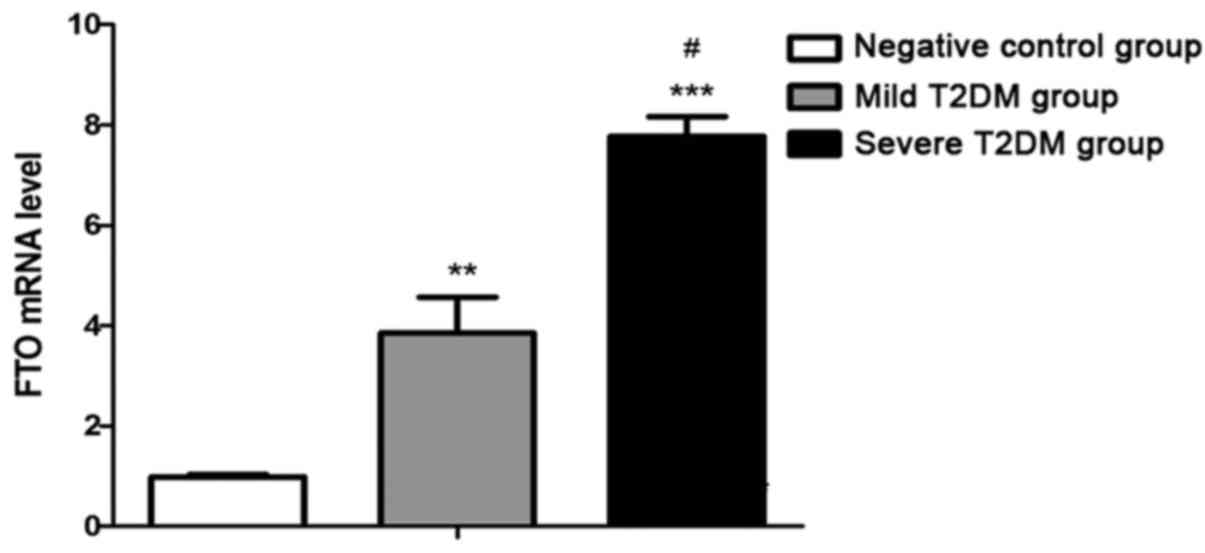
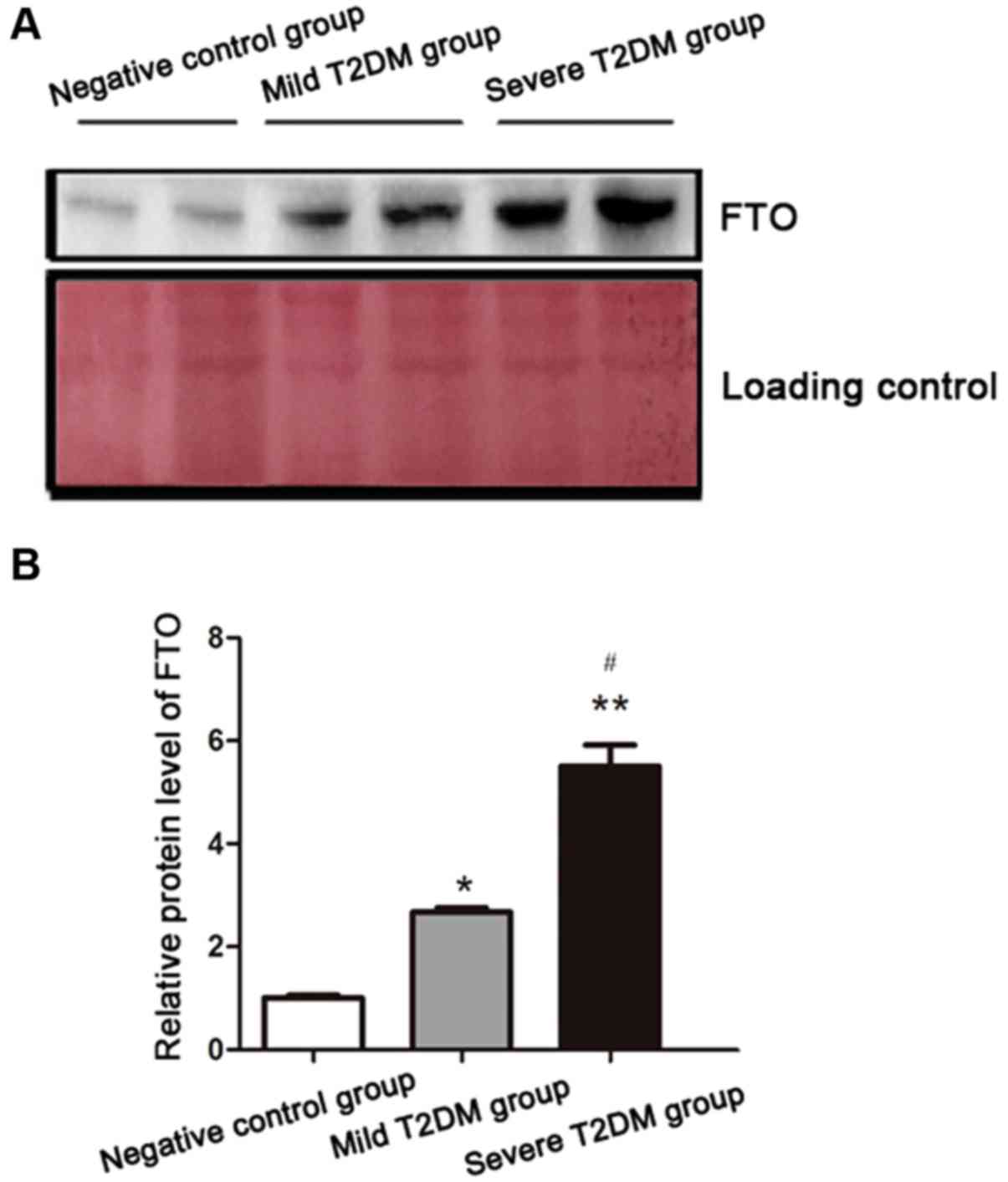
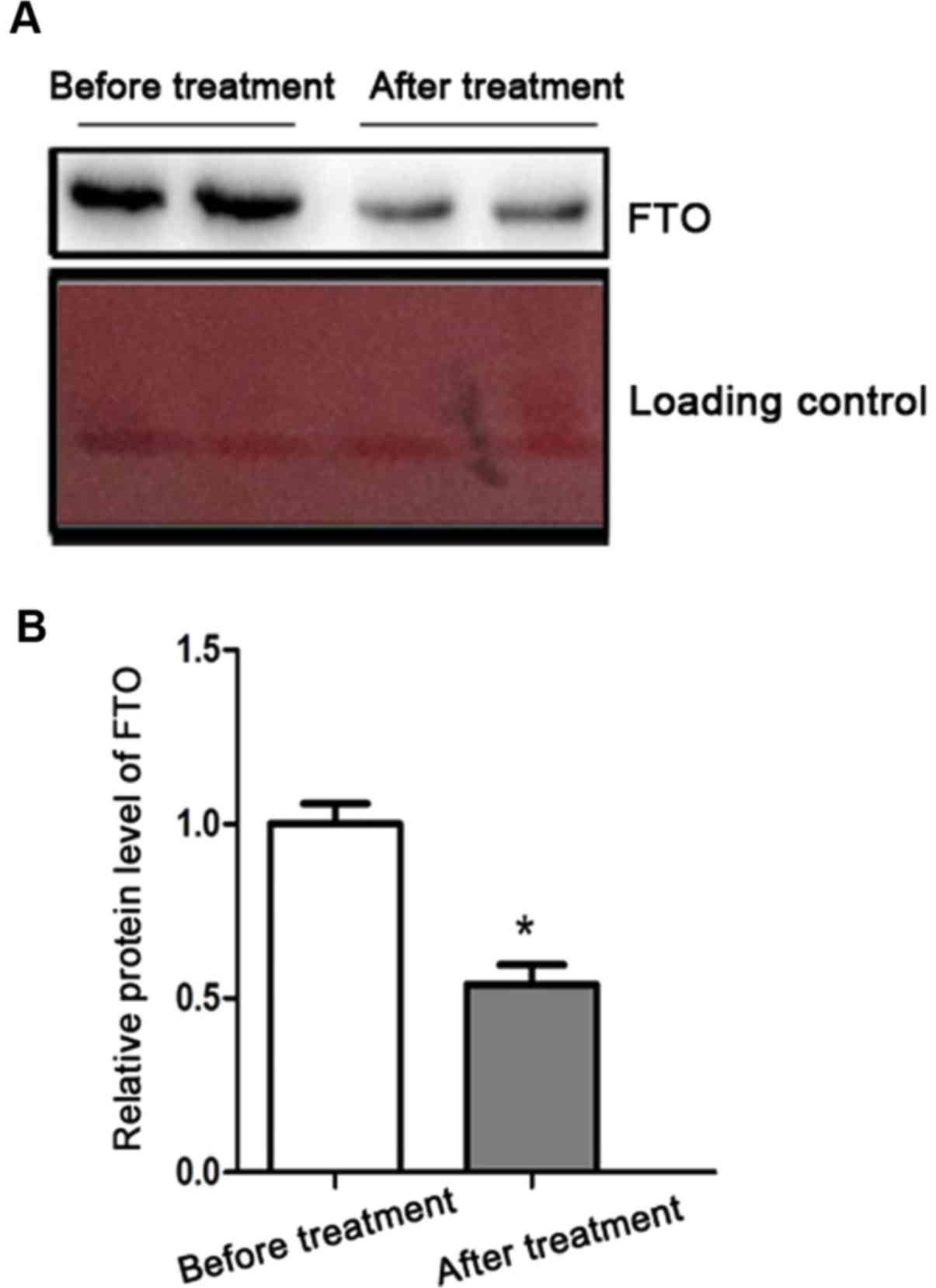
|
1
|
Dandona P, Aljada A and Bandyopadhyay A:
Inflammation: The link between insulin resistance, obesity and
diabetes. Trends Immunol. 25:4–7. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sheehan MT: Current therapeutic options in
type 2 diabetes mellitus: A practical approach. Clin Med Res.
