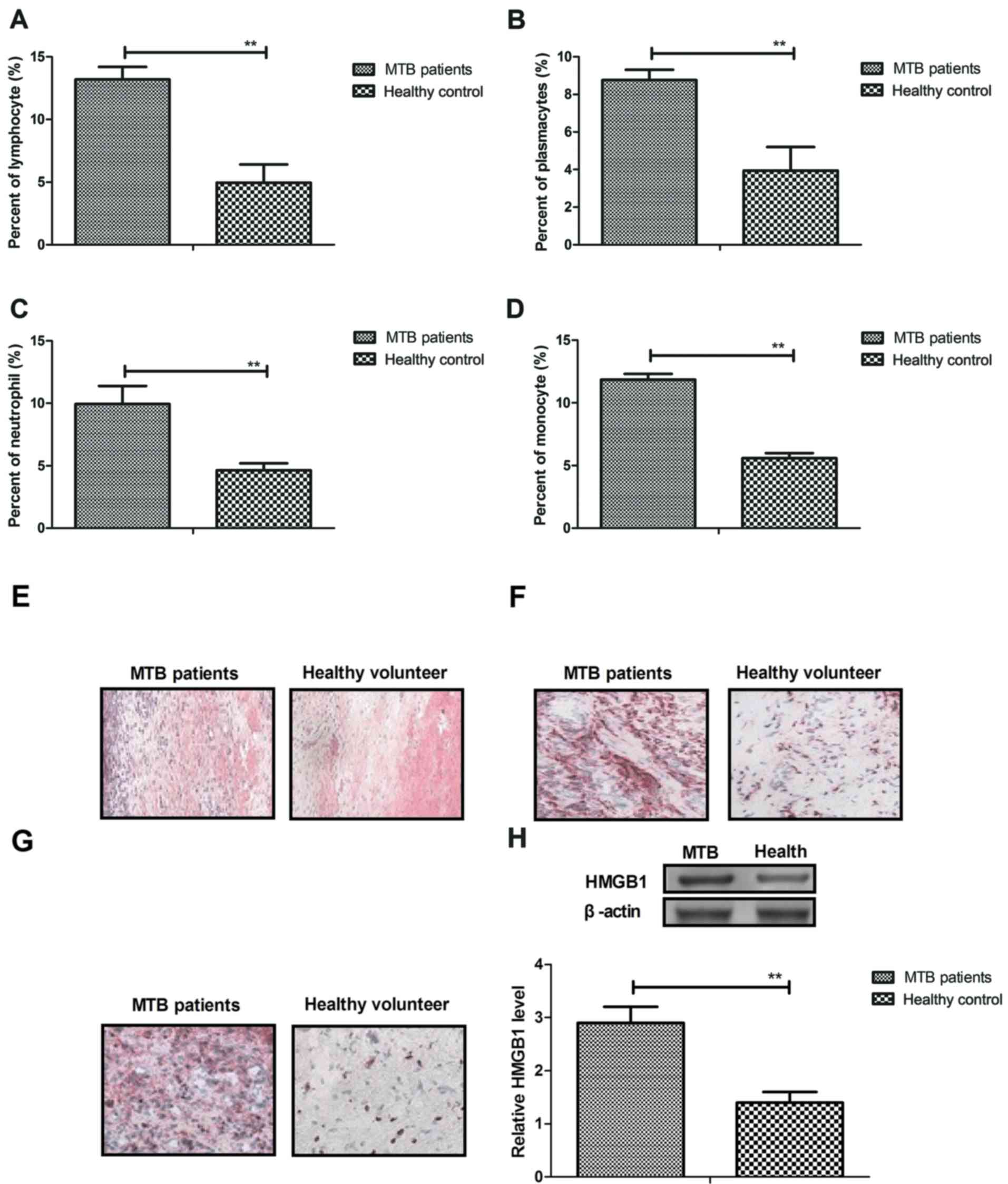
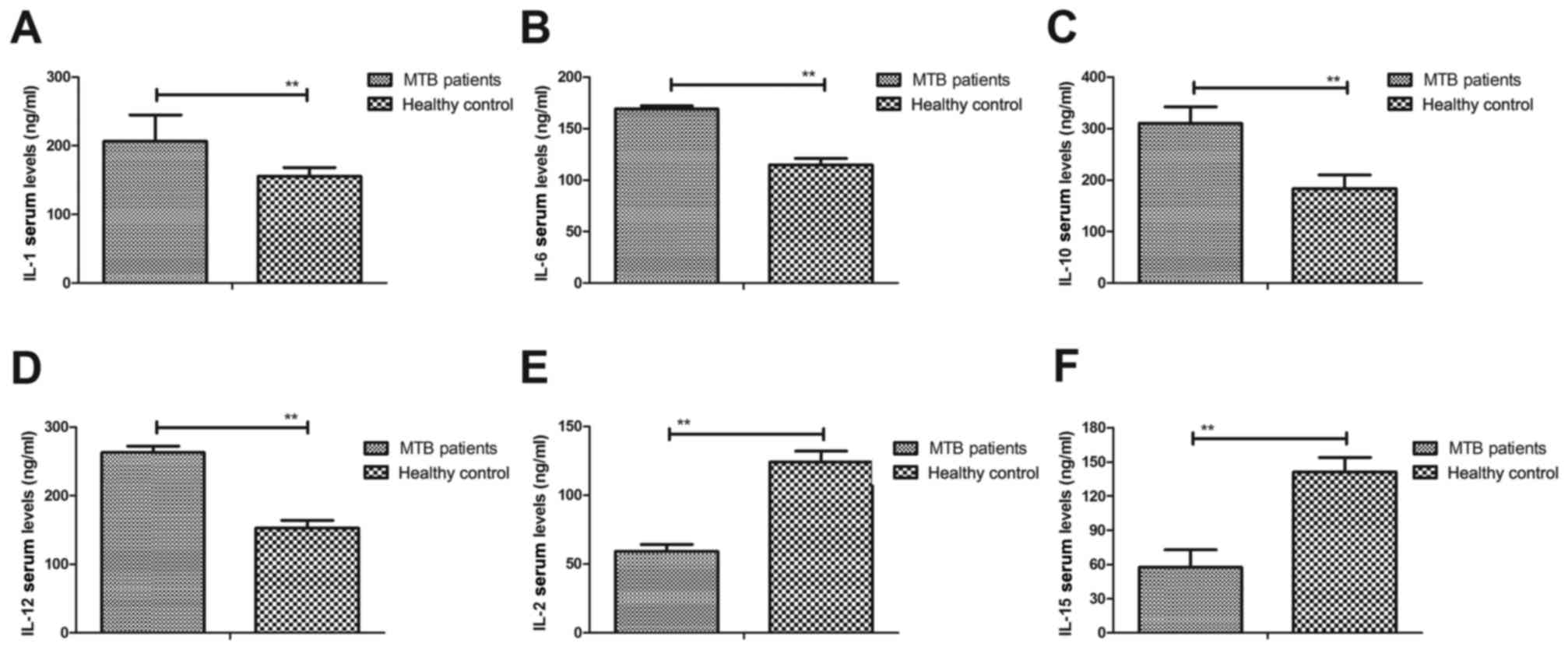
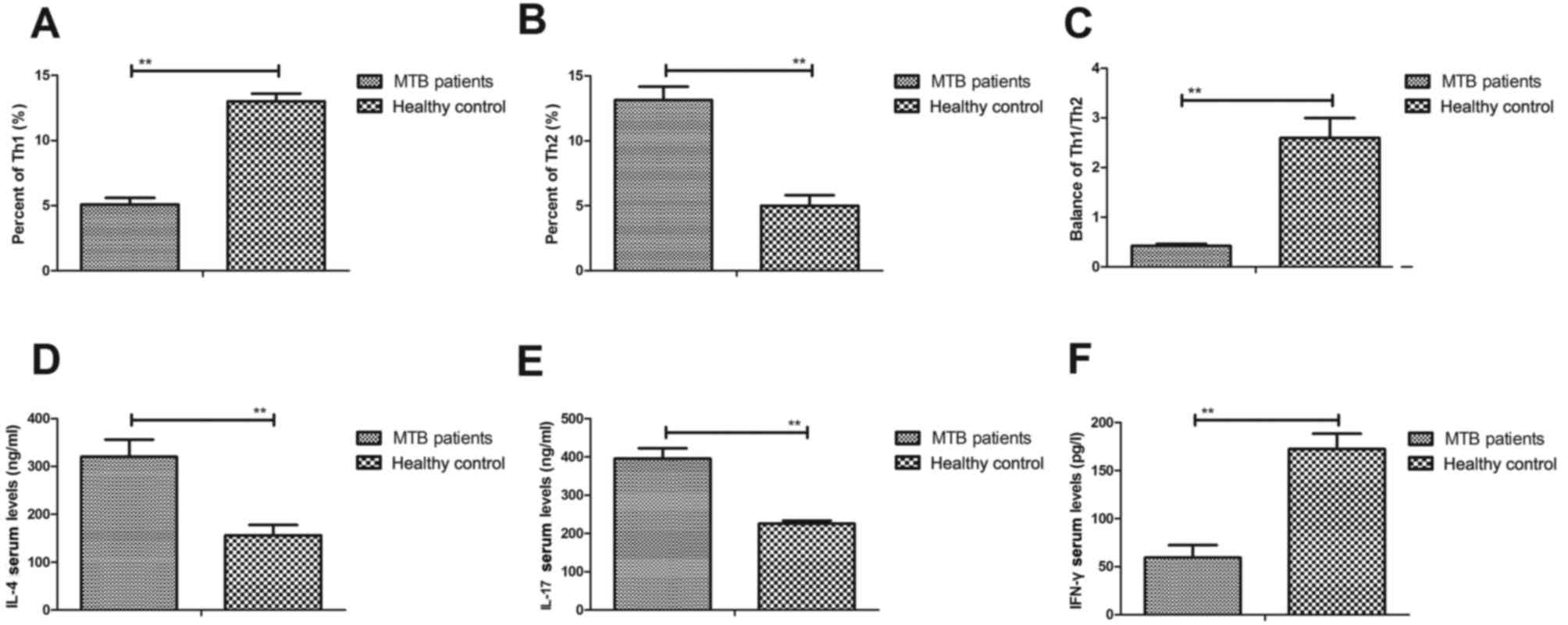
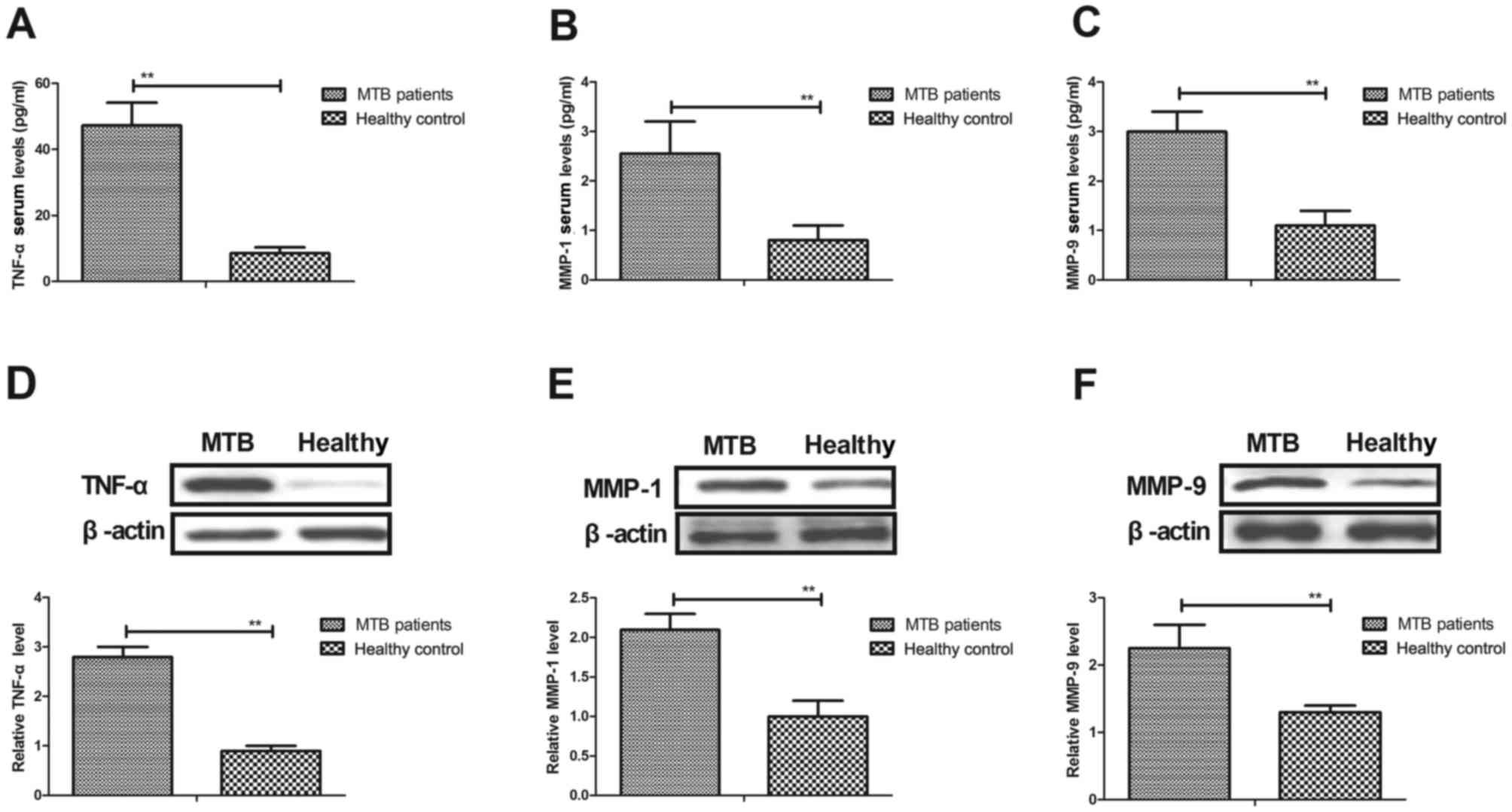
|
1
|
Mahmoud ES, Baharoon SA, Alsafi E and
Al-Jahdaly H: Acute respiratory distress syndrome complicating
community-acquired pneumonia secondary to mycobacterium
tuberculosis in a tertiary care center in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med
J. 37:973–978. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sood S, Yadav A and Shrivastava R:
Mycobacterium aurum is Unable to Survive Mycobacterium tuberculosis
latency associated stress conditions: Implications as non-suitable
model organism. Indian J Microbiol. 56:198–204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
