Shih CH: Biochanin A, a phytoestrogenic isoflavone with
selective inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4, suppresses
ovalbumininduced airway hyperresponsiveness. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:6350582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan JW, Tham CL, Israf DA, Lee SH and Kim
MK: Neuroprotective effects of biochanin A against
glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells via apoptosis
inhibition. Neurochem Res. 38:512–518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Breikaa RM, Algandaby MM, El-Demerdash E
and Abdel-Naim AB: Multimechanistic antifibrotic effect of
biochanin a in rats: Implications of proinflammatory and
profibrogenic mediators. PLoS One. 8:e692762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rah B, Amin H, Yousuf K, Khan S, Jamwal G,
Mukherjee D and Goswami A: A novel MMP-2 inhibitor
3-azidowithaferin A (3-azidoWA) abrogates cancer cell invasion and
angiogenesis by modulating extracellular par-4. PLoS One.
7:e440392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiménez-Orozco FA, López-González JS,
Nieto-Rodriguez A, Velasco-Velázquez MA, Molina-Guarneros JA,
Mendoza-Patiño N, García-Mondragón MJ, Elizalde-Galvan P,
León-Cedeño F and Mandoki JJ: Decrease of cyclin D1 in the human
lung adenocarcinoma cell line A-427 by 7-hydroxycoumarin. Lung
Cancer. 34:185–894. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM
and Zhou BP: Stabilization of Snail by NF-kappaB is required for
inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell.
15:416–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
DeNardo DG, Andreu P and Coussens LM:
Interactions between lymphocytes and myeloid cells regulate
pro-versus anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:309–316.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qian BZ and Pollard JW: Macrophage
diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell.
141:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Breikaa RM, Algandaby MM, El-Demerdash E
and Abdel-Naim AB: Multimechanistic antifibrotic effect of
biochanin A in rats: Implications of proinflammatory and
profibrogenic mediators. PLoS One. 16:e692762013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Banjerdpongchai R, Khawon P and Pompimon
W: Phytochemicals from Goniothalamus griffithii Induce Human Cancer
Cell Apoptosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:3281–3287.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shyur LF, Chen CH, Lo CP, Wang SY, Kang
PL, Sun SJ, Chang CA, Tzeng CM and Yang NS: Induction of apoptosis
in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by phytochemicals from
Anoectochilus formosanus. J Biomed Sci. 11:928–939. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Torisu H, Ono M, Kiryu H, Furue M, Ohmoto
Y, Nakayama J, Nishioka Y, Sone S and Kuwano M: Macrophage
infiltration correlates with tumor stage and angiogenesis in human
malignant melanoma: Possible involvement of TNFa and IL-1alpha. Int
J Cancer. 85:182–188. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rayburn ER, Scharri SJ and Zhang R:
Anti-inflammatory agents for cancer therapy. Mol Cell Pharmacol.
1:29–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ricchi P, Zarrilli R, Di Palma A and
Acquaviva AM: Anti-inflammatory drugs in colorectal cancer: From
prevention to therapy. Br J Cancer. 88:803–807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM
and Zhou BP: Stabilization of Snail by NF-kappaB is required for
inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell.
15:416–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|