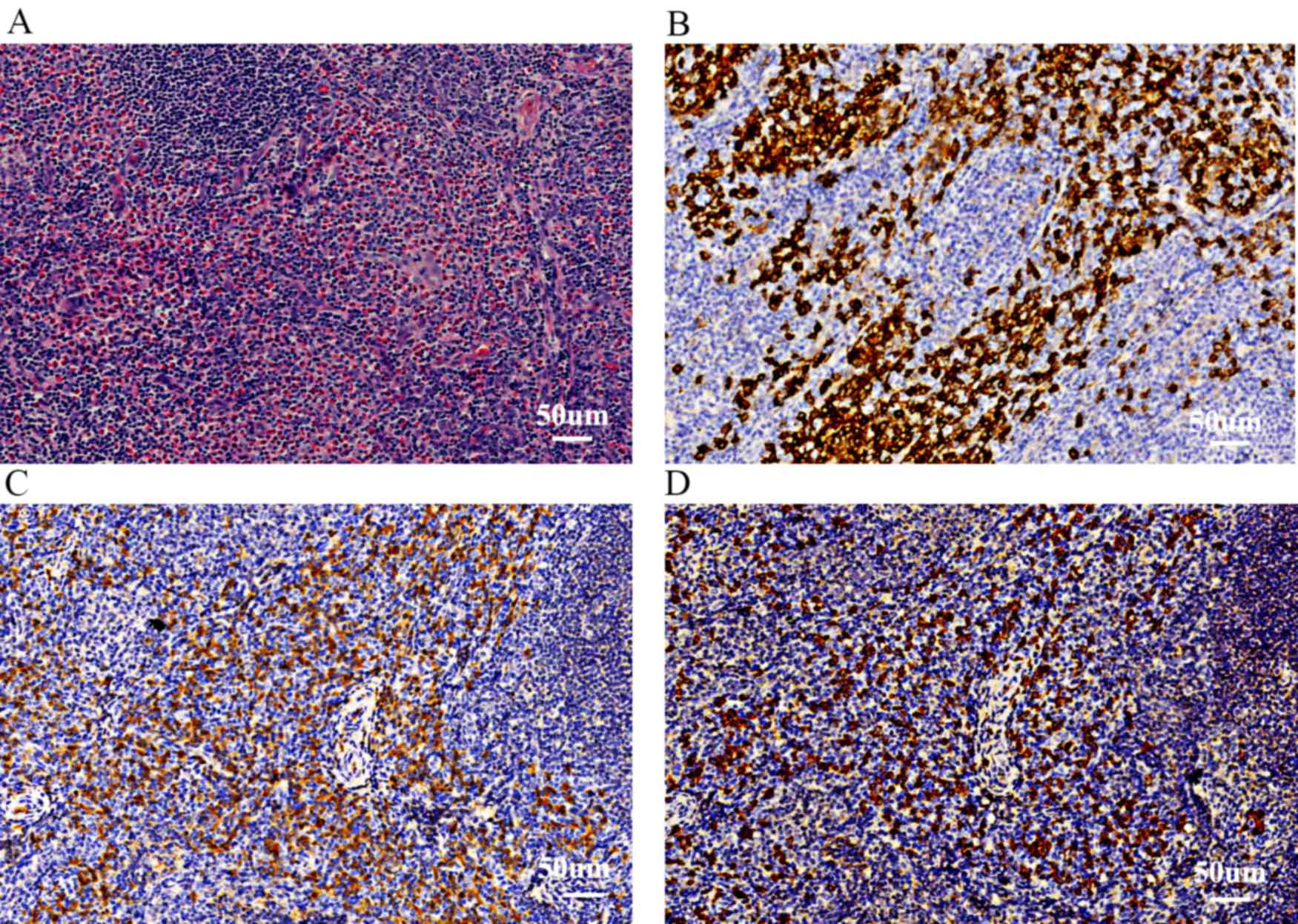
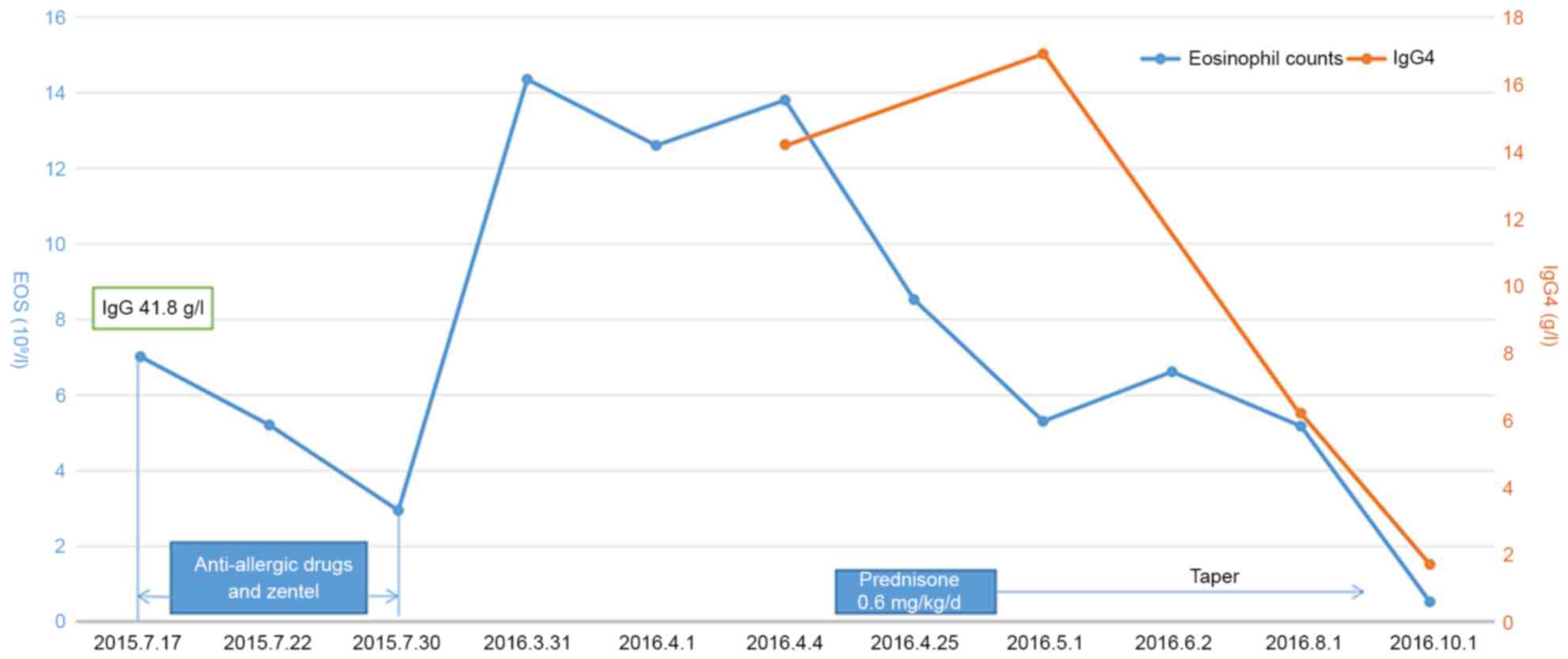
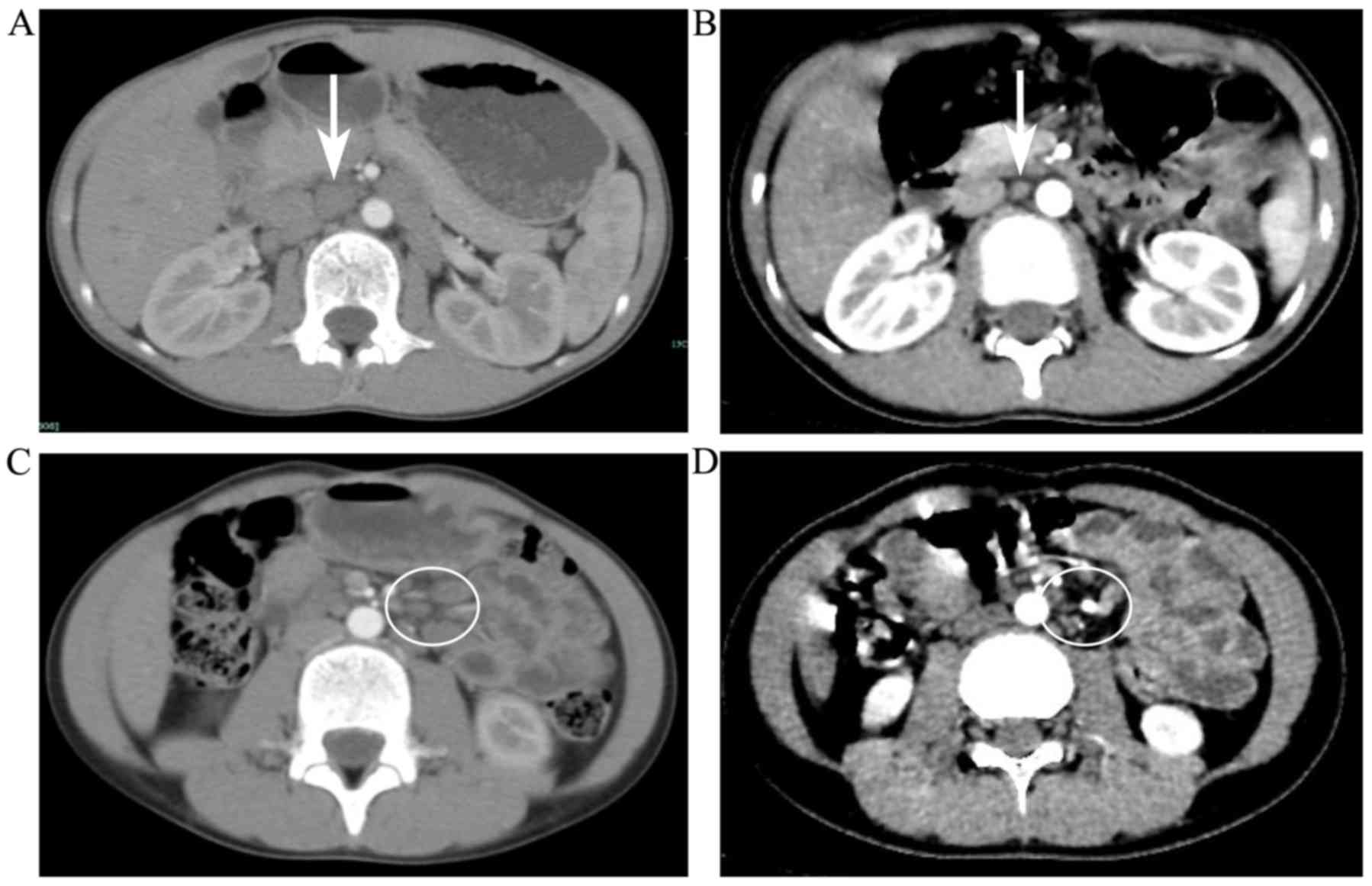
|
1
|
Tefferi A, Gotlib J and Pardanani A:
Hypereosinophilic syndrome and clonal eosinophilia: Point-of-care
diagnostic algorithm and treatment update. Mayo Clinic Proc. 85:pp.
158–164. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Crane MM, Chang CM, Kobayashi MG and
Weller PF: Incidence of myeloproliferative hypereosinophilic
syndrome in the United States and an estimate of all
hypereosinophilic syndrome incidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
126:179–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tefferi A, Patnaik MM and Pardanani A:
Eosinophilia: Secondary, clonal and idiopathic. Br J Haematol.
133:468–492. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ganeva M, Gancheva T, Lazarova R, Troeva
J, Baldaranov I, Vassilev I, Hristakieva E and Tzaneva V:
Carbamazepine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic
symptoms (DRESS) syndrome: Report of four cases and brief review.
Int J Dermatol. 47:853–860. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gotlib J: World Health
Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2014 update on
diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol.
89:325–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vardiman JW: The World Health Organization
(WHO) classification of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid
tissues: An overview with emphasis on the myeloid neoplasms. Chem
Biol Interact. 184:16–20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schaller JL and Burkland GA: Case report:
Rapid and complete control of idiopathic hypereosinophilia with
imatinib mesylate. MedGenMed. 3:92001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheah CY, Burbury K, Apperley JF, Huguet
F, Pitini V, Gardembas M, Ross DM, Forrest D, Genet P, Rousselot P,
et al: Patients with myeloid malignancies bearing PDGFRB fusion
genes achieve durable long-term remissions with imatinib. Blood.