WHO: Tuberculosis, . http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/October.
2017
|
|
4
|
Maruri F, Sterling TR, Kaiga AW, Blackman
A, van der Heijden YF, Mayer C, Cambau E and Aubry A: A systematic
review of gyrase mutations associated with
fluoroquinolone-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and a proposed
gyrase numbering system. J Antimicrob Chemother. 67:819–831. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Georghiou SB, Magana M, Garfein RS,
Catanzaro DG, Catanzaro A and Rodwell TC: Evaluation of genetic
mutations associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to
amikacin, kanamycin and capreomycin: A systematic review. PLoS One.
7:e332752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Phelippeau M and Petureau F: Severe
pulmonary tuberculosis in the ICU, diagnosis and treatment. Rev
Pneumol Clin. 71:294–296. 2015.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Silva DR, Gazzana MB and Dalcin Pde T:
Severe tuberculosis requiring ICU admission. J Bras Pneumol.
38:386–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo H, Pang L and Xie J: Biosynthesis and
regulation of mycolic acids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-a review.
Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 52:146–151. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiappini E, Bonsignori F, Accetta G,
Boddi V, Galli L, Biggeri A and De Martino M: Interferon-gamma
release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection in children: A literature review. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:335–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiappini E, Accetta G, Bonsignori F, et
al: Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 25:557–564.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lamrabet O and Drancourt M: Genetic
engineering of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A review. Tuberculosis
(Edinb). 92:365–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raslan WF, Rabaan A and Al-Tawfiq JA: The
predictive value of Gen-Probe's amplified Mycobacterium
tuberculosis direct test compared with culturing in
paraffin-embedded lymph node tissue exhibiting granulomatous
inflammation and negative acid fast stain. J Infect Public Health.
