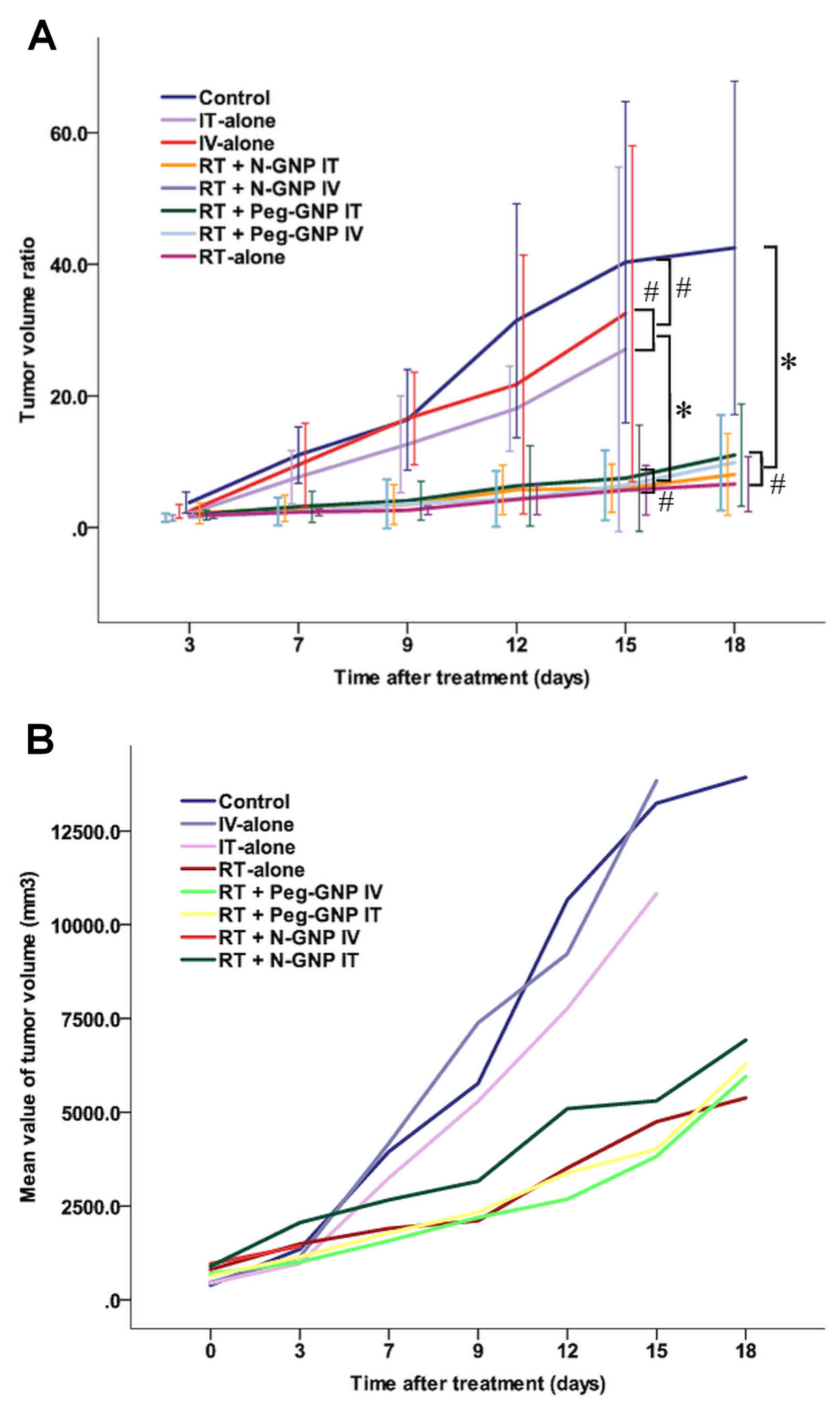
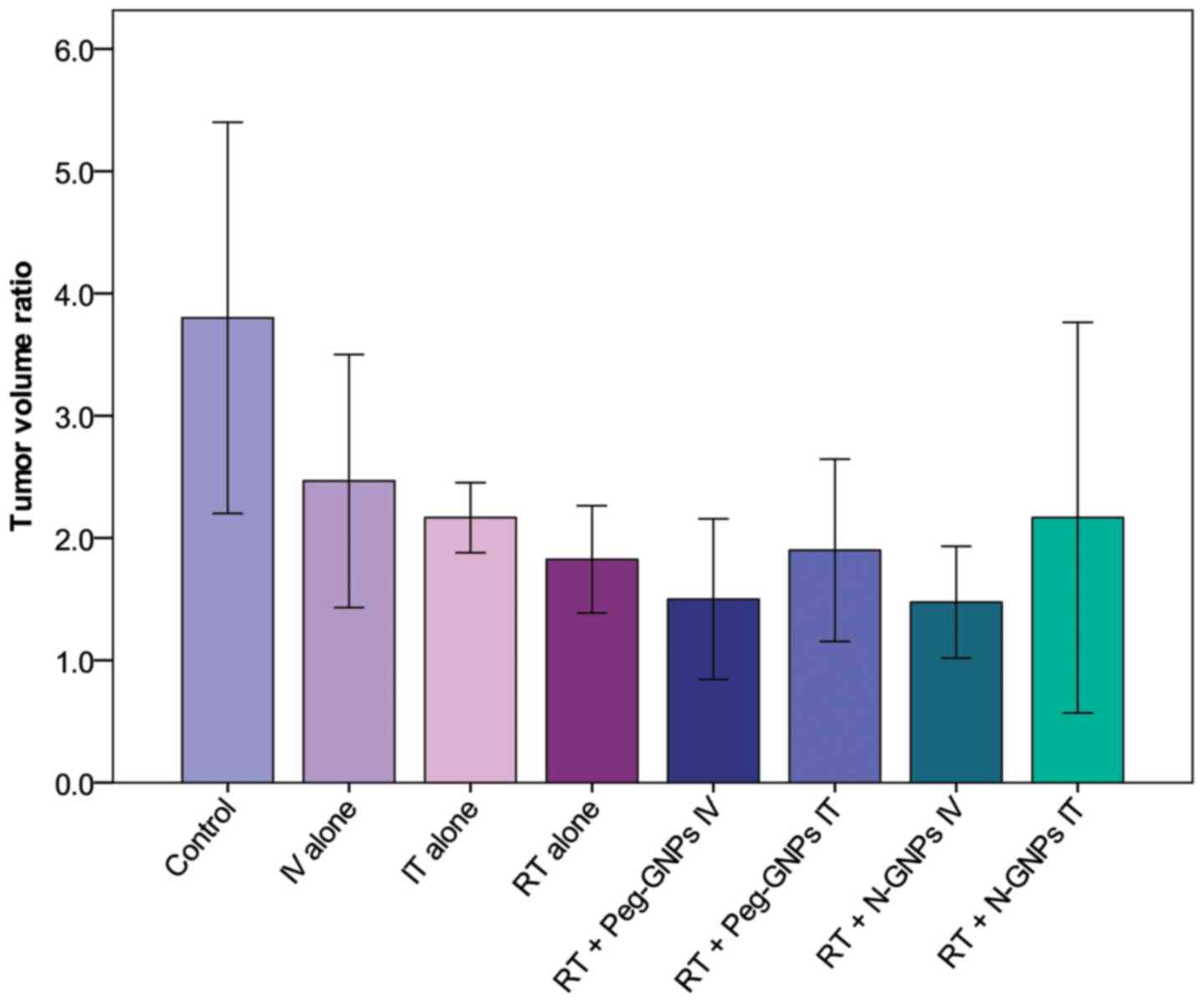
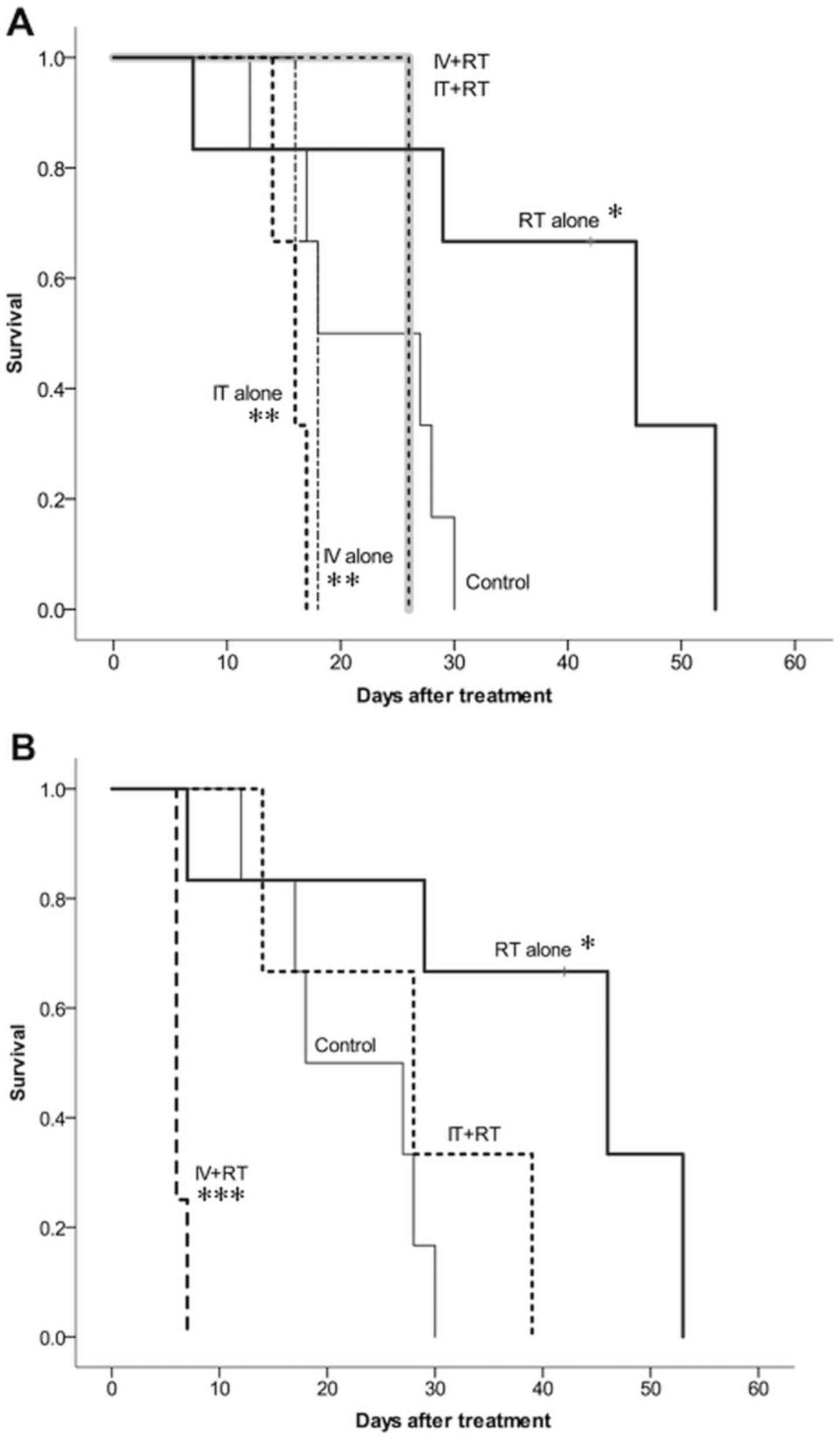
|
1
|
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN and Smilowitz HM:
The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys
Med Biol. 49:N309–N315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hainfeld JF, Dilmanian FA, Slatkin DN and
Smilowitz HM: Radiotherapy enhancement with gold nanoparticles. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 60:977–985. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mesbahi A: A review on gold nanoparticles
radiosensitization effect in radiation therapy of cancer. Rep Pract
Oncol Radiother. 15:176–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jain S, Hirst DG and O'Sullivan JM: Gold
nanoparticles as novel agents for cancer therapy. Br J Radiol.