123:3574–3577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ogbogu PU, Bochner BS, Butterfield JH,
Gleich GJ, Huss-Marp J, Kahn JE, Leiferman KM, Nutman TB, Pfab F,
Ring J, et al: Hypereosinophilic syndromes: A multicenter,
retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to
therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 124:1319–1325.e3. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fauci AS, Harley JB, Roberts WC, Ferrans
VJ, Gralnick HR and Bjornson BH: NIH conference. The idiopathic
hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clinical, pathophysiologic, and
therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 97:78–92. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quiquandon I, Claisse JF, Capiod JC,
Delobel J and Prin L: alpha-Interferon and hypereosinophilic
syndrome with trisomy 8: Karyotypic remission. Blood. 85:2284–2285.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cofrancesco E, Cortellaro M, Pogliani E,
Boschetti C, Salvatore M and Polli EE: Response to vincristine
treatment in a case of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome with
multiple clinical manifestations. Acta Haematol. 72:21–25. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M,
Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Sumida T, Mimori T, Tanaka Y, et al:
A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): General
concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 22:1–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stone JH, Brito-Zerón P, Bosch X and
Ramos-Casals M: Diagnostic approach to the complexity of
IgG4-related disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 90:pp. 927–939. 2015;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friedrichs K, Gluba S, Eidtmann H and
Jonat W: Overexpression of p53 and prognosis in breast cancer.
Cancer. 72:3641–3647. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M,
Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Yoshino T, Nakamura S, Kawa S, et
al: Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease
(IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 22:21–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jingzhi S, Lifang Z and Meiyun F:
IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: A case report. Zhong hua shi yong nei
ke za zhi. 08:721–723. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Sato Y and Yoshino T: IgG4-related
lymphadenopathy. Int J Rheumatol. 2012:5725392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K, Morito T,
Mizobuchi K, Tanaka T, Inoue D, Shiomi H, Iwao H and Yoshino T:
Multicentric Castleman's disease with abundant IgG4-positive cells:
A clinical and pathological analysis of six cases. J Clin Pathol.
63:1084–1089. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sato Y, Notohara K, Kojima M, Takata K,
Masaki Y and Yoshino T: IgG4-related disease: Historical overview
and pathology of hematological disorders. Pathol Int. 60:247–258.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stone JH, Zen Y and Deshpande V:
IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 366:539–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M,
Mahajan VS, Della Torre E, Lee H, Kulikova M, Deshpande V, Pillai S
and Stone JH: Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease,
independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis.
74:190–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frizzera G, Peterson BA, Bayrd ED and
Goldman A: A systemic lymphoproliferative disorder with morphologic
features of Castleman's disease: Clinical findings and
clinicopathologic correlations in 15 patients. J Clin Oncol.
3:1202–1216. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, Kitagawa K,
Morikawa Y, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y, Imai K, Saeki T,
et al: Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan
lymphoproliferative syndrome: Analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related
disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1310–1315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sato Y, Kojima MK, Takata K, Morito T,
Asaoku H, Takeuchi T, Mizobuchi K, Fujihara M, Kuraoka K, Nakai T,
et al: Systemic IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: A clinical and
pathologic comparison to multicentric Castleman's disease. Mod
Pathol. 22:589–599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yokoyama A: Interleukin-6 (IL-6)/soluble
IL-6 receptor. Nippon Rinsho Japanese J Clin Med. 63 Suppl
8:S72–S74. 2005.
|
|
27
|
Nakamura M, Iwamoto O, Chino T, Todoroki K
and Kusukawa J: Diagnostic dilemma of IgG4-related primary
localized cervical lymphadenopathy associated with aberrant IL-6
expression level. Diagn Pathol. 11:432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S and Stone JH:
IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 385:1460–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bain BJ, Gilliland DG, Vardiman JW and
Horny HP: Chronic eosinophilic leukaemia, not otherwise specified.