7:251–256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gunluoglu G, Yazar EE, Veske NS, Seyhan EC
and Altin S: Mean platelet volume as an inflammation marker in
active pulmonary tuberculosis. Multidiscip Respir Med. 9:112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sahin O and Ziaei A: The role of
methotrexate in resolving ocular inflammation after specific
therapy for presumed latent syphilitic uveitis and presumed
tuberculosis-related uveitis. Retina. 34:1451–1459. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dorhoi A and Kaufmann SH: Perspectives on
host adaptation in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis:
Modulation of inflammation. Semin Immunol. 26:533–542. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zumla A, Rao M, Parida SK, Keshavjee S,
Cassell G, Wallis R, Axelsson-Robertsson R, Doherty M, Andersson J
and Maeurer M: Inflammation and tuberculosis: Host-directed
therapies. J Intern Med. 277:373–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsenova L, O'Brien P, Holloway J, Peixoto
B, Soteropoulos P, Fallows D, Kaplan G and Subbian S: Etanercept
exacerbates inflammation and pathology in a rabbit model of active
pulmonary tuberculosis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 34:716–726.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Caspers L, Makhoul D, Ebraert H, Michel O
and Willermain F: Clinical manifestations of patients with
intraocular inflammation and positive QuantiFERON-TB gold in-tube
test in a country nonendemic for tuberculosis. Am J Ophthalmol.
158:646–647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aranday-Cortes E, Hogarth PJ, Kaveh DA,
Whelan AO, Villarreal-Ramos B, Lalvani A and Vordermeier HM:
Transcriptional profiling of disease-induced host responses in
bovine tuberculosis and the identification of potential diagnostic
biomarkers. PLoS One. 7:e306262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen WL, Sheu JR, Chen RJ, Hsiao SH, Hsiao
CJ, Chou YC, Chung CL and Hsiao G: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Upregulates TNF-α Expression via TLR2/ERK signaling and induces
MMP-1 and MMP-9 production in human pleural mesothelial cells. PLoS
One. 10:e01379792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mayordomo L, Marenco JL, Gomez-Mateos J
and Rejon E: Pulmonary miliary tuberculosis in a patient with
anti-TNF-alpha treatment. Scand J Rheumatol. 31:44–45. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mihăltan F: TNF-alpha blockers, rheumatoid
arthritis and pulmonary tuberculosis. Pneumologia. 56:212–216.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang CH, Lin HC, Lin SM, Huang CD, Liu CY,
Huang KH, Hsieh LL, Chung KF and Kuo HP: MMP-1(−1607G) polymorphism
as a risk factor for fibrosis after pulmonary tuberculosis in
Taiwan. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 14:627–634. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ong CW, Elkington PT, Brilha S, Ugarte-Gil
C, Tome-Esteban MT, Tezera LB, Pabisiak PJ, Moores RC,
Sathyamoorthy T, Patel V, et al: Neutrophil-Derived MMP-8 drives
AMPK-dependent matrix destruction in human pulmonary tuberculosis.
PLoS Pathog. 11:e10049172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nowak K, Hanusch C, Kölbel HC, Schwarzbach
M, Post S, Beck G, Gebhard MM, Metzger R and Hohenberger P:
Alterations of tumor and normal tissue of human lung cancer
resection specimens after isolation perfusion. J Physiol Pharmacol.
58 Suppl 5:501–511. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bajnok A, Kaposi A, Kovacs L, Vasarhelyi
B, Balog A and Toldi G: Analysis by flow cytometry of calcium
influx kinetics in peripheral lymphocytes of patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Cytometry A. 83:287–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Cai Y, Cheng Q, Hu Y and Xiao H:
Imbalance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in patients with pulmonary
tuberculosis. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 25:535–537. 2002.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cavalcanti YV, Brelaz MC, Neves JK, Ferraz
JC and Pereira VR: Role of TNF-Alpha, IFN-Gamma and IL-10 in the
development of pulmonary tuberculosis. Pulm Med. 2012:7454832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Anand SP and Selvaraj P: Effect of 1, 25
dihydroxyvitamin D(3) on matrix metalloproteinases MMP-7, MMP-9 and
the inhibitor TIMP-1 in pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin Immunol.