85:101–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cooper DR, Bekah D and Nadeau JL: Gold
nanoparticles and their alternatives for radiation therapy
enhancement. Front Chem. 2:862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Babaei M and Ganjalikhani M: The potential
effectiveness of nanoparticles as radio sensitizers for
radiotherapy. Bioimpacts. 4:15–20. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rahman WN, Bishara N, Ackerly T, He CF,
Jackson P, Wong C, Davidson R and Geso M: Enhancement of radiation
effects by gold nanoparticles for superficial radiation therapy.
Nanomedicine. 5:136–142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamada M, Foote M and Prow TW: Therapeutic
gold, silver and platinum nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 7:428–445. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang AZ, Langer R and Farokhzad OC:
Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs. Annu Rev Med. 63:185–198.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Herold DM, Das IJ, Stobbe CC, Iyer RV and
Chapman JD: Gold microspheres: A selective technique for producing
biologically effective dose enhancement. Int J Radiat Biol.
76:1357–1364. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coulter JA, Jain S, Butterworth KT,
Taggart LE, Dickson GR, McMahon SJ, Hyland WB, Muir MF, Trainor C,
Hounsell AR, et al: Cell type-dependent uptake, localization, and
cytotoxicity of 1.9 nm gold nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine.
7:2673–2685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jain S, Coulter JA, Hounsell AR,
Butterworth KT, McMahon SJ, Hyland WB, Muir MF, Dickson GR, Prise
KM, Currell FJ, et al: Cell-specific radiosensitization by gold
nanoparticles at megavoltage radiation energies. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 79:531–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chang MY, Shiau AL, Chen YH, Chang CJ,
Chen HH and Wu CL: Increased apoptotic potential and dose-enhancing
effect of gold nanoparticles in combination with single-dose
clinical electron beams on tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Sci.
99:1479–1484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mousavie Anijdan SH, Mahdavi SR, Shirazi
A, Zarrinfard MA and Hajati J: Megavoltage X-ray dose enhancement
with gold nanoparticles in tumor bearing mice. Int J Mol Cell Med.
2:118–123. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang XD, Wu D, Shen X, Chen J, Sun YM,
Liu PX and Liang XJ: Size-dependent radiosensitization of
PEG-coated gold nanoparticles for cancer radiation therapy.
Biomaterials. 33:6408–6419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Joh DY, Sun L, Stangl M, Al Zaki A, Murty
S, Santoiemma PP, Davis JJ, Baumann BC, Alonso-Basanta M, Bhang D,
et al: Selective targeting of brain tumors with gold
nanoparticle-induced radiosensitization. PLoS One. 8:e624252013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hainfeld JF, Smilowitz HM, O'Connor MJ,
Dilmanian FA and Slatkin DN: Gold nanoparticle imaging and
radiotherapy of brain tumors in mice. Nanomedicine (Lond).
8:1601–1609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang M and Thanou M: Targeting
nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol Res. 62:90–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brun E, Sanche L and Sicard-Roselli C:
Parameters governing gold nanoparticle X-ray radiosensitization of
DNA in solution. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 72:128–134. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vecchio G, Galeone A, Brunetti V, Maiorano
G, Sabella S, Cingolani R and Pompa PP: Concentration-dependent,
size-independent toxicity of citrate capped AuNPs in Drosophila
melanogaster. PLoS One. 7:e299802012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi SY, Jeong S, Jang SH, Park J, Park
JH, Ock KS, Lee SY and Joo SW: in vitro toxicity of serum
protein-adsorbed citrate-reduced gold nanoparticles in human lung
adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 26:229–237. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Noël C, Simard JC and Girard D: Gold
nanoparticles induce apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress events
and cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins in human neutrophils. Toxicol
In Vitro. 31:12–22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Butterworth KT, Coulter JA, Jain S, Forker
J, McMahon SJ, Schettino G, Prise KM, Currell FJ and Hirst DG:
Evaluation of cytotoxicity and radiation enhancement using 1.9 nm
gold particles: Potential application for cancer therapy.
Nanotechnology. 21:2951012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|