1:189–200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ballantyne GH, Gumbs A and Modlin IM:
Changes in insulin resistance following bariatric surgery and the
adipoinsular axis: Role of the adipocytokines, leptin, adiponectin
and resistin. Obes Surg. 15:692–699. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Imamura M and Maeda S: Genetics of type 2
diabetes: The GWAS era and future perspectives (Review). Endocr J.
58:723–739. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Loos RJ and Yeo GS: The bigger picture of
FTO: The first GWAS-identified obesity gene. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
10:51–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Claussnitzer M, Dankel SN, Kim KH, Quon G,
Meuleman W, Haugen C, Glunk V, Sousa IS, Beaudry JL, Puviindran V,
et al: FTO obesity variant circuitry and adipocyte browning in
humans. N Engl J Med. 373:895–907. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hinney A, Nguyen TT, Scherag A, Friedel S,
Brönner G, Müller TD, Grallert H, Illig T, Wichmann HE, Rief W, et
al: Genome wide association (GWA) study for early onset extreme
obesity supports the role of fat mass and obesity associated gene
(FTO) variants. PLoS One. 2:e13612007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Mei H, Chen W, Jiang Y, Sun W, Li
F, Fu Q and Jiang F: Study of eight GWAS-identified common variants
for association with obesity-related indices in Chinese children at
puberty. Int J Obes. 36:542–547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Abarin T, Yan Wu Y, Warrington N, Lye S,
Pennell C and Briollais L: The impact of breastfeeding on
FTO-related BMI growth trajectories: An application to the Raine
pregnancy cohort study. Int J Epidemiol. 41:1650–1660. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kunji ER, Aleksandrova A, King MS, Majd H,
Ashton VL, Cerson E, Springett R, Kibalchenko M, Tavoulari S,
Crichton PG, et al: The transport mechanism of the mitochondrial
ADP/ATP carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:2379–2393. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rydén L, Standl E, Bartnik M, Van den
Berghe G, Betteridge J, de Boer MJ, Cosentino F, Jönsson B, Laakso
M, Malmberg K, et al Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular
Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), ; European
Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), : Guidelines on
diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: Executive
summary. Eur Heart J. 28:88–136. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ribola FA, Cançado FB, Schoueri JH, De
Toni VF, Medeiros VH and Feder D: Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on
weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:199–211. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szulinska M, Gibas-Dorna M,
Miller-Kasprzak E, Suliburska J, Miczke A, Walczak-Gałezewska M,
Stelmach-Mardas M, Walkowiak J and Bogdanski P: Spirulina maxima
improves insulin sensitivity, lipid profile, and total antioxidant
status in obese patients with well-treated hypertension: A
randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:2473–2481. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miyazaki Y, Mahankali A and Matsuda M:
Effect of pioglitazone on abdominal fat distribution and insulin
sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Diabetes. 5:2992000.
|
|
15
|
Bhat A, Koul A, Rai E, Sharma S, Dhar MK
and Bamezai RN: PGC-1α Thr394Thr and Gly482Ser variants are
significantly associated with T2DM in two North Indian populations:
A replicate case-control study. Hum Genet. 121:609–614. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Freathy RM, Timpson NJ, Lawlor DA, Pouta
A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Ruokonen A, Ebrahim S, Shields B, Zeggini E,
Weedon MN, et al: Common variation in the FTO gene alters
diabetes-related metabolic traits to the extent expected given its
effect on BMI. Diabetes. 57:1419–1426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung YC, Webby CJ,
Saudek V, Hewitson KS, Yeo GS, McDonough MA, Cunliffe S, McNeill
LA, et al: The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a
2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science.
318:1469–1472. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo J, Ren W, Li A, Ding Y, Guo W, Su D,
Hu C, Xu K, Chen H, Xu X, et al: Fat mass and obesity-associated
gene enhances oxidative stress and lipogenesis in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 58:1004–1009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Robertson RP, Harmon J, Tran PO, Tanaka Y
and Takahashi H: Glucose toxicity in β-cells: Type 2 diabetes, good
radicals gone bad, and the glutathione connection. Diabetes.
52:581–587. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kajimoto Y and Kaneto H: Role of oxidative
stress in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1011:168–176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Speakman JR, Rance KA and Johnstone AM:
Polymorphisms of the FTO gene are associated with variation in
energy intake, but not energy expenditure. Obesity (Silver Spring).
16:1961–1965. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wåhlén K, Sjölin E and Hoffstedt J: The
common rs9939609 gene variant of the fat mass- and
obesity-associated gene FTO is related to fat cell lipolysis. J
Lipid Res. 49:607–611. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|