133:126–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gonzalez-Angulo Y, Wiysonge CS, Geldenhuys
H, Hanekom W, Mahomed H, Hussey G and Hatherill M: Sputum induction
for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 31:1619–1630.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Badyal RK, Kataria AS, Sachdeva K and
Kapoor S: Macrolithiasis in pulmonary tuberculosis: An autopsy
report with review of literature. Indian J Pathol Microbiol.
55:119–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Davis JL, Cattamanchi A, Cuevas LE,
Hopewell PC and Steingart KR: Diagnostic accuracy of same-day
microscopy versus standard microscopy for pulmonary tuberculosis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 13:147–154.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Elipashev AA, Nikol'skii VO and Shprykov
AS: Prognostic value of morphological signs of the activity of
tuberculous inflammation in patients with circumscribed
drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Arkh Patol. 72:40–43.
2010.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaminskaia GO, Popov EV and Romanov VV:
Comparison of systemic manifestations of inflammation in torpid
pulmonary tuberculosis and respiratory sarcoidosis. Probl Tuberk
Bolezn Legk. 1–29. 2008.
|
|
35
|
Skogmar S, Schön T, Balcha TT, Sturegard
E, Jansson M and Björkman P: Plasma levels of neopterin and
C-reactive protein (CRP) in tuberculosis (TB) with and without HIV
coinfection in relation to CD4 cell count. PLoS One.
10:e01442922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Koguchi Y, Kawakami K, Uezu K, Fukushima
K, Kon S, Maeda M, Nakamoto A, Owan I, Kuba M, Kudeken N, et al:
High plasma osteopontin level and its relationship with
interleukin-12-mediated type 1 T helper cell response in
tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 167:1355–1359. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Iliaz S, Iliaz R, Ortakoylu G, Bahadir A,
Bagci BA and Caglar E: Value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in the
differential diagnosis of sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. Ann Thorac
Med. 9:232–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Azfar SF and Islam N: Suppression of
mycobacterium tuberculosis induced reactive oxygen species and
tumor necrosis factor-alpha activity in human monocytes of systemic
lupus erythematosus patients by reduced glutathione. Oman Med J.
27:11–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim K, Sohn H, Kim JS, Choi HG, Byun EH,
Lee KI, Shin SJ, Song CH, Park JK and Kim HJ: Mycobacterium
tuberculosis Rv0652 stimulates production of tumour necrosis factor
and monocytes chemoattractant protein-1 in macrophages through the
Toll-like receptor 4 pathway. Immunology. 136:231–240. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Worodria W, Menten J, Massinga-Loembe M,
Mazakpwe D, Bagenda D, Koole O, Mayanja-Kizza H, Kestens L, Mugerwa
R, Reiss P, et al: Clinical spectrum, risk factors and outcome of
immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients with
tuberculosis-HIV coinfection. Antivir Ther. 17:841–848. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Katti MK: Assessment of serum IL-1, IL-2
and IFN-γ levels in untreated pulmonary tuberculosis patients: Role
in pathogenesis. Arch Med Res. 42:199–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chowdhury IH, Choudhuri S, Sen A,
Bhattacharya B, Ahmed AM, Hazra A, Pal NK and Bahar B: Serum
interleukin 6 (IL-6) as a potential biomarker of disease
progression in active pulmonary tuberculosis following
anti-tuberculosis drug therapy. Mol Immunol. 63:601–602. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Scola L, Crivello A, Marino V, Gioia V,
Serauto A, Candore G, Colonna-Romano G, Caruso C and Lio D: IL-10
and TNF-alpha polymorphisms in a sample of Sicilian patients
affected by tuberculosis: Implication for ageing and life span
expectancy. Mech Ageing Dev. 124:569–572. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Erdemli SB, Gupta R, Bishai WR, Lamichhane
G, Amzel LM and Bianchet MA: Targeting the cell wall of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Structure and mechanism of L,
D-transpeptidase 2. Structure. 20:2103–2115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sheen P, O'Kane CM, Chaudhary K, Tovar M,
Santillan C, Sosa J, Caviedes L, Gilman RH, Stamp G and Friedland
JS: High MMP-9 activity characterises pleural tuberculosis
correlating with granuloma formation. Eur Respir J. 33:134–141.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|