2008.
|
|
30
|
Batu ED, Arici ZS, Orhan D, Kiratli H and
Özen S: Immunoglobulin G4-related orbital disease: Report of two
pediatric cases. Clin Exp Rheum. 33:409–410. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Caso F, Fiocco U, Costa L, Sfriso P, Punzi
L and Doria A: Successful use of rituximab in a young patient with
immunoglobulin G4-related disease and refractory scleritis. Joint
Bone Spine. 81:190–192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Corujeira S, Ferraz C, Nunes T, Fonseca E
and Vaz LG: Severe IgG4-related disease in a young child: A
diagnosis challenge. Case Rep Pediatr. 2015:1407532015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gillispie MC, Thomas RD and Hennon TR:
Successful treatment of IgG-4 related sclerosing disease with
rituximab: A novel case report. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 33:549–550.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Griepentrog GJ, Vickers RW, Karesh JW,
Azari AA, Albert DM and Bukat CN: A clinicopathologic case study of
two patients with pediatric orbital IgG4-related disease. Orbit.
32:389–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hasosah MY, Satti MB, Yousef YA, Alzahrani
DM, Almutairi SA, Alsahafi AF, Sukkar GA and Alzaben AA:
IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis in a 7-year-old Saudi girl.
Saudi J Gastroenterol. 20:385–388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jariwala MP, Agarwal M, Mulay K and
Sawhney S: IgG4-related orbital inflammation presenting as
unilateral pseudotumor. Indian J Pediatr. 81:1108–1110. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kalapesi FB, Garrott HM, Moldovan C,
Williams M, Ramanan A and Herbert HM: IgG4 orbital inflammation in
a 5-year-old child presenting as an orbital mass. Orbit.
32:137–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mannion M and Cron RQ: Successful
treatment of pediatric IgG4 related systemic disease with
mycophenolate mofetil: Case report and a review of the pediatric
autoimmune pancreatitis literature. Pediatr Rheum Online J.
9:12011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Miglani RK, Murthy D, Bhat R and Kumar AK:
Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis mimicking
cholangiocarcinoma in a young boy. J Postgrad Med. 56:140–142.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mittal R, Ganguly A, Rath S, Das B and
Mishra A: IgG4-related orbital inflammation presenting as bilateral
proptosis in a child. Eye (Lond). 28:1264–1266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nada R, Gupta A, Kang M, Rawat A, Sood A,
Ahluwalia J and Singh S: Hepatic mass and coagulopathy in a
ten-year-old boy with fever. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:19772015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Naghibi M, Ahmed Aal Badri AM, Bateman AC,
Shepherd HA and Gordon JN: The successful treatment of
IgG4-positive colitis with adalimumab in a patient with
IgG4-related sclerosing disease-a new subtype of aggressive
colitis? J Crohns Colitis. 7:e81–e84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pasic S, Ristic G and Djuricic S:
PReS-FINAL-2276: IgG4 related disease in a 10-year-old girl.
Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 11 Suppl 2:P2662013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Prabhu SM, Yadav V, Irodi A, Mani S and
Varghese AM: IgG4-related disease with sinonasal involvement: A
case series. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 24:117–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sane M, Chelnis J, Kozielski R and
Fasiuddin A: Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease with
orbital inflammation in a 12-year-old girl. J AAPOS. 17:548–550.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zakeri H and Kashi Z: Variable clinical
presentations of Riedel's thyroiditis: Report of two cases. Case
Rep Med. 2011:7092642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ibrahim SH, Zhang L and Freese DK: A
3-year-old with immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis. J Pediatr
Gastroenterol Nutr. 53:109–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Melo JC, Kitsko D and Reyes-Múgica M:
Pediatric chronic sclerosing sialadenitis: Küttner tumor. Pediatr
Dev Pathol. 15:165–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Notz G, Intili A and Bilyk JR:
IgG4-related dacryoadenitis in a 13-year-old girl. Ophthal Plast
Reconstr Surg. 30:e161–e163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pifferi M, Di Cicco M, Bush A, Caramella
D, Chilosi M and Boner AL: Uncommon pulmonary presentation of
IgG4-related disease in a 15-year-old boy. Chest. 144:669–671.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rosen D, Thung S, Sheflin-Findling S, Lai
J, Rosen A, Arnon R and Chu J: IgG4-sclerosing cholangitis in a
pediatric patient. Semin Liver Dis. 35:89–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Karim F, Loeffen J, Bramer W, Westenberg
L, Verdijk R, van Hagen M and van Laar J: IgG4-related disease: A
systematic review of this unrecognized disease in pediatrics.
Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 14:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Islam AD, Selmi C, Datta-Mitra A, Sonu R,
Chen M, Gershwin ME and Raychaudhuri SP: The changing faces of
IgG4-related disease: Clinical manifestations and pathogenesis.
Autoimmun Rev. 14:914–922. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pieringer H, Parzer I, Wöhrer A, Reis P,
Oppl B and Zwerina J: IgG4-related disease: An orphan disease with
many faces. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 9:1102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tavil B, Aytaç S, Unal S, Kuskonmaz B,
Gumruk F and Cetin M: Hypereosinophilic syndrome: Hacettepe
experience. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 38:539–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Alfaham MA, Ferguson SD, Sihra B, et al:
The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Arch Dermatol.
132:583–585. 2001.
|
|
57
|
Williams K, Ware JA, Abiodun A,
Holland-Thomas NC, Khoury P and Klion AD: Hypereosinophilia in
children and adults: A retrospective comparison. J Allergy Clin
Immunol Pract. 4:941–947.e1. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nagamura N, Ueno S, Fujishiro H and Oonuma
H: Hepatitis associated with hypereosinophilia suspected to be
caused by HES that also presented with the pathological features of
IgG4-related disease. Intern Med. 53:145–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nagao Y, Yamanaka H and Harada H: A
patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome that manifested with
acquired hemophilia and elevated IgG4: A case report. J Med Case
Rep. 6:632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Aoyama T, Matsumoto T, Uchiyama A, Kon K,
Yamashina S, Suzuki S, Ikejima K, Yao T, Kuwatsuru R and Watanabe
S: Recurrent severe acute hepatitis caused by hypereosinophilic
syndrome associated with elevated serum immunoglobulin G4 levels.
Clin J Gastroenterol. 7:516–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Clayton F, Fang JC, Gleich GJ, Lucendo AJ,
Olalla JM, Vinson LA, Lowichik A, Chen X, Emerson L, Cox K, et al:
Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults is associated with IgG4 and not
mediated by IgE. Gastroenterology. 147:602–609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mattoo H, Della-Torre E, Mahajan VS, Stone
JH and Pillai S: Circulating Th2 memory cells in IgG4-related
disease are restricted to a defined subset of subjects with atopy.
Allergy. 69:399–402. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, Kawano M, Yamada
K, Takahira M and Nakanuma Y: Th2 and regulatory immune reactions
are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis
and cholangitis. Hepatology. 45:1538–1546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake
K, Hayashida JN, Maehara T, Shinozaki S, Kubo Y and Nakamura S: Th2
and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and
the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthr Rheum. 64:254–263. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Ohana M, Nakase H,
Uose S, Inai M, Matsushima Y, Katamura K, Ohmori K and Chiba T:
Autoimmune-related pancreatitis is associated with autoantibodies
and a Th1/Th2-type cellular immune response. Gastroenterology.
118:573–581. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Della Torre E, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS,
Carruthers M, Pillai S and Stone JH: Prevalence of atopy,
eosinophilia, and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy.
69:269–272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tsuboi H, Matsuo N, Iizuka M, Tsuzuki S,
Kondo Y, Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Matsumoto I, Nakamura S and Sumida
T: Analysis of IgG4 class switch-related molecules in IgG4-related
disease. Arthr Res Ther. 14:R1712012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Nakashima H, Miyake K, Moriyama M, Tanaka
A, Watanabe M, Abe Y, Sato H, Nakamura S and Saito T: An
amplification of IL-10 and TGF-beta in patients with IgG4-related
tubulointerstitial nephritis. Clin Nephrol. 73:385–391. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tabata T, Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Egawa N,
Setoguchi K, Tsuruta K, Obayashi T and Sasaki T: Serial changes of
elevated serum IgG4 levels in IgG4-related systemic disease. Intern
Med. 50